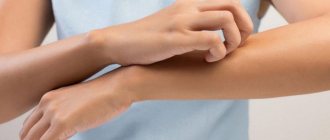
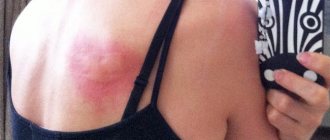
Causes and signs of skin allergies
An allergy is the body's reaction to exposure to a foreign substance (allergen). One of the most common manifestations of this response is urticaria. Modern experts have been able to prove that eczema, diffuse neurodermatitis, dermatitis and some other skin diseases can also have an allergic origin.
Among the main allergens that provoke skin rashes are:
- Food: eggs, chocolate, nuts, citrus fruits, strawberries, high-fat milk, seafood, honey.
- Medicines: antibiotics, analgesics, sulfonamides.
- Plant fingers: birch, quinoa, ragweed, alder and some others.
- Animal wool, fluff, feather.
- Sun, frost, strong wind.
- Chemical substances.
Recently, skin manifestations of allergies have become increasingly diagnosed. Experts attribute this to poor environmental conditions, poor diet and an abundance of stress. People at particular risk include hairdressers, people employed in industrial production, and healthcare workers.
Shortly after exposure to the allergen, negative signs of the disease begin to appear:
- The skin turns red and tissue swelling is noted.
- Severe itching begins.
- Rashes of various structures appear: blisters, small rashes, and so on.
- The skin peels off greatly and cracks form on its surface.
If you comb the epidermis at such a moment, the wounds become re-infected. This is fraught with the development of purulent processes. The sooner treatment is started, the greater the chance of preventing the development of complications.
Allergies are more often diagnosed in people with weakened immune systems. People who have suffered serious illnesses, take medications, or have bad habits need to be especially careful.
Use of ointments
Treatment of an allergic skin reaction is individual for each patient. Hormonal and non-hormonal ointments are selected depending on the severity of the allergic manifestation. The peculiarity of local-spectrum hormonal medications is that their active components block the production of special antibodies in the body. Depending on the type of active substances, allergy ointments have a strong or medium degree of impact.
Prednisolone and Hydrocortisol are hormonal ointments that have a weak effect; these medications are prescribed for mild allergic reactions. The drugs can be used to treat allergies in infants and women during pregnancy.
Medications with moderate effects - Fluorocort, Afloderm, Zinacort - have a local spectrum of action, which are prescribed by a doctor for moderate severity of allergic manifestations on the skin. Taking them on your own is highly not recommended; during treatment, you must follow the dosage and duration of the course.
If the skin rash is pronounced, active hormonal medications are prescribed - Elokom, Sinalar, Advantan.
They are prescribed in cases where skin allergies threaten complications in the functioning of the body and there is a need to immediately stop the symptoms. These potent substances are prescribed only by the attending physician, and the patient must follow the exact dosage and duration of administration to avoid adverse reactions.
A local non-hormonal spectrum anti-allergy remedy is characterized by a mild effect and the absence of a high risk of unwanted reactions. You can use such medications without a doctor’s prescription. It is better to select non-hormonal drugs that contain the substance lanolin; it helps to quickly relieve unpleasant allergy symptoms - rash, itching of the skin, swelling.
How do allergy pills work?
Histamine becomes the mediator of allergies in the body. Normally, this substance is found in the “fat” cells of the human body in a calm state and does not cause any harm. After exposure to the allergen, it enters the active phase. This negatively affects the functioning of the respiratory, muscular and nervous systems, and worsens the condition of tissues.
Drugs that have an antihistamine effect reduce the amount of histamine released from mast cells during an allergic reaction. Due to this, such medications have the following effects on the body:
- Eliminate itching.
- Relieves tissue swelling and redness.
- They help quickly heal rashes and the wounds that form after them.
- Prevents the development of bronchospasm.
- Normalizes blood pressure.
- Stabilizes body temperature.
First generation antihistamines not only prevent the production of histamine, but also block the functioning of histamine receptors. Because of this, severe adverse reactions may develop: drowsiness, decreased mental activity, a sharp decrease in visual acuity, dryness of the mucous surfaces of the oral cavity.
Modern third-generation medications do not have such disadvantages. They are produced on the basis of substances that are synthetic analogues of hormones produced by the adrenal glands. Such drugs are used only in severe forms of the disease. The use of hormonal antiallergic drugs is indicated in situations where other drugs do not have the desired effect.
Boosting immunity
The manifestation of an allergic reaction is observed against the background of decreased immunity. This is expressed in the accumulation of immunoglobulin E, as well as disruption of the cellular component of immune defense. As a result, the body is unable to resist infectious diseases.
Taking antihistamines has a positive effect on the body's protective functions. But they are not able to completely restore immunity. Therefore, simultaneously with the main course of treatment, the use of immunomodulatory techniques will be required. The therapy program consists of the use of specialized medications, lifestyle adjustments, and the use of alternative medicine.
Eliminating the allergen
The key factor in treatment is eliminating the allergen. To do this, first of all, it is necessary to conduct allergy tests and find out which substance caused the negative reaction of the body. After this, contact with the identified allergen should be avoided. For example, if the cause of the disease is dust, you will have to wet clean the apartment every day, get rid of carpets, soft toys and other things that can accumulate a large amount of dirt.
Today, a therapy method using an allergen has been developed. It is introduced into the human body in small quantities. This allows the body to produce enough protective antibodies. This method of treatment allows you to eliminate the cause of the allergy and prolong the period of remission. After completing a full course, the need for antihistamines completely disappears.
1st generation medications
First generation medications against skin allergies are now practically not used, as they have a high risk of developing side symptoms and negatively affect the functioning of the central nervous system. Nevertheless, they are still on sale in large and small pharmacies, and some people, trying to cure allergies on their own, buy drugs from this group. A significant advantage of 1st generation medications for skin allergies in adults is their speed of action, but their disadvantage is their short-term effect (no more than 5 hours).
It is not recommended to take 1st generation allergy medications for a long time, as they depress the central nervous system. These drugs are especially not suitable for people who constantly drive vehicles or work with complex mechanisms, due to the fact that under the influence of these antihistamines, attention and concentration are dulled. It is strictly forbidden to simultaneously take antihistamines for skin allergies and alcoholic beverages, sleeping pills and sedatives.
Another significant disadvantage of these 1st generation anti-allergy medications is that the body quickly gets used to them, and the medicinal components cease to have the desired effect on the body after a while, so every month it is necessary to change one drug to another. Side effects include tachycardia, impaired urination, dry mucous membranes in the oral cavity, frequent constipation, decreased visual acuity and hearing.
A good medicine for allergic manifestations on the skin of the 1st generation, which is characterized by its speed and duration of action, is Suprastin.
This is a universal remedy, which, although it belongs to the 1st generation drugs, is still in demand and has a universal effect. Suprastin is prescribed for various allergic reactions, regardless of the type of their manifestation and the type of allergen.
The advantage of Suprastin is the absence of a cumulative effect of its main components in the circulatory system; accordingly, it can be used for a long period. The disadvantage of Suprastin is depression of the central nervous system, which can cause drowsiness in the patient, and there is a decrease in concentration and attention.
Treatment of skin allergies with antihistamines
Drug therapy is the only effective way to cope with skin allergies. Antihistamines can be divided into groups based on their generation. Highlight:
- First generation medicines. They have a short-term effect, so their long-term use is required. As a result, a large dose of antihistamines enters the body, which entails side effects. The active ingredients from such drugs can enhance the effectiveness of other drugs. For skin allergies, Suprastin, Diphenhydramine and Diazolin, Fenistil are prescribed.
- Second generation drugs. They have a smaller list of side effects compared to first generation drugs. After completing the course of treatment, the effect lasts for a couple of weeks. The use of the following skin allergies is indicated: Acrivastine, Astemizole, Claritin.
- Third generation drugs. Such products have a minimal number of side effects and effectively combat the cause of allergies. They do not have a negative effect on the functioning of the cardiovascular system. This group includes Zyrtec and Telfast. They appear to be most effective against idiopathic urticaria.
Antihistamines must be used in strict accordance with the instructions and recommendations of a specialist. Only a doctor can choose a specific medication and its dosage.
If adverse reactions occur, the use of the drug is suspended. After this, you must consult your doctor.
Types of Allergy Medicines
Tablets are the most common pharmaceutical form of antihistamine medications. Finding an effective allergy remedy on your own is almost impossible, and even dangerous. Only a doctor can prescribe medications if he has transcripts of medical tests taken by the patient. The main task of allergy pills is to inhibit the production of the substance histamine in the body, which is produced in large quantities in case of contact with an irritating factor.
A universal medicine for allergies, produced in the form of tablets, is Suprastin, and Tavegil has also proven itself well. Both medications quickly relieve unpleasant symptoms, but they have one significant drawback. Tavegil and Suprastin have a depressing effect on the central nervous system, which is expressed in the patient in the form of severe drowsiness, apathy, and fatigue.
It is not recommended to take these allergy medications on a regular basis.
Suprastin and Tavegil, which relieve symptoms of allergies, regardless of the type of its manifestation, are emergency aid.
Corticosteroids are available in tablets - these are strong hormonal medications; they are prescribed in cases where there is no positive dynamics from taking other antihistamines. Treatment of an allergic reaction with corticosteroids can only be carried out with the permission of the attending physician, since these drugs have a high probability of adverse symptoms.
Allergic skin rashes are usually treated with topical medications - ointments, gels and creams. Medicines for external use, depending on their composition, can be hormonal or non-hormonal. Various ointments and creams against skin allergies are used as emergency remedies and for frequent use for chronic manifestations of allergies that occur in cases where a person cannot physically protect himself from contact with the allergen.
Non-hormonal allergy medications can be used without the consent of a doctor, they do not have a high risk of side symptoms, and can be used for a long time. Local-spectrum hormonal agents are prescribed only by a doctor; they must be used for a certain course duration.
Allergies are treated with combination medications.
These are products that contain hormones and substances with an antibacterial and antifungal spectrum of action.
Review and characteristics of effective drugs
Modern pharmacies offer a wide range of drugs designed to combat allergies. They are available in the form of ointments, gels, tablets, drops, and solutions for intravenous administration. Among the most effective drugs are:
- Levocetirizine. Available in tablet form and in the form of drops. A clear effect appears 20 minutes after taking the drug. The medication is prohibited for use during pregnancy. Widely used for urticaria of all types.
- Suprastin. Has a toxic effect on the body. Its advantage is a short period of relief of an attack of an allergic reaction. The effect appears after 10 minutes.
- Fenistil – gel. The drug is considered completely harmless. Approved for use from 1 month. Has a high antipruritic effect. Available in the form of a gel, which is easily applied to the affected areas of the skin. The drug begins to act half an hour after use.
- Cetirizine. It is made in the form of syrup, drops and tablets. A noticeable improvement is observed an hour and a half after application. Its effect lasts throughout the day. It is used for various types of skin rashes, including itchy dermatoses.
- Claritin. Used to treat adults and children. Available in the form of tablets and syrup. Does not cause sedation. Allowed for course use.
The use of such medications allows you to quickly neutralize the effects of the allergen. During treatment, it is necessary to give up bad habits and adhere to the principles of proper nutrition.
Antihistamines in the practice of a therapist
Patients with acute manifestations of allergies often turn to a general practitioner or family doctor for help. Competent treatment helps to quickly relieve symptoms of the disease.
In the future, such patients should be referred to a specialist - an allergist, who will conduct an examination, clarify the diagnosis and draw up an individual treatment program. The most common first-line drugs in a therapist's practice when treating patients for allergic diseases are antihistamines.
Antihistamines are used for classic allergic diseases, such as allergic rhinitis, conjunctivitis of pollen, household, epidermal and fungal etiology. This group of drugs is also widely used for skin diseases accompanied by itching (acute and chronic urticaria, atopic dermatitis, contact dermatitis). Be sure to prescribe antihistamines for severe manifestations of allergies: Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock.
Some features of the action of antihistamines make it possible to expand the indications for prescribing these drugs. For example, suprastin is able to penetrate the blood-brain barrier and interact with histamine and muscarinic receptors, which causes a decrease in the excessive activity of the sneezing center in the medulla oblongata and alleviates the condition of patients with ARVI in the first days of the disease. The drug blocks parasympathetic stimulation of the nasal glands, reduces vascular dilatation and extravasation, which leads to a decrease in nasal fluid excretion during colds. Taking suprastin for respiratory infections is recommended by WHO. The drug can be used from the first month of life.
Allergic diseases are widespread, affecting about 10% of the world's population, and there are significant fluctuations in this value - from 1 to 50% or more in different countries, regions, and among individual population groups. The study of the underlying mechanisms of allergic diseases has great social significance.
Using the example of allergic rhinitis, you can see what happens in the tissues of the body. The main role in this process is played by the so-called mast cells located under the nasal mucosa. Under the influence of an allergen, individuals with a genetic predisposition experience increased production of specific substances (antibodies). Antigens and antibodies are fixed on the mast cell, which contains up to 500 histamine granules. The cell is activated and histamine is released, which, being a biologically active substance, causes the dilation of blood vessels, increasing their permeability with the formation of edema and the release of a large amount of fluid into the external environment. Hypersecretion of mucus by glands located in the nasal cavity is also observed. Allergies can develop to plant pollen, mold spores, animal hair, and house dust. Accordingly, it is necessary to take measures to remove the allergen from the environment (for example, using an air purifier); At the same time, most patients require drug therapy, during which antihistamines are widely used.
Histamine was synthesized in 1907.
In 1909, it was extracted from ergot. A series of studies carried out in the 20s. XX century made it possible to establish that histamine is the most important mediator of such allergic manifestations as anaphylactic shock, rhinitis, bronchial asthma, and urticaria. Humans have H1, H2 and H3 histamine receptors.
The study of antihistamines began in the late 1930s, and 10 years later they began to be used to treat various diseases. H1 blockers are drugs traditionally used for allergic diseases. In our country, research work was also carried out on the synthesis of antihistamines, which was crowned with success. In the laboratory of M. D. Mashkovsky, an original group of H1-antihistamine drugs that have no analogues was created - fenkarol (hifenadine) and bicarfen (INN - siquefenadine, a new trade name histafen). This group of drugs has a dual mechanism of action: they not only block H1 receptors, but also activate the enzyme diamine oxidase (histaminase), reducing the concentration of histamine in tissues.
H2 blockers are used to treat peptic ulcers because they inhibit the secretion of hydrochloric acid. In the early 1980s. H3 receptors were discovered, present predominantly in the central nervous system.
Indications for the prescription of antihistamines (H1-blockers) are seasonal and year-round allergic rhinitis, urticaria, allergic conjunctivitis, pruritic dermatoses, including atopic dermatitis. The action of H1 blockers is due to their competitive binding to histamine receptors. The drugs have different durations of action. An ideal H1 antagonist should provide complete and rapid disappearance of allergic symptoms, maintain the effect for a long time and not cause side effects.
There are I (see Table 1) and II generation H1 blockers.
First generation H1 blockers are rapidly absorbed both when taken orally and when administered by injection. Their pharmacological effect appears after 30 minutes. Most drugs are excreted in the urine after 24 hours in an inactive form. With prolonged use, addiction develops and there is a need to replace the drug. Most of the side effects of H1-agonists are associated with penetration into the central nervous system. They have a hypnotic effect. But if first generation drugs are taken before bedtime, the effects of sedation are minimized. However, the hypnotic, antiemetic and anti-anxiety effects are sometimes used for medical purposes. Antihistamines are prescribed before operations, to prevent motion sickness, and for severe skin itching. During treatment, it is necessary to avoid alcohol, which can enhance the hypnotic effect. When applied topically, an anesthetic effect can be observed. In addition, most first generation drugs cause dry mouth. They should be prescribed with caution for glaucoma and prostate adenoma.
In general, H1 blockers are fairly safe, and most are over-the-counter medications.
Serious side effects such as dizziness, palpitations, nausea, vomiting, and urinary retention are rare. Children sometimes have paradoxical reactions in the form of overexcitation (for example, when taking diphenhydramine).
The activity of H1-blockers is approximately the same, therefore, when choosing a drug, they are guided by its side effects, experience with use and effectiveness in a given patient. First generation H1 antagonists, at least in the near future, will remain in the arsenal of drugs for wide clinical use. This is due to the accumulated 50 years of experience in the use of these drugs, the availability of injectable drugs that are absolutely necessary for the treatment of acute allergic conditions. In addition, it should be noted the relatively low cost of drugs in this group.
Chemical modification of the first drugs led to the emergence of new drugs with improved characteristics.
Let us note one interesting property of some antihistamines. We have already mentioned the mast cell, which contains large amounts of histamine granules. The bulk of drugs act only at the level of histamine receptors, when damage to the cell itself has already occurred. A number of drugs have a stabilizing protective effect on the membrane of this cell, resulting in a dual-action antiallergic effect. This mechanism manifests itself when the drug is used for several months, so the category of patients suffering from chronic allergic diseases requires long-term use of the so-called basic drugs (see Table 2).
| Table 2 H1 antagonists and mast cell stabilizers |
Zaditen has been used in clinical practice for decades. The drug has a satisfactory clinical effect and a good safety profile, which allows its use in pediatric practice. Pediatricians and therapists often prescribe zaditen for chronic allergic diseases, given its basic effect.
If drowsiness occurs, it is necessary to take the drug at night. Cases of weight gain are extremely rare.
For allergic rhinitis and urticaria, fenistil is widely used. In addition, the use of fenistil in the form of a gel is indicated for local allergic reactions, such as those observed, for example, with insect bites, as well as itching that bothers patients with sun, mild household and industrial burns. The drug is used for itching that occurs with infectious diseases, such as measles, rubella, and chickenpox. It should be noted that the drug can be prescribed to children from the first month of life. The itching relieves after a few minutes, the skin calms down, and a feeling of coolness appears. The drug adheres well to the skin and does not stain clothes due to its non-greasy and transparent base.
Thus, fenistil can be characterized as a drug with high antihistamine activity, the ability to quickly and persistently relieve allergy symptoms, long-term antipruritic effect, and good tolerability. Fenistil has a wide range of dosage forms, which provides flexible dosing for all groups of patients.
Since the late 1970s. The period of introduction of second generation antihistamines into widespread medical practice began. It should be noted that they are highly selective in blocking H1 receptors and lack interaction with other receptors. The antiallergic effect begins after 20 minutes and lasts for quite a long time - up to 24 hours. These drugs are produced only in tablet form. They are used 1 or 2 times a day. This is preferable to taking 1st generation antagonists 3 times a day. Second generation drugs do not cause addiction or sedative effects. These are the undoubted advantages of the new funds. Patients who, for example, drive a car, and others who need to maintain the ability to perceive and process information, certainly prefer this generation of antihistamines (see Table 3).
At the same time, information is accumulating about this group of drugs, their advantages and disadvantages.
Over the past period, it has been revealed that terfenadine, which is a second generation drug, has a cardiotoxic effect. By the beginning of the 1990s. 250 cases of arrhythmias were reported with the use of terfenadine. All these cases were analyzed, aggravating factors were identified, and in Russia the drug was withdrawn from the pharmacy chain. New, highly selective and safe antihistamines have now appeared on the domestic market.
At the moment, fexofenadine (trade names - fexadine, telfast), a pharmacologically active metabolite of terfenadine, has appeared. It successfully meets the highest requirements: it highly selectively blocks H1 receptors, i.e. it has a high affinity for histamine receptors, is a non-sedative, has a high level of safety, and, unlike its predecessor terfenadine, does not have a cardiotoxic effect. The drug has an anti-inflammatory effect (suppresses eosinophil-induced release of inflammatory mediators and IgE-mediated activation of basophils and histamine release). Its high therapeutic activity has been demonstrated in chronic urticaria, allergic rhinoconjunctival syndrome, and, more recently, atopic dermatitis.
Fexofenadine is used at a dose of 120 mg for respiratory allergies and at a dose of 180 mg for skin rashes once a day. It does not require hepatic metabolism, so it can be used in patients suffering from liver pathology. Eating does not reduce the absorption of the drug. With long-term use of fexofenadine there is no accumulation effect.
For chronic urticaria of various etiologies, cetirizine (Zyrtec, Cetrin) is successfully used. But it is characterized by a greater likelihood of sedation than other second-generation antihistamines (sedation may develop in approximately 20% of patients receiving cetirizine in therapeutic doses). In this regard, the drug potentiates the effect of alcohol. Also, cetirizine is not recommended for use by persons whose profession requires special attention or when driving a car. The drug is characterized by a rapid onset of clinical effect due to insignificant metabolism. Duration of action - 24 hours. Does not have a negative effect on the heart. An important property of cetirizine is its ability to suppress the infiltration of eosinophils, the key cells of the late phase allergic response.
For allergic dermatoses (urticaria, atopic dermatitis, neurodermatitis, pruritus, allergic contact dermatitis), ebastine (kestin) is highly effective, since due to its lipophilic properties it penetrates well into the skin. After taking Kestin once a day for 5 days, it retains its activity for 3 days, which, on the one hand, excludes the resumption of symptoms if you accidentally miss taking the drug, on the other hand, it allows you to use it according to the economical intermittent regimen we have developed: 5 days of administration , 3 days break, for 1-2 months during the period of expected seasonal exacerbation of allergic diseases.
Desloratadine (Erius) is a highly effective antihistamine with high affinity for H1-histamine receptors. It has been proven that Erius does not cause anticholinergic symptoms (dry mouth, blurred vision), does not affect psychomotor function (including without increasing its impairment with simultaneous alcohol consumption) and does not cause drowsiness. The drug inhibits many mediators involved in the development of systemic allergic inflammation. Erius is widely used in clinical practice for the treatment of allergic rhinoconjunctival syndrome and allergic rhinitis.
To date, approximately 150 drugs are known that have antihistamine activity, but not all of them have found use in allergy practice. The history of the creation of one group of antidepressants is interesting. In the 1950s drugs with antihistamine activity were synthesized, and further studies showed that these drugs are also characterized by specific psychotropic activity. These drugs are now included in the list of drugs used to treat depression (amitriptyline).
Let us dwell in more detail on the use of H1 blockers.
- Allergic rhinitis responds well to treatment with antihistamines. Itching in the nose, sneezing and mucus secretion are reduced, and the effect on nasal congestion is less effective. It should be noted that drugs are more effective in the early stages of the disease, at the first appearance of symptoms. For respiratory allergies, taking Kestin 10 mg per day, Telfast 120 mg, or Erius is indicated. It should be noted that Erius reduces nasal congestion. Local intranasal forms of antihistamines: azelastine (allergodil), levocabastine (histimet) are characterized by high efficiency in the treatment of allergic rhinitis.
The drug azelastine (allergodil) is a derivative of phthalazinone and, like other second-generation antihistamines, binds preferentially to peripheral rather than central receptors. It has a wide spectrum of antiallergic effects. Available in the form of a nasal spray and eye drops. The therapeutic effect of Allergodil appears within the first 15–20 minutes after administration of the drug and continues for a long time (from 10 to 12 hours).
The antihistamine drug levocabastine (histimet) is a selective blocker of histamine H1 receptors, designed specifically for topical use. The duration of action of histimet lasts for 12 hours, which allows the drug to be used 2 times a day.
For vasomotor rhinitis, first generation H1 blockers are less effective, but due to their M-anticholinergic action they reduce swelling and mucus secretion.
- Acute urticaria. H1 blockers quickly reduce rashes and itching. A particularly good result is observed in acute urticaria of allergic etiology.
- For angioedema, an injection of an antihistamine (tavegil or suprastin) in combination with diuretics and glucocorticoids is mandatory.
- For chronic urticaria, basic therapy with second-generation antihistamines (ebastine, cetirizine, acrivastine, loratadine) is prescribed.
- For toxicerma and contact dermatitis, antihistamines are used as a symptomatic remedy to reduce itching.
- With the development of serum sickness and the presence of urticaria, antihistamines are also prescribed. It should be noted that they do not affect arthralgia, fever and visceral manifestations.
- In case of anaphylactic shock, Tavegil and Suprastin are used as part of complex therapy after injection of adrenaline and in the absence of a sharp decrease in blood pressure.
- Considering the sedative and anti-anxiety effect of some first generation antihistamines, they are included in premedication before operations and surgical procedures. Atarax has proven itself well for anxiety, autonomic hyperactivity, and sleep disorders.
- Sometimes first generation antihistamines are prescribed to prevent motion sickness.
- In combination with other drugs, H1 blockers are used to prevent complications during transfusion of blood components and X-ray contrast studies.
- In the preoperative period, antihistamines along with other medications are prescribed to patients with an allergic constitution in order to prevent the occurrence of pseudo-allergic (liberatory) reactions and to better tolerate surgical stress. For example, with polypotomy in patients with polypous rhinus sinusopathy and concomitant bronchial asthma.
- Let's take a closer look at the use of first generation antihistamines for atopic dermatitis. You should remember about the painful itching, which greatly worries patients, as a result of which there is not a single patient who would not use this group of drugs. Itching causes scratching, which can increase the likelihood of secondary infection. Itching often causes sleep disorders and disruption of adaptive mechanisms. Itching is essentially the equivalent of pain, although its mechanism has not been fully studied to date. An important fact is that the nerve endings that perceive itching contain receptors sensitive to histamine. This is the basis for the use of antihistamines in the treatment of patients with atopic dermatitis.
It is necessary to note many years of experience in the successful use of these means and the lack of alternatives. In addition, antihistamines are indicated in the presence of concomitant respiratory allergies.
Second generation antihistamines also reduce skin itching. A study of fexofenadine (Telfast) showed inhibition of both daytime and nighttime itching already 1 day after starting to take the drug 60 mg 2 times a day. The positive effect was maintained throughout the entire treatment period. If skin itching persists even during remission, it is possible to combine first generation drugs, which are best taken at night, with the latest generation drugs prescribed during the day.
If you have an allergic disease, the advice of a competent doctor is very important, who will help you choose a modern and safe antihistamine.
Yu. V. Sergeev, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor T. P. Guseva Institute of Allergology and Clinical Immunology, Moscow
How to treat skin allergies in adults?
It is easy to get confused in the modern variety of allergy medications. Therefore, you should not self-medicate. The choice of specific medications should be made by a doctor. In this case, it is necessary to take into account:
- The severity of the disease.
- Characteristics of skin rashes.
- Manifestation of accompanying symptoms.
- Presence of other diseases.
- Patient's age.
The medications need to be changed every few weeks. Over time, allergens lose sensitivity to the active substance and it must be replaced with another. The duration of therapy is also selected individually.
Among the most effective remedies against skin allergies is Diazolin. It is taken after meals. It helps to quickly relieve itching, swelling of tissues, and eliminate rashes. The medication is prohibited for use by people suffering from diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, during pregnancy, as well as in the presence of individual intolerance to the components.
Erius is considered one of the most modern drugs. It turns out to be effective against all types of allergies. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, taking medication is allowed only in exceptional cases.
2nd and 3rd generation drugs
The best allergy medications are 2nd and 3rd generation. These are antihistamines with an improved formula, they do not have a high risk of side symptoms, and have a wide spectrum of action. Medicines differ from 1st generation medicines in the following characteristics:
- absence of sedative and cardiotoxic effects;
- no inhibitory effect on the central nervous system;
- high effectiveness for all types of allergies;
- possibility of long-term use.
Treatment of allergies with 2nd and 3rd generation antihistamines is prescribed by the attending physician if the drugs belong to the hormonal group. The most common are Loratadine, Astemizole, Acrivastine, Cetirizine, Ebastine, Fexofenadine, Acelastine. In addition to the absence of side symptoms, the new generation of medications are characterized by a long-lasting effect - up to 48 hours, which means that the patient does not need to take medications frequently.
Antihistamines can provoke side symptoms only in 2 cases: if the patient takes too much of the drug or has individual sensitivity to individual components.
The most common 3rd generation drugs that can be used by older people and children, including patients with chronic diseases, are the drugs Loratadine and Cetirizine. Loratadine is available without a doctor's prescription, has a quick and long-lasting effect, side symptoms from taking this medication are rare and are associated with improper use.
Loratadine is approved for use in children aged 12 months and older.
Cetirizine is a 3rd generation antihistamine with a broad spectrum of action. This medicine is recommended for use for skin allergies. It is recommended to use Cetirizine for a long time in order to further reduce the severity of the allergic reaction. Children can use Cetirizine from the age of 2 years.
Allergy tablets for children
If a child suffers from allergies, then the choice of medications must be taken with full responsibility. In the absence of proper therapy at an early age, there is a high probability of developing serious complications: bronchial asthma, autoimmune pathologies, and so on.
Only a specialist can choose a drug that is suitable for a child based on the results of a medical examination. The following medications are used most often:
- Pipolfen. The injection form of the drug is approved for use from two months of age. Pipolfen in pill form can only be given to children over 6 years of age.
- Fenistil. From the first month of the baby’s life, medicine is prescribed in the form of a gel or drops. Capsules are approved for use only for children over 12 years of age. Fenistil is especially effective for food allergies, as well as reactions to changing weather conditions.
- Peritol. This drug is prescribed from the age of two. It is often prescribed for allergies to frost. Quickly relieves itching, swelling of tissues, and also eliminates rashes.
Allergy is a serious disease that requires proper treatment. Self-medication in such a situation is fraught with the development of complications. Therefore, at the first sign of a problem, you should consult a doctor.
Effective ointments for allergies
Preparations for the treatment of skin rashes in gel form are used externally. The ointment quickly penetrates the site of inflammation, moisturizes and heals the skin. The products are divided into hormonal and steroid-free.
La-cree
Cosmetic cream relieves inflammation and burning from insect bites. La-Cri restores damaged tissues, is quickly absorbed, and does not leave marks on clothes. The product moisturizes the skin well. The cream is approved for use from the first days of a child’s life. Suitable for regular use if you are not allergic to herbs and bee products. Cons: strong smell, high cost (390 rubles).
Advantan
New generation hormonal drug. Use once a day to relieve itching on the skin. The ointment is prescribed for dermatitis - childhood, bacterial or contact. You can treat a rash that occurs due to nervousness. Antiseptic is indicated from 4 months of age. The ointment is not used on open wounds, for tuberculosis or syphilis, or acne. The duration of treatment for adults is up to 3 months, for children – up to 30 days. The drug is expensive - 680 rubles.
Fucidin
A product from the group of antibiotics based on fusidic acid. An ointment or cream is prescribed for bacterial infections of soft tissues, ulcers or boils. Fucidin is used for inflammation of the sweat glands. The product has low toxicity and can be used for allergies. The active substance does not enter the blood; the course of treatment is 7–14 days. The cream is contraindicated if the components are intolerant. The product is allowed to be used from birth. Cost – from 500 rub.
Psilo-balm
The drug blocks the production of histamine during insect bites, chickenpox, urticaria, and contact with plants. The gel eliminates swelling and redness of the skin, reduces capillary permeability. The balm has an analgesic and antipruritic effect. Hypersensitivity to the components of the product causes an allergic rash. The gel is effective when used early, but does not help with food allergies. Prescribed to children from 2 years of age. Cost – 257 rubles.
Fenistil
Ointment or drops are often used to treat children and prevent skin rashes after vaccination. Fenistil quickly eliminates the symptoms of all types of allergies: food, contact, mosquito and bee bites. Cannot be used by people with glaucoma, bronchial asthma or an enlarged prostate. The medicine has a mild sedative effect. Cost – from 334 rubles.