Urology
2502
no comments
Male testicles are a very delicate organ; they require regular examination, as they can be subject to various inflammatory processes and pathologies. Sometimes a man develops a lump on his testicle; it can cause a pinching, a blow, or a certain disease. Pathologies of the male genital organs can be quite dangerous, so urgent consultation with a doctor is necessary. The article will present photos of the pathology and talk about the causes and methods of treatment.
What is spermatocele
A spermatocele is a dense formation of the testicle and its epididymis, which contains seminal fluid and sperm. Usually the disease is asymptomatic, because the size of the tumor is small and the cyst grows very slowly. In some cases, the patient may complain of pain in the scrotum. A cyst is formed due to disruption of the normal outflow of fluid in the ducts. Benign formation is often diagnosed in children and adolescents during puberty (6-14 years), as well as middle-aged men (40-50 years). In both cases, the reasons are age-related changes.
Causes of pathology
A seminal cyst, or spermatocele, can be acquired or congenital. In a child, a lump appears due to the formation of gland ducts. The formation will not be large, the maximum size does not exceed 2-2.5 cm. The cavity of the cones is filled with a thick yellowish liquid, which does not contain sperm or impurities.
A lump on the testicle in men may appear due to any acquired disease. The reasons may be:
- any injuries (severe compression, impacts, cuts or tears);
- inflammatory diseases (most often vesiculitis, orchitis, deferentitis or epididymitis);
- frequent hypothermia of the body;
- lack of regularity in sexual activity (too frequent or infrequent contacts);
- postoperative changes;
- constant stress.
The result of the influence of these unfavorable factors is that the functional ability of the ducts is impaired, secretion accumulates in their compartments, stretching the walls, and a lump is formed under the testicles. In men, such a neoplasm can be of different sizes, shapes, structures, and have different contents. Inside it may contain a substance of different colors, which, as a rule, contains signs of sperm.
Neoplasms predominantly form on the left testicle, but it happens that a cyst also appears on the right one. Any swelling may indicate a pathological process. Reviews indicate that the cause of the disease in most cases is a combination of several provoking factors. Only careful attention to your own health will help prevent pathology from developing.
Causes
Most pathologies of the reproductive system in men, including compaction in the testicle, occur for the following reasons:
- pelvic inflammatory diseases;
- circulatory disorders;
- carrying heavy objects, excessive physical activity;
- poor nutrition, vitamin deficiency;
- weak immunity
- hypothermia and overheating;
- passive lifestyle;
- endocrine disorders, hormonal imbalances;
- genetic predisposition.
To say exactly what caused the formation of a lump in the testicle, it is necessary to undergo an examination. Let's look at several common diseases in which a nodule or lump may appear on the testicle. It is important to note that all diseases are presented for informational purposes. You should not self-diagnose and begin treatment, since it is very difficult to distinguish pathologies from each other without examination.
Spermatocele
A testicular cyst or spermatocele is formed if the outflow of secretions from the epididymis is disrupted. As a result, a cavity filled with fluid forms in the area of the epididymis or spermatic cord.
Description of spermatocele:
- painless;
- dense but flexible;
- located above the testicle;
- has a round shape.
A lump appears on the testicle with spermatocele against the background of inflammatory diseases and injuries of the scrotum. The disease can also be congenital. The pathology does not manifest itself in any way and does not interfere with reproductive function. As a rule, patients consult a doctor at the moment when the lump becomes very large.
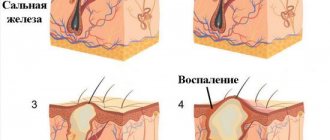
Inflammation
Orchiepididymitis or an inflammatory process in the testicle and appendages is accompanied by the appearance of a compaction in the testicle. In addition, the patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- enlargement of the entire testicle;
- testicular pain;
- the lump is painful;
- the skin turns red and may become hot.
Inflammation of the scrotal organs is a very dangerous condition that can lead to serious complications, infertility, and impotence. Epididymitis orchiepididymitis severely disrupts the reproductive function of men and requires complex therapy.
Oncology
A lump on or inside the testicle may indicate the development of a tumor. Malignant testicular tumors are classified as germinogenic and non-germinogenic. The first are formed from the epithelium, these include the following tumors:
- chorionepithelioma;
- seminoma;
- teratoblastoma;
- embryonal cancer.
Non-germinogenic ones begin to grow from the main tissue of the testicle, these include:
- Leydigoma;
- sarcoma;
- sertolioma.
Of all these types of cancer, seminoma is the most common. This pathology develops gradually and asymptomatically, which is why it is dangerous. When palpating the testicle, you can feel a small nodule that gradually enlarges. The lump in the testicle itself does not hurt, but as it grows, it irritates the surrounding tissues, so pain appears.
Testicular cancer requires treatment in the early stages, otherwise it begins to metastasize, which leads to the spread of harmful cells throughout the body. The sooner the patient begins treatment, the greater his chances of survival.
A benign testicular tumor is very rare; in more than 90% of cases, patients are diagnosed with cancer. A benign tumor is characterized by the appearance of a painless lump, which soon turns into a malignant form.
Varicocele
Varicose veins of the spermatic cord or varicocele are one of the most common male diseases. Most often, varicocele forms in the left testicle due to the structural features of the male genital organs.
At the initial stages of the disease, the compaction cannot be felt. Over time, the vein swells and can be detected by palpation. The lump in the testicle with varicocele is soft and does not hurt when pressed. But the disease is accompanied by pain in the scrotum and male infertility.
Hydrocele
Hydrocele of the testicle occurs due to a violation of the outflow of seminal fluid. This is facilitated by swelling, infections, injuries, and cancer. With a hydrocele, there are no symptoms, but the patient can feel a painless lump.
If the dropsy is very large, then there are difficulties with urination, pain and heaviness in the scrotum. When palpating the lump, you feel that there is liquid inside. If a hydrocele is accompanied by an infection, then pus forms inside the seal.
Hernia
A testicular hernia in men is a disease in which abdominal organs descend into the scrotum. The lump inside the testicle has a round shape, the veins swell and the patient is bothered by pain.
A hernia can develop as a complication of varicocele and hydrocele, with excessive tension and pressure in the abdominal cavity, after trauma to the genital organs. Obese men and athletes who train too much are at risk of getting a hernia.
Localization Features
The checker that popped up between the groin and leg is small in size and resembles a small bean. This may be inflammation of the lymph nodes. The reasons are the first signs of prostatitis, various neoplasms (both benign and malignant), any sexually transmitted diseases, colds, the presence of parasites in the body, viruses and infections, fungus of the lower extremities.
Is there red skin around a lump on a man’s testicle, and does it feel painful when pressed? This can be caused by mechanical damage to the abdomen, the formation of wen, sarcoma, and inguinal lymphogranulomatosis. In this case, growths appear on the left or right side of the scrotum or between the testicles. With this disease, one or more lumps may appear.
A lump on a man’s right testicle or on the left appears due to an inguinal hernia. Pathology is caused by reasons that entail weakening of the peritoneal muscles. This may be a regular severe cough or improper distribution of physical activity.
If a lump appears under the testicle (closer to the anus), then this may be due to dermatological reasons. Often this is a wen, carbuncle or boil. But a painful neoplasm can be a harbinger of paraproctitis or prostatitis.
It is not recommended to make a diagnosis yourself. It is advisable that the exact disease be determined by the attending physician. If a man has a lump on his testicle, this may indicate worsening hemorrhoids and other inflammatory processes, sexually transmitted diseases, a general decrease in immunity, and so on.
Symptoms of spermatocele
A spermatocele may not cause any discomfort for a long time, so a man consults a doctor when the lump becomes very large and painful. The disease can be determined independently. Symptoms in this case may be as follows:
- a lump forms on the scrotum, which does not cause discomfort; upon palpation, a dense neoplasm without compactions is determined;
- pain due to the fact that the increasing size of the cyst puts pressure on the testes and nearby organs, causing pain;
- the pain becomes intense, especially sharp when walking or having sexual intercourse, if the cyst ruptures as a result of injury or overfilling.
Lymphadenitis is characterized by many symptoms, including enlargement of the inguinal lymph nodes. A small lump is felt, body temperature rises, and pain appears in the groin area. Many patients say that in severe cases, pressure may release pus.
A hernia has other symptoms. The pain increases as the disease progresses. Swelling appears at the location of the lump, and if the skin around it turns red, then the hernia may be pinched.
In the event that a lump near the testicle in men is the result of the development of prostatitis or paraproctitis, a lot of unpleasant symptoms appear. The patient's temperature rises, severe pain and discomfort appear, and the skin around the tumor becomes redder. This requires immediate consultation with a specialist.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, a man needs to see a doctor. The specialist will conduct a survey and examination using palpation. The first step will be an ultrasound examination to confirm the presence of a lump and determine what it consists of.
In the future, the patient may be prescribed the following tests and studies:
- MRI;
- testicular biopsy;
- diaphanoscopy;
- blood and urine tests;
- spermogram, etc.
The doctor prescribes all tests individually, depending on the preliminary diagnosis. So, for testicular cancer, you need to perform a biopsy and MRI, for varicocele, you will need Dopplerography to study the condition of the vessels, and diaphanoscopy allows you to diagnose hydrocele.
Self-examination
Every man should regularly self-examine his genitals. This will help you identify a lump or bump on the testicle in a timely manner and consult a doctor. It is worth noting that a tubercle on the testicle can occur at any age, even before 30 years of age. Therefore, young men should be taught to conduct self-examinations.
Rules for conducting self-examination of the testicles to identify compaction:
- The first step is to remove your underwear and place one leg on a chair to allow easy access to the testicles. Before self-examination, it is better to warm up in the shower so that the testicles relax.
- It is necessary to take a mirror and examine the genitals from all sides. If growths, bumps, rashes or redness appear on the scrotum or penis, this is a bad sign.
- The next step is to begin palpation. With one hand you need to hold the penis, and with the other you need to feel the testicle. Palpation should be carried out slowly, rolling the testicle, without missing a single centimeter. The testicle is normally smooth and homogeneous; in the upper part there is a soft formation - this is the appendage.
- You need to pay attention to your feelings. There should be no pain during palpation, as well as during erection and urination. If pain appears in the testicle, this may indicate the presence of a disease.
You need to conduct a self-examination for the presence of a lump in the testicles regularly, at least once a month. If alarming signs appear, there is no need to panic, but it is better to consult a doctor as soon as possible.
Spermatocele therapy
If the disease is asymptomatic, no special treatment is required. A wait-and-see approach is used, but it is necessary to visit a specialist from time to time (the regularity will be determined by the doctor) to monitor the dynamics. If the scrotum increases in size, pain, or discomfort due to deformation of the surrounding tissues, surgery is necessary. As part of drug therapy, analgesics are used to relieve pain and anti-inflammatory drugs.
Removal of a testicular cyst is a surgical operation that is performed under local anesthesia. If intervention is necessary due to the appearance of a lump under the testicles in men, a small incision is made under the optical device. The cyst is removed, leaving the tissue of the testicle and epididymis intact. A biopsy of the contents of the spermatocele is required.
Afterwards, the patient is given a suspension for two or more days to support the scrotum. In the reviews, patients indicate that in the first few days it is necessary to apply an ice pack to the operation site to prevent hematomas and eliminate swelling.
In rare cases, needle aspiration and sclerotherapy are used. Aspiration is carried out by puncture of the most prominent part of the scrotum with a special needle. If necessary, the doctor uses ultrasound control. During sclerotherapy, a special solution is injected into the spermatocele cavity, followed by massage to evenly distribute the drug. Within a month after the procedure, observation by a urologist is necessary.
Hernia treatment
If lumps on the testicles in men (photo below) are caused by a hernia, then the only treatment option is surgery. Surgery can be postponed if the tumor is not painful, does not cause discomfort and is small in size. But if you ignore a hernia for a long time, then there is a risk of strangulation (in this case emergency intervention is indicated) and subsequent infertility.
If there is no infringement, the doctor can still choose a wait-and-see approach in order to accurately develop surgical treatment tactics over the next period of time. If there are contraindications to surgery, wearing a special bandage is recommended to protect the hernia from strangulation. Patients who belong to this group need to be especially careful in treating chronic cough and other diseases that provoke increased pressure in the peritoneum.
Treatment
Treatment for a lump in a man’s testicle will directly depend on the cause of its appearance. For inflammation, anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics will be prescribed. Spermatocele is treated surgically or not treated at all if the cyst is small and does not cause inconvenience.
Varicocele severely impairs reproductive function and requires surgical intervention. Testicular cancer will also require surgery, as well as chemotherapy and radiation therapy; the course of treatment is selected by a specialist individually. Hydrocele of the testicle is treated by removing fluid from the testicle, and anti-inflammatory therapy is also indicated. Hernia is treated mainly surgically.
Thus, most diseases that cause a lump in the testicle require surgical treatment. The sooner therapy begins, the fewer complications there will be. Therefore, when a lump appears, you must immediately visit an andrologist and undergo an examination.
Therapy for lymphadenitis
With pain and a lump on the testicle in men, lymphadenitis can be diagnosed. Treatment of the disease in the acute stage is conservative. Antibiotic therapy is carried out (medicines are selected based on the sensitivity of microbes found in tests), vitamin therapy, and UHF. You should not ignore taking vitamins - reviews confirm this. Complete rest of the affected area is indicated. In case of purulent lymphadenitis, it is necessary to open the lesion according to the principles of managing purulent wounds. Additionally, in this case, detoxification and antibacterial therapy is prescribed.
Chronic lymphadenitis requires treatment of the underlying disease, which supports the inflammatory process in the lymph nodes. Specific forms of the disease are treated taking into account the underlying inflammatory process (tuberculosis, syphilis, gonorrhea, actinomycosis, and so on). Timely treatment will help avoid the spread of pathology.
Cancer
The most serious reason that leads to the formation of a white lump on the testicle in men is oncology. The tumor can be benign or malignant. Malignant ones are rare. Only a small percentage of young and middle-aged men have testicular cancer, and in older men the disease is practically not registered, but it is still necessary to be examined to exclude the presence of a dangerous neoplasm.
With oncology, patients experience severe discomfort, burning and itching in the groin area, and sometimes the mammary glands can become enlarged due to the production of female hormones. The prognosis is favorable only if the tumor is detected in the early stages. Treatment involves removal of the testicle and additional radiation or chemotherapy.
Photos of lumps on the testicles in men
Now you know that the appearance of a lump on a testicle does not bode well, and a visit to the doctor is considered a vital step. Even if the formation does not manifest itself in any way, an ultrasound of the scrotal organs will help to prevent most terrible diseases in time.
Lump in children
A lump in the groin area in a child requires consultation with a surgeon. Most often, an inguinal hernia or dropsy is diagnosed. If the child is less than a year old, the lump is not painful and does not increase in size, then regular monitoring is indicated. Congenital dropsy is caused by intrauterine disorders. This pathology in boys under three years of age is facilitated by the pathological course of the mother’s pregnancy and conditions accompanied by a constant violation of intra-abdominal pressure.
Physiological dropsy, which provokes the formation of a lump on the testicles, in most cases goes away on its own and does not require medical intervention. If the disorder is caused by some other disease, then treatment of the primary disease is necessary. Intense dropsy (fluid accumulates inside and is not removed anywhere) requires a puncture, but there is a high risk of relapse. Surgical treatment is recommended when indicated at the age of one and a half to two years. This is a recommendation from doctors; reviews from parents confirm that this is the optimal age at which the child tolerates the intervention normally.
Possible diseases
Unfortunately, not all testicular lumps are considered safe. There are a number of pathologies that require immediate surgical intervention to save the patient’s life:
- Hydrocele. A disease in which fluid begins to accumulate in the membranes of the testicle. At the initial stage, you may think that a lump is growing in the scrotum. As the process progresses, the testicle (usually a pathological process is observed in one of the organs) may increase in size, hurt when pressed, and feel heaviness. The reasons for the appearance may lie in old injuries of the groin area and inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system. Treatment is only surgical, the goal of which is to completely remove the accumulated fluid.
- Varicocele. A very insidious disease that occurs in many men after 50 years of age. At a young age, the appearance of varicocele can be provoked by heavy physical activity, lack of regular sex life, and a predisposition to varicose veins. At the initial stage it does not manifest itself in any way. Starting with grade 2 varicocele, small bumps may appear on the testicle, which can be felt when the abdominal muscles are tense. Varicocele grades 3 and 4 are already visible to the naked eye. Treatment is only surgical. The Marmara operation is considered the most effective.
- Epididymal cyst. Depending on their size, cysts can negatively affect testicular function, which can affect sperm quality. The reason for the appearance may lie in inflammatory processes of the scrotal organs and genital infections (which usually occur with sluggish symptoms). If the cyst increases in size and puts pressure on the organ, the man may experience pain in the groin during ejaculation or discomfort during sexual intercourse. Diagnosis includes palpation of the formation and ultrasound of the scrotal organs. Small cysts that are not accompanied by any symptoms do not require treatment. Large formations are removed using a radio wave scalpel. The duration of the operation is on average 30-40 minutes.
- Testicular injuries. After fights, falls and aggressive sex. Dried blood may feel like a lump. There is sharp pain in the scrotum, heaviness in the testicle, blood during urination and in semen. A visit to a urologist is mandatory, as there is a risk of developing atrophy of one of the testicles.
Separately, I would like to take out malignant tumors that can affect the scrotum. Usually occurs in older men. The oncological process can be triggered by the presence of inflammatory processes in the genitourinary system, cysts and other formations in the testicles that can degenerate into malignant tumors. In advanced cases there is a risk of death. Treatment involves removing the tumor within healthy tissue (in half of the cases the entire testicle is removed).