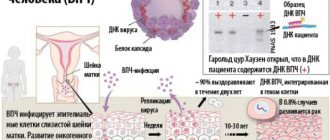
Human papillomavirus, commonly abbreviated as HPV.
This is the causative agent of the most common infectious pathology of mucous membranes and skin throughout the world, the so-called. papillomavirus infection.
There are about 200 types of this virus.
About a fifth of which can be transmitted through sexual contact, damaging the organs of the urogenital system.
This pathogen is of particular concern due to the connection between infection and cancer pathologies.
Thus, 93% of episodes of cervical cancer in women are caused by this particular virus, of which 70% are HPV types 16 and 18.
That’s why, if a woman’s HPV 16 is detected in tests during an examination, the doctor strongly recommends additional studies.
So what is it: HPV 16 genotype in women?
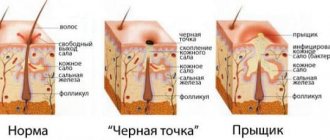
All papillomaviruses are conventionally divided into three main groups depending on their oncogenic danger:
- non-oncogenic, causing flat/plantar/vulgar warts (types 1, 3, 2, 4, 41, 10, etc.), not capable of causing malignant transformations
- low risk, causing the development of anogenital warts (otherwise called genital warts), resembling characteristic cauliflower buds, epidermoplasia verrucous, laryngeal papillomatosis (types 5, 17, 12, 6, etc.), can extremely rarely, under very “favorable” conditions, cause malignant process
- high risk, capable of causing neoplastic changes in women in the area of the uterine cervix, bowenoid papulosis (HPV types 16 and 18, 33, 31, 39, 35, 58, 56, 45, 68, 59, 52, 51), have been proven to provoke the overlap of various factors oncological processes
Thus, the answer to the question of whether HPV 16 infection is dangerous for a woman’s health has been determined: it is this type of virus that poses a serious threat.
However, the presence of a pathogen does not mean the presence of a disease.
In addition, HPV infection has an interesting feature: the ability to self-heal.
That is why in a situation where a certain amount of HPV type 16 DNA is detected in women during laboratory tests, it is important not to panic.
You just need to follow your doctor's recommendations and undergo regular examinations with a gynecologist.
Causes and symptoms of appearance
The main route of transmission of the pathogen is considered to be direct contact with the mucous membranes and skin of an infected person. Contact-household infections are not excluded, when the use of common household items can lead to infection. This is possible due to the long-term presence of the virus in exfoliated epithelial cells.
Men do not develop stable immunity to HPV 16. With repeated infection, a relapse is possible when, as a result of the influence of internal and external factors, the papillomavirus begins to actively multiply.
These factors include:
- sexual intercourse with a carrier of infection;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- decreased immunity due to hypovitaminosis, cancer, immune diseases, taking certain medications, exposure to low temperatures, ionizing radiation;
- damage to the skin and mucous membranes.
Considering the risk of developing cancer, factors that increase the likelihood of dangerous consequences include:
- smoking;
- other sexually transmitted infections;
It has been proven that nicotine derivatives have the properties of mutagens and can cause cancer.
STIs often occur together with HPV in men. Such cases are difficult to treat; the affected area increases due to a strong decrease in local immunity, which plays a key role in the fight against the pathogen.
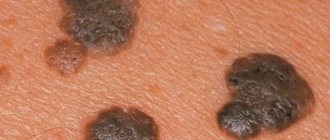
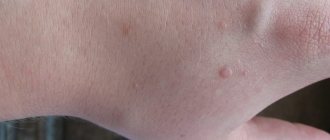
The human papillomavirus causes genital warts. The appearance of HPV type 16 in men is characterized by the following symptoms:
- growths of soft consistency;
- lobular structure;
- resemble cauliflower due to growth on the surface;
- have a leg (in most cases narrow);
- identical in color to healthy tissues;
- can be multiple or single;
- when irritated, they change color to red, there is itching, burning or pain during hygiene procedures;
- prone to the formation of erosions, then ulcers with purulent, foul-smelling discharge;
- characteristic localization is the border between the skin and mucous membrane.
The manifestation of symptoms of the disease depends on the state of the DNA of the pathogen.
Viral DNA, integrated into the genetic apparatus of the target cell, begins to multiply, then they speak of a productive infection, in which clinical signs appear - condylomas. When viral DNA is not integrated into the nuclear material, the disease enters the stage of non-productive infection, in which viral particles do not reproduce and there are no clinical symptoms.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Where does HPV type 16 come from in women?
According to WHO, up to 80% of the population is infected with HPV.
But only about 10% of those infected have clinical manifestations.
The answer to the question of how HPV 16 is transmitted to women is well known: the main route of infection is sexual contact.
Including anal-genital and oral-genital, with an infected partner.
HPV has a very high prevalence: almost 80% of women by the age of 50 have been infected at least once.
At the same time, the virus has a tendency to self-eliminate.
So it is not possible to establish the probability of infection after a single contact.
This is why it is so important not to neglect preventive measures during casual sexual acts.
Infection of a child by the mother at the time of birth is possible with viruses of types 6 and 11 - the cause of such a disease in children as respiratory papillomatosis.
No other types of virus, including HPV type 16, usually cause problems during pregnancy in either women or newborns.
There are only isolated cases of infection of newborns by mothers with bowenoid papulosis.
Therefore, routine HPV testing is not recommended by any international/national guidelines.
The incubation period varies from three months to several years.
It is possible to become infected with several types of viruses at the same time.
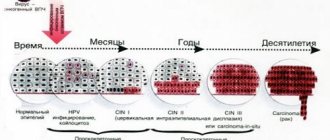
After entering the body, the virus infects the tissue covering the surface of the body and organs - the epithelium, namely its inner part (basal layer).
The virus inside the cell may not affect chromosomes or integrate into the genome.
The last option, the so-called. the malignant form is manifested by the appearance of cells with altered DNA, which multiply and form a tumor.
Thus, if a woman is a carrier of HPV type 16, 18, 6, 11 or others, the following conditions are possible:
- latent course of infection, when the virus does not affect cellular DNA, women have no clinical manifestations, and infection is detected only by PCR
- the appearance of such clinical manifestations as condylomas, warts, papillomas, the virus does not change the cellular genome, but provokes increased cell proliferation (the problem is detected by the presence of symptoms, PAP test, PCR method)
- the development of neoplastic changes (dysplasia), when the virus made a change in the DNA of the cell and caused corresponding changes in the latter (such changes are called koilocytosis), the situation is confirmed by PCR, PAP test, histological and colposcopic examination
- carcinoma, when the pathogen has changed the cellular genome and caused the formation of a large number of altered (“atypical”) cells – invasive cancer (the diagnosis is confirmed by PCR, Pap test, histological and colposcopic studies)
In most situations (up to 90%), the body heals from the virus within about 2 years.
The development of symptoms is observed only in 1-5% of infected people.
With regard to HPV 16, causes of severe clinical symptoms in women include:
- early onset of sexual activity
- having multiple sex partners
- multiple pregnancies/births before age 20
- smoking
- chronic cervicitis
- decreased immune defense, for example, due to concomitant HIV infection (with a normal functioning immune system, cancer in an infected woman can develop in 15-20 years, while in an HIV-infected woman - in 5-10 years, while HIV also increases the likelihood HPV infection)
HPV 16
Hello, lovely girls. My story began with the fact that after many attempts to get pregnant, which were unsuccessful, I turned to G. in order to find out the reason for our mistakes. Everything was fine with me, except for candidiasis and an increased number of leukocytes in the smear. G. prescribed treatment for candidiasis, after which I took a smear again, as a result, the number of leukocytes doubled. The doctor said that apparently it’s just my body and an increased number of leukocytes is normal for me. This answer did not suit me and I went to another clinic. They sent me for PCR, where it turned out that I have HPV type 16 and apparently my white blood cells are going wild because of it. She prescribed three months of treatment with Allokin-alpha and other medications, plus contraception. I probably paid about 30 thousand for all these medications, so that G. could assure that these were all effective drugs and improvements would be “immediate”, well, for my health and purpose, to get pregnant I don’t mind anything, I bought everything, did all the manipulations. 45 days after treatment, I take an HPV test, but only in a quantitative manner and what do I see...NO changes, according to the doctor, the load is still high (5.4), apparently this rubbish is sitting in your little erosion, it needs to be removed, plus thrush has appeared , we need to treat. As a result (I already wrote about this once) she prescribes me a huge stack of drugs again, but against thrush for three months and again with protection, although I warned her that I had a purulent sore throat and took a strong antibiotic, perhaps because of this the thrush appeared , no, he says, you have it chronic =( But why didn’t she see it during the whole year of my visits to her. In general, I’m still being treated, but then another problem appeared, although at that time it seemed to me that it was a miracle... there was a 10-day delay. I ran to G. at her place of residence, told everything about how they were treated, what they did... her eyes, of course, were the size of nickels... I found out from her (and I also read on the Internet) that HPV is not treated at all before the age of 30, if the cytology is good that he can leave the body on his own and that he cannot sit in erosion, since it’s all at different cellular levels, looking at my erosion, she said that it is so small and just slightly on the surface that don’t even think about touching it I took a smear and it turned out that I didn’t have thrush, although my white blood cells were really elevated, most likely it was passed on to me from my husband if he had or had inflammation. She prescribed inexpensive medications for me and anti-inflammatory medications for my husband for prevention. She reassured me that with my body I can easily get pregnant and all my supposedly terrible illnesses do not affect B. in any way. These same words were later confirmed by a fertility doctor, who was also surprised by my HPV treatment. In general, at the moment I’m putting my microflora in order. I will no longer go to the private clinic where I was treated. And then...I don’t even know...I’ve already explored everything in myself, except for lapora, this will probably be my last step towards natural conception. The story turned out to be huge, but I left out a lot of points, thanks to everyone who read =)
Manifestations of HPV infection
In most situations, when infected with HPV in general and, in particular, HPV 16, women, as well as men, have no symptoms.
Sometimes a sign of infection can be warts and condylomas (in the case of the presence of a virus from the low-oncogenic/non-oncogenic group).
With HPV 16 infection, women may experience precancerous changes on the cervix.
This is revealed during a gynecological examination.
Or preventative, or when the patient consulted a doctor for another reason, for example, with complaints of unusual discharge.
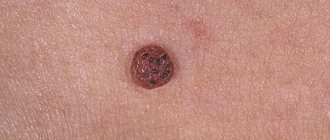
The main diseases caused by HPV 16 are bowenoid papulosis and dysplasia of varying degrees.
With bowenoid papulosis, dense brownish, reddish or flesh-colored papules appear in the labia, pubis, inguinal and perianal areas.
They merge into large warty surfaces up to 2 cm in diameter.
The disease is characterized by a chronic, long-term course.
Malignancy develops in 3% of episodes (degenerates into squamous cell carcinoma), although self-healing is more often diagnosed.
Cervical dysplasia is a precancerous change and requires serious consideration.
Since this pathology may not be diagnosed in a timely manner due to its asymptomatic course, most countries in the world have adopted cervical cancer screening programs.
There are several classification approaches for dysplasia and cervical cancer.
They are based on the results of morphological/cytological studies (studies of cell changes).
According to the International Classification of Diseases, 10th revision, there are:
- mild dysplasia - minor proliferation and changes in epithelial cells, often a similar condition is detected during inflammatory processes in the uterine cervix and is eliminated after appropriate anti-inflammatory therapy
- moderate dysplasia - changes affect the entire lower layer of the epithelium
- severe dysplasia - the entire length of the epithelium is affected, the cell structure is noticeably changed
- cervical cancer (otherwise known as squamous cell carcinoma) – detected during colposcopic examination, confirmed cytologically and histologically
Moderate and severe dysplasia in most episodes is caused by exposure to the virus.
Signs of cervical cancer are detected only in the last stages and include:
- bleeding between menstrual periods, irregular, after sexual intercourse
- unpleasant smell of discharge
- vaginal discomfort
- pain in the pelvic area, back, legs
- weight loss
- fatigue, lack of appetite
- unilateral swelling of the legs
As the disease progresses, the severity of symptoms may increase noticeably.
Diagnosis of HPV infection
Anogenital warts, caused by viruses type 6 and 11, are easily detected during a gynecological examination.
Identification of such formations is an indication for additional examination of the uterine cervix, and, if necessary, the urethra (urethroscopy).
The main method for detecting neoplastic changes caused by HPV is the Pap test.
It is a cytological study of smears from the uterine cervix.
In general, oncocytology is a method for detecting cancer cells in the cervix and vagina.
Samples of material for study are taken during a gynecological examination using special cyto-brushes and are absolutely painless.
A distinction is made between simple oncocytology, when the cells under study are immediately applied to slides for microscopy.
And liquid, when the cells are pre-treated with a special solution and dye.
The latter type is the PAP test.
After processing the material with two types of dyes, changes in the cell nuclei and cytoplasm are easily detected in the sample using microscopy.
The type of pathological process is preliminarily determined: inflammatory, malignant, or other.
Then, based on the severity and nature of the changes, a differential diagnosis of possible conditions is carried out.
The PAP test is included in the screening system for detecting cervical cancer in all developed countries.
Its annual holding is recommended for all females who have reached the age of 20 years.
Cytological signs of HPV infection include:
- koilocytosis - the appearance of characteristic koilocyte cells with voluminous uneven nuclei, vacuoles (absent normally) and clearing zones near the nuclei
- dyskeratocytosis - the appearance of keracite cells with dark nucleoli and characteristically altered cytoplasm
If the PAP test reveals a change in cellular structures, the following is carried out:
- colposcopic examination with acetic acid examination and test with Lugol's solution
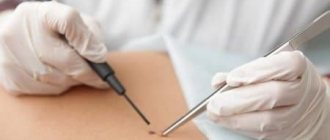
- histological examination – small fragments of tissue are studied under a microscope (the latter are obtained by targeted biopsy)
Colposcopic signs of infection:
- lightening of areas treated with acetic acid
- uneven staining with Lugol's solution
- the presence of characteristic outgrowths (for low-oncogenic types of the virus)
According to international recommendations, diagnostic tactics for detecting disorders using the PAP test include:
- The first option is to repeat the examination after three months, in case of normality, repeat after six months and a year, in case of abnormality - colposcopic examination
- The second option is to immediately conduct a colposcopic examination; if no abnormal abnormalities are detected, cytology is repeated six months later (for oncogenic types of the virus). If necessary, a biopsy and canal curettage are performed. In a situation with insufficient reliability of colposcopic data, anti-inflammatory, estrogen therapy is recommended, followed by repeating the study
- The third option is to determine the type of virus using the hybrid capture method (the so-called Daijin test, Digene) or PCR (polymerase chain reaction). Detection of HPV type 16 or another oncogenic virus in women (the norm is the complete absence of the pathogen) is an indication for colposcopy
Typing of papillomaviruses by PCR has a high diagnostic value in terms of determining the type of virus and its belonging to a high-risk group of oncology.
Also to predict the likelihood of developing cancer against the background of existing neoplastic changes in the cervical epithelium.
Qualitative analysis produces a result in the format “there is a virus of this type / not.”
The quantitative method (real-time PCR) allows you to detect viral DNA even in very low concentrations from 10 to 100 copies in a sample.
Can be used to track the dynamics of infection.
Due to the fact that young women have a high rate of self-healing from HPV, PCR is recommended to determine the type of virus only after the age of 30.
A blood test to determine antibodies to HPV has no diagnostic value and is carried out only for research purposes.
As for the problem of preferring the Digene test or PCR, it is important to consider that the first method determines the number of HPV type 16 and other types in women from 5000 copies.
Whereas PCR “senses” a significantly lower content.
This point is significant from the point of view that this is the number that is clinically significant.
Those. More than 5,000 copies were detected against the background of neoplastic conditions - a high risk of oncology.
And detection of a smaller amount does not allow predicting the risk of developing cancer against the background of dysplasia.
In general, the analysis data allows the doctor to decide whether to start treatment or limit himself to observation.
Treatment methods for HPV 16 in men
Treatment of HPV in men, including type 16, is carried out by a dermatologist, but consultations with a urologist, proctologist, or oncologist may be required. It all depends on the location of the growths. At the moment, there are no drugs that can completely eliminate the pathogen from the body. The fight against growths, as sources of infection, allows us to reduce the patient’s contagiousness and the concentration of the virus. In some cases, the disease resolves on its own, thanks to the immune system.
Pharmacy drugs
Treatment of HPV type 16 in men involves antiviral drugs with an immunomodulatory effect.
- Aldara cream contains imiquimod, a substance that stimulates the immune response. Does not have direct antiviral activity. The action is based on stimulation of interferon synthesis. The cream is used strictly according to the instructions and personal hygiene is observed daily due to side effects.
- Acyclovir ointment is an antiviral agent. It disrupts the process of viral DNA synthesis and prevents the assembly of new viral particles. Used mainly against herpes, effective against HPV in men.
- Isoprinosine increases the activity of T-lymphocytes and macrophages, suppresses DNA assembly due to disruption of ribosome functions.
- Lykopid stimulates the activity of immunocompetent cells, and an antiviral effect is realized.
- Interferon has an antiviral and immunomodulatory effect.
Medicines are used in combination with hardware removal methods.
Traditional medicine methods are not as effective in treating HPV strain 16 in men as official medications. You may harm your health.
Removal methods
Hardware methods for removing manifestations of HPV type 16 in men include:
- diathermoelectrocoagulation;
- laser therapy;
- cryotherapy;
- radio knife
Diathermoelectrocoagulation or electric knife is a method based on the ability of conductors with high resistance to heat up when current passes. High temperature ensures thermal melting of tissues, cauterization of papillomas occurs. As a result of the procedure, a scab is formed, which is rejected after a week. The only contraindications are cardiac arrhythmias of organic origin and the presence of a pacemaker.
Laser therapy is based on the ability of a laser to sharply increase the temperature of intracellular and intercellular fluid to high values. The liquid evaporates and the cells are destroyed. By adjusting the depth of the lesion, layer-by-layer evaporation of the pathological focus is carried out. Vessels are cauterized. As a result, a scab is formed. Large HPV growths are removed in several stages.
Cryotherapy is the use of low temperatures that cause ischemic necrosis in the affected area. After three days, a demarcation zone is formed, and dead tissue is rejected. The method is widely used due to its painlessness.
Radio knife - the use of radio waves. The method is painless and bloodless. Does not leave scars. The risk of relapse and infectious complications is minimal.
If oncology is suspected, surgical excision of the growth is performed within healthy tissue.
Treatment of HPV infection
Which doctor treats HPV 16 in women?
Treatment of HPV infection can be carried out by a gynecologist, oncologist, infectious disease specialist, or venereologist.
It is important to understand that accidental detection of the virus in the absence of clinical changes is not an indication for therapy.
Only if highly oncogenic viruses (HPV 16) are detected in women, the doctor decides what to do next.
Is it necessary to undergo diagnostic examinations and examinations more frequently or to prescribe additional studies?
Only a specialist can determine whether it is necessary to treat HPV 16 in women, taking into account the presence/absence of changes induced by the virus.
In a situation with HPV, it is important to trust your health only to highly professional specialists who are familiar with international protocols for managing the infection.
This is especially important when infected with HPV 16, which provokes malignant pathologies in women (reviews on the Internet or from friends will help you decide on an institution and a doctor).
Today, in women, treatment for HPV 16 is based on the removal of atypically changed epithelium.
It should be understood that if women have an infection, there are currently no drugs that destroy the virus itself.
Any international treatment regimen for HPV 16 does not include any antiviral agents.
At the same time, specific treatment for HPV 16 is carried out, in which it is recommended that women take drugs with immunomodulatory and antiviral activity.
It is believed that such drugs mobilize the immune system to fight the virus.
Such products have not been sufficiently tested for effectiveness in clinical trials.
Accordingly, there is no reliable data on the cure rate.
Despite this, many patients note a significant improvement in their well-being after using them.
Immunocorrective therapy for HPV 16 in women includes:
- with human recombinant interferon or its inducers, suppositories (Viferon, Genferon), Isoprinosine, Cycloferon, etc.
- with an immunostimulating effect - Lykopid, Polyoxidonium, etc.
- B vitamins, omega acids and dietary supplements
Often, before prescribing a drug treatment regimen, an analysis of the immune status (immunogram) is recommended.
With determination of indicators of the activity of monocytes, neutrophils, lymphocyte function, levels of immunoglobulins, CD16+, CD8+, CD4+ and others.
Unfortunately, for many drugs, data on the safety of use, complications and relapses after use have not been obtained.
Therefore, it is recommended to refrain from using them for people with:
- autoimmune diseases
- malignant formations (for cervical cancer can be prescribed only after completion of surgical treatment)
- allergic reactions
- bronchial asthma, etc.
As for the generally accepted approach to the management of HPV infection in the international medical community, the following points are positioned here:
- There is no medicine to remove the virus from the body, but the likelihood of self-healing is very high, especially at a young age
- If there are no changes in cellular structures and a virus from a high oncogenic risk group is identified, more frequent and careful monitoring of the patient is carried out
- If changes caused by the activity of the virus are detected, therapy is carried out aimed at eliminating pathological changes
For bowenoid papulosis caused by HPV type 16, tumors are removed using the following methods:
- Mohs excision
- laser therapy
- cryodestruction
- electrocoagulation
- local application of ointments with cytostatics (5-fluorourocil, prospidin, fluorofur)
- intralesional administration of interferon
- oral administration of Neotigazon capsules
Precancerous conditions and the first stages of cervical cancer are highly treatable.
The changed cells are removed using cryotherapy.
For dysplasia, organ-preserving operations are performed: conization of the cervix with a scalpel, electrosurgically, laser with preliminary canal curettage.
For localized forms of the tumor, surgical treatment is carried out, for a widespread process - radiation and chemotherapy.
Taking into account the fact that eliminating the result of virus activity does not remove the infectious agent itself.
The risk of recurrence of pathological changes remains, which, in turn, requires further monitoring of the patient.
In addition, the possibility of HPV reinfection cannot be excluded.
After implementing any treatment option, follow-up tests are recommended.
Since there is a possibility of spontaneous elimination of the virus within 2 years from the moment of infection.
A separate problem is presented by persons with HPV against the background of HIV infection.
It has been proven that the risk of developing cancer in such women is higher, as is the risk of HPV infection itself.
Although primary HPV infection was detected more often, which is associated with the greater prevalence of this virus.
Moreover, the worse the patient’s immune status, the higher the likelihood of her developing HPV-induced cancer.
Therefore, people with HIV status are recommended to undergo HPV testing more frequently.
Treatment is carried out using the same methods as for those uninfected with HIV, with additional specific therapy aimed at suppressing the activity of the immunodeficiency virus.
Rumyantseva, md.
Why do we even have to discuss these types of HPV? Because HPV is the cause of cervical cancer, and types 16/18 are the most “aggressive” of all.
Not all women with HPV 16/18 will develop cervical cancer, but among all cases of cervical cancer, one of these types is responsible for 70%. Let's figure out how to prevent this from happening.
1. If less than 10 years have passed since the beginning of sexual activity, getting tested for HPV is pointless. The virus can still easily “go away” from the body, but you will spend enough nerves. According to most recommendations, it makes sense to get tested for HPV starting at age 25-30.
2. If more than 10 years have passed since the beginning of sexual activity (or you are over 30 years old), an HPV test should be taken together with a PAP test (cytological examination of a smear from the cervix). If HPV type 16/18 is detected, it is worth doing a colposcopy.
3. If HPV 16/18 is detected, but there are no changes according to the PAP test and colposcopy, you need to repeat the study after 1 year, nothing more.
4. If changes are also detected in the Pap test, a biopsy will most likely be required. If there is no change in the PAP test, a biopsy may also be needed, but much less frequently.
5. Based on the results of the biopsy, you will receive a histological report. In the best case scenario (and this happens most often), the histology will indicate that the affected area is harmless (dysplasia) and has been removed entirely. In this case, there is every reason to hope that after 6 months the virus will no longer be in the body. In the worst case scenario, histology results will reveal a severe lesion (precancer/cancer) extending beyond the removed area. Then extended surgery will be required.
6. HPV does not cause inflammation of the cervix/vaginal discharge/itching/burning/pain during sexual intercourse. It is pointless to get tested for it with these complaints and manifestations.
7. There is no cure for HPV!!!
Neither injections, nor suppositories, nor pills will help get rid of HPV.
8. BUT! The body can get rid of the virus itself within 2 years from the moment of infection (which happens in 90% of cases).
9. The vaccine does not cure HPV! Vaccination is most reasonable before the onset of sexual activity, when infection has not yet occurred! I wrote in detail about HPV vaccination here.
Total:
If HPV type 16/18 is detected, a Pap test and colposcopy must be done, and further tactics depend on the results of these studies. There is no cure for HPV!!!
Take care of yourself!
More information about HPV in the articles:
- HPV: general information
- Low risk HPV
- HPV and cervical cancer
- Vaccination against HPV