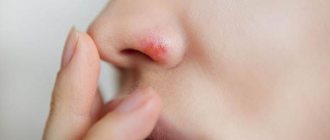
Despite its apparent simplicity (think of it as a banal pimple), this sore can cause serious intracranial complications and lead to serious consequences in adults and children. Because the reasons for its occurrence can be completely different - from poor nutrition to a common cold, we decided to examine this topic in more detail.
What is a nasal boil?
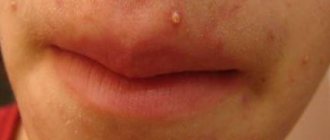
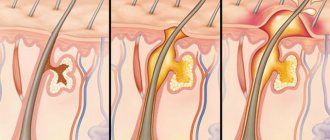
This disease is an acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle and nearby tissues - the sebaceous gland and its fiber. Such an abscess is located in the nose: in the area of the wings and in the vestibule area, where there are hair follicles.
When a boil appears in the nose, and after it similar formations appear on other parts of the body (chest, stomach, face, etc.), doctors diagnose “furunculosis”.
If several closely spaced abscesses merge with each other, a carbuncle forms. With this problem, the body’s inflammatory response increases several times, and the disease is much more severe.
In medical documentation, the nasal boil code according to ICD 10 is designated as J34.0. This data is not very important for the patient, but is important for the specialist and the statistical data office.
Reasons for its appearance
What causes this sore in the nose? The key cause is infection. Most often these are various types of staphylococcus (Staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria), less often the problem is caused by streptococci.
In addition to infection, the following factors contribute to the development of the disease:
- Hypothermia.
- Vitamin deficiencies.
- Microdamage to the skin due to impacts, scratching, etc.
- Injury.
- The habit of squeezing a purulent pimple in the nose can lead to widespread inflammation.
- Some somatic pathologies (diabetes mellitus and others.)
Important! Some staphylococci and streptococci can normally live on human skin and mucous membranes. When unfavorable factors coincide, the disease develops.
Causes of appearance and psychosomatics
A nasal boil (can be treated with antibiotics) is a painful pustule (blister filled with pus) with necrosis in the center (the core of the formation). Boil occurs in 45% of cases of all pyoderma (purulent-inflammatory diseases).
Boils in the nose area form in all age categories. But most often they occur between 15 and 45 years old. In men, ulcers appear 1.5 - 1.7 times more than in women.
A boil in the nose is associated with the influence of aureus, epidermal, saprophytic staphylococcus or hemolytic streptococcus (rarely). These are opportunistic bacteria that can harm the body only under certain circumstances. For example, staphylococcus and streptococcus multiply when immunity decreases.
There are risk factors, the presence of which increases the likelihood of a boil.
Namely:
- Skin damage. The likelihood of infection increases when a cut, abrasion or other violation of the integrity of the cover appears. This item also includes surgical interventions - rhinoplasty (correction of nasal deformities), installation of implants. Additionally, skin damage is possible when removing nasal hair using forceps.
- Runny nose. The integrity of the skin is compromised if you rub the cover with paper napkins.
- The presence of other purulent pathologies.
How to treat a boil in the nose depends on the cause - Diseases. The infection can spread from other organs. This item includes sinusitis (inflammation in the maxillary sinuses), tonsillitis (acute damage to the lymphatic pharyngeal ring), and dental caries.
- Reduced immune defense. This may be due to frequent hypothermia, stressful situations, and climate change. Immunity is affected by overwork, lack of vitamins or microelements, prolonged and uncontrolled use of medications (for example, corticosteroids). Additionally, the likelihood of a boil appearing with an unbalanced diet and excessive physical activity increases. Immunity also decreases with various diseases - malignant tumor, HIV, diabetes. Additionally, it is possible that protection may be weakened when undergoing a course of chemotherapy or anemia (reduced amount of hemoglobin and red blood cells).
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. If a person rarely washes his body, the skin becomes greasy and the number of pathogenic microorganisms increases. Additionally, this includes failure to clean the house in a timely manner and the use of someone else’s personal hygiene items (razor, towel). A boil can also occur if a person touches his face with dirty hands.
- Working conditions. Inhalation of dusty air or constant contact with fuels and lubricants.
- Increased sweating. Excess sebum is an ideal breeding ground for pathogenic microorganisms.
In psychosomatics there is an opinion that the formation of a boil is associated with reaching the peak of negative emotions. That is, anxiety, fear, anger come out in an unnatural way (an abscess).
Clinical picture of the disease
At the very beginning, a limited area of redness appears on the skin with unclear boundaries and swelling of the tissues. When you feel this place it hurts a lot.
Over time, swelling spreads to the lip, cheek and other nearby areas of the face.
A limited cone-shaped infiltrate appears on the skin, which sharply hurts when touched.
The key symptoms are sharp pain and swelling in the affected area. This is the infiltration stage .
A few days later, a yellow-white abscess, the so-called core, appears at the top of the infiltrate.
Throughout the course of the disease, until the purulent lesion is opened, the patient is bothered by general symptoms: weakness, fever, headaches, joint aches, loss of appetite and other signs of intoxication. The so-called abscess stage .
After the abscess in the nose is opened, the resolution stage . General symptoms weaken and the patient’s well-being improves significantly.
The abscess opens independently or after surgery. In some cases, an abortive course of the disease is observed, when the infiltrate resolves without spontaneous drainage.
Possible complications
Such inflammation in the nose can progress under unfavorable conditions. Contributes to the spread of infection: inadequate treatment, diabetes, decreased immunity and other problems.
The veins of this zone are closely connected with the venous network of the orbit and skull. Through them, the infection can penetrate into the orbit and cranial cavity, causing the development of severe complications. The most dangerous consequences of the disease:
- Inflammation of the fiber of the orbit. The eyelids become swollen and red, and exophthalmos is observed (“bulging” of the eye forward, less often to the side). Pain in the eyeball area.
- Thrombosis of the orbital veins. Swelling of the eyelids and eyes; thrombosed veins can be felt. Exophthalmos, sharp pain that intensifies with eye movement. Vision decreases and the mobility of the eyeballs is limited.
- Sepsis. This is a complex of symptoms and syndromes that is associated with a massive intake of bacteria and their toxins into the body from a purulent source of infection. Severe multiple organ disorders are observed (damage to the heart, kidneys, liver, etc.).
- Thrombosis of the cavernous sinus. A serious condition that is accompanied by general cerebral symptoms (blurred consciousness, vomiting, headache).
Symptoms of meningitis (stiff neck muscles, photophobia, etc.) are added. Swelling of the eyelids, exophthalmos, chemosis, drooping eyeballs, retinal hemorrhages and other signs of damage.
The risk of complications increases if the boil is under the nose. This area of the nasolabial triangle (also called the “triangle of death”) has a good blood supply, and the infection can quickly spread into the cranial cavity.
Attention! You should never squeeze out pimples and ulcers in this area yourself.
Possible complications and consequences
The prognosis is favorable if the boil is detected and treated in a timely manner. Most often, complications occur when a person does not see a doctor or squeezes out a boil on his own.
The boil is characterized by the consequences:
- Eye diseases. This list includes blindness, inflammation of the orbit, displacement of the eyeball (bulging).
- Thrombophlebitis of the facial veins is inflammation of the vein wall and the formation of a blood clot.
- Thrombosis of the intracranial venous system. The complication involves the formation of blood clots in the veins of the brain and nearby vessels. As a result, ischemia (lack of oxygen) develops.
- Inflammation of the brain. For example, meningitis.
- Sepsis is a purulent-septic disease that involves blood damage. The infection spreads throughout the body, is severe, and threatens human life.
- Sinus damage. This item includes frontal sinusitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane in the area of the frontal sinuses), sinusitis (the process affects the maxillary sinuses).
- Death. May be associated with meningitis, sepsis.
A furuncle is an inflammation in a hair follicle or sebaceous gland. The abscess can be localized in various places, but the most dangerous is the face. A boil in the nose is characterized by redness, soreness, and swelling of the skin. If a boil appears, you should contact an otolaryngologist. The specialist will conduct a survey and examination, and, if necessary, refer the patient for diagnostics.
Next, treatment is prescribed, which includes the use of medications and folk remedies. A boil can be characterized by consequences (meningitis, sepsis, etc.). To reduce the likelihood of complications, you must follow your doctor's recommendations.
Differential diagnosis
Not every pimple inside the nose and on it should be regarded as this pathology. There are several diseases with which this problem needs to be differentiated:
- Herpes in the nose. This is a viral disease, which is characterized by the appearance of small, painful blisters. When these bubbles open, they reveal erosions. Gradually, erosions heal with the formation of crusts. Locally, the patient feels pain and severe itching. It appears against a background of reduced immunity or a cold.
- Folliculitis (sycosis). This is a chronic pustular lesion of the hair follicles, which develops due to staphylococcus. Sycosis is more common in men due to endocrine and nervous disorders. The disease tends to spread and become chronic. Small pustules constantly open up and dry out, forming purulent crusts, under which there is bleeding mucous membrane. The patient complains of itching, burning and discomfort in the affected area; the process often affects not only the vestibule area, but also the hairs on the man’s beard.
- Fungal invasion. With this problem, the patient is bothered by itching, burning, and whitish deposits form on the mucous membrane, which prevent the person from breathing normally.
- Acne (acne). Inflammation of the sebaceous glands on the skin. They are located on any part of the body. Blocked sebaceous glands lead to the proliferation of bacteria and the appearance of unpleasant acne.
Not every cold in the nose is a dangerous abscess. If in doubt, you should visit a specialist to clarify the diagnosis and select therapy, since an internal pimple in the nose can be anything.
Eczema and erysipelas of the nose
In some cases, the reason why sores constantly form in the nose is eczema. This pathology most often develops in children and adults suffering from purulent sinusitis, in response to constant irritation of the dermis by secretions.
The first sign of the disease is redness and swelling of the surface of the skin at the entrance to the nostrils, then small, fluid-filled blisters appear. When they burst, they leave a wet surface on which cracks and crusts form.
Patients in such cases complain of pain and itching in the affected areas and, trying to remove dry crusts, further aggravate the process.
Erysipelas is an equally serious disease of the nasal area. It develops due to small abrasions that occur at the wings of the respiratory organ as a result of squeezing out small suppurations, picking the nose, etc. If at the time of injury an infection gets into the wounds, then the process can cover the entire nasopharynx and even lead to a narrowing of the larynx.
How to treat a boil in the nose
Boils in the nose are treated conservatively and surgically. Drug therapy is used at the infiltration stage, while the purulent-necrotic core has not yet matured. Prescribed systemically:
- Antibacterial drugs from the group of penicillins, cephalosporins or macrolides.
- Antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil). To reduce swelling and eliminate the allergic component of the pathology.
- Analgesics and antipyretics (Diclofenac, Paracetamol, Ibufen).
- Balanced diet and vitamins.
- Anticoagulants (Aspirin). Used to prevent orbital and intracranial complications.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures.
Local treatment includes the use of various ointments and creams that are applied to the affected area. Use:
- Levomekol. The most popular ointment for boils in the nose. It contains chloramphenicol, which has anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects. Used in purulent-necrotic processes, its effectiveness does not decrease in the presence of pus. How to apply it: soak gauze pads and place them on the affected area, change such dressings 2 times a day. The duration of therapy depends on the severity of the disease.
- Ichthyol ointment. The active substance is ichthyol, which has an antimicrobial effect. Used in the complex treatment of eczema and pustular skin diseases. Apply to the inflamed area 2-3 times a day, use a bandage if necessary.
- Tetracycline ointment. The active ingredient is the antibiotic tetracycline. Apply to the affected area after pre-treatment of the inflamed area with an antiseptic (for example, Miramistin and others).
Antibiotic therapy
Antibiotics are used in the following cases:
- complications of purulent inflammation of the hair follicle in the form of lymphadenitis (enlargement and pain of regional lymph nodes);
- increase in body temperature up to 39⁰С;
- presence of concomitant general diseases (diabetes mellitus, HIV).
Antibiotic therapy is carried out with the following medications:
- Penicillins (ampicillin, amoxicillin, amoxiclav). These antibiotics kill staph infections.
- Cephalosporins (cefazolin, ceftriaxone, cefuroxime, cefotaxime). Their pronounced therapeutic effect is observed at the low cost of the antibiotic.
- Gentamicin, which has high bactericidal effectiveness. But the drug is contraindicated for children and pregnant women.
- Levomycetin, which is used only locally.
How is surgical treatment performed?
At the stage of abscess formation, when the formed purulent core of the boil is visible, a wide opening of the abscess is performed and the purulent masses are removed. A drain is placed in the wound and a bandage with an antiseptic is applied. This procedure is performed under local anesthesia or short-term anesthesia.
Surgery is performed against the background of conservative therapy. The patient continues to receive antibiotics, anticoagulants and other drugs. The abscess cavity is drained until the discharge of pus stops.
After which the drainage is removed, and bandages soaked in ointments and solutions (sodium chloride, levomekolev and others) continue to be applied to the wound area.
Traditional methods of treatment
What to do if you don’t have a single drug at hand, and it’s impossible to get them. Alternative medicine suggests using traditional recipes and conducting treatment at home.
What methods can you use:
- Camphor oil. It has an antiseptic effect. You need to treat the inflamed area with this remedy 3-4 times a day.
- Raw potatoes. Grind a small potato on a fine grater, soak gauze in the juice and apply to the affected area. Change dressings 2-3 times a day.
- Onion juice and aloe. Mix onion and aloe juice in equal proportions and wipe the abscess with this mixture.
- Calendula. 20 gr. Mix dry calendula with Vaseline and lubricate the sore with the resulting cream.
- Drugs that enhance immunity and have an anti-inflammatory effect (chamomile, string, eleutherococcus, ginseng, etc.) are taken orally in the form of decoctions and tinctures
Traditional methods of treatment are good for mild manifestations of the disease and in combination with conservative therapy.
If a purulent core forms, acute intoxication, or signs of infection spreading, you should immediately stop fighting on your own and seek help.
How does a nasal boil develop and how dangerous is it?
Boil in the nose (can be treated with topical agents) has a classification.
The boil is divided into the following stages:
- Initial. The skin around the nose turns red, the borders do not have a clear shape. Additionally, pain occurs in the place where the boil appears. Discomfort increases when palpating the skin. Swelling is also noticeable, which can spread to adjacent tissues - cheeks, lips.
- Infiltration. It is characterized by the gradual (over 1–2 days) formation of a cone-like compaction. In the center of the formation you can see a dark dot - this is an area of tissue necrosis (death).
Additionally, there is pain, which is aching (in any position of the body) and sharp (when pressing on the boil) in nature. Swelling also increases. The duration of this stage is from 1 to 3 days.
- Abscess formation. This stage occurs 3 to 7 days after the onset of symptoms. The center of the formation becomes soft, the density of the tissue at the site of the lesion decreases. On top of the boil you can see a yellow-white rod. Over the course of 2–3 days, it forms into an abscess. During maturation, severe pain and tension in the soft tissues of the nose are noted. Discomfort increases when talking, chewing food, or palpating a boil. The pain does not decrease even at night, the person cannot sleep fully. Intoxication (a condition that occurs under the influence of toxic substances) cannot be ruled out, the signs of which are weakness and malaise, an increase in body temperature up to 39 degrees.
- Permissions. The boil is opened independently or with the help of a surgeon. The rod breaks through, this is accompanied by the release of exudate (liquid). Additionally, a person’s well-being improves, temperature and pain decrease. After the boil cavity is emptied, it fills with new connective tissue and heals. In the first 3–4 days, a retracted scar remains on the skin, then it becomes less noticeable.
The main danger of a boil is the possibility of a deep necrotic core.
There is a chance that the inflammation will spread to nearby tissues that surround the boil. Additionally, the boil is located on the face, which means inflammation of the brain, loss of hearing and vision cannot be ruled out. Also, after a boil, scars and bumps may remain on the face. Additionally, some people do not attach much importance to the boil; they open it themselves, and do not always remove the pus. As a result, there is a possibility of blood poisoning, spread of pus into surrounding tissues, and the boil becoming chronic.
If it doesn't work
If a boil formed in the nose does not cause complications and does not take the general condition of the body beyond normal limits, in this case treatment is carried out on an outpatient basis. Treatment at home involves taking antibiotics (macrolides, cephalosporins, fluoroquinolones) and vitamins, as well as treating the lesion itself with Celestoderm, Triderm, and Vishnevsky ointment. Drugs such as Olfen and Diclofenac help relieve inflammation.
Until the abscess noticeably appears, ointment must be used. If an infiltrate is detected adjacent to the boil, the treatment method is changed. Usually the patient's general condition worsens. In this case, physiotherapy is not resorted to, since it can provoke vasodilatation, which in turn leads to blood clots entering the vessels of the skull.
In this situation, a reasonable measure is the use of a laser that irradiates the blood. With frequent appearances of infiltration in tissues, a specialist can conclude that purulent necrosis has formed inside the tissues. In this situation, he must squeeze out the boil and clean out the epithelial particles. In addition, it is necessary to establish drainage.
In the case of normal progression of furunculosis for a long time without independent elimination of the process, it makes sense to use autohemotherapy, combining it with traditional treatment aimed at the general strengthening of the patient’s body.
Furuncle during pregnancy
During this exciting period, hormonal changes occur, and the woman’s immunity decreases so that the pregnancy can develop normally. Against this background, a pimple may appear inside or outside the nose.
First of all, you need to visit a specialist to find out an accurate diagnosis. If it is a boil, then at the infiltration stage, medications approved during pregnancy are selected (antibiotics from the penicillin group, ointments, antiseptics).
How to anoint an abscess on a pregnant woman?
You can use levomekol ointment, which is approved for use at this time.
At the stage of abscess formation, surgical opening of the abscess is performed. This problem during pregnancy must be treated and monitored, since hormonal imbalances increase the likelihood of complications.
Furuncle in a child's nose
This problem often occurs in childhood. The main reason is children's love of scratching and picking at this place with dirty hands.
In its development, the abscess goes through all the same stages as in an adult:
- Infiltration. The area of skin turns red and swells, and a painful protrusion appears.
- Abscess formation. A purulent core is formed, a whitish abscess is visible on the head.
- Recovery. It is emptied of pus and gradually the edges of the wound heal, and the swelling and redness subside.
The principles of treatment are the same as for an adult. Dosages of antibiotics and other drugs are chosen taking into account the age of the baby. If necessary, it is opened under short-term anesthesia or sedation.
Why does the boil love the nose?
The causes of a purulent boil in the nasal cavity, near the wings of the nose are often associated with:
- with violations of hygiene rules, scratching the nasal cavity with dirty hands and infection;
- using insufficiently clean towels and handkerchiefs;
- inaccurate removal of long hair in the nasal passages and causing microtraumas into which bacteria penetrate.
Common causes of boils can be associated with chronic diseases, diabetes, hypothermia, decreased body defenses, lack of vitamins, metabolic disorders, physical and mental fatigue, and a long-term stressful situation.
Often boils appear in the spring, which is associated with decreased immunity and increased sweating, which is an ideal environment for pustular skin diseases.
Boil on the nose
If a person has a boil on his nose, then it is not a boil. Since this diagnosis means inflammation of the hair follicle, and there are no hair follicles deep in the nose or at its tip, therefore the diagnosis of “boil on the tip of the nose” is incorrect.
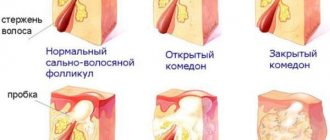
Inflammation of the tip of the nose is more often associated with blockage and infection in the sebaceous glands. This process is also called blackheads, pimples or acne.
How to get rid of this process? Surgical removal is practically not used, only in cases of widespread purulent process.
Conservative methods are used: creams, lotions, ointments that relieve inflammation and reduce sebum production. Normalize metabolism, rearrange nutrition and lifestyle. For severe acne, hormones and systemic antibiotics are prescribed.
Ways to treat rashes
The cause of the rash determines further treatment methods . For example, some acne may go away on its own without the use of pharmaceutical products. Others imply the mandatory use of not only antiviral drugs, but also agents with antibacterial activity.
The method of conservative treatment of cold rashes is based on eliminating the viral infection, eliminating the symptomatic picture and strengthening the body’s local immune defense.
For reference! When furunculosis is diagnosed in a patient, a purulent focus is opened in a hospital setting.
Elimination of symptoms
Rashes in the nose can be accompanied by unpleasant sensations - pain, itching, which can be eliminated with the use of antiviral drugs in the form of an ointment. High selectivity of action and minimal toxicity of Zovirax, Vivorax.
The virostatic effect of medications allows you to effectively eliminate the symptoms of inflammatory manifestations within 5-10 days . It is necessary to treat not only the damaged area, but also the entire painful area around the rash.
The boil is localized in most cases on the tip of the nose, somewhat less often - on the wings of the nose and on the skin of the nasal septum
The daily norm is equal to 5-6 procedures , with a minimum frequency of four hours . To treat the damaged area, you should use medical gloves to avoid the spread of infection.
Important! During treatment, it is necessary to observe the rules of personal hygiene, avoid contact in the form of kisses with healthy people, since the use of antiviral ointments does not provide protection against infection.
To treat acne of bacteriological origin, you should use ointments with antibiotic action - “Baneocin”, “Levomekol”, “Levomycetin”, etc. The specifics of using the ointment are specified in the manufacturer’s instructions.
How to fight an infection
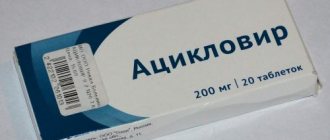
Elimination of the infectious process is directly related to strengthening the patient’s immune defense. Strengthening antiviral protection occurs when medications containing the active component, acyclovir, are included in the therapeutic treatment regimen.
These drugs can be used orally, topically (by dropping into the nose), rectally (suppositories). The therapeutic effect is enhanced by the simultaneous use of drugs with acyclovir in different dosage forms (combine tablets with suppositories, drops).
A fairly effective representative of the drug group is Viferon. In case of normal immune status, the daily dosage of the drug is equivalent to four doses of the drug, 200 mg each, with an obligatory interval of six hours .
Dosage and course of treatment may vary depending on the age and individual characteristics of the patient.
Nasal antiviral drops - Ingaron, Interferon - will help support local immunity. Prescribed in a short course - 5-7 days, 2-3 drops three to five times a day.
You can view the full list of antiviral drugs for the nose here.
How to get rid of a pimple on your nose at home
Using traditional medicine recipes will speed up the healing process and reduce discomfort.
The affected area can be lubricated with sulfur gruel . Remove sulfur from matches by diluting them a little with water. No less effective are lubricating acne with essential oils (eucalyptus, fir), as well as using valocordin or camphor alcohol .
The use of sea buckthorn oil or garlic-honey ointment (grate 1 clove of garlic, add 1 teaspoon of honey) will allow the rash to dry out in the shortest possible time .
It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out pimples in the nose on your own.
Due to the fact that the inflammatory process inside the nose precludes the use of various types of lotions or compresses, an alternative method of exposure is inhalation procedures . Any medicinal herb (coltsfoot, chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, oak bark) is suitable for these purposes. For 250 ml. boiling water – 20 gr. dry mixture .
This amount is enough for one inhalation. Inhale the vapors for 5-7 minutes, three times a day .
Important! Independent methods of treating nasal rashes require prior consultation with a doctor.
Furuncle on the bridge of the nose
On the bridge of the nose, ulcers can form in the eyebrow growth area, since a large number of hair follicles are concentrated there.
Clinical symptoms and treatment of the process are the same as for other localizations. More often, orbital complications develop due to the proximity of the orbit.
Treatment is carried out by an otorhinolaryngologist. Patients with this pathology are preferred to be treated in a hospital setting so that they can dynamically monitor the development of the disease and promptly prevent the consequences of a boil on the nose, a photo of which you can see above.
Surgical removal of a boil from the nose
The opening of a raised boil occurs in a hospital setting. This procedure is carried out at the last stage, when the abscess is already mature and the rod cannot break through. It is also recommended to remove the abscess at a temperature above 39 degrees, if it lasts for several days, or when signs of general intoxication appear.
Removal is carried out as follows:
- Local anesthesia is administered before the procedure. Most often, an injection of Lidocaine or Novocaine is sufficient for these purposes.
- The boil cavity is opened using a scalpel.
- The contents of the abscess are removed, and the surgical site is treated with antiseptic solutions.
- Sometimes it may be necessary to install a drainage - a special rubber strip that allows the remaining pus to escape.
- For particularly large abscesses and sufficiently large incisions, stitches are applied.
In some cases, further use of antibiotics will be required. After surgery, recovery occurs in approximately 3-5 days.