Human papillomavirus infection (HPV) can “sleep” in the body for many years without manifesting itself. Not a single area of the skin, including the groin area, is immune from the uncontrolled growth of keratocytes, provoked by the sudden activity of a pathogenic agent. Papillomas in the groin can not only cause physical discomfort, but can also become malignant, that is, degenerate into malignant neoplasms.
Causes
Most of the world's inhabitants are carriers of the virus. It is transmitted from an infected person to a healthy person - through intimate intimacy or during childbirth from mother to baby.
You can also catch the infection at home if you neglect basic personal hygiene rules, for example, using someone else’s towel. People who regularly visit a public bath, swimming pool or sauna are at risk.
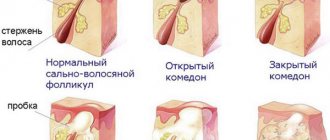
The non-cellular infectious agent responsible for the formation of papillomas in the area of the lower edge of the abdominal region easily penetrates the epithelium when there are various kinds of microscopic lesions on the skin. Once in the body, the virus penetrates the DNA of cells and causes them to divide uncontrollably. The result of this pathological process is skin growths of bizarre shape, which can be localized anywhere.
The immune system is able to hold back an insidious virus for a long time , preventing it from expanding its violent activity. Even a slight weakening of the immune status, caused by a serious illness, prolonged stress, exposure to toxic substances, deficiency of vitamins and microelements, allows the infectious agent to become more active and break through the protective barriers.
What is papillomatosis
A disease caused by viruses (HPV) is called papillomatosis. It is characterized by the formation of specific formations on the skin or mucous membrane. The virus can enter the body both sexually and through everyday life: through small cracks and wounds on the body. For a long time, the disease may not reveal itself, but be activated under the influence of:
- herpes virus;
- bad habits;
- suppressed immunity.
Externally, these formations are similar to moles and rise slightly above the epithelium. At first, they do not cause much discomfort in a person. The only inconvenience may be rubbing the “warts” with underwear. Formations may occur:
- on the genitals;
- in the larynx;
- on eyelids;
- in the anal area;
- on the mammary glands;
- on the fingers.
Symptomatic picture
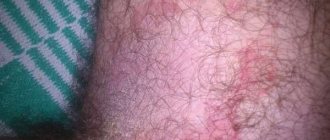
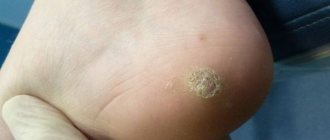
For a long time, a person may not even be aware of the presence of benign tumors of viral etiology on the body, since they do not cause him inconvenience or pain. In the early stages of the disease, papilloma in the groin in women and men can easily be mistaken for common acne. The color of the skin may remain unchanged, but in most cases, colonies of pathologically overgrown epithelial cells have a yellowish or light brown color.
Skin growths, consisting of nodules and resembling cauliflower inflorescences, are penetrated by a dense network of small capillaries, so when mechanical damage occurs they begin to bleed, and when bacterial flora attaches, purulent inflammation occurs. Large and old papillomas often cause pain, severe itching and burning, irritation when touched and rubbed by underwear.
Types of neoplasms in the intimate area
Tumor-like formations in the lower abdomen can be of different types and differ not only in the viral strain that caused them, but also in appearance. In medical practice, the following clinical variants of papillomas in the groin area are distinguished:
- Filiform (acrochords). Upon closer examination, this type of skin neoplasm looks like a bundle of intertwined threads. The length of papillomas, soft to the touch and elastic, can reach 5 mm. Such growths are most often found in the fairer sex, especially during the period of hormonal changes in the body.
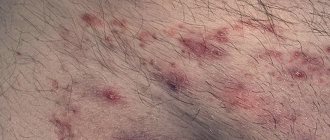
- Pointed. Visually they resemble a cone, represented by small flesh-colored papillae. It is these growths that often cause an inflammatory reaction, itching, burning and bleeding in the groin. In addition, long-existing genital warts can easily transform into a malignant tumor.
Characteristics of filiform condylomas
Visually, such tumors look like a bundle of threads, which is why they got their name. However, such a feature of the growth can be seen only with a strong magnification. They also differ in the following features:
- Size from one to 6 millimeters. Such papillomas grow mainly in length, which is why they cause significant discomfort to the patient;
- This papilloma on the thigh is very soft to the touch. The growth is elastic, and is most often found among the female rather than male population of the earth;
- Most often, such benign tumors can be found near the fold between the leg and torso and on the pubic bone;
- Thread-like growths are not found on the genitals of both sexes, but they can affect other areas of the body in parallel with the groin area.
Diagnostic methods
If, during a physical examination, the doctor finds signs of papillomavirus infection in the patient, he is obliged to refer him for additional examination. It is not enough just to know that the virus circulates in the blood; it is much more important to identify its strain, since the infectious agent can be either relatively harmless or deadly. It is also necessary to be tested for the presence of HPV if a young couple is planning to have a child, and both partners must be tested.
Laboratory research is carried out using the polymerase chain reaction method. This is an experimental screening method for detecting various viruses by detecting their DNA in samples of biological material. Some patients are perplexed when faced with an ambiguous situation in which the groin area is affected by papillomas and condylomas, but the tests give a negative result. This happens if at one time a human papillomavirus infection led to the formation of epidermal neoplasms, but subsequently the immune system became stronger and suppressed the activity of the pathogen.
Prevention
The human papillomavirus is very common, making it difficult to avoid getting infected. But following a number of rules will reduce the risk of infection:
- pay enough attention to intimate hygiene;
- avoid casual sexual contact, if you are not sure about your partner during intimacy, use a condom;
- after visiting the toilet, especially in public places, wash your hands thoroughly;
- do not use other people’s bath accessories, do not wear other people’s shoes;
- do not sit on a bench in a sauna, public bath or swimming pool without laying something on it, do not walk barefoot in these places;
- before planning a pregnancy and during it, get tested for HPV and, if necessary, undergo therapy prescribed by a doctor to reduce the likelihood of infecting the child;
- strengthen the immune system by hardening and taking vitamin and mineral complexes;
- stop drinking alcohol, get rid of nicotine addiction;
- regularly devote time to sports, be outside;
- Eat a balanced diet; your diet must include fresh vegetables and fruits;
- give yourself enough time to rest;
- Get a medical examination every 6 months.
If papillomas occur in the groin, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible and undergo the therapy prescribed by him. This will reduce the risk of complications.
Principles of treatment
Despite the fact that the morphological features of the papillomavirus have not been fully studied, doctors have many effective methods of combating neoplasms in the intimate area. Treatment must certainly be comprehensive and include measures mainly aimed at eliminating the causative agent of the disease and strengthening immune function. The choice of method for removing growths is determined by how widespread the pathological process is and what type of papillomas you have to deal with.
Surgical intervention and hardware therapy
A person suffering from papillomavirus infection must clearly understand that a delicate problem is unlikely to go away on its own, so it is necessary to be prepared for a radical scenario - surgery. The patient may be offered the following types of tumor removal:
- Traditional operation. The popularity of this method of treating papillomas in the groin in men and women is gradually fading. Many people do not favor excision of growths with a scalpel also because it is associated with certain health risks, pain and long-term rehabilitation.
- Laser therapy. Tumor-like formations are removed with a carbon dioxide laser beam. Cauterization occurs pointwise without damaging the surrounding tissue. After all the manipulations, an inconspicuous spot remains on the skin, which, however, disappears after two weeks.
- Cryodestruction. The essence of the non-invasive technique is to briefly expose the growths to very low temperatures. The area treated with liquid nitrogen loses sensitivity and turns white. Flash freezing leads to the destruction of pathological tissues.
- Electrocoagulation. To remove the layer of overgrown epithelium, the specialist uses low-frequency current. The new growths are burned out, and in their place a crust forms, which falls off after a few days.
- Radiosurgery. To remove papillomas, a radio knife is used - a special instrument that is a thin tungsten thread.
Use of medications
Although surgical removal of papillomas and warts in the groin in women and men can achieve lasting results, to prevent relapses, doctors often prescribe pharmaceutical drugs to their patients that inhibit the abnormal growth of epithelial cells. The use of the following medications has a beneficial effect on the course of the disease:
- Antiviral drugs. Considering the fact that specific drugs and vaccines that destroy HPV simply do not exist, it is not possible to completely expel the virus from the body. However, some systemic and local remedies can relieve the unpleasant symptoms of the pathology.
- Immunostimulants. To improve the body's defenses, it is useful to include herbal adaptogens, immunomodulators and vitamin-mineral complexes in the therapeutic course.
Under no circumstances should you attempt to remove a papilloma without consulting a qualified specialist. Rash steps can result in a chemical burn or even more disastrous consequences.
Recipes of traditional healers
Traditional medicine recipes can only be used if the attending physician has given the go-ahead. The following practice-tested natural remedies will help you get rid of papillomas in the groin:
- Celandine. Within a month, the new growth should be lubricated with juice squeezed from the plant stem. If papillomas appeared relatively recently, the likelihood of them disappearing after such procedures is quite high.
- Walnut. To prepare the healing mixture you will need several crushed kernels and a small amount of purified kerosene. The mixture of ingredients must be applied to the affected areas of the skin, covering the top with plastic wrap.
- Table vinegar. Mix the liquid component with a handful of wheat flour and form a small ball, which should be applied to the growth, securing it securely.
- Propolis. This famous beekeeping product is truly capable of working miracles, and this can be seen if you apply it to problem areas of the skin for two weeks.
Traditional medicine recipes can only cope with tumors that have recently appeared and have not had time to grow much. If the papillomas have finally formed and look like large warts, there is nothing left to do but contact a dermatologist, who will develop the most suitable treatment regimen.
What do papillomas look like?
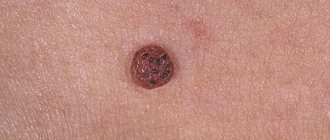
Many people do not know what papilloma looks like on the genitals in men, and cannot distinguish it from other dermatological formations, for example, warts. Experts say that these growths in men are no different from papillomas that grow in women. In advanced cases, they look like pinkish clusters and resemble the comb of a rooster. There are such types of pathological growths:
- ordinary - the simplest, benign neoplasms. First, a round papule appears on the body, then it grows and becomes rough. Sometimes small papillomas grow around it;
- thread-like, more common after 40 years. First, a compaction forms, then it coarsens and stretches, acquiring a thread-like outline;
- flat, on the face, and on the upper part of the body, they look like oval growths of a dark color. They rise slightly above the rest of the skin surface. Often grow in groups;
- pointed, similar to papillae, can be multiple or single. They often merge with each other. They are transmitted only sexually and are characterized by a recurrent course.
Possible complications
Any papilloma is a time bomb, the danger of which increases very slowly and often completely unnoticed. The owner of skin growths in the groin area should beware of the following complications:
- Spread of papillomas to neighboring areas of the body. As a rule, this is facilitated by damage to one or more neoplasms. Without taking appropriate measures, viral growths can spread to the inner thighs, buttocks, penis, scrotum, labia minora, and area near the anus.
- Attachment of a secondary infection. Constant contact of neoplasms with rough tissue is fraught with the appearance of microscopic cracks, which become gateways for the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
- The emergence of oncology. HPV is a potentially oncogenic virus. The main danger of papillomas in the groin area in women is that a viral infection can enter the internal genital organs and thereby create a threat of cervical cancer.
Preventive measures
The truism says that it is much easier to prevent a dangerous disease than to heroically fight it. This also applies to skin tumors that arise in the perineum. Since a strong immune system plays a decisive role in preventing human papillomavirus infection, it is important to lead a healthy lifestyle, avoid hypothermia, and take a responsible approach to treating even a mild cold.
We must not forget about the rules of personal hygiene. In a bathhouse, sauna or swimming pool, you cannot take other people's rubber slippers and bench mats.
Particular attention should be paid to the prevention of sexually transmitted diseases. You should only have sex with trusted partners, without ignoring condoms. During pregnancy, you need to be tested for HPV carriage, and if necessary, take preventive measures to avoid infecting the child.
Papillomas in the groin, unlike small piquant moles on the face, do not add additional charm. Doctors strongly recommend getting rid of them, since tumors can begin to grow, which can lead to unpredictable consequences. Fortunately, today there are many painless ways to remove skin tags that leave no scars or scars.
Traditional therapy
Folk remedies are accessible, but have lower efficiency - in order to remove formations with their help, you will need to use the components for 1 month. To remove genital papules in men, it is recommended to use:
- Fresh juice from raw potatoes - apply to pathological skin several times a day.
- Aloe - a leaf with the juicy side is applied to the formation every day for 2-4 weeks.
- An apple cut in half is used to grate the formations. It contains acids that help reduce and then completely remove the infectious formation.
Harsh products should not be used in the genital area. Subsequently, after removal of the papules, you will need to monitor your lifestyle, strengthen your immune system, and observe personal hygiene rules.
How to get rid of a wart using an apple: unconventional treatment methods
Previous post
Wart on the upper eyelid: how to remove using surgical methods and folk remedies
Next entry