Exfoliative dermatitis (Ritter's disease) is a severe infectious skin lesion that is most common in newborns. This type of disease develops according to the malignant variant of pemphigus and is characterized by hyperemia of the skin, the formation of blisters, which transform into erosions.
The inflammatory process begins in the oral cavity, gradually spreading throughout the body and significantly worsening the condition of patients. Premature babies are most susceptible to the disease, after 14 days of life. Very rarely, Ritter von Ritterstein disease appears in babies after 2-4 days of life. The earlier pathological symptoms appear, the more severe the possible complications.
What is exfoliative dermatitis
A group of dermatological pathologies affecting the skin is called exfoliative dermatitis. It has an acute course and occurs against the background of other types of dermatosis (atopic dermatitis, psoriasis), systemic diseases or infections.
Exfoliative dermatitis in adults is provoked by a decrease in immune defense and the presence of primary eczematous conditions. The mechanism of development of erythroderma in infants is based on the reactivity of the skin. The penetration of bacteria through a thin layer of the epidermis of a newborn under the influence of unfavorable factors causes the formation of blisters.
Disease prevalence statistics
Ritter's disease is a rare pathology - 1% of all patients visiting a dermatologist.
It occurs in different age categories, but most often affects newborns and people over 55 years of age.
Men are less susceptible to dermatitis than women - an approximate ratio of 2.3:11.2.
Why is Ritter's disease dangerous?
The disease is dangerous because epithelial detachment reduces its protective properties and this increases the chances of a primary or secondary bacterial infection. Under unfavorable conditions, there is a high risk of developing sepsis and death. The consequences of the disease can be manifested by the following conditions:
- dehydration;
- acute enterocolitis (inflammation of the small and large intestines);
- pneumonia;
- phlegmon (inflammation of the subcutaneous tissue);
- meningitis;
- peritonitis (inflammation of the peritoneum);
- otitis.
Complications
- Peritonitis.
- Otitis.
- Phlegmon.
- Enterocolitis.
- Pneumonia.
- Meningitis.
It all depends on how quickly parents see a doctor after the onset of symptoms. With proper and timely treatment, the prognosis is favorable. however, in the most severe cases, death can occur.
Exfoliative dermatitis (photos of the main symptoms are in this article) often causes the development of other diseases. Among them: otitis media, peritonitis, acute enterocolitis, phlegmon, meningitis, pneumonia.
As for the prognosis, it is very optimistic for adults. The body copes with the infection quite quickly, of course, not without proper treatment, and you can get rid of the disease in 14 days.
Only severe forms of exfoliative dermatitis threaten serious complications. In the case of infants, it can even be fatal. The percentage of deaths from pathology in adults is negligible. However, a patient of any age needs constant care and treatment.
In adult patients, the prognosis is favorable. If you follow all medical recommendations and receive adequate treatment, recovery occurs within 2 weeks. In severe cases of the disease, adults may have complications such as loss of hair and nails, inflammation of the liver, spleen, and lymph nodes.
In children, complications are much more serious and they develop much more often.
Post Views: 1,796
Regenerative stage
The third (regenerative) stage of the disease occurs when its course is favorable. There is a decrease in redness and swelling, epithelization of erosive elements. After this, the child recovers.
Mild forms of the disease are characterized by a difficult to recognize course without pronounced skin lesions. After just a couple of weeks, there is a decrease in inflammation and the end of the disease, which is accompanied by abundant peeling of the skin. Similar variants of the development of Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis are most often found in older children.
With accompanying septic complications (pneumonia, otitis, meningitis, pyelonephritis, phlegmon, acute enterocolitis), it becomes very difficult for a child to tolerate Ritter’s exfoliative dermatitis.
Features of the disease
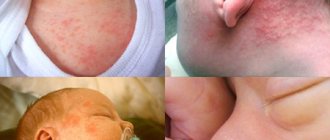
This severe form of infectious epithelial damage in newborns manifests itself in the form of redness followed by the formation of “flaccid” blisters. After some time, the bubbles turn into erosions.
The disease initially affects the dermis area around the mouth, and then affects the entire skin of the baby. In addition to redness and blisters, the child’s general condition is disturbed. Redness and peeling cover up to 90% of the entire epithelium area.
The diagnosis is quite easy to establish, given the typical clinical picture of the disease. When making a diagnosis, other dermatological diseases of the skin that have similar symptoms are usually excluded.
The risk group includes premature babies, low birth weight babies, and babies who have suffered a birth injury.
- In adults, this type of dermatitis occurs over the age of 40 years.
- At the same time, in representatives of the fair sex, the disease is observed 4 times more often.
The doctor will tell you in detail about exfoliative dermatitis in the video below:
Local treatment
- The bubbles are opened and their remains are removed.
- Erosions are covered with antiseptic and glucocorticoid ointments.
- Bathing and washing the baby is carried out in warm water with potassium permanganate.
Stages of development of exfoliative dermatitis
Signs of Ritter's disease in adults and children depend on the stage and severity of the exfoliative form. Mild dermatitis can occur without phase 2 of the disease. Moderate and severe forms of pathology are characterized by the presence of all 3 stages:
- Erythematous – swelling, blistering, fever.
- Exfoliative – the formation of exudate, which causes the Nile symptom (skin detachment).
- Regenerative – the temperature decreases, erosions heal.
Symptoms of the erythematous stage of the disease
The duration of the stage is 1-3 days. Exfoliative lesions begin with redness of the skin on the head, torso and perineum, then the legs and arms become hyperemic. The red spots have a clear shape. General symptoms of dermatitis:
- fever;
- spotted plaques;
- swelling;
- peeling of the skin, itching;
- crust formation;
- the appearance of blisters with fluid;
- migraine;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Signs of the exfoliative phase
The duration of the stage is 2-5 days. Watery blisters increase in size and open, forming erosions. Exudate (liquid) oozes from them, causing pain and burning.
The affected skin begins to peel off upon mechanical contact and resembles a 2nd degree burn.
- Ointment for fungus in human ears
- Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp - treatment with pharmaceutical, cosmetic and folk remedies
- Cream for atopic dermatitis - a list of hormonal and non-hormonal agents for treatment
The top layer of the epidermis becomes crusty. Associated symptoms:
- chills;
- nail deformation;
- hair loss;
- indigestion;
- tachycardia;
- oily feces
Regenerative stage
The duration of the final stage of dermatitis is 7-10 days. Swelling subsides, redness decreases, erosions dry out and heal. The stage is characterized by fine and large cell peeling of the skin. In the absence of a secondary infection and proper treatment, the pathology resolves within 10-16 days.
Typical clinical picture
Most often, the disease manifests itself 7-14 days after the birth of the child. Moreover, the earlier Ritter’s exfoliative dermatitis develops, the more severe it will be. The course of the disease includes 3 successive stages:
- Erythematous.
- Exfoliative.
- Regenerative.
Each of these stages has its own characteristic clinical picture.
In older children, Ritter's dermatitis is milder, but it is also accompanied by skin lesions
We recommend studying this topic:
What is bullous dermatitis and methods of its treatment
4005
0
0
reading information
Erythematous stage
This stage of exfoliative dermatitis is characterized by the appearance of hyperemia (redness) of the skin around the mouth and navel. First, hyperemia spreads to the areas of natural folds, the navel and anus, and then to the entire surface of the skin.
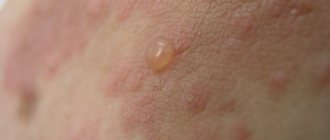
This stage of dermatitis is characterized by the formation of tissue swelling. In the future, this leads to stratification of the epidermis and the appearance of fairly large blisters. Their upper pole is not tense. Such bubbles open quite quickly. The skin itself in the affected area takes on an appearance somewhat similar to tissue paper. After opening the bubbles, a red shiny surface is exposed. In this case, there is no pus or other pathological discharge.
Advice! If redness occurs around the mouth and near the navel in a child, you should immediately consult a dermatologist. If you cannot get to this specialist, then a pediatrician will provide all the necessary assistance.
Exfoliative stage
This stage is the most difficult. It is characterized by the following clinical picture:
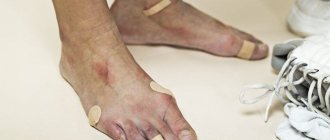
- Erosion develops at the site of burst blisters.
- Erosion tends to merge into one large affected area.
- The child's general condition is serious.
- Loss of body weight.
- Low level of appetite.
- Increase in body temperature to 40 oC.
- Diarrhea.
In the absence of treatment and supervision by specialists, all these symptoms are quite capable of leading to the most negative consequences for the newborn.
The regenerative phase of the development of Ritter's dermatitis is accompanied by an improvement in the child's condition
Regenerative stage
If Ritter's dermatitis is treated successfully, then the exfoliative stage passes into the regenerative stage. It is characterized by gradual healing and epithelization of erosions. The child's condition is improving. He gets an appetite. Gradually the child begins to gain weight. The outcome of this stage is the complete recovery of the newborn.
In some cases, exfoliative dermatitis can be relatively mild. This is most often observed in older children. In this case, the skin in the affected areas peels off, and body temperature may rise slightly.
Important! The course of Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis can significantly worsen if the patient experiences septic complications in the form of pneumonia, pyelonephritis, meningitis, etc. In this case, it is often necessary to provide care to a newborn in the intensive care unit.
Laboratory tests will determine the degree of dysfunction of the main body systems
Treatment of pathology
In newborns, symptoms of exfoliative dermatitis appear a few (up to 14) days after the birth of the child, and occur in three stages.
Erythematous stage
Depending on the severity of the disease, various signs may appear. At the initial stage, the patient begins to feel the following ailments:
- the affected areas become covered with small bubbles with viscous contents;
- after a certain period of time, the bubbles connect with each other and burst, which leads to the formation of bloody crusts;
- excessive peeling of the skin;
- change in skin color.
With active development, this disease without the required treatment passes into a more severe stage, which is accompanied by the following symptoms in humans:
- deformation of nails with their subsequent falling off;
- atypical dryness of mucous membranes;
- there is intense hair loss;
- severe itching in the affected areas;
- cardiopalmus;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Important to remember! At the first signs of a skin disease, you need to seek help from a specialist! This will help avoid subsequent complications. In addition to the fact that the skin exfoliates due to blistering and peels off, it also has the property with this disease to continue to peel further along the skin of the entire body
In addition to the fact that the skin exfoliates due to blistering and peels off, it also has the property with this disease to continue to peel further along the skin of the entire body.
It is this feature that most often characterizes this disease, and also causes a lot of trouble for patients. The quality of life is so deteriorating that it is simply impossible to do without the help of doctors.
Before connecting one or another therapy to the healing of an illness, a group of symptoms is identified in the patient.
The disease has its stages:
- Erythematous.
- Exfoliative.
- Regenerative.
Typically, the disease can develop at rates of varying intensity: both slowly and quickly. The main symptoms of exfoliative dermatitis are:
- increased body temperature, but the patient feels severe cold;
- with the rapid progression of dermatitis, the skin sharply turns red and thickens, scales and crusts appear on it;
- exfoliative dermatitis is also characterized by enlarged lymph nodes;
- a lot of fluid is released through the inflamed skin;
- the affected area is very itchy, causing the patient a lot of discomfort and suffering.
Ritter's exfoliative dermatitis in newborns
Infants also have 3 stages of dermatitis, but there are features of the course:
- Erythroderma begins with redness of the umbilical and oral areas. Then it moves onto large folds of the body and merges into one spot.
- In the second stage, babies have a sharp rise in temperature, diarrhea and vomiting.
- The third phase is characterized by the disappearance of symptoms of general intoxication, healing of wounds, and rapid growth of the epidermis.
- The younger the child, the more severe Ritter's exfoliative disease is.
Symptoms of the disease in adults
Exfoliative dermatitis in adults has some differences. So, on the skin, starting from the torso, head and perineum, and then, moving to the limbs, areas of redness and thickening appear. Bubbles appear in the affected areas, which merge and then open, revealing eroded surfaces. They itch, ooze fluid, and cause pain and burning in those areas. A little later, the erosions become covered with crusts, which begin to peel off greatly.
If exfoliative dermatitis develops against the background of a skin disease, then the described changes - redness, swelling, the appearance of blisters, and then erosions - are observed at the sites of existing dermatitis or dermatosis. The latter, before “giving way” to redness and bullae, worsens for a short time.
General symptoms of the disease are also noted:
- fever;
- enlarged and painful lymph nodes;
- feeling of chills;
- increased heart rate;
- feeling of dry mouth;
- nail deformation;
- baldness;
- the appearance of oily - shiny and difficult to wash - feces.
If the cause of exfoliative dermatitis is a malignant blood disease (leukemia, lymphoma), then an enlargement of the liver is observed, which is manifested by constant heaviness in the right hypochondrium. In addition, the volume of the spleen increases, so when walking quickly, running, or performing loads, heaviness is felt in the left hypochondrium.
Therapeutic measures
Exfoliative dermatitis in adults is not nearly as dangerous as in children. Hence the difference in the degree of urgency of treatment.
Although even adults often have to undergo infusion therapy due to the large loss of protein, iron and electrolytes.
Treatment methods are determined by three points:
- the severity of the pathology;
- the age of the patient (directly related to the first point);
- and the possible cause of the disease, if one can be determined.
Therapeutic method
Based on local treatment.
Skin areas are treated with salicylic alcohol to disinfect and prevent secondary infection.
Emollients are used:
- Emolium;
- Lipikar;
- Atopic et al.
- Emollients restore pH and water-electrolyte balance of the skin.
- They form an additional lipid layer that prevents moisture loss.
- Promote the synthesis of elastin and collagen in the thickness of the dermis.
For severe inflammation, hormonal ointments can be used:
- Akriderm;
- Advantan;
- Hydrocortisone;
- Prednisolone;
- Sinaflan.
Zinc oil or zinc paste is often used.
Drug treatment
If exfoliative dermatitis is observed in newborns, urgent intensive use of antibiotics is required, which are prescribed parenterally.
Since this implies a severe staphylococcal infection, the following is used:
- cephalosporins of the latest generations (Cefotaxime, Cefepime, Ceftaroline);
- or macrolides (Roxithromycin, Josamycin).
Antistaphylococcal plasma and antistaphylococcal gamma globulin are administered. Infusion therapy with Dextran (analogue - complex saline solution) is used against dehydration.
In adults, drug treatment is highly dependent on the underlying causes.
In severe forms, systemic glucocorticosteroids are used:
- Prednisolone;
- Dexamethasone;
- Diprospan.
For cascading allergies, antihistamines can be used:
- Suprastin;
- Ebastine;
- Loratadine;
- Erius (Desloratadine).
For autoimmune pathologies, the use of special immunosuppressants (Azathioprine).
For infection - antibiotics.
Folk recipes
Folk remedies can serve as a good additional therapy, and also act as a preventative measure.
Examples of folk recipes:
- add one teaspoon of birch tar to any hypoallergenic cream, heat it in a water bath to 70 degrees, lubricate skin lesions 2 times a day;
- add 50 g of sour cream to freshly prepared mashed potatoes, wrap in a bandage or gauze and apply this compress to the affected areas for one hour;
- Gauze compresses soaked in yarrow decoction help a lot.
Before using traditional recipes, notify your dermatologist.
Unpleasant complications
Various complications often arise.
Loss of protein, iron, electrolytes and water can lead to damage to internal organs.
Inflammation can trigger a secondary infection. The same Staphylococcus aureus, which is normally found in small quantities on the skin of many people.
Less commonly, chronic skin inflammation threatens the generation of atypical cells (oncological neoplasms).
Reasons for the development of the disease
The pathology is due to different reasons, depending on the age group. Factors of exfoliative dermatosis:
- bacterial infection;
- prematurity;
- birth injury;
- skin sensitivity.
In adults, exfoliative dermatitis develops for complex reasons. They are divided into groups:
- diseases of internal organs (enterocolitis, pancreatitis, heart failure);
- major skin diseases (scabies, exfoliative keratolysis, toxic necrolysis, lichen ruber, seborrheic dermatitis);
- malignant tumors (lymphoma, myeloma, leukemia);
- systemic pathologies (dermatomyositis, lupus erythematosus, diabetes mellitus);
- infectious diseases (tuberculosis, hepatitis, Lyme disease, typhus);
- side effect from taking medications (barbiturates, antibiotics, blood pressure medications).
How to treat Ritter's dermatitis
In adults, therapy for mild to moderate exfoliative forms of pathology is carried out on an outpatient basis.
Only severe cases require hospitalization.
The treatment tactics for the exfoliative form are to establish the cause of the disease, alleviate symptoms, and normalize electrolyte balance.
The duration of treatment is 1-2 weeks. Mild and moderate degrees of dermatitis disappear without consequences. In severe cases of the disease, a secondary infection is observed, which increases the risk of possible complications in adults and death in newborns.
Treatment methods for the disease in adults
Treatment of dermatitis in adult patients is carried out by 2 methods - therapeutic and medicinal. The first includes:
- oral rehydration using ready-made solutions (Regidron, Gidrovit);
- skin softening procedures - baths with potassium permanganate (potassium permanganate), emollients (remedies that eliminate dryness and itching);
- phototherapy (for psoriasis) – treatment with light waves of different lengths.
Drug therapy consists of the use of drugs with local and systemic effects. The surface of the skin is treated first:
- antibacterial water-soluble agents (Oflocain, Levomekol);
- aniline dyes (solution of brilliant green, methylene blue);
- bactericidal agents (Fukartsin, Salicylic alcohol) - on areas of the skin not damaged by dermatitis.
- compresses with silver nitrate.
Systemic drugs are prescribed for severe dermatitis and developing complications:
- Corticosteroids - hydrocortisone ointment topically, intravenous injections of Prednisolone for 10 days.
- Glucocorticoids – Prednisol 1 tablet for 10 days.
- Antibacterial drugs - cephalosporins, macrolides, penicillin orally or intramuscularly for 5-7 days.
- Antifungals - Terbinafine, Ketoconazole once a day, 250-400 mg.
- Immunosuppressants – Methotrexate infusions (7-10 days).
- Antihistamines – Zyrtec, Xyzal 1 t per day, 1-2 weeks.
- Antiviral - Valtrex (2 t 2 times a day, 5 days), Acyclovir (2-4 t 3 times a day, 10-14 days).
Features of treatment for children
Premature newborns are placed in sterile incubators - separate boxes that are supplied with oxygen and have the necessary temperature for drying out erosions.
If the baby is more than a month old, he is placed with his mother in a separate room.
It is disinfected daily - quartz treatment, surface treatment with antiseptics.
The treatment strategy for dermatitis in children is to use the following drugs:
- antibiotics (Tseporin, Kefzol);
- probiotics (Bifidum, Lactobacterin);
- plasma, immunoglobulin against staphylococcal infection (Timalin);
- rehydration infusions (Polyglyukin, Hemodez);
- treatment of burst epithelium with alcohol-free dyes (Fukartsin), zinc oil, powders with xeroform.
Local preparations
Local treatment for dermatitis is the most effective. In mild and moderate forms of the disease, it is often possible to achieve a cure with ointments, creams and lotions, without resorting to systemic therapy. Only a dermatologist can prescribe specific medications.
Typically used in the treatment of dermatitis:
- Anti-inflammatory ointments: Erythromycin ointment, Levomekol;
- Glucocorticosteroid drugs: Akriderm ointment, Lokoid cream and lotion;
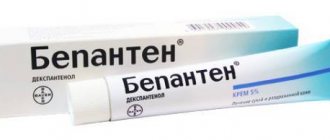
- Ointments that restore the skin surface: Bepanten, Radevit;
- Anti-itch ointments: Fenistil;
- Keratolytic ointments: Lorinden, salicylic-zinc paste.
Systemic treatment
Systemic drugs are used to treat severe forms of dermatitis, as well as allergic skin inflammations. Drugs are selected based on the diagnosis and characteristics of the patient’s body.
A dermatologist, depending on the type of dermatitis, may prescribe:
- Detoxification therapy: activated carbon, Polysorb;
- Antihistamines: Kestin, Loratadine, Cetrin;
- Calcium preparations: calcium gluconate, calcium chloride;
- Sedatives: extracts of valerian, motherwort, Afobazol, Glycine.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies are the most popular method of treatment, but there is always a danger of aggravating the disease and intensifying the problem. Therefore, it is worth using traditional methods of treatment only after consultation with your doctor and not instead of classical therapy, but together with it.
Traditional recipes for the treatment of dermatitis:
- Periwinkle. Make a decoction: pour about 300 grams of dry leaves of this plant with 1 liter of water, when it boils, wait another 10 minutes. When it cools, strain and add to the bath. Take a bath for at least 15 minutes. Apply the boiled cake to problem areas of the skin.
- Sophora japonica. The fruits of this tree can cope well with itchy skin. It is enough to boil 100 grams of fruit in 0.3 liters of water. Then wet the gauze or bandage and apply it to the itchy area of skin.
- A series. Take one tablespoon of powder from the string. Brew the herb with 150 milliliters of water. Leave for 4 hours.
Diet
Treatment of any dermatitis should begin with following a hypoallergenic diet, especially if the dermatitis is of an allergic nature.
Hypoallergenic products:
- poultry meat,
- veal,
- mutton,
- skim cheese,
- cucumbers,
- zucchini,
- fresh cabbage,
- vegetable oils,
- cereal porridges,
- fermented milk products without chemical additives,
- green apples,
- black bread.
You should not eat foods such as:
- chocolate,
- coffee,
- red vegetables and fruits,
- horsemeat,
- citrus,
- strawberries and strawberries,
- sauces and mayonnaise,
- industrial canned products,
- all types of tropical fruits.
Stories from our readers!
“I suffered from dermatitis. His hands and face were covered with small spots and cracks. No matter what I tried, the drugs only helped for a while. A colleague advised me to order this cream.
Finally, thanks to the cream, I completely got rid of the problem. After the third procedure, the burning and itching disappeared, and after 4 weeks the signs of dermatitis disappeared. I am very pleased and recommend using this cream to all people suffering from skin problems.”
Basic diagnostic methods
Diagnosis of this disease most often does not pose a serious problem. Exfoliative dermatitis has a characteristic clinical picture. The high rate of development of the main symptoms convinces the doctor of the correctness of the diagnosis.
To accurately determine the nature of the pathological process, additional diagnostics are necessary. The following methods are used:
- bacterial seeding of discharge from blisters and other skin defects;
- PCR and RPR research;
- general blood and urine analysis;
- blood chemistry.
Sowing of the discharge is carried out on special nutrient media. After colonies of the pathogen grow on these media, it is clarified which microorganism caused the development of the disease. In the future, doctors are able to conduct special studies on the sensitivity of the identified pathogenic microflora to certain antibiotics.
Note. Treatment of exfoliative dermatitis with broad-spectrum antibacterial agents begins even before the sensitivity of the microflora to specific drugs is established.
Antibiotics are the mainstay of treatment for exfoliative dermatitis
Diagnostic tests
Diagnostic studies are necessary to confirm the diagnosis, as well as to differentiate this disease from syphilitic pemphigus and bullous dermatitis, which have a similar clinical picture. The following methods are used to determine pathology:
- Bacterial culture of discharge from blisters. It is carried out in order to identify the causative agent of the infection, as well as to select effective antibacterial agents. Unlike bullous dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis reveals staphylococcal and, less commonly, mixed flora.
- PCR. Polymerase chain reaction is necessary as an additional research method with which one can identify a particular pathogen. Used to differentiate congenital syphilis from exfoliative dermatitis.
Folk remedies for exfoliative dermatitis
Treatment of dermatitis using folk remedies is considered effective. Popular recipes:
- 300 g of dry string, pour 2 liters of water, boil for 15 minutes. After an hour, lubricate the sores with the prepared decoction 5-6 times a day for 10 days. Children can take baths with a decoction of the string. The duration of the procedure is 5-7 days.
- 2 tbsp. l. Brew 500 ml of boiling water with chamomile. Leave the product for half an hour, then strain. Drink ½ glass 4 times a day for 2 weeks.
Prevention
Methods for preventing the development of exfoliative form of pathology in adults:
- treat dermatitis in a timely manner;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- avoid allergens;
- treat chronic diseases;
- strengthen your immune system;
- follow your diet.
Prevention of dermatitis in newborns:
- conduct a blood test before childbirth to identify staphylococcal and streptococcal infections;
- monitor the use of antiseptics, gloves, and gauze bandages by medical staff when in contact with the baby;
- require daily disinfection of the room;
- Maintain hygiene after leaving the hospital.
Treatment
Treatment of exfoliative dermatitis of newborns is carried out in incubators supplied with oxygen. They maintain the required temperature and sterility. Under such conditions, erosions dry out. Additionally, the lesions are wiped with alcohol-free dyes.
If the baby is one month old, he is placed in a box with his mother. The ward is cleaned with antiseptics and quartzed several times a day.
To select antibiotics, material is taken from the surface of erosions and sent for bacterial culture. Then the baby is injected intravenously with antibacterial drugs, anti-staphylococcal immunoglobulin and plasma with antibodies to staphylococcus.
Treatment of exfoliative dermatitis in adults with mild to moderate severity is carried out at home. The initial task is to eliminate the cause of the disease (lower sugar levels, stop taking antibiotics, compensate for autoimmune pathology).
Local therapy consists of treating the lesions with aniline dyes and water-soluble antibacterial ointments (Levomekol, Oflocaine). Compresses with silver nitrate are also used. In the presence of psoriasis or fungal infection, PUVA therapy is used.
For systemic therapy, Prednisolone, antibiotics (in the presence of bacteria), antimycotics (in the presence of fungi), isotreonine preparations (in the presence of lichen erythematosus) are used.