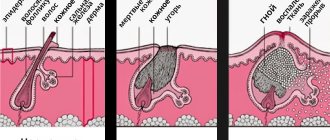
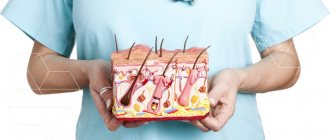
Hidradenitis is an inflammation of the apocrine sweat glands located in the axillary region, around the nipples, in the groin, on the scrotum and labia majora in women, in the umbilical region, around the anus. Hidradenitis of the scalp is extremely rare. Apocrine glands have a special structure - their apical cells are constantly destroyed and mixed with sweat. The secretion of these glands contains a lot of cholesterol and fat, its thickness is increased, and it has a unique, individual smell. Most often, hidradenitis develops in the axillary region, where the sweat glands are large and their passages are tortuous. The disease refers to pyoderma or purulent skin lesions.
Who gets hidradenitis most often?
Middle-aged women are more likely to develop axillary hidradenitis as a result of injury during hair removal or shaving. In men, the groin area suffers. In general, the disease develops in people aged 15 to 55 years, since apocrine glands actively function during the childbearing period. Often, the development of inflammation is facilitated by violations of personal hygiene rules. The disease can take a recurrent form.
People with dark skin are at risk because their gland ducts are wide and short, making it easy for bacteria to penetrate through them.
Causes of hidradenitis
Hidradenitis is most often caused by streptococcus and staphylococcus, but can also be E. coli and other microbes.
The most common causes of hidradenitis and provoking factors:
- increased sweating;
- obesity;
- skin diseases - diaper rash, eczema;
- endocrine diseases, especially diabetes;
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- excessive use of deodorants;
- difficult working conditions - dust, harmful emissions;
- immunodeficiency states;
- rough depilation, injuries from shaving, scratching;
- wearing tight clothing, leading to chafing of the skin;
- the presence of a focus of bacterial infection in the body;
- severe stress conditions;
- hereditary anatomical features of the structure of apocrine glands.
How does hidradenitis manifest?
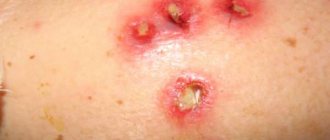
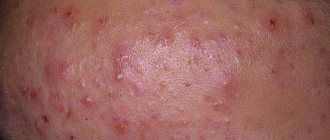
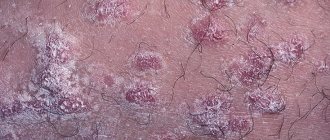
The symptoms of hidradenitis are typical and difficult to confuse with other diseases. The initial manifestation is persistent itching, then small subcutaneous nodules appear, which increase every day. The process is accompanied by pain, discomfort and even limitation of movements. The nodules gradually increase in size and begin to protrude above the skin level. The surrounding tissues swell and acquire a purplish-bluish tint. This is followed by softening of several nodules, openings that secrete pus, sometimes mixed with blood.
The disease received its popular name (“bitch udder”) because of the characteristic appearance of the affected area: a swollen, reddened circle with white discharge.
The general condition suffers little, there is usually no fever. There is discomfort and slight malaise. The addition of symptoms of general intoxication indicates either the spread of infection or the development of complications.
Opening the abscess improves the general condition, the pain subsides, and mobility increases. If there are no complications, then the ulcers are completely emptied and heal with the formation of a retracted scar. The entire development cycle of the disease with timely assistance is 2 weeks.
Sometimes the course of the disease becomes chronic when the nearby sweat ducts become inflamed. In this case, the affected area alternates between old scars from healed ulcers and fresh areas of suppuration. A painful infiltrate forms, the skin over which is lumpy and inflamed. This condition can last a month or longer. In this case, hospital treatment may be necessary.
Signs of the disease
The pathology begins with redness in the armpit area. A painful lump, a pea-sized nodule, gradually appears, and the aching, twitching pain intensifies. The lump grows and becomes like a purplish-red lump. If treatment is not started, necrosis of the skin over the source of infection occurs and an abscess develops. Pus begins to ooze from the node.
After five days, the abscess bursts, the contents pour out of the wound, and an ulcer forms. Gradually, it heals with the formation of scar tissue. The disease lasts up to two weeks. At this time, patients complain of fever, malaise, headache, decreased ability to work, limited mobility of the shoulder and entire arm. The inflammatory process often affects not one gland, but several. An incompletely cured disease can develop into chronic axillary hidradenitis.
Furuncle or hidradenitis?
To begin adequate treatment, you need to be able to distinguish between these inflammatory processes.
Boils, or boils, are purulent inflammation of hair follicles that like to be localized under the armpits. An abscess occurs due to poor personal hygiene and excessive sweating, especially in hot weather. The abscess takes a very long time to mature, causes severe pain, the site of inflammation turns red, and red stripes appear along the lymph nodes.
Complications of hidradenitis
Weak people or those left without medical care may develop an abscess or cellulitis, and extremely rarely, sepsis. Often, HIV/AIDS becomes a provoking factor in the development of complications.
The most likely cause of complications is lack of care for the skin surrounding the inflamed gland. On dirty, macerated or weeping skin, the infection spreads very quickly, capturing more and more new areas. For an abscess to form, it is enough for several nearby glands to become inflamed. In this case, the ulcers merge, melting neighboring tissues, destroying subcutaneous tissue, sometimes reaching the muscles.
Phlegmon is the next stage of development of an abscess. This is a diffuse inflammation that develops most rapidly in the subcutaneous tissue. Phlegmon can develop both near the site of primary inflammation and at a distant site.
Abscess and phlegmon are accompanied by signs of general intoxication, sharply aggravating the patient’s condition.
Sepsis occurs when pathogenic microbes enter the general bloodstream. In this case, ulcers can form in any organ; this is an extremely dangerous condition.
Conservative treatment
Treatment of hidradenitis is most successful in the early stages, when inflammation is just beginning or 1-2 glands are affected. The patient can seek help from a dermatologist.
At CELT you can consult a dermatologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,200
- Repeated consultation – 2,000
Make an appointment
Therapeutic tactics depend on many factors: location of hidradenitis, age, gender, concomitant diseases, general level of health.
If a single gland is inflamed or located far from each other, the most important thing is to carefully care for the surrounding skin, repeatedly wipe it with any alcohol (boric, salicylic, camphor). Constant removal of secretions, coupled with the tanning effect of alcohol, will help prevent the infection from spreading. The hair around the site of inflammation should be carefully trimmed.
You should not take baths in the midst of illness; bathing promotes the spread of infection. The site of inflammation should be covered with a tight bandage, secured with a band-aid and use a shower.
To fully recover, you need to follow a diet with limited sweets, alcohol, spices and seasonings for at least 3 months. A therapeutic diet that strengthens the defenses is recommended. You need to eat a lot of vegetables and fruits rich in natural compounds: cabbage, apples, citrus fruits, carrots, rose hips, walnuts. Natural stimulants such as tinctures of eleutherococcus and ginseng, plantain juice, and rosehip decoction are useful. It is advisable to supplement your diet with pharmacy multivitamins.
Conservative treatment is prescribed by a doctor. Most often these are antibiotics - semi-synthetic tetracyclines or other groups, which are selected based on the results of a bacterial examination. If staphylococci are detected, the appropriate gamma globulin or vaccine can be used.
Until the ulcers are completely formed, the skin must be treated with various antiseptics: strong (96%) alcohol, brilliant green, tincture of iodine. If the area of inflammation is extensive, it is injected with antibiotic solutions with novocaine. Sometimes semi-alcohol dressings are required, which are changed as they dry. Ointments cannot be used, they increase the area of suppuration.
Under no circumstances should you try to squeeze out or otherwise open the abscess yourself. Any inept manipulation leads to the spread of pus in the tissues, which only leads to a worsening of the condition. The likelihood of complications with this approach increases many times over.
Diagnostics
Hidradenitis can be determined based on a blood test. Since the symptoms of the disease are similar to other skin diseases, inexperienced patients, trying to make a diagnosis on their own, confuse it, for example, with furunculosis. By examining blood tests, you can identify characteristic signs of inflammation: an increased number of white blood cells and a high erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR).
Additionally, microflora from the inflamed area is examined. This helps the doctor choose the right antibiotics for further treatment of hidradenitis.
In chronic cases, doctors recommend an immunogram for the disease. It will tell you the state of the body’s protective functions. If there are corresponding violations, treatment will be prescribed by an immunologist. Basically, patients with inflammation of the apocrine glands require the help of a dermatologist or surgeon. Pregnant women should consult their gynecologist.
Surgical treatment of hidradenitis
Surgical intervention is required if the center of inflammation has already softened or spontaneous opening of the abscess has occurred. At the same time, it does not make sense to open and drain one abscess, because in the thickness of the tissue there are many small forming suppurations. A wide incision is made, giving access to the entire inflammatory infiltrate. The incision should reach the border of healthy tissue. All pus is removed, and then all fatty tissue in the area of inflammation. Drains are installed, healing always occurs by secondary intention.
At CELT you can consult a surgeon.
- Initial consultation – 2,700
- Repeated consultation – 1,800
Make an appointment
In case of recurrent or chronic course, when inflammation is repeated many times, radical surgery is required. This treatment takes place in two stages.
First, the area of chronic inflammation is opened with a wide incision and all affected subcutaneous tissue is removed. The surgical wound is healed openly and the necessary antibiotics are used.
When the wound is clean and healthy granulations appear in it, the diseased skin and subcutaneous tissue are completely removed. The resulting defect is covered with the patient’s own skin flap obtained from another area. They preserve the blood supply to the transplanted flap, which significantly speeds up healing. This technique is called autodermoplasty.
Dividing the operation into two stages is necessary in order to achieve complete tissue healing. If such an operation is performed in one stage, the skin flap will not take root due to suppuration, and a rough scar will form.
Folk remedies
Many recipes for eliminating hidradenitis are proven and effective.
Recipe 1
- sour cream;
- butter;
- cottage cheese.
All components are mixed in equal parts until a homogeneous paste is formed. A cold compress is applied to the inflamed areas and secured tightly. It is recommended to apply the milk mixture overnight. In the morning, the bandage is removed dry. If there is no butter and sour cream, the abscesses are covered with ordinary squeezed cottage cheese.
Recipe 2
To eliminate primary and repeated abscesses, honey cake is used. Add flour to 15 grams of honey and knead the dough. It is applied as a compress before bedtime. To enhance the effect, the mixture is covered with polyethylene or cling film. Fresh cake is mixed daily for the procedure.
Recipe 3
- 50 grams of laundry soap;
- 50 grams of onions;
- 150 grams of melted pork lard (intestines).
All ingredients are mixed until a homogeneous mixture is obtained, which must be cooled. To treat hidradenitis, the resulting ointment is applied to a thick layer of gauze and applied to the abscesses. For fixation, polyethylene and adhesive are used. The dressing is changed 2 times a day. With intense discharge of pus, the bandage with ointment is changed more often. The product can be stored in the refrigerator for up to 10 days.
Recipe 4
- rosin;
- beeswax;
- butter.
All ingredients are mixed in equal proportions and melted in an enamel pan until boiling. After cooking, the homogeneous mass is cooled. It is applied to a bandage folded in several layers, applied to hidradenitis and secured with an adhesive plaster. The compresses are changed constantly until the pus is completely released from the formation.
If folk remedies do not help, and the symptoms intensify, you need to seek qualified help from a specialist. This will prevent the development of sepsis, which is fraught with serious complications.
You can find out more about this disease in the video below:
Additional treatments
In some cases, X-ray therapy is used, which destroys the sweat glands. Ultrasound therapy, electrophoresis and other physiotherapeutic methods can be used to treat prolonged and recurrent forms. Everything is determined by the specific clinical situation.
CELT doctors use all possible methods to completely relieve a person from suffering. The patient is only required to promptly contact a dermatologist or surgeon.
Make an appointment through the application or by calling +7 +7 We work every day:
- Monday—Friday: 8.00—20.00
- Saturday: 8.00–18.00
- Sunday is a day off
The nearest metro and MCC stations to the clinic:
- Highway of Enthusiasts or Perovo
- Partisan
- Enthusiast Highway
Driving directions
How to treat
It is important to start therapy immediately, before the inflammation reaches an advanced stage. Therefore, as soon as a small lump appears under the armpit, you need to consult a doctor. The disease is dangerous to health because it can lead to the development of blood sepsis.
Diet
During treatment, a patient with hidradenitis will need to follow proper nutrition, the purpose of which is to increase immunity and reduce blood glucose. You should stick to the diet for 3 months. It is important to remove alcohol, treats, fatty and spicy foods from your diet.
The menu should be filled with fortified and healthy dishes, so you need to eat the following products:
- sour milk and milk products;
- cereal porridge;
- fish;
- vegetables;
- fruits and berries;
- nuts;
- greenery.
The main thing to remember is one rule - food that will be included in the daily diet must be rich in vitamins B, A, E, C, as well as microelements such as iron, calcium and phosphorus.
Local disinfection
As the disease progresses, it will be necessary to treat the affected skin every day. To do this, you should follow these recommendations:
- Trim armpit hair with alcohol-treated scissors. You should not shave during treatment, as this may cause additional infection.
- To reduce the inflammatory process and disinfect the seal, you need to wipe the skin with antiseptics 2 times a day. This can be calendula tincture, alcohol, iodine, brilliant green, salicylic solution.
- Also, a couple of times a day it is necessary to apply compresses consisting of a cotton pad soaked in chlorophyllipt to the bump.
If simple procedures are started in a timely manner, the subcutaneous lump may resolve on its own.
Immunotherapy
For prolonged infectious hidradenitis, immunotherapy will be required. The patient will be prescribed complex vitamins that are aimed at strengthening the immune system, and, as is known, it is immunity that helps overcome diseases.
The following complexes are considered the most popular:
- Aevit;
- Vitrum;
- Revit;
- Centrum;
- Alphabet;
- Complivit.
They should be taken according to the instructions or advice of a specialist. Vitamins will help not only strengthen the immune system, but also improve the general well-being of the patient. In advanced cases, injections are prescribed.
Conservative therapy
The inflammatory process without the formation of an abscess can be cured using conservative methods. In addition to prescribing antibiotics, drugs to strengthen the immune system and physiotherapeutic procedures included in the complex of conservative therapy, the attending physician may recommend the following groups of medications:
- Antihistamines. Needed to reduce swelling of tissues on the damaged part of the skin. These include Suprastin, Diazepam, Zyrtec, Telfast and Claritin.
- Medicines based on isotretinoin. The substance is aimed at reducing sebum production and reducing the activity of sweat glands. These are Roaccutane capsules, retinoic ointment and Retasol solution.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. Needed to reduce inflammation, pain and body temperature. Paracetamol, Nise, Panadol, Baralgin M, Ibuprofen.
- Combined preparations for local action. They relieve pain, reduce inflammation, dry out and, in more advanced cases, draw out pus and have a healing effect. Vishnevsky ointment, Levomekol, Ichthyol ointment, Teymur paste, Pimafukort.
All medications are effective only if they are taken wisely and according to the instructions. Only regular treatment and completion of the full course of therapy will help eliminate such an unpleasant disease.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are prescribed when the above medications have not brought a positive result and the disease continues to progress. Antibiotics relieve inflammation, pain and destroy pathogenic microflora.
Therapy with antibacterial drugs cannot be interrupted. The course of treatment can last from 7 to 14 days.
Most often, the following antibiotics are prescribed for hidradenitis under the arm:
- Flemoclav;
- Amoxiclav;
- Unidox;
- Ampicillin;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Tsifran;
- Erythromycin;
- Tetracycline;
- Doxycycline.
Antibiotics are aimed at destroying the cell wall of bacteria and blocking protein synthesis, which is vital for their development and growth. Proper use stops the reproduction and spread of infection.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic procedures are mainly prescribed in the attenuation stage of the disease or after surgery to speed up tissue healing.
The following methods are used for hidradenitis:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- magnetic therapy;
- laser therapy;
- high frequency currents;
- electrophoresis;
- infrared irradiation;
- ultrasound therapy.
In the event that a cavity filled with pus has already formed inside the lump, warming procedures are strictly contraindicated.