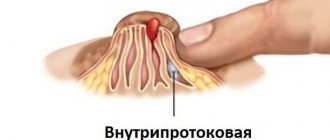
What is inflammation of the sweat glands (hidradenitis in Latin)
Hidradenitis is a purulent process caused by the introduction of a staphylococcal pathogen into the hair follicle with the occurrence of inflammation in the apocrine sweat gland. All sweat glands in the body differ not only in their heterogeneous structure, but also in their location on the human body. Hidradenitis affects the apocrine glands located in the skin of the genital organs, in the anus, around the ear canal, and most of all in the armpits. Being large formations, they form and excrete sweat fluid containing a high concentration of lipids. The cells of the sweat glands that secrete secretions are often found in the sweat themselves.
Typically, inflammation of the sweat glands occurs during periods of hormonal changes, such as puberty or menopause. Most often, inflammation occurs on one side, but cases of bilateral hidradenitis also occur.
How the anomaly manifests itself, photo
The disease hidradenitis is acute; the onset of the inflammatory process in the sweat glands can be determined by the appearance of the following signs:
- The onset of the disease is manifested by the formation of a small node, no more than two centimeters in diameter.
- As inflammation develops, itching appears.
- After a certain time, usually on the fifth day of the disease, the node enlarges and adheres to the skin. At this stage, itching gives way to pain and discomfort.
- As a result of blockage of the sebaceous glands, black dots appear around the node. Such signs correspond to the spread of the infectious process throughout the skin.
- Due to stagnation of blood in the capillaries, the skin surrounding the node changes color to red-violet.
- A feverish state occurs with loss of strength and weakness. Most often, this stage of the disease is accompanied by high fever.
- The patient suffers from insomnia and loss of appetite.
- The affected area in the armpit becomes swollen.
- As a result of the impact on the nerve endings, severe pain appears in the form of lumbago.
- There is a significant increase in the abscess.
- Due to intoxication of the body, malaise and headache occur, patients feel lethargy and significant malaise.
- If an infectious process develops, the cause of which is a staphylococcal pathogen, purulent contents will collect in the node, causing necrosis of the surrounding tissues. The node itself becomes softer, with a source of pus appearing in the center of the node.
If such a condition occurs, it is necessary to urgently seek surgical help. The final stage of inflammation of the sweat gland is the opening of the formed abscess. If the process is brought to a spontaneous end, then this can happen even from a sudden movement or when pressing. Immediately after opening the abscess, the patient feels relief, the temperature drops and the pain goes away. Under no circumstances should you refuse further treatment once you feel better. After opening, the sweat gland remains the same source of infection, so to completely stop the inflammation it is necessary to carry out drug treatment.
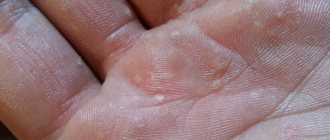
What causes atheromas to form?
As is known, lipomas, which include atheroma, are formed when the sebaceous ducts are blocked by a viscous secretion or keratinized skin cells. The following factors contribute to the development of the pathological process:
Atheromas do not grow into surrounding tissues and do not compress them
- genetic diseases;
- hyperhidrosis;
- acne;
- inflammation of the epidermis;
- metabolic disorders leading to changes in the consistency of sebum;
- failure to comply with hygiene rules;
- squeezing pimples;
- long-term use of cosmetics;
- damage to the sebaceous glands;
- hormonal imbalances;
- inflammation of the hair follicles.
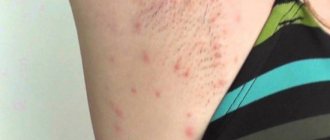
Inflammation of the sweat glands in the armpit
Inflammation affecting the sweat glands in the armpits is common. A similar condition occurs when minor skin lesions become infected during shaving or as a result of injury from growing hairs. Inflammation of the sweat glands is often caused by the aggressive effects of disinfectant cosmetics that irritate the skin. Decreased immunity, endocrine changes, hormonal imbalance, etc. contribute to the occurrence of disorders in the condition of the skin in the armpits.
This kind of inflammation brings the patient a lot of suffering, as it is accompanied by significant, painful symptoms. Often the formation of abscesses with hidradenitis is complicated by the development of lymphadenitis, affecting the lymph nodes located in the armpits.
Inflammation can spread to several sweat glands, after which several foci begin to form in the axillary zone in the form of a common area with inflammation, occupying the entire armpit. If left untreated, a serious complication occurs with the formation of phlegmon with severe extensive purulent inflammation, which is a very unfavorable prognosis.
Prickly heat
Miliaria is one of the special forms of dermatitis, which manifests itself as a result of irritation of skin tissue due to excessive sweating.
Miliaria can occur due to increased body or environmental temperature. And also in case of failure to comply with the rules of personal hygiene at the proper level. Because of this, the function of the sweat and sebaceous glands of the skin is disrupted, which causes a skin response.
Often infants are susceptible to this disease, since their skin is still too thin and does not have a good protective function. But the disease occurs in adults due to various disorders in the endocrine system, excess weight, and also with prolonged use of thick, non-breathable clothing.
Inflammation of the sweat glands in the groin
Inflammation of the sweat gland in a woman’s groin area most often occurs on the labia majora. This is manifested by a change in the skin with its redness and signs of swelling and hardening. Closed apocrine canals stop secretion, where it accumulates to form pus. Visually, the formation of hidradenitis resembles the disease of furunculosis, but differs from it in the absence of a central core.
Inflammation of the sweat glands in the groin occurs gradually and is not much different from hidradenitis, which affects the sweat gland in another part of the body.
- The initial stage of the disease is characterized by the formation of subcutaneous nodes with inflammation in them. Everything is accompanied by severe itching and pain. The nodes quickly increase in size, taking on a pear-shaped shape.
- The maturation of the resulting nodes is characterized by the development of severe swelling in the groin, a change in skin color with the appearance of a red or bluish tint, and the formation of pus. The patient's condition worsens, and the pain does not subside even at rest.
- The subsequent condition is accompanied by the opening of the abscess with the release of a large amount of pus. The pain subsides, the condition improves, and a scar forms at the site of the inflamed node.
The entire inflammatory process continues for two weeks, however, the danger is that such focal inflammation can be multiple with the formation of new foci of inflammation that do not heal for a long time. Often, hidradenitis in the groin area becomes chronic, alternating periods of remission with relapses. This usually happens in the absence of proper therapy or due to improper treatment.
Severe complications of the purulent form of hidradenitis in the groin threaten the following conditions:
- Development of lesions at the affected sites that are difficult to treat;
- The formation of fistulas communicating with the abdominal cavity, with the rectal cavity and even with the bladder.
Severe complications, which are accompanied by a long course and are difficult to respond to drug therapy, can cause purulent arthritis and other, no less dangerous, diseases.
Anhidrosis
Anhidrosis is the inability of the sweat glands to secrete sweat normally. There are both partial and complete anhidrosis. This disease is often called hypohidrosis. In the early stages, diagnosing anhidrosis is quite difficult.
Typically, this disease can be caused by skin injuries or the use of inappropriate and low-quality medications for the treatment of the cardiovascular system. But there is a congenital inability to sweat normally.
The causes of this disease also include:
- mental disorders;
- disruptions in the functioning of the nervous system;
- dehydration of the body.
The first symptoms of anhidrosis in a patient may be: a sharp increase in temperature, lack of sweating in certain areas of the skin. In this case, the body will try to compensate for the lack of cooling in one area, as a result of which the secretion of secretions in another area of the skin increases sharply.
Frequent flushes of blood to the face and neck and goosebumps are possible despite the high ambient temperature. With complete anhidrosis, the patient is prohibited from performing any physical exercises or being exposed to various physical activities, as heat stroke may occur. And without timely assistance, death is possible.
Main and specific causes of inflammation of the sweat glands
The following body conditions should be considered as the main causes of inflammation of the sweat gland:
- Smoking;
- Hormonal disorders;
- Development of infection;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Impaired patency of sweat channels;
- Changes in the skin due to its thickening.
The main causative agent of infection is staphylococcus, the activity of which causes the development of occlusion. As a result of the changes that occur, Schiff acid is produced with the formation of prickly heat, complicated by inflammation of the sweat glands.
A variety of provoking factors are considered to be specific causes. One of them is menstrual irregularities in women. Often this reason is the presence of excess weight, which contributes to changes in metabolic processes in the genitals. In this case, an increased amount of androgens is observed in the body.
Inflammation of the sweat glands can be caused by exposure to a chemical irritant or mechanical irritation received during depilation of the groin and axillary area.
Causes of prickly heat:
The main cause of prickly heat is insufficient ventilation of certain areas of the skin in the areas of natural folds: the axillary zone, groin, knee and elbow bends. In women, the area under the mammary glands is also affected. In children and adults with very thick hair, prickly heat appears behind the ears. Miliaria also appears in areas of the body that are constantly under thick clothing (bras, swimming trunks, diapers, bandages and bandages).
Contribute to the development of prickly heat:
- clothing made of thick, synthetic, non-breathable fabrics;
- high air temperature combined with high humidity;
- various injuries and abrasions of the skin;
- using various oily cosmetics that clog pores.
Factors that cause inflammation of the sweat glands
The main factors causing inflammation in the sweat gland may be:
- The main predisposing factor is genetic predisposition. Autosomal dominant inheritance often leads to inflammation.
- Decreased immunity when the body's defenses are unable to cope with the cause of inflammation.
- Endocrine. The cause may be diabetes mellitus, pathologies of the thyroid gland, kidneys or adrenal glands.
- The possibility of participation in the development of pathology of sex hormones in the form of an excess of androgens is allowed.
- Diseases. Concomitant chronic cases of diseases in the form of hepatitis, HIV, tuberculosis, helminthiasis.
- Exacerbation of inflammation of the sweat glands in women usually occurs before menstruation and after pregnancy. During pregnancy and after menopause, the severity of the disease usually decreases.
- Allergic skin reaction, dermatitis.
- Mutation processes. It has been noted that inflammation can be caused by mutations in the psen1, psenen and ncstn genes. It is in them that the cellular proteins components of gamma secretase are produced.
- Obesity. The presence of excess weight contributes to mechanical irritation of problem areas of the skin, and also causes occlusion and maceration (processes that cause the dissolution of the intercellular substance), which leads to constant moisture in the skin with softening and redness.
Wearing tight or non-breathable clothing can cause skin irritation and subsequent inflammation. Some medications, such as oral contraceptives or medications containing lithium, can also cause inflammation of the sweat glands.
Causes
Hidradenitis is a purulent disease of the sweat glands and belongs to pyoderma. The most common cause of hidradenitis is Staphylococcus aureus. The pathogen penetrates the apocrine glands directly through their excretory ducts or through the lymphatic ducts through damage to the surface layer of the skin. Skin damage can occur during shaving, epilation, or scratching the skin due to itchy dermatoses. Constant wetting and maceration of the skin due to increased sweating also leads to a decrease in its barrier function and the penetration of microorganisms.
- immunosuppressive conditions;
- skin damage (abrasions, scratches, including those formed after shaving);
- diaper rash;
- violation of hygiene regime;
- use of depilatory agents;
- diseases of the endocrine system (for example, diabetes);
- dysfunction of the sweat glands;
- obesity;
- obstruction of the sweat gland duct;
- secondary bacterial infection.
The development of an infectious process in the apocrine gland occurs when the body’s defenses are weakened. The occurrence of hidradenitis is promoted by: a shift in the pH of sweat to the alkaline side, neglect of hygiene rules, endocrine diseases (disorders of the gonads, diabetes, obesity), chronic inflammatory processes.
Symptoms
Symptoms of the disease rarely force a patient with inflammation of the sweat gland to seek medical help when they first appear. Typically, patients try to manage on their own, using a variety of methods to eliminate inflammation. A visit to the doctor is usually made in case of serious complications or severe pain that does not decrease within several days and interferes with normal functioning.
Persistent inflammatory processes in the sweat gland can cause the formation of fistulous tracts under the skin, combining several areas with abscesses. In this case, it is usually impossible to recover completely; you can only achieve stable remission, interrupted from time to time by exacerbations.
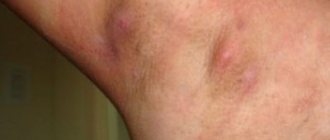
Hidradenitis develops gradually, smoothly moving from one stage to another. Each stage of the disease is accompanied by characteristic symptoms. Inflammation of the sweat glands can be determined by the following signs:
- The presence of a painful node on the skin surrounded by redness.
- The appearance of itching and pain.
- If the gland in the armpit is inflamed, it becomes painful to move your arm. With further development of inflammation, pain is felt even in a calm state.
- Development of edema.
- Deterioration in general health, headache, weakness, fever.
- Purulent contents of the nodes may be observed, with the absence of the main rod in them.
If the necessary treatment is not carried out, the infection can enter the blood and cause serious complications. At the first symptoms of hidradenitis, it is important to immediately consult a doctor, where, in addition to an external examination, you may need to conduct additional diagnostics and do a blood test. When the diagnosis is confirmed, an increased level of leukocytes and a decrease in red blood cells will be detected in the blood.
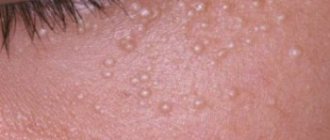
Crystalline
Children are most susceptible to crystalline prickly heat. White or translucent small (up to 1 mm) bubbles form on the skin. These bubbles very often merge and form larger lesions. The blisters may burst and become easily infected. As with other forms of prickly heat, peeling and severe itching are observed. Swelling of the skin may occur, which can lead to false suspicions of measles, chickenpox and urticaria.
They occur throughout the body and, if a secondary infection occurs, can cause the formation of pustules (pyoderma) and diaper rash.
The basis for the treatment of prickly heat in both children and adults is the opening of air access to the skin and strict adherence to hygiene rules.
You should not wrap your child up tightly or wear tight clothes that increase sweating; you should also avoid wearing synthetic clothing in humid climates.
If there are rashes, drying measures are carried out: treatment with powders and a weak solution of manganese. Affected areas of the skin should be treated with antiseptics and non-greasy ointments with betamethmzone or preparations containing menthol can be applied topically to relieve itching.
If there is a bacterial infection, antimicrobial medications should be started.
When dealing with heat rash, do not use oils, creams and greasy lotions, as they can aggravate the situation.
You should also definitely consult a dermatologist and begin treatment for the primary manifestations of hyperhidrosis. Physical activity should be avoided and acclimatization to the hot climate should be slow.
Diagnostics
If symptoms of inflammation of the sweat glands appear, you should consult a dermatologist for diagnostics and an accurate diagnosis. To do this, you will need to obtain the following results:
- Conduct a general blood test;
- To identify the c-reactive protein component, a biochemical blood test is required;
- In case of prolonged inflammation and in case of relapses, an immunogram is necessary;
- Bacteriological seeding of material to identify the causative agent of infection and determine its resistance to antibacterial therapy;
- If you suspect the formation of a fistula with the bladder, a urine test is necessary.
When conducting diagnostics, it is important to identify any differences from furunculosis and lymphadenitis, since, although they have common symptoms, the etiology and treatment methods for these pathologies are different.
Hurley staging system
This system is designed to classify skin pathologies such as psoriasis, acne and hidradenitis suppurativa. The system includes three groups or stages that characterize the skin changes and tissue scarring that occur.
- First stage. Consists in the formation of abscesses, which can be single or multiple, without fistulas or scars.
- Second stage. It is characterized by relapses with the formation of single or multiple abscesses, followed by the formation of fistulas and scars. They can occur simultaneously in different parts of the body.
- Third stage. Diffuse or widespread rashes are detected, as well as communicating fistulous passages along the entire length of the affected area.
More common is the first stage of the disease, which is diagnosed in more than 68 cases out of a hundred of all patients with hidradenitis suppurativa. The second stage is observed in only 28 percent of patients, and the last, most severe third stage accounts for only 4 percent.
Although the Hurley system is convenient for practitioners and easy to use, it is not the only one. It is not able to reflect the features of the septic process and does not take into account the degree of development of erythema and the amount of purulent contents discharged. The very assessment of the patient’s condition in accordance with the three stages is unable to accurately determine the moment when therapeutic treatment should be replaced by surgical treatment.
Sartorius staging system
It is this six-step system that allows you to more accurately assess the condition of a patient with hidradenitis and the severity of the disease itself. This method is able to reflect the number of elements of a skin rash, the distance between existing lesions.
- Pure degree - with the absence of nodes;
- Minimum degree – with single nodes;
- Moderate degree - with the presence of less than five inflammatory nodes without fistulas and abscesses, or the presence of a single active abscess or one fistula without the presence of additional inflamed nodes;
- Medium degree - existing inflammatory nodes in the amount of less than five and one abscess, one active fistula with the presence of one or more nodes with inflammation, or up to ten inflammatory nodes with 2 - 5 fistulas or abscesses;
- Severe degree - with existing active fistulas and abscesses from 2 to 5, and more than ten inflammatory nodes;
- Very severe - with more than 5 abscesses or draining fistulas.
This system is more accurate, it allows you to estimate the number and types of lesions. In the Sartorius staging system, each point is assessed with a certain number of points, after which a general and regional score is obtained. Based on the findings obtained, the direction of further treatment is determined.
Treatment methods
Modern medicine does not have the ability to provide adequate therapy and effective methods for completely eliminating hidradenitis; treatment usually depends on the degree of damage and the severity of the pathological process.
- As a rule, these can be warm compresses of vinegar with distilled water, as well as light antiseptic agents with a cleansing effect and hydrogen peroxide.
- Hydrotherapy and balneotherapy.
- Warm sitz baths with distilled vinegar.
The use of these methods makes it possible to prevent bacterial infection of lesions. The main treatment for severe cases of inflammation involves the use of medications. In the absence of positive results from the therapy, patients with inflammation of the sweat glands, especially purulent in nature, are prescribed surgical treatment.
Methods for removing atheroma
Such neoplasms are treated using operations such as laser and radio wave exposure and classical surgery. Radio wave destruction is considered the most effective and safe, as it does not require subsequent sutures. The operation has a short recovery period and good cosmetic effect. Is it possible to get rid of atheroma without surgery?
No ointments, lotions or tablets can eliminate sebaceous cysts
No ointments, lotions or tablets can eliminate a sebaceous gland cyst. Attempts to squeeze out its contents do not bring positive results either. The atheroma shell remains in place and continues to produce contents. In addition, opening the atheroma with non-sterile instruments can provoke inflammation, which will require urgent surgical intervention. There are no specific preventive measures. It is believed that atheromas most often occur in people suffering from hyperhidrosis or having oily skin. Regular hygiene procedures using products that reduce sebum secretion help prevent the development of benign tumors. Equally important is proper nutrition; you must avoid eating fatty and fried foods, coffee, and alcohol.
Laser hair removal
Laser hair removal is a radical method that allows you to remove hair by destroying its follicles using laser radiation for this purpose. After a procedure affecting the hair, after a few weeks, its cells are destroyed and the hair shaft with the dead root falls out.
The laser can affect the sweat gland itself using its thermal energy. After this, the gland is blocked and sweat production stops. When hyperhidrosis, which is one of the main causes of inflammation in the sweat gland, is eliminated, cases of hidradenitis become rare.
Studies have shown that the use of a laser with a wavelength of 1064 nanometers is useful for inflammation of the sweat glands.
Before starting laser treatment, that is, using laser hair removal or curettage, it is important to be firmly convinced that increased sweating belongs to isolated pathologies and is not a manifestation of any disease. It makes no sense to eliminate excessive sweating, for example, during menopause, using surgery. The use of medications that normalize the general condition of such patients will also relieve excessive sweating.
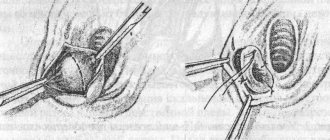
Surgery
For long-term inflammation that takes a chronic form, an effective method of treating hidradenitis is wide excision of the affected tissue through surgery. In case of inflammation of the sweat glands in the armpit area, phalloplasty is usually used with the application of a thoracodorsal flap, which is taken from another part of the body, along with a vein, nerve and thoracodorsal artery.
Surgical treatment is indicated for purulent discharge; it involves incising the nodule and installing drainage. This allows you to eliminate the inflammation itself and get rid of the remaining fragments of purulent contents. After the wounds heal, treatment is carried out with antibiotics and disinfectants.
How is the treatment carried out?
Treatment of hidradenitis is carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. From the first days, the patient must adhere to a strict diet, exclude spicy foods, sweets from the diet, and eliminate smoking and alcohol.
Treatment is accompanied by the use of antibiotics and sulfonamides. The patient should definitely use various types of immuno-strengthening agents and vitamins. Nitrofurans and autohemotherapy are also applicable. For local treatment, dry heat, UHF and ultraviolet irradiation are used.
What medications should you take?
The use of medications can be carried out in the form of injections or tablets. For effective treatment, several medications are prescribed that correspond to the form of the disease and the presence of changes caused by the pathology. So:
- As antibiotics, drugs that suppress inflammation in the form of ceftriaxone or summed are prescribed.
- To prevent further spread of inflammation, hormonal agents are prescribed, injected directly into the inflammatory focus itself. Typically, prednisolone injections are used for this.
- To enhance immunity, immunomodulators in the form of gamma globulins are used.
- Iodinol, mimarastine or chlorhexidine are used to disinfect the skin in the area of inflammation.
Any treatment for inflammation of the sweat glands should be prescribed only by specialists and carried out under medical supervision.
Home therapy
Drug treatment will be more effective when supplemented with home therapy methods, which should also be carried out after the approval of the attending physician. First of all, it is necessary to get rid of the pain, for which the surface of the inflamed lesion is wiped with alcohol or chlorhexidine. Treatment will benefit from using a pharmacy tincture of calendula, half diluted with water.
After this, a bandage with Vishnevsky ointment, ichthyol ointment or levomekol is applied to the inflamed node.
Change it at least twice a day, leaving it overnight. Subsequently, it will be sufficient to treat the affected area with iodine or brilliant green.
Treatment of hidradenitis
In the first three days, hidradenitis under the arm looks like a painful subcutaneous node. If adequate treatment is prescribed during this period, the compaction may resolve.
1) Antibiotics are taken orally, and in case of complicated hidradenitis they are administered intramuscularly. The minimum duration of treatment is from 5 to 10 days, but if necessary, the doctor can extend the course to several weeks.
| Name of the drug and dosage regimen | Mechanism of therapeutic action |
| Tetracycline. 250 mg 4 times a day or 500 mg 3 times a day. | Tetracyclines penetrate the bacteria and inhibit the synthesis of protein necessary for the production of new microorganisms. Bacteria cannot multiply and the spread of infection stops. |
| Cephalexin. 0.5-2 grams 2 times a day every 12 hours. The course of therapy is 7-14 days. | Cephalosporins act on growing and developing bacteria, disrupting their cell membrane. |
| Erythromycin. 1-2 tablets every 6 hours (4 times a day). The course of treatment is 7-10 days. | Macrolides differ from other antibiotics in being well tolerated. They stop the proliferation of bacteria and protect healthy cells from infection. They penetrate well into the skin and reach high concentrations there. |
| Clindamycin in the form of lotions. 2% solution in the form of lotions. A gauze napkin of 4-6 layers is moistened in the solution and applied to the sore spot. As it dries, re-wet it every 20 minutes. | They stop the reproduction and cause the death of bacteria. Including streptococci, staphylococci, anaerobic microorganisms that cause chronic hidradenitis. |
At home, self-medication with antibiotics is unacceptable . Only an experienced specialist can prescribe a drug that will effectively act on the pathogen. In addition, it is necessary to take into account contraindications and individually adjust the dose of the antibiotic.
2) At the same time, other drugs are also included in the complex treatment of hidradenitis:
- Antihistamines relieve swelling and irritation of the skin (tavegil, cetrin) 1 tablet 2 times a day;
- Corticosteroid injections into the lesion reduce inflammation (prednisone). The dose is selected individually;
- Immunostimulating agents strengthen the general immune system (tincture of echinacea, eleutherococcus, ginseng) 15 drops 3 times a day;
- Specific immunotherapy is necessary for frequent relapses of hidradenitis (staphylococcal immunoglobulin, antifagin, toxoid, T-activin). Drugs are administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly only after consultation with a doctor;
- Isotretinoin capsules are taken in the early stages and in combination with surgical treatment. This drug reduces the activity of the skin glands and improves the healing of lesions. Take for a long time. The dose is calculated based on weight at 0.1 mg/kg per day.
Forecast
In the absence of treatment or if it is not completed, inflammation of the sweat glands can result in a chronic course, as well as complications in the form of anemia, amyloidosis or arthropathy with secondary damage to the joints. Soft tissue swelling may develop in the form of severe lymphedema in the lower extremities. The third stage of the disease threatens with unopened fistulas, the lack of treatment of which can lead to the formation of squamous cell carcinoma. Surgery can usually stop the inflammatory process. The number of relapses in this case is minimal and amounts to no more than 2.5 percent.
Timely treatment contributes to the rapid recovery of the patient after suffering inflammation, excluding cases of unwanted recurrence. At the same time, it is necessary to comply with hygienic requirements and get rid of concomitant diseases that could cause the development of inflammation in the sweat glands.
How to cure hyperhidrosis
Treatment of hyperhidrosis is carried out using conservative or surgical methods. During surgery, the patient's sweat glands are removed from the armpit; this method does not exclude the possibility of relapse of the disease, since over time the cells are restored and the procedure will have to be repeated. It is also possible to use ultrasound on human sweat glands or perform a procedure for injecting butulinum toxin A (Botox). The procedure for injecting butulinum toxin helps to cope with hyperhidrosis for about 6 months, but after that the procedure will have to be repeated. Also in the treatment of hyperhidrosis, drying of the skin by electrophoresis is used, but this method is usually applicable only to the feet and palms.