Furuncle is an inflammatory process of the skin, which is caused by the penetration of infection (bacteria) into the structures of the hair follicle. The vestibule of the nose is lined with skin containing a large number of hair follicles. Therefore, if an infection gets into them, a boil may occur.
A furuncle of the nasal vestibule is a rather serious disease, which should be treated with great caution and in no case should you self-medicate. If you suspect that you have a nasal boil, be sure to consult a doctor; you need qualified help.
How does a nasal boil develop?
The initial acute stage of the disease is characterized by a feeling of discomfort in the vestibule area. Pain appears, which can be of varying intensity - from not too strong to unbearable. Often the pain intensifies at night. If the boil turns black in the middle, this indicates that the root of the boil has formed. Characteristic symptoms:
- hyperemia of the affected area;
- swelling;
- pain at the site of the lesion;
- pain when pressed;
- increased body temperature (systemic symptom).
A laboratory blood test may reveal toxemia. In the next stage (purulent boil), if measures were taken at the wrong time or the treatment was not adequate, the symptoms become more complicated. Diagnosed:
- thrombus formation in the area of the angular vein (outwardly resembles the appearance of a thickened cord);
- increase in general body temperature to significant values;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- swelling of the eyelids, hyperemia of the mucous membrane of the eye, difficulty moving the eyeballs, pain;
- blurred vision;
- bulging eye.
If you do not receive qualified help, swelling of the optic nerves may occur, which leads to complete or partial paralysis of the eye muscle.
Localization Features
When deciding on the pathology of a boil inside the nose, how to treat the phenomenon, it is important to understand its location, since the range of drugs used is limited for different localizations of the boil.
A boil can appear in the following places:
- on top of the nose, spreading from the tip to the bridge of the nose, on the wing of the nose;
- inside the nostrils, nasal passage on the mucous membranes, which is dangerous due to the rich vascularization and the risk of pus penetrating into the adjacent sinuses and brain;
- on the bridge of the nose (a relatively safe place), the risk of pus penetrating when the abscess is independently squeezed into the frontal sinuses remains.
Forms
The disease has two stages: in the first, the formation of an infiltrate (closed boil) occurs. In the second, pus appears, the pain intensifies and additional symptoms develop. Pus forms at the site of infiltration if you do not consult a doctor in time. In the first stage, the boil does not hurt much. The second stage is characterized by a deterioration in general condition and increased pain. Often in the second stage it is necessary to resort to surgical treatment of the boil. Complications after opening a boil usually develop if the opening was performed in violation of the rules of asepsis or by a non-specialist. The boil incision should not be wetted, as this promotes re-entry of infection and complicates the regeneration process. Is it possible to squeeze out a boil on your own? Attention! Under no circumstances should such attempts be made, as this can cause serious complications that threaten health and even life.
Treatment with folk remedies
A boil in the nose (can be treated with NSAIDs) is an formation for which the use of folk recipes is allowed. They have a herbal composition, so the likelihood of side effects is low. Folk remedies accelerate the maturation of the boil and draw out the pus. The doctor may recommend complex treatment, that is, a combination of medications and prescriptions.
When a boil appears, the following folk methods are effective:
- Aloe juice. The plant eliminates inflammation, accelerates wound healing, and kills germs.
A compress can be used to eliminate a boil.
- You should take 1 aloe leaf and cut it into 2 parts (lengthwise).
- Place the plant on the boil (cut side).
- You can secure the aloe with a bandage or bandage.
- Keep the compress for 30 – 40 minutes, apply 3 – 4 times a day.
- To enhance effectiveness, you can leave the compress overnight.
If the abscess is large and protrudes strongly above the skin, the aloe must be crushed. You can also squeeze out the juice of the plant and apply it to a sterile gauze pad and apply it to the boil.
- Honey. The component has an anti-inflammatory, warming, disinfecting effect. Additionally, honey accelerates the maturation of the boil, reduces swelling and pain. The component is used as a compress.
- To prepare it, you need to mix the same amount of natural liquid honey and flour (wheat or rye).
- Next, form a cake, apply it to the boil, and secure it with a bandage.
- The compress needs to be changed 2 – 3 times a day.
- The recipe should be used until the boil is ripe.
- Garlic. The product destroys pathogenic microorganisms. For boils, apply a compress of garlic.
- To prepare it, you need to finely chop or grate the product.
- To reduce the likelihood of skin burns during use, you should mix garlic with raw potatoes, laundry soap or baked onions in equal proportions.
- The compress should be applied to the abscess every day and kept for 2–3 hours. The prescription can be used at night.
- Use should be stopped when the boil opens.
The recipe is not suitable for use by people with sensitive skin.
- Calendula. Another name for the plant is marigold. The component has anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and antibacterial effects. If there is a boil, use calendula ointment.
- To prepare it you should take 1 tsp. dry crushed flowers of the plant and 1 tbsp. l. Vaseline.
- Mix everything thoroughly and leave for 8 – 12 hours.
- Apply the ointment to a sterile gauze pad, apply to the boil and secure with a bandage.
- The compress should be changed daily for a new one.
- Herbal tincture. The product is used to disinfect the surface of the boil.
- To prepare the recipe you need to mix 1 tbsp. l. dried and crushed nettle root, 0.5 tbsp. l. garlic (pre-chopped).
- Add 500 ml of boiled water to the mixture.
- Close the jar with a lid and leave for 7 days in a dark place.
- After preparing the product, lubricate the boil 2 – 3 times a day.
- The mixture can be stored in the refrigerator.
- Laundry soap. The recipe has antiseptic properties.
- To prepare, you will need laundry soap, which should be crushed with a knife and placed in a water bath.
- After softening the component, you need to add milk to the container (2 times more soap).
- Cook the mixture until it reaches the consistency of sour cream, wait until it cools.
- Apply the mixture to a bandage, apply to the boil, and secure with a bandage.
- It is important to change the compress daily. The recipe is used until the pus leaves the formation.
- Blue clay. The product cleanses the skin of toxins, stimulates metabolic processes, and draws pus from the boil.
- To prepare, you need to take 3 tbsp. l. blue clay, 1 tbsp. l. apple cider vinegar.
- Mix the ingredients thoroughly, add water until the consistency becomes thick.
- Apply the mixture to the boil and secure a sterile gauze pad on top. It is necessary to change the compress 2 times a day.
How does staphylococcus bacteria get into the nose and develop a boil?
A person can be a carrier of infections and not know it. Under suitable conditions (hypothermia, decreased general protective properties, exacerbation of any chronic pathology of the body, stress, increased physical activity, alcohol abuse), streptococci or staphylococci begin to manifest themselves. The formation of a boil is promoted by:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- hazardous production;
- hypothermia or overheating of the body;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- unbalanced diet with insufficient amounts of vitamins, minerals, microelements;
- endocrine diseases;
- reduced immunity.
Causes of an abscess
The formation of a boil in any place on the body occurs due to the fault of pathogenic bacteria - staphylococci and streptococci.
Normally, they live on the skin of every person in small quantities (from 10 to 30%). However, when the body's protective response decreases, bacteria begin to multiply rapidly, causing the formation of an abscess.
Both external and internal causes can contribute to the appearance of an abscess.
External factors include:
- Damage to the mucous membrane. The nasal mucosa is a very delicate area and is often subject to injury when cleaning the nasal passages. Doing this with dirty hands and overgrown nails can introduce not only cocci, but also other dangerous infections, nasal fungus.
- Hair plucking. Instead of a safety trimmer, curling irons are often used. The procedure not only brings discomfort and pain, but also opens the door to infection. Each plucked hair is nothing more than a micro-wound. Until regeneration occurs, it will be susceptible to bacterial attack.
- Dysfunction of the nasal mucosa. The mucus in the nose itself is a protection against infections. After using medicinal drops, with increased dry air or a change in climate, the functioning of the mucous membrane may change. Reduced protection causes bacterial damage.
- Improper functioning of the sebaceous glands. Excess sebum becomes an ideal breeding ground for bacteria. The vestibule of the nose, nasolabial triangle, wing of the nose, nostril are the most common areas of damage for this reason.
Internal problems include:
- weakened immunity after viruses and bacteria;
- inflammation of the sinuses, bacterial infections of the nasopharynx (sinusitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, sore throat);
- blood diseases, endocrine disorders (anemia, diabetes mellitus);
- spring vitamin deficiency, food poor in vitamins;
- oncological diseases;
- hypothermia of the body;
- hormonal changes, including during adolescence and menopause.
The one-time appearance of a boil is not a reason to fall into attacks of hypochondria. However, repeated or multiple inflammations are a signal for a mandatory visit to the doctor.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis should only be carried out by a doctor in a clinical setting. The doctor conducts an external examination, collects anamnesis and prescribes the necessary laboratory and diagnostic measures. Laboratory tests include: a general blood test, determining the number of neutrophils and ESR, a urine and blood test for carbohydrate content to exclude diabetes mellitus. In some cases, the material is examined to determine the pathogen (smear culture and antibiotic sensitivity determination). If necessary, consultation with doctors of related specialties (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, dermatologist) is carried out.
Symptoms
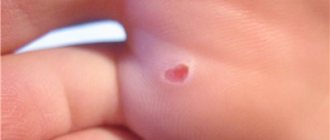
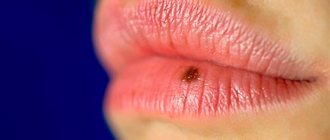
The primary focus of the inflammatory process is surrounded by atrophied soft tissue. But the core of the abscess itself is formed from elements of the hair follicle. The patient experiences headaches, fever and other signs characteristic of general intoxication. When taking a blood test, changes in the inflammatory pattern can be observed. Already on the 5th day, an abscess is observed in the center of infiltration.
The photo shows how a boil works:
When the abscess matures, severe tissue tension occurs, which causes severe pain. Its attenuation occurs as the boil opens. Body temperature also returns to normal. According to ICD 10, the disease has code J34.0.
Complications
It is extremely rare that due to a weak immune system or diabetes mellitus, inflammation can spread, resulting in the following complications:
- septal abscess;
- perichondritis of the nasal septum;
- retrograde thrombophlebitis;
- thrombosis of the cavernous sinus;
- pyaemia (pyema).
A boil in the nose is a fairly common phenomenon today. Bacteria such as streptococci and staphylococci can affect its development. It is strictly forbidden to squeeze it out, since an unsuccessful outcome can lead to serious complications. Treatment can be conservative or surgical. It all depends on the stage of the pathological process.
Stages
The formation of a boil in the nose can occur in three stages. Each of them has its own characteristics.
Infiltration stage
Its duration is several days. It occurs as a response of the body to the penetration of microbes into the hair follicle. Redness occurs around the hair, the skin becomes tight and swells.
The pain is felt when touched, and its intensity increases, as a result of which it becomes permanent. These symptoms indicate the development of acute folliculitis.
Stage of suppuration and necrosis
On the 3rd day, a pustule forms. It has a conical shape and is presented in the form of a vesicle, inside of which pus is concentrated. The process of its maturation is characterized by the presence of a necrotic core. This stage is accompanied by the presence of a local and general clinical picture.
Most often these are headaches, poor appetite, fever, chills. At the peak of inflammation, the boil breaks through and its contents come out. An ulcer appears in its place.
Healing stage
The resulting wound heals gradually. After 3 days, a bluish-red scar will be present in its place. Then its color will be pale and unnoticeable. The total duration of the inflammatory process should not exceed 10 days.
This information from the article will help you understand how to rinse your nose with Miramistin for sinusitis.
And here is how Staphylococcus aureus in the throat and nose is treated and by what means. This article explains it in great detail.
What Staphylococcus aureus looks like in a child’s nose and what means you can get rid of this problem is described in great detail in this article: https://prolor.ru/n/simptomy/zolotistyj-stafilokokk-v-nosu-u-rebenka.html
But what medications for Staphylococcus aureus in the nose are the most effective and how to make the right choice is described in great detail in this article.
Furuncle according to ICD-10: what types of diseases are identified
A furuncle is one of the manifestations of purulent-inflammatory diseases, characterized by damage to the hair follicles, a number of adjacent soft tissues and sebaceous glands.
A furuncle is a formation on the surface of the skin in the form of a dense painful node, the diameter of which can be several centimeters, on average it does not exceed 3 cm. In the central part there is a necrotic core, which is covered with a pustular formation.
Gradually, the abscess begins to soften, and in the area of the rod, the presence of an abscess with an area of fluctuation can be determined. When the pustule ruptures, necrotic contents will drain from the cavity and it will become free. In the area of the boil there will remain a focus with developed inflammation.
The boil, whose code is defined as L02, can be divided into several types.
In the modern classification according to ICD-10, codes are defined for boils in accordance with their anatomical location:
- face L02.0,
- neck L02.1,
- body L02.2,
- buttocks L02.3,
- limbs L02.4,
- other parts of the body L02.8,
- with unspecified localization L02.9.
Cause of inflammation
The main reason for the development of a boil is the addition of a bacterial infection.
The source may be staphylococcal and streptococcal flora, which exhibit their pathogenic properties.
These microbes may normally be present on the surface of the skin and not cause pathological conditions, but in the presence of provoking factors, an inflammatory process develops.
Among them are:
- Decreased immune strength of the body. It can be caused by severe metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus, autoimmune diseases), severe somatic conditions, infections (tuberculosis, hepatitis, sinusitis, etc.), long-term treatment with glucocorticoids, cytostatics, immunosuppressants, and chemotherapeutic agents.
- Decreased local immunity. These include unfavorable factors that affect the areas where boils appear. Such conditions include constant trauma to the skin when using clothing that does not correspond to weather conditions, size, diseases accompanied by severe itching (clinic of atopic dermatitis, scabies, eczema, etc.).
Prevention
The following are preventive measures:
- Normalization of lifestyle, including proper nutrition and physical activity aimed at maintaining immune strength.
- Compliance with hygienic measures aimed at eliminating the growth of pathogenic flora and normalizing protective forces.
- Timely elimination of excessive sweating and excessive work of the sebaceous glands.
- When pyoderma rashes appear, it is necessary to identify the underlying cause and timely treatment of the skin to remove microbes.
- Correction and treatment of somatic pathologies, chronic infections, malignant neoplasms.
- Self-treatment of a boil, as well as removal of purulent formations in the face and nearby vessels, is not allowed.
- Timely consultation with a specialist and treatment of boils, taking into account the determination of sensitivity to antibacterial agents.
Source: https://mfarma.ru/dermatologiya/mkb-10-furunkuleza