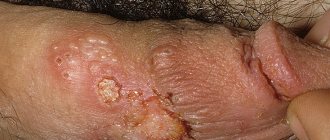
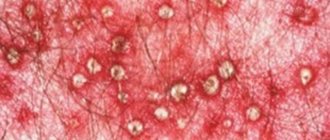
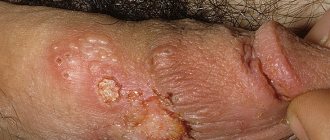
If the skin in the groin begins to peel, then this is the first signal to take a closer look at your lifestyle, since the reason may lie not only in poor hygiene, but also in fungal diseases, which can be contracted in public places or through close bodily contact with sick person. You should see a doctor if additional clinical signs appear in the form of severe itching, swelling and dry spots. Most often, this problem worries men aged 20-45 years, less often women aged 25-24 years.
Scabies and peeling in the groin
After infection, the incubation period lasts from several to 14 days.
Upon careful examination, on the first day after infection, you may notice peeling in the groin area.
It is the entry point for the pathogen – the scabies mite.
The first signs of pathology appear as small erythematous papules.
The rash forms in groups or spreads across the skin. Severe itching develops, worsening at night.
The itching is sometimes so unbearable that patients scratch the rash, resulting in wounds.
Scabies is diagnosed by an infectious disease specialist or dermatologist.
Based on anamnestic data and examination, a diagnosis is made.
The most popular anti-scabies drug is benzyl benzoate.
The medicine is produced in the form of an emulsion, has low toxicity, and quickly and effectively fights pathogens.
To completely eliminate mites, the skin over the entire body should be treated, not just the affected areas.
The exception is the head (hairy part), provided there are no signs of disease.
During the treatment period, it is forbidden to take a shower or bath, as this contributes to the spread of infection throughout the body.
After complete recovery, clothing and bedding should be disinfected.
Itching is a symptom of disease
If you are very itchy between your legs after eliminating all possible everyday causes, then most likely the problem relates to pathological processes in the body.
Many diseases, including sexually transmitted diseases, are manifested by itching in the perineum. These include:
- Scabies is a contagious dermatological disease (what scabies looks like). Its development occurs due to the activity of the scabies mite. This parasite is localized mainly on the pubis, inner thighs and between the toes and hands. In these places, the epidermis is less protected.
- Pediculosis pubis - parasitic insects (lice) in the course of their life activities leave black excrement on the underwear. Their bites, which lead to the appearance of red-blue spots on the pubis, itch between the legs in the groin.
- Fungal infections - pathological reproduction of fungal-like microorganisms on the mucous membranes of the genitals occurs with a sharp decrease in immunity, direct contact with the carrier, after taking antibiotic drugs. The most common disease is candidiasis. In women, it manifests itself as severe itching of the vagina and labia, with a characteristic white discharge. In men, the scrotum, pubis and penis itch.
- Genital herpes is an infectious disease caused by the herpes virus type 2. Infection occurs through contact and sexual contact. When the virus is activated, a herpes rash in the form of small blisters with clear liquid covers the pubis, scrotum or buttocks. As they mature, a person experiences severe itching and soreness of the surrounding skin. After some time, the bubbles burst, merging into one spot, and ulcers form.
- STDs - diseases such as mycoplasmosis, syphilis, gonorrhea and others lead to itching between the legs due to characteristic rashes and changes in the microflora of the mucous membranes of the genital organs. In addition, symptoms of sexual diseases include pain in the lower abdomen, pus and blood in the urine and vaginal discharge. In men with trichomoniasis, it itches between the leg and the balls, and a false urge to urinate appears.
Many diseases that cause itching in the perineum, without timely diagnosis and effective treatment, can lead to serious consequences. But worse than impotence and infertility are irreversible changes in internal organs due to STDs, leading to death.
Peeling in the groin with lichen planus and lichen rosea of Zhiber
The causes of these two diseases are a decrease in the protective properties of the body.
The following manifestations are characteristic of lichen planus:
- a flat papular rash of bright red color (with an admixture of purple or crimson tint) appears in the groin area
- on the surface the rash shines and there is slight peeling with poorly detachable scales
- sometimes the rashes are similar to psoriasis
Symptoms of pityriasis rosea often develop after a cold, against the background of reduced immunity:
- one papule up to 2 cm in diameter (maternal plaque) of a pink hue is formed in the groin
- after some time, yellowness and slight peeling appear in the center of the papule
- after 2-3 days, pink spots up to 1 cm in diameter form throughout the body
- Over time, the spots begin to peel off
As a rule, the two diseases described above are diagnosed without much difficulty by visual examination.
For lichen planus, a histological examination of tissue taken from the affected area is prescribed.
Sedatives and antihistamines are prescribed.
Corticosteroid drugs are prescribed.
Zinc ointment is prescribed and applied 2 times a day to the affected areas of the skin.
In the first 7-10 days after the development of symptoms, bathing and showering are excluded.
Ultraviolet irradiation is used in a course of 7 procedures and vitamin therapy with a high content of vitamin C.
Treatment
A specialist can advise you on how to treat this problem based on the underlying cause.
In case of atopic dermatitis, the patient is restricted from contact with a potential provocateur and is prescribed a course of antihistamines (Cetrin, Diazolin, Prednisolone, etc.). If peeling is caused by pathogenic microflora, then the patient is prescribed a course of antibiotics. coricosteroids and exfoliants.
Among the medications for external use, ointments include Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Lamisil, etc. The duration of their use is 7-10 days, the frequency of application is on average 2 times a day. They show their activity against fungal microflora.
To treat thrush, women are prescribed vaginal suppositories, tablets and ointments (Geskikon, Fluconazole, etc.). The course of treatment is selected by the doctor individually.
To prevent the penetration of pathogenic microflora, it is recommended to treat the inflammation site with iodine. It is imperative to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene and avoid sexual contact.
To treat pubic lice, special shampoos, sprays or ointments are used. A prerequisite is the treatment of all clothing and personal items with disinfectants.
Only a specialized specialist can tell you how to treat psoriasis in the groin area. Therapy in this case is selected individually. The drugs are taken during the period of exacerbation, the duration of treatment can take more than one year.
It is worth noting that erythrasma and epidermophytosis have different pathogen natures, so in the first case the patient is prescribed antimycotic therapy, and in the second - antibacterial.
If epidermophytosis in men is not treated on time, the infection will spread to the scrotum, thighs, etc. Erythrasma is transmitted through household contact. Therefore, during treatment it is necessary to limit intimacy and the use of the same hygiene items.
Prevention measures
Like any other disease, peeling can be avoided in advance; for this, it is recommended to fulfill the following conditions:
- wear underwear only made from natural materials;
- limit wearing tight clothing that can rub the delicate skin of the groin area;
- if you are overweight, treat the horse folds with special products that will reduce sweating and, as a result, irritation of the skin;
- observe the rules of intimate hygiene;
- do not overuse saunas, swimming pools, etc.;
- have a protected sex life.
By following these simple rules you can significantly reduce the risk of developing this unpleasant symptom.
Conclusion
Peeling and itching in the groin area are very common. This symptom is especially felt in the summer, when the skin folds sweat a lot and irritation appears there.
Timely use of medications helps avoid worsening the condition. Your doctor will help you choose an effective drug, based on the reason that caused the peeling of the skin in the groin.
What does eczema peeling look like?
Eczema develops as a result of exposure to various negative factors.
Among them are diseases of the hepatobiliary system, urinary tract, digestive organs, thyroid gland, as well as external factors (thermal or chemical).
Redness and severe peeling in the groin can occur with the contact form of the disease.
In this case, itching and inflammation are also present. In this case, the pathology may be caused by certain materials (latex).
When exposed to cosmetics and too frequent water procedures, papules containing pathological exudate may appear in the groin, skin dryness increases and irritation occurs.
The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture and examination of the patient.
To eliminate eczema, antiallergic drugs are prescribed to reduce inflammation and itching.
The most commonly used are Claritin, Loratadine, Tavegil.
If necessary, medications are prescribed in injection form.
Glucocorticoids are also used - Prednisolone or Betamethasone, sedatives, vitamin complexes, sorbents.
For local treatment, use Trimistin or Sinaflan (antibacterial agents with corticoids).
Physiotherapeutic procedures are also used - ultraviolet irradiation, laser radiation, exposure to magnetic radiation).
Allergenic foods are excluded from the diet.
How to get rid of the disease
Healing intimate areas is often complicated by psychological problems. Not every man can immediately decide to visit a doctor; at best, he will try to get rid of the problem using “folk” remedies. This approach cannot be considered effective; it often entails the exact opposite effect, expressed in complications of various kinds. In all of these cases, the most accurate diagnosis is required, followed by the selection of treatment methods. If you consult a doctor in a timely manner, most perineal pathologies are relatively easy to treat, without complications or relapses. Before consulting a doctor, you can and should take measures to reduce the likelihood of the disease spreading and reduce discomfort:
- Refuse to use tight synthetic clothing in favor of loose ones made from natural materials.
- Stop taking medications that can cause irritation.
- Review the set of detergents used during water procedures.
- Avoid sexual intercourse before visiting a doctor.
Peeling with psoriasis
Psoriasis is a skin lesion of non-infectious etiology, rarely occurring in the groin.
Early signs of the disease appear in the form of increased dry skin, peeling and mild hyperemia.
Sometimes itching occurs, which leads to scratching and peeling of large scales.
Rashes in the form of plaques do not cause itching or pain, but cause aesthetic discomfort.
The causes of pathology are stressful situations.
Diagnosis consists of identifying characteristic large scaly papules and taking an anamnesis.
Treatment of psoriasis consists of taking sedatives and antihistamines, eliminating the main factor that led to the stressful situation.
Erythrasma
A bacterial infection masquerading as a fungal disease. Corynebacteria infect the skin, causing the appearance of painless brownish spots with a flaky surface. The lesions occupy fairly large areas of the body. They are clearly limited from healthy skin. Gradually, the center of the affected areas lightens or becomes brown. There is no itching or burning. The course of the pathology is chronic. Therapy consists of external treatment with disinfecting ointments and solutions. For significant lesions, oral antibiotics are prescribed. Ultraviolet rays have a beneficial effect.
Genital herpes in the groin
Genital herpes refers to viral diseases transmitted through sexual intercourse.
The herpes simplex virus affects the urethra, the skin of the groin, and the rectum.
Clinical signs are as follows:
- symptoms arise from the urethra - soreness, burning and swelling develop
- general weakness
- then small blistering rashes with transparent contents form on the genitals and groin
- peeling may occur early in the development of symptoms due to increased dryness of the skin, together with a feeling of discomfort and itching in the groin
After the examination, the doctor prescribes a test of material, which is collected from the affected area (PCR from the skin for herpes).
Treatment regimen:
- use of antiviral medications - Famciclovir, Acyclovir, which alternate with interferon
- local treatment - applying Gerpferon ointment
Causes of itching in the groin area
The intensity of genital itching is due to the location of a large number of nerve endings in this part of the body. When epidermal cells are damaged due to mechanical or biological damage, they send impulses to the brain.
This process is necessary to suppress the inflammatory process by increasing blood flow in the capillaries. As a result, excess fluid accumulates in the skin, its temperature rises and a very unpleasant symptom occurs.
Itching between the legs may occur:
- after poor quality hair removal;
- insufficient/excessive personal hygiene;
- use of synthetic and shaping underwear;
- using alkaline detergents;
- wearing poor quality sanitary pads.
The listed reasons mainly explain why women have itching between their legs. Their genital area is much more sensitive to external stimuli.
But the male sex often faces a similar problem due to the use of condoms, lubricants and devices for sexual games. They lead to the development of an allergic reaction on the skin, causing unbearable itching.
What does diaper rash look like in the groin?
Diaper rash occurs when you sweat excessively and wear tight clothes made of rough materials.
Diaper rash manifests itself in the form of hyperemia that occurs in the folds of the skin.
A distinctive feature is the symmetry of symptoms and high humidity of the epidermis.
After some time, the skin dries out and cracks form, causing pain and discomfort.
Before the formation of hyperemic areas, the skin begins to peel off as a result of friction.
Therapy consists of daily washing (2 times a day) with boiled warm water and drying the skin.
Sometimes talc (baby powder) is used.
In cases of fungal or bacterial infection, antibiotics or antifungal medications are prescribed.
Causes of dryness between legs
Conventionally, the causes of dry skin in the area of the inner thigh can be divided into types: pathological and those that are not caused by disease.
Pathological
Dry skin on the inner thigh is most often caused by infectious and fungal diseases. The skin between the legs is peeling, what could it be:
- Inguinal athlete's foot. This is one of the types of fungus. The pathology is accompanied by the formation of dry, flaky spots on the skin, which do not disappear after using moisturizing emulsions. Over time, the spots begin to swell, become rougher and more painful, and the dry scales become blistered. In advanced cases, the spots increase in size by 3-4 times. You can become infected with athlete's foot in public places: baths, saunas, swimming pools.
- Erythrasma. The disease is accompanied by the formation of brown spots on the thighs, which initially have a smooth texture. Over time, the skin begins to harden, and the problem area becomes covered with dry scales. They can hurt and cause discomfort when walking.
- Rubrophytia. A fungal disease, the main symptoms of which are red, scaly patches that appear on the inner thighs. As the pathology progresses, the skin swells, becomes rough, and acquires a bluish tint. You can catch rubrophytosis in public places, as well as when wearing things of a carrier of the infection.
- Psoriasis. With psoriasis, red dry spots on the thighs do not cause pain or severe discomfort to the patient. In this case, the scaly surface peels off during movement and friction. In its advanced form, the pathology can spread to healthy areas of the skin.
- Candidiasis. Candidiasis or thrush is a pathology caused by fungi of the genus Candida. The disease is accompanied by severe dryness of the skin between the legs, itching, and discomfort when walking. In advanced cases, ulcers and erosions with secretions may form on the skin.
- Hormonal disbalance. With hormonal changes, serious changes occur in the body, which lead to the appearance of rashes on the labia, pimples, dryness and peeling. At risk are teenagers, pregnant women, and people who are regularly exposed to stress.
If the skin between the legs itches and peels, this may indicate the progression of sexually transmitted pathologies that occur with frequent changes of sexual partners and neglect of contraception.
Causes not accompanied by disease progression
Dry skin on the thighs is often a common allergic reaction that can occur in the following cases:
- long-term drug therapy;
- use of detergents containing aggressive components;
- abuse of certain foods (citrus fruits and other exotic fruits, chocolate, dairy products);
- wearing underwear made from unnatural fibers, which does not allow the skin to breathe and causes blockage of the sebaceous glands.
The allergy manifests itself almost immediately after interaction with its causative agent. It manifests itself in the form of redness on the skin, which over time begins to itch, peel, and cause discomfort when walking. The allergy can also spread to other areas of the body: lower back, arms, lower legs.
Peeling abrasions can appear with sudden weight gain. In such cases, the volume of the thighs increases, which leads to their friction during walking and the appearance of ulcerated wounds. Patients in such cases complain of severe pain when walking, burning, and swelling. With subsequent use of body talcum powder, the unpleasant symptoms go away on their own within a week.
Itching and peeling in the thigh area sometimes occurs due to banal neglect of intimate hygiene or tinea versicolor. If a person rarely showers and does not wash himself every evening after going outside, then over time, particles of dust and dirt remaining on the skin lead to the formation of inflammation. More often, all this happens in patients with increased work of the sweat glands.
Another reason that causes dry skin is poor diet. People who eat exclusively junk food are deficient in beneficial vitamins and macroelements. This leads to a deterioration in the general condition of the skin, the appearance of dryness, pigmentation, and rashes.
Streptoderma in the groin
Streptoderma occurs due to damage to the skin by streptococci.
The infectious disease manifests itself in the form of the formation of round elements with purulent contents and a flaky surface.
The rash reaches up to 10 cm in diameter and has irregular contours.
Infection with streptoderma is possible through close contact with an infected person.
The asymptomatic period lasts up to 10 days.
The tests consist of bacterial culture of scrapings, which makes it possible to identify the pathogen in the material.
For isolated rashes, local therapy is prescribed, consisting of treating the affected areas with methylene blue or brilliant green.
Before treatment, the blisters with pus are carefully pierced with a sterile needle.
At the end of the procedure, a sterile bandage with disinfectants for local treatment is applied to the areas with the rash).
The procedure is carried out in the morning and evening.
The resulting crusts are softened with Vaseline, after which a day later they can be easily and painlessly removed.
Additionally, vitamin therapy and physiotherapeutic procedures (UVR) are prescribed.
Pubic lice in the groin
Pubic lice are transferred to the skin of a healthy person from an infected person.
More often during sexual intercourse or when sharing towels or bed linen.
This type of parasite affects only humans; infection from animals is excluded.
The first manifestations occur 30 days after infection in the form of severe itching that occurs at the site of the bites.
As a rule, the affected area is the pubis.
But the infection can also spread to the skin of the groin area, thigh and even arms.
Next, hyperemia and irritation occurs, leading to peeling of the skin.
Small bluish spots form at the bite sites.
Signs of pediculosis are detected upon examination.
Treatment is carried out using various topical preparations containing benzyl benzoate.
Sulfur ointment is also used.
Before applying the medicine, you should shave the hair in the affected area.
Among anti-pediculosis products, Nittifor and Spray-Pax are especially popular, since these products can be applied on top of the hair.
After treatment, bedding and clothes should be boiled or soaked in boiling water, adding bleach.
Tinea versicolor (pityriasis versicolor) and peeling in the groin
With pityriasis versicolor, a fungal infection of the skin in the groin occurs.
The cause of the disease is a hot climate or a period of solar activity.
Small spots with clear boundaries appear on the skin.
Mushrooms provoke disorders in the production of melanin, which is responsible for pigmentation.
Therefore, the affected areas of skin enlarge over time and appear lighter in color compared to the surrounding skin.
After the spots merge, slight pityriasis-like peeling is observed.
To confirm the diagnosis, a test is performed using an iodine solution.
The causative agent of the pathology can be identified by examining scrapings.
Antifungal drugs are prescribed orally and for topical use.
Prevention of violation
To prevent skin problems in the groin, it is recommended:
- Choose the right underwear and other clothing, choosing the right size and material.
- The use of clothing made from non-natural materials is limited.
- Observe the rules of personal hygiene, especially when visiting a bathhouse or swimming pool.
- Use only your own things.