Causes
Dyshidrosis does not occur for any one specific reason. This disease is a symptom of trouble in the human body, it occurs as a result of problems in the digestive system or in the endocrine system, due to nervous exhaustion and a predisposition to allergies to some substance.
Often the cause of dyshidrosis is a fungal infection of the skin, called mycosis, which provokes allergic reactions and signals trouble in the human immune system.
This disease is seasonal - most often blisters on the skin of people prone to this disease appear in spring and autumn.
At this time, it is important for patients to eliminate factors that provoke dyshidrosis. Should be avoided:
- severe stress;
- overwork;
- eating allergenic foods;
- alcohol abuse;
- contacts with household chemicals and some cosmetics.
Dyshidrosis mainly affects people with a tendency to sweat profusely in the age category from twelve to forty years.
Classification
Depending on the depth of the lesion, the severity of the pathological process, and the causes of development, several types of dyshidrosis are distinguished.
True
The cause of the pathological process is dysfunction of internal organs and systems. In particular, hormonal imbalance, weakened immunity, and digestive problems. The disease begins with the appearance of small transparent blisters under the skin on the fingertips and pads.
Accompanied by slight itching and dry skin. Since the bubbles are located under a dense layer of skin, it is impossible to crush them. The use of a moisturizing cosmetic product does not provide relief. The itching gets worse in the evening. After a few days, the bubbles begin to increase in size, protrude to the surface, and their skin ceases to be dense. When scratched, they burst and eczema appears.
A different course of events is possible when the blisters begin to disappear on their own after a few days, the itching decreases, and the skin becomes moderately moist again. This situation indicates the normalization of natural processes in the body; the immune system itself has coped with the pathology. Patients are often at a loss as to why dyshidrosis appeared and how it disappeared.
Dyshidrotic eczema
Appears as the disease progresses or initially has clear signs of eczema. It develops rapidly when exposed to unfavorable factors - stress, nervous exhaustion, physical fatigue, poor diet, alcohol consumption, skin irritation from household chemicals. Unlike the first case, dyshidrotic eczema begins with redness of the epidermis, swelling, and itching. After a while, small transparent bubbles appear.
The rash increases, the blisters burst, and in their place wet spots appear, and then crusts. The skin thickens and cracks. At this stage, a secondary infection often occurs. Inflammation and itching intensify, pustules appear, redness spreads to the outer side of the hands or leg in the case of foot dyshidrosis. In addition, general health worsens. There is weakness, malaise, irritability, fatigue, a slight increase in temperature, headache, sleep disturbance.
Dry lamellar dyshidrosis
There is no rash or blisters. The disease begins with redness, swelling, and peeling. As it progresses, cracks of varying depths appear, burning, itching, and secondary infection occurs.
Symptoms
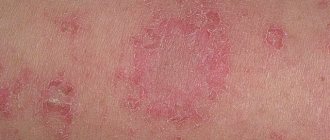
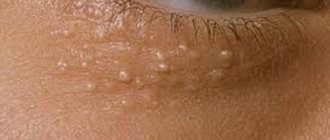
Symptoms of dyshidrosis are localized mainly in the carpal region (on the surface of the palms) and on the feet (on the soles and between the toes). The skin is covered with intraepidermal vesicles that resemble sago grains. Small bubbles gradually increase and reach the size of a pea. Serous fluid becomes noticeable through the dense membranes. If pathogenic bacteria penetrate, inflammatory reactions may occur with the formation of purulent abscesses. The localization sites of such neoplasms become swollen, and the skin around them turns red. The patient is concerned:
- intense itching;
- burning in the affected area;
- slight painful sensations when scratching.
After the bubbles burst, the patient enters a regressive stage:
- skin peels;
- crusts and cracks form.
New vesicles often do not appear. At the affected sites, renewed layers of the epidermis are formed.
Dyshidrosis in children
Often appears in infants and children under 5 years of age. The main reasons are weak immunity and unformed intestinal microflora. Any product, detergent, fabric can provoke a dermatological disease. In adolescents, the pathological process begins against the background of hormonal changes, poor nutrition, nervous tension, excessive physical activity, and weakened immunity.
There is a hereditary factor, a tendency to allergies, autoimmune disorders, abnormalities in the functioning of the endocrine system and nervous system. In this case, the frequency of relapses does not decrease with age. A rash or eczema appears after aggressive exposure to unfavorable factors, or against the background of a decrease in the body’s protective functions - after an illness, before and after menstruation, against a background of depression. Violation of sweating and metabolic processes occurs with poor nutrition, strict diets, overeating, and excess weight.
Diagnostics
Specific methods for diagnosing the disease dyshidrosis have not been developed, therefore, when making a diagnosis, a dermatocosmetologist relies on studying the symptoms of the disease. One of the important signs for making a diagnosis is the seasonality of relapses and their frequency.
During the diagnostic process, it is important to exclude skin lesions of fungal origin, since very often similar symptoms occur with mycotic dermatitis. For this reason, the patient is tested to detect various fungi. In addition, a patient with dyshidrosis is prescribed a comprehensive examination in order to identify the causes that provoked this skin disease.
Types of dyshidrosis and localization on the body
As already mentioned, dyshidrosis is localized on the human body in only two places - on the hands and on the feet, so there are only two types of this disease: dyshidrosis of the skin of the hands and dyshidrosis of the skin of the feet.
As a rule, it affects people with excessive sweating of the skin on the palms and soles, and the disease worsens in winter and becomes more pronounced.
However, in hot weather, especially in humid climates, similar rashes may appear on other parts of the body. In severe cases, a persistent form of the disease may appear, in which its external manifestations do not depend on the time of year and do not disappear even with adequate treatment.
Treatment
Therapy for dyshidrosis should be comprehensive. For this disease, a dermatologist can treat with physiotherapeutic methods:
In the process of treating dyshidrosis, the patient takes anti-inflammatory and antihistamine medications. In severe cases of the disease, treatment is carried out with glucocorticosteroid drugs together with diuretics. For a small rash, use various ointments containing sulfur, tar, naphthalene, as well as various mash and pastes for indifferent purposes. In case of acute form of rashes on the skin, severe pain can be relieved by:
- lotions with Burov's liquid solution;
- ethacridine;
- amidopyrine;
- lactate;
- furatsilin.
If the blisters become infected, you should immediately see a doctor. During the period of acute dyshidrosis of the hands and feet, water procedures that use cosmetics and soap are contraindicated. It is also important for a patient with dyshidrosis that the affected areas of the skin do not come into contact with various acidic and chemical substances; rain, snow, sun, wind, as well as fur products, wool and synthetics should be avoided. For dyshidrosis of the hands and feet, warm baths with herbal decoctions of celandine, chamomile, oak bark and sage will be very useful. Such baths can have a soothing effect on the skin, relieve itching and have a disinfecting effect. They must be taken once a day, the procedure should last twenty minutes.
List of ointments for the treatment of dyshidrosis of the hands and feet: rules of use
Ointments help reduce the severity of symptoms, prevent secondary infections and other complications. Products for external use are usually used as part of complex therapy. The type of drug and course of treatment are determined by the doctor based on the clinical picture.
Levomekol
Combined drug with antimicrobial properties. The product has a dehydrating effect and can be used for purulent processes. The product is preheated to body temperature and applied to gauze pads. Bandages are applied daily until symptoms subside.
Zinc ointment
A dermatoprotective agent based on zinc oxide is prescribed in the initial stages of the disease. It has immunobiological properties and gives a wide therapeutic effect:
- dries out the epidermis;
- absorbs pathogenic microorganisms, toxins, allergens that cause pathological processes;
- has an antiseptic effect;
- forms a dense protective film that protects against exposure to irritants.
Be sure to read:
Homeopathic Arnica ointment for the treatment of bruises and hematomas
The ointment is applied to the affected areas three times a day for a month.
Ichthyol ointment
The drug is an anti-inflammatory and also has a local anesthetic and antiseptic effect. Active ingredients are distillation products of bituminous shale and thiophene (about 10%). When applied to the affected area, it causes mild irritation of nerve endings with a further decrease in their sensitivity. Softens the stratum corneum, helping to cleanse the ducts of the sweat glands and normalize sweating.
Contraindications include sensitivity to the components of the product. Ichthyol ointment is applied twice a day, the duration of the course is determined by the doctor. Long-term use of the medication can cause irritation and hyperemia (redness) of the skin.
Tetracycline ointment
Broad-spectrum antibiotic. Prescribed for bacterial skin infections. The ointment is contraindicated for pregnant and lactating women with renal failure. The product is used for no more than 2 weeks. With long-term treatment, the drug causes allergies and hemostasis disorders.
Salicylic ointment
A drug based on salicylic acid is prescribed to reduce inflammation, eliminate and prevent infection of the dermis. Effect of salicylic ointment:
- dissolves the stratum corneum, promoting the release of fluid from the ducts;
- destroys microbes and pathological formations;
- causes reactions aimed at reducing pain, improving blood circulation, nutrition and tissue functions;
- suppresses the inflammatory process.
The ointment is applied to the affected area in a thin layer and covered with a napkin. Before application, the affected area is cleaned and treated with an antiseptic. The bandage is done 2-3 times a week.
Fluorocort
A glucocorticosteroid that effectively combats dyshidrosis. The drug is also prescribed for eczema, atopic and contact dermatitis. The active substance trimcinolone has the following effects:
- reduces the feeling of irritation and burning;
- reduces vascular permeability, promotes the removal of fluid from tissues;
- reduces inflammation;
- inhibits the formation of histamine, suppressing the allergic reaction.
Fluorocort is used to treat areas with rashes 2-3 times a day. If necessary, use an occlusive (sealed) dressing. The average duration of therapy is 5-10 days, in severe cases - 25 days.
Losterine
Dermatotropic non-hormonal agent. The cream contains naphthalan, salicylic acid, dexpanthenol. The cream is included in complex therapy to prevent exacerbation of the disease and prolong remission. Loserine has the following effects:
- protects the epidermis from microbial damage;
- neutralizes itching caused by allergies;
- reduces sweating by thickening the epidermis;
- reduces the inflammatory response;
- stimulates regeneration processes.
Be sure to read:
Top 9 effective Chinese remedies for psoriasis
Losterine is applied to previously felt areas with rashes 2-3 times a day. The duration of the course is 4 weeks; in case of severe dyshidrosis, the course is repeated after a break of 10 days.
Elokom
Hormonal ointment, the action of which is aimed at reducing and eliminating inflammation and itching. The therapeutic effect is provided by the main active substance of Ekolom - the glucocorticosteroid mometasone:
- reduces the inflammatory process;
- eliminates the symptoms of an allergic reaction;
- reduces irritation of nerve receptors, suppressing the unpleasant sensations of tingling and burning;
- promotes the removal of exudate from tissues.
Elocom is used to treat the affected areas once a day, rubbing in with gentle movements until completely absorbed. The duration of therapy depends on the effectiveness and tolerability of the drug by the patient.
Triderm
Combined hormonal drug with broad antibacterial activity. The drug eliminates primary and secondary infections, fungal infections. Active against staphylococcus, klebsiella, trichophyton, etc. In addition to being antibacterial, Triderm has an antipruritic, antiexudative effect, reduces inflammation and itching.
Triderm is applied in the morning and before bed to the affected areas and surrounding tissues. To ensure therapeutic effectiveness, the drug is used regularly. The duration of treatment is determined depending on the size of the lesion and the patient’s response.
Laticort
A glucocorticosteroid based on hydrocortisone, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Laticorm has the following effects:
- inhibits inflammatory reactions;
- reduces swelling and redness of the skin;
- eliminates allergy symptoms, including itching;
- removes exudate from tissues;
- immunosuppressive;
- anti-shock.
Laticorm is applied to areas with blistering rashes 2-4 times a day. If the dynamics are positive, the number of applications per day is reduced to 1-2 times. The duration of therapy should not exceed 2 weeks.
Prevention
Prevention of the disease is based on:
- dietary nutrition, in which it is necessary to limit as much as possible the consumption of salty, fried, canned, alcohol, food allergens, coffee;
- avoiding direct contact with irritating substances and household and industrial allergens;
- wearing clothes and underwear only from natural fabrics;
- careful control of body hygiene, timely treatment of all infectious diseases, elimination of foci of skin inflammation, antiseptic treatment of any skin injuries;
- preventive consultations with a dermatologist, regular examinations and preventive courses of treatment for eczema.