- 3.1 Removing build-up
Papilloma on the tonsil is a common disease. This benign throat tumor accounts for 40% of cases. What are the reasons for the appearance of unpleasant growths, which, moreover, are not so easy to immediately detect; what to do with tonsils on which a “ridge” has appeared and what treatment will doctors offer?
Features of the disease
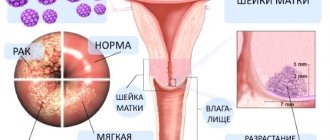
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common group of viruses that has oncogenic potential. HPV can have a productive or transformative effect on epithelial cells of the skin and mucous membranes. As a result of the first, a benign formation appears - papilloma, while the second can lead to cancer.
Thus, papilloma is an external manifestation of HPV. According to statistics, of all formations in the oropharynx, 40% are papillomas. The tonsils, their arches and the soft palate are the most common places of occurrence.
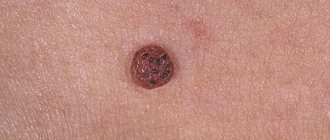
In appearance, papilloma is a nodule with a papilla. It is attached to the mucosa with the help of a short or long stalk. The growths can be located singly or in groups. Young children under 5 years of age, as well as women during periods of hormonal imbalance, for example, during pregnancy or menopause, are most susceptible to the disease.
Important!
If a tumor is detected in a child on the tonsil, as well as if he/she develops a cough or hoarseness for no reason, you should immediately consult a specialist. In children, papillomas can grow rapidly, covering the arches of the tonsils and the palate, thereby preventing the normal supply of oxygen to the lungs.
What not to do?
These are tonsillar plugs or stones; they form in the lacunae - the recesses of the tonsils. Their color, size, shape, and consistency depend on the composition. Most often, white lumps of soft consistency are observed; in some cases, if the composition contains calcium compounds, the lumps can be dense.
White lumps in the lacunae are formed from exfoliated old mucosal cells, bacteria and a small amount of food debris. Sometimes the lumps contain pus, and then they acquire an unpleasant odor and a yellowish tint.
You should know! When white and yellow lumps appear, a person experiences a sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the tonsils, a sore throat and bad breath.
Causes of papillomatosis
The appearance of papillomas on the mucous membrane is a consequence of HPV penetration into the body. If the disease affects the tonsils, then, as a rule, the virus belongs to types 6 and 11.
HPV can be in a person’s body and not cause him harm as long as the immune system performs its protective functions. When it weakens, microorganisms are activated, the epithelium grows, and papillomas appear.
The reasons why immunity decreases may be the following:
- the presence of chronic diseases of the ENT organs (tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, otitis media);
- long-term use of antibiotics and hormonal drugs;
- the presence of chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- disturbances in the functioning of the endocrine glands;
- stress, poor diet, lack of vitamins.
In addition, factors such as:
- smoking, addiction to alcohol;
- regular consumption of food that burns the mucous membranes;
- hormonal imbalance;
- taking OK by women; heredity;
- bad ecology;
- the presence of dental diseases and ineffective oral hygiene.
Routes of infection
The papilloma itself is not transmitted from person to person, but HPV infection occurs. However, it is impossible to predict how he will behave, whether papilloma will appear or not, since this is due to many factors.
REFERENCE! According to statistics, the human papillomavirus is present in the bodies of approximately 90% of the world's population.
You can become infected with HPV regardless of age and in the following ways:
- Through sexual contact , this is the most common variant of infection in adulthood. Sexual contact can cause infection. Even having a condom can only reduce the risk of infection, but not completely eliminate it.
- At home . Transmission occurs through common household items or hygiene products - a towel, washcloth, razor. This route of infection is most common in children, since they often play with the same toys, eat with the same cutlery, and drink from the same glasses. You can also become infected in public places - these are baths, saunas, swimming pools. Intranatally. During passage through the birth canal, the virus is transmitted from mother to baby. With this method of infection, the baby’s pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi are most often affected.
- HPV poses the greatest danger to persons with a suppressed immune system as a result of chemotherapy , transplantation, as well as the presence of HIV, AIDS, and cancer in the body. In addition, if a person has sexually transmitted diseases, for example, ureaplasmosis, candidiasis, gonorrhea, then they increase the risk of infection.
Important!
The penetration of the virus through certain areas of the body does not mean that this is where it is activated and papillomas will appear.
Types of growths on the tonsils
In order to select effective treatment in the future, you should take into account the types of papillomas. The following types are distinguished depending on:
Lifetime:
- Congenital.
- Acquired.
- Children's.
- Recurrent.
- Adult.
Affected area:
- Limited, concentrated in one place.
- Widespread, occupying many areas.
- Obstructive, making breathing difficult.
Effects on the respiratory tract and their changes:
- First degree. Characterized by mild difficulty breathing, hoarseness and noise.
- Second degree. It manifests itself in a feeling of anxiety, shortness of breath, and lack of oxygen.
- Third degree. Causes loss of consciousness and asphyxia.
Cancer risk levels:
- Benign.
- Malignant.
HPV symptoms
If the papilloma on the tonsil is small, then, as a rule, it does not manifest itself in any way. Only with its growth does shortness of breath and hoarseness appear. In the future, the disease may become more complicated:
- unpleasant sensations reminiscent of the presence of a foreign object;
- discomfort and soreness;
- difficulty breathing;
- cough;
- impaired swallowing reflex;
- in rare cases, pain radiating to the neck and submandibular area.
As a rule, the growth of papillomas in adults occurs on one side of the throat, while in children both halves are affected. As a result, children suffer more severely from the disease, and symptoms may be as follows:
- heavy breathing after physical activity, and then at rest;
- outdoor games or running are accompanied by paroxysmal coughing;
- attack of suffocation, lips and nasolabial triangle turn blue.
After a child has suffered diseases of the ENT organs, the formation of papilloma on the tonsils is possible. Parents can see it themselves by examining the oral cavity. It is very important to consult an otolaryngologist in a timely manner, since the disease is more dangerous the younger the baby is.
Important!
The smaller the child, the more severe and faster the disease progresses, since the respiratory organs are small and the connective tissue is not fully formed.
Whitish lumps in the tonsils
Often something white is found on the tonsils, resembling a cheesy film or whitish lumps. This may indicate the development of a yeast-like fungus of the genus Candida on the surface of the mucous membrane of the tonsils. This pathology does not cause significant accompanying symptoms. The patient may experience discomfort in the throat, dryness and burning of the mucous membrane.
A more dangerous condition, in which a white pimple forms on the tonsil or many of them in the throat area, is diphtheria. In this case, the patient experiences severe intoxication of the body, with fever and sore throat. Diagnostic signs of the development of diphtheria include the formation of a white-gray coating, which is difficult to remove, leaving behind bleeding erosions.
Diagnostic methods
If you suspect the presence of papilloma, you must visit an otolaryngologist, who will visually examine the mucous membrane and determine the presence of a formation, its location, size, as well as the degree of damage to the surrounding organs. In order not to confuse papilloma with other diseases, additional techniques are used.
Diagnostics can be carried out using:
- Laryngoscopy , where the doctor visually examines the larynx using a laryngoscope. There are two types - direct and indirect.
- Microlaryngoscopy . It is performed under general anesthesia using an operating microscope.
- Laryngostroboscopy and electroglottography , allowing to identify disturbances in the functioning of the vocal cords.
- Computed tomography . It consists of a layer-by-layer study that allows obtaining three-dimensional images.
- Autofluorescence study to clarify the boundaries of the growth and identify hidden papillomas.
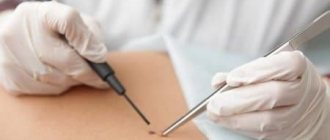
- Biopsy , which is performed if there is bleeding or a large lesion. To do this, a piece of papilloma is taken with a needle and examined under a microscope.
- PCR , which helps to accurately distinguish papilloma from other formations, as well as identify its type, since each has its own risk of oncogenicity.
- Histology . This study is carried out after removal to determine the presence of cancer cells in the formation.
Alarming symptoms
As the size of the papillomas increases, the voice becomes duller.
Tonsil papilloma manifests itself in different ways. The patient himself sometimes cannot adequately describe the sensations, because he does not associate mild discomfort in the throat with this disease. Characteristic signs of the disease are:
- causeless sore throat;
- feeling of a foreign body in the throat;
- unusual sensations when chewing or swallowing food.
As the tubercle grows, the voice may also change (becomes duller), and breathing problems may appear. To make a diagnosis, an otolaryngologist only needs a visual examination of the affected area. Additional studies are not prescribed. The exception is the bleeding of the neoplasm and its rather large size. Then a biopsy is performed. To finally confirm the verdict “papilloma”, methods such as PCR or Digene test for HPV are used (patented technology that allows you to identify specific fragments of the DNA of the virus).
Treatment options
Only a doctor can make decisions about treatment options for a particular patient. As a rule, it includes the removal of papilloma in combination with the use of medications.
The following methods can be used to remove papilloma:
- Surgical removal with a scalpel . It is carried out under local anesthesia and can be: Extralaryngeal is used in severe cases of the disease, when there is a risk of asphyxia. The patient's larynx is incised and growths are removed through the incision. Intralarynx is used for patients over 8 years of age. Special instruments help remove papillomas, and control is carried out using a laryngeal mirror.
- Laser removal is the safest and most painless method. It is also the most effective, since after its use the risk of relapse is the lowest. There are no scars after treatment.
- Radiotherapy lasts 20 minutes. Papillomas and affected areas are removed using a radio wave scalpel, after which a crust appears at the site of the intervention. After the wound has completely healed, it goes away. This method is the second most popular after laser.
- Cryodestruction is the cauterization of growths with liquid nitrogen. The entire operation takes a few minutes, and after 2-3 days the tissue dies and goes away along with the papilloma.
- Electrocoagulation is the removal of papillomas with high frequency electric current. This allows the blood vessels that feed the growths to glue together. After which, after a few days, the formation will wither and disappear.
- Ultrasound removal involves applying a hydrogen peroxide applicator to the affected tonsil. Then, under the influence of ultrasonic waves, oxygen molecules penetrate into the tissues, causing the death of the virus.
- Chemical cauterization involves influencing formation using: Potassium permanganate; silver or lead nitrate; perhydrol.
Medicines are one of the components of treatment for HPV. The doctor may prescribe:
- antiviral agents;
- drugs containing interferon;
- immunomodulators;
- chemotherapy drugs;
- hormonal agents.
In adults
The attending physician chooses one of the removal methods, taking into account contraindications for a particular case.
So, pregnant women should not use:
- radio wave destruction;
- removal using ultrasound;
- cauterization with chemicals.
The radiofrequency method is not used in patients:
- with disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- in the stages of exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- in the presence of cancer.
Electrocoagulation additionally cannot be used in patients with bleeding disorders and intolerance to electrical procedures.
In children
Surgery in children is possible only under local anesthesia. The methods used to remove papillomas in a child are as follows:
- cryogenic;
- electrocoagulation;
- ultrasonic.
They are less traumatic, painless, effective, and also have an easier process of restoring damaged areas.
Contraindications are cases when the child:
- there are open wounds in the oral cavity;
- elevated temperature;
- cold intolerance;
- blood diseases.
Peritonsillitis
Peritonsillitis is considered as one of the forms of an abscess that forms near the tonsil. Streptococci lead to its development. If the tonsils do not cope with their main task, then the pathogen actively multiplies at the site of the lesion and beyond.
The lump with paratonsillitis gradually changes its color. This process occurs along with the development of an abscess.
The organs at the site of the lesion swell. They become hyperemic. The patient begins to complain of increased body temperature and severe general condition. Along with this, he has bad breath and his voice is nasal.
To alleviate his condition, a person has to keep his head tilted to the side where the lesion is located.
A lump on the tonsil caused by paratonsillitis is treated with antibiotics. Additionally, a course of antihistamines is prescribed.
To alleviate the person's condition, an abscess will need to be opened. After surgery, analgesics and vitamins are prescribed to strengthen the immune system. The patient also needs to regularly rinse the mouth until it is completely healed.
Possible complications of HPV
Papillomas on the tonsils are the most dangerous in childhood due to the narrower lumen of the larynx in children. The formation can grow into the palate and palatine arches, which further reduces the respiratory lumen. Respiratory failure develops.
In the absence of emergency medical assistance, asphyxia may occur. Therefore, if a child has a growth on the tonsil, it is necessary to begin treatment as soon as possible.
For adults, papillomas are less dangerous, however, complications can occur. One of the most dangerous is degeneration into a malignant formation.
REFERENCE! According to statistics, in 20% of cases papillomas can lead to cancer, therefore in modern medicine their presence is considered a precancerous condition.
Growing into the trachea, lungs and bronchi, papillomas can lead to respiratory failure. Another possible complication is cicatricial stenosis of the larynx, which appears with frequent relapses and subsequent treatment.
How to treat
White pustules - what are they? An abscess occurs on the gland at the site of penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into its tissue. Actively multiplying, they provoke local inflammation of the affected area and the accumulation of pus (exudate) in it.
A specific membrane is formed around the source of microbial penetration, which prevents the infection from spreading to healthy tissue. When a lot of exudate accumulates, the ulcers open on their own, and the patient’s general condition improves.
- A detected white spot or plaque on the tonsil should under no circumstances be removed on its own. This can cause injury to the mucous membrane and further spread of infection.
- Choose your own treatment (rinses, mouth irrigation, antibiotics, antihistamines and painkillers). Without a diagnosis, such therapy will not only be ineffective, but can also worsen the patient’s condition and cause complications in other body systems.
- Do not try to squeeze out the pus. When pressing on an abscess (purulent abscess), the release of pus may intensify and microbial infection from the tonsils will spread to neighboring tissues, or pustules will begin to form inside the tonsils.
- You cannot warm your throat, drink hot drinks, or make hot compresses - this will further activate putrefactive processes.
- Contact with others until the cause of purulent formations is determined. Reason: if the tonsils fester, there is an infection in the body that is transmitted by airborne droplets. When in contact with other people, it can be transmitted to them.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with Tooth restoration in the presence of a root: methods, technology, reviews
Prevention of neoplasm
No preventive measures can guarantee that a person will not become infected with HPV. As already noted, most people are carriers of the virus, many of whom are not even aware of its presence. However, it may not manifest itself in any way. To do this, you need to maintain good immunity. This will help:
- hardening and physical exercise;
- walks in the open air;
- varied diet rich in vitamins and microelements;
- no hypothermia;
- rejection of bad habits.
Important!
Oral hygiene is of particular importance in maintaining immunity. It is necessary to promptly treat dental diseases, maintain hygiene in public places, and refrain from promiscuity.