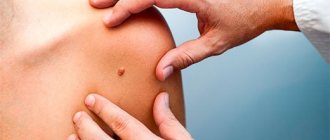
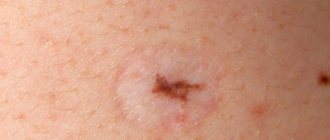
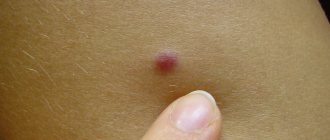
Dermatofibroma refers to benign skin tumors that form from the deep layers of connective tissue. These are small nodules with a diameter of up to 10 mm. They have a smooth surface, color varies from flesh to dark brown, grayish, brown. They are located mainly on the feet. The doctor determines whether it is worth removing dermatofibroma individually for each patient. The risk of degeneration into a malignant tumor is low.
- CAUSES AND SYMPTOMS
- TYPES OF DERMATOPHIBROMA OF THE SKIN
- REMOVAL OF DERMATOPHIBROMA
- POSSIBLE COMPLICATIONS
- TREATMENT AT THE PODOLOGY CLINIC
- COST OF SERVICES
Reasons for appearance
Until recently, the main cause of the formation of dermatofibromas was considered to be the body's reaction to insect bites, but now this theory is not officially supported. It has not been determined exactly why such pathologies can occur on the human body . Based on the anamnesis of those suffering from this disease, we can name only probable factors for the development of these neoplasms:
- Genetic predisposition . If one of your close relatives suffered from these skin pathologies, the likelihood of developing dermatofibroma increases.
- Floor . These tumors occur much more often in women than in men.
- Bad ecology . Living in polluted areas - close to major highways, factories and factories, as well as working in hazardous industries can contribute to the development of these pathologies.
- Age . Dermatofibromas mainly affect adults; they are almost never found in children.
- Skin damage . All kinds of injuries, injections and insect bites can contribute to the development of the disease (although this has not been proven for sure).
Dermatofibromas often appear in people who suffer from the following diseases: tuberculosis, acne, chicken pox, liver dysfunction.
Types of education
There are three types of this skin tumor:
- Dermatofibroma lenticular . It is a cluster of small reddish nodules of a dense structure, each of which is about 1 cm in diameter. Most often, such dermatofibroma is formed as a result of trauma to the skin. Development is slow.
- Dermatofibroma soft consists of soft lobular formations similar to folds. Their sizes vary and their color is yellowish or dark blue. This type of dermatofibroma is localized on the torso or face.
- Hard dermatofibroma consists of many dense lobules of a flesh-colored or reddish hue, their size is about 2 cm in diameter. They can appear on any part of the body and may disappear spontaneously over time.
Find out everything about the causes and treatment of pemphigus after clicking on the link.
How to quickly heal a callus on the heel? This article has the answer!
Varieties
In medicine, the following types of dermatofibroma are distinguished:
- soft - develops due to herbs or skin damage and is characterized by slow growth. According to the name, it has a soft structure with a smooth or folded surface. Location: face and upper half of the body. The color is practically no different from healthy skin, and the size can be absolutely varied, but no more than two centimeters;
- hard - has the shape of a sphere, with clearly defined edges. The only type that can occur either singly or in clusters of several tumors. It is dense to the touch, and the color can be flesh-colored or brown. There is a possibility of spontaneous extinction;
- nodular - a sphere-shaped neoplasm on the skin, its color can range from barely noticeable to dark brown. The size does not exceed one centimeter.
Dermatofibroma
Symptoms and diagnosis
Dermatofibroma is characterized by the following features:
- A nodule-shaped compaction appears on the surface of the skin. If damaged, it may bleed.
- When you squeeze the seal with your fingers, it bends inward.
- The color of dermatofibroma is always different from the shade of healthy skin. Most often, this seal is brown or grayish in color, and in rare cases it is black or dark red.
- Touching a dermatofibroma can cause pain and itching.
- Only a small part of the deratofibroma rises above the surface of the skin. Its bulk is located in the skin tissues. To the touch, the seal has a dense structure and a smooth surface. These formations are most often localized on the legs, lower legs, arms and rarely on the torso.
Often, dermatofibroma does not cause any acute discomfort to the sick person. Its development continues for a very long time, sometimes this formation can disappear on its own, or can develop into dangerous malignant tumors.
Attention! It is necessary to visit a doctor at the first signs of this disease, since some types of skin cancer in the initial stages of development show exactly the same symptoms as the relatively harmless dermatofibroma.
Diagnosis of this disease is made through a visual examination of the patient by a doctor. In most cases, a biopsy is prescribed - taking a sample of a small part of the formation and examining it under a microscope. This allows us to identify the potential risk of developing cancerous tumors.
Dermatofibroma after removal
Dermatofibroma is a benign skin formation. But in some situations, the neoplasm becomes malignant. Therefore, doctors recommend removing the nevus.
Causes
Dermatofibroma of the skin is considered a benign tumor, the causes of which are not yet fully understood. Pathology studies are ongoing. Doctors are inclined to hereditary factors.
According to the results of many years of research, it was noted that pathology was more common in people with dermatofibromas in their family. Women are more susceptible to the disease.
Education strikes the fair sex after reaching 30 years of age.
In a child, pathology can develop after 5 years, but this happens extremely rarely. Teenagers also suffer from this disease in exceptional cases. The disease is considered adult. Sometimes the formation occurs in a newborn child - a congenital defect. Heredity or a list of other concomitant chronic diseases is important here.
- The presence of a viral infection - papillomas, herpes and others;
- Frequent injury to the skin;
- Deep puncture of the dermis with a sharp object;
- Insect bite with deep damage to the skin;
- Inflammatory processes on the skin – acne;
- Dermatofibroma can be provoked by chickenpox, which the patient suffered;
- Lung disease – tuberculosis;
- The presence of chronic pathology of the liver or other organ;
- Immune system disorders;
- Interaction with chemical or radioactive substances;
- Living in a polluted ecological area.
Characteristics of the disease
Dermatofibroma is a nodular neoplasm, formed from a number of undifferentiated reticular cells. The tumor does not spread to neighboring tissues. The root of the pathology is deep under the skin - hence the name: benign intradermal type of formation. Common locations are on the leg, on the back, in the shoulder area and other parts of the arms.
The appearance of the following forms of tumors is recorded on reticular cells - fibrocytoma, histiocytoma. The structural composition of dermatofibroma consists of fibrocytes with fibroblasts, containing a large nucleus and iron with lipids. Sometimes a number of capillaries with endothelial cells and histiocytes are present. The presence of any element is responsible for the density and appearance of the nodule.
The pathology grows slowly, does not affect healthy tissue, and the possibility of spreading throughout the body through the blood is excluded. The internal structure is homogeneous, without the presence of additional branches.
The location of the base deep in the dermis forms a formation in the form of a pit or flat plate on the skin. Sometimes a tumor grows, rising above the skin in the form of a button.
Dermatofibroma cannot develop into cancer.
Removing the nodule leaves a scar at the site of the lesion. After removal, a relapse is likely - the cell remains and begins to grow again.
The ICD-10 code for the pathology is D23 “other benign neoplasms of the skin.”
Signs of the disease
- Visualization of a round or hemispherical nodule on the skin or under the skin with a diameter of up to 10 mm.
- The color of the nodule ranges from black to yellowish-pink - with possible inflammation in the center.
- No itching effect or painful syndrome.
- To the touch, the tumor is smooth without defects; after scratching, traces of injury appear.
- When compressed, a pitting effect is formed.
- Absence of swelling and spread of processes throughout tissues and hematopoiesis.
- The increase in size is slow, without external deformations.
The tumor often develops singly (solitary) on the legs, shoulders, hands, and back. Very rarely, granulomatous formations are recorded on the face, in the breast area and on the sole.
Sometimes there are multiple chaotically located fibromatoses of the skin, developing at different time intervals.
Injury leads to bleeding of the nodule, which can cause tissue inflammation. The location of the formation in injured areas requires surgical removal.
Types of pathology
Dermatofibroma can easily be confused with a mole or wart due to its external similarity. The root of the nodule extends far into the skin. The formation consists of fibroblasts and histiocytes. If the tumor contains more fibroblasts, dermatofibroma has a type of fibrous elements. An excess of histiocytes indicates a nodule with histiocytic predominance.
There are different types according to their structure:
- Solid dermatofibroma has clear boundaries with a dense body. Found in single and multiple versions. The shape is usually spherical or lobular with a diameter of up to 20 mm. It can dissolve on its own after some time. Color ranges from leathery to dark red.
- The lenticular appearance is formed after trauma to the skin. The color is always red or black. Grows slowly, does not exceed 10 mm. There are two types - single and multiple.
- Soft dermatofibroma grows externally on a stalk with a soft texture and resembles a flabby nodule with an uneven structure. It takes on any color and is found everywhere.
- Fibroxanthoma contains Touton cells with the presence of several nuclei and xanthoma pathogens.
- Sclerosing hemangioma is distinguished by a large number of different vessels and is capable of sclerosing.
Diagnostics of education
A mole or wart may resemble a dermatofibroma. It can be distinguished by the presence of a characteristic pit when the edges of the nodule are compressed.
To clarify the diagnosis, you need to see a doctor and undergo additional examination. For dermatofibroma, dermatoscopy is performed - the affected tissues are examined with a special apparatus.
Biopsy and histology can determine the prognosis of tumor development. To do this, you need to take part of the biological material from the affected area. For a biopsy, a scraping is taken - scarification. Aspiration is carried out with a thin needle, incision - part of the nodule is pinched off, excision - the entire nodule is removed and sent to the laboratory.
A change in color indicates structural changes in the tumor. Extensive research is required. It is necessary to exclude pigmented nevus and distinguish it from dermatofibrosarcoma, melanoma, Kaposi's sarcoma, etc. Oncological dermatofibrosarcoma can develop into a malignant formation that is not reproduced in traditional treatment.
Source: https://o-kak.ru/dermatofibroma-posle-udalenija/
Folk recipes
Folk remedies can help little in the treatment of this disease. Some remedies can only relieve painful symptoms or stop the development of dermatofibroba. The most common recipes are:
- Camphor alcohol. If you cauterize the seals with a cotton swab soaked in camphor alcohol, you can reduce the size of the tumors, and sometimes get rid of them completely. Such procedures may cause a burning sensation in the patient, but there is no need to worry about this - this is just a reaction of deformed skin to alcohol.
- Magnesia. If dermatofibroma has just appeared, magnesium will help get rid of it, which is applied to the sore spot and left for 10-15 minutes. Then you need to rinse it thoroughly with water. can be used instead of magnesium .
- Correct diet. To prevent the development of dermatofibromas and other skin pathologies, it is necessary to eat a fiber-enriched diet. The diet must include a lot of vegetables and a variety of fruits.
Do you know how to treat lichen in humans? Read useful information.
Why do age spots appear on the body? This article has the answer!
After clicking on the link, you can find out everything about the symptoms of demodicosis on the face.
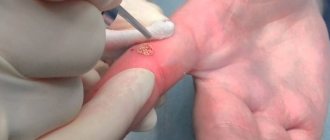
Surgical intervention
Surgical removal of dermatofibroma is prescribed in cases where the lump is located in areas most susceptible to injury, or if it severely spoils a person’s appearance.
Surgery is the only reliable way to get rid of this skin formation once and for all.
The operation itself is quite simple, it does not last long and is completely painless, since it is performed under local anesthesia. If the operation is performed in the morning, the patient is allowed to go home in the evening of the same day.
If surgery was performed correctly, the likelihood of complications or side effects is almost zero. Otherwise, abscesses may occur that will require continued treatment.
Since when removing a dermatofibroma you have to deeply cut the skin, after the operation there will definitely be a scar that will need to be properly cared for. At first it will be very itchy and clearly visible on the body. Gradually, the scar will become less noticeable, but it will never disappear. Half a month after the stitches are removed, measures can be taken to eliminate the scar.
Now there are a huge number of ways to make the scar less noticeable or eliminate it completely.
- The simplest method is to use a special gel that helps keloid scars dissolve. It is recommended to carry out procedures for treating a scar with this gel under the supervision of a professional cosmetologist who knows how to properly apply the gel to the skin and can give useful recommendations for skin care.
- Laser scar removal.
- Surgical removal of the scar. It is prescribed only in cases where the scar is very large and cannot be eliminated by other methods.
- Steroid injections can help reduce the appearance of scars and reduce inflammation.
Melanoma vs Dermatofibroma, or why visit a dermatologist
What do we usually read/hear about visiting a dermatologist? Usually it all comes down to the fact that if you have a LOT of moles , or suddenly some suspicious mole , then you need to visit this very dermatologist. Otherwise, what is there to do there?
OK. Let's look at two photos (clickable):
One of these photographs shows a dermatofibroma , and the other shows an amelanoma . Find 5 (or at least a couple) differences. Found it? I doubt it
Source: https://www.vladlive.com/vse/nabolelo/melanoma-vs-dermatofibroma-ili-zachem-poseshhat-dermatologa/
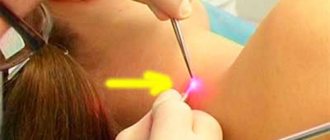
Modern methods
Nowadays, it is possible to fight dermatofibroma with more progressive methods than surgery. For example, treating a tumor with liquid nitrogen can eliminate the external manifestations of the disease, leaving no scars on the skin. The only disadvantage of this procedure is the likelihood of re-formation of skin growths.
Laser removal has proven itself much better . In one operation, many formations can be eliminated at once. After laser removal, there are almost no noticeable marks left on the skin - only light spots that do not pose a serious cosmetic defect to a person. The main disadvantage of this operation is its fairly high price.
Treatment
After confirming that the nodules are benign, the doctor often decides not to treat or remove them surgically. If there is no symptom of pain or itching, do not disturb the nodule. The decision to remove is made for cosmetic reasons. If the tumor has grown in a short period or is painful, the question arises of cutting out the diseased area with a scalpel or laser using the Surgitron device.
To prevent nodules from developing into cancer, the following measures are taken:
- Using a traditional scalpel with local anesthesia, the nodule is excised, capturing a healthy area.
- Laser treatment can cure a tumor with a small residual scar, but there is a risk of relapse.
- At the moment, the hospital often uses the cryodestruction method - freezing with liquid nitrogen.
Before using a laser or cryodestruction, a histological examination of the diseased area is carried out. After traditional removal, the biological sample is examined for cancer cells. If after some time the formation appears again, it becomes painful when pressed, you should urgently consult a doctor.
Preventative tips
Since the reasons for the development of this skin pathology have not yet been fully elucidated, there are no specific preventive measures against dermatofibroma.
The only thing that can be advised in this case is to avoid skin damage, as well as treat other skin diseases in a timely manner, monitor your health and follow a proper diet.
It is rarely possible to predict the development of dermatofibroma. In some cases, it disappears on its own, in others it can begin to grow rapidly and lead to serious complications, including malignant tumors. In any case, if the slightest painful symptoms appear, especially bleeding, you should contact a medical facility as soon as possible.
Below is a video in which you can see how to remove dermatofibroma:
Classification
For this pathology, a classification has been determined, dividing it into several types according to different characteristics.
According to cell specificity
Depending on the cells that form the tumor, two types of pathology are distinguished:
- Benign. It is formed from cells of fibrous tissue, which, under the influence of certain reasons, switched to a disorderly and uncontrolled process of division.
- Malignant. The rarest type of fibroma, which is formed from cancer cells. They lead to the death of healthy tissue cells and their replacement with pathological formations.
According to the rate of formation
Based on the speed of tumor development, they are classified into:
- Limited . They have a slow growth rate, stopping at a certain diameter. As a rule, such fibroids do not grow more than 10 cm, as they have a restraining capsule. They maintain their size throughout their lives.
- Diffuse . They have no growth restrictions and are localized on the legs in the thickness of the muscle tissue. As it develops, nearby vascular and glandular tissues are involved in the pathological process.
By localization
Based on their location, fibroids are divided into two types:
- Plantar. They are located on the arches of the feet and are characterized by pain, which is especially noticeable when walking.
- Dermatofibromas . They can be localized on any part of the leg. Mainly located on the inner thighs.