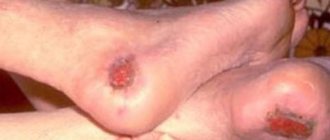
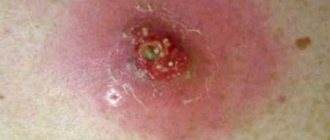
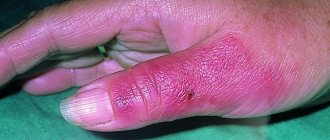
Furunculosis is a skin disease in which inflammation of the sebaceous glands and hair follicles occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic microbes into them. If treatment is not started in time, there is a risk of purulent complications. Your doctor will tell you which antibiotics for boils in the groin, under the arm, or on the face will have a therapeutic effect. Self-treatment of this disease can lead to serious consequences.
With furunculosis, it is important to start treatment on time
In what cases is it necessary to take antibiotics for furunculosis?
Treatment of furunculosis with antibiotics provides a quick recovery when the boil is on the cervical area or on the head. This placement of the abscess is dangerous because it leads to infection entering the brain. An abscess provokes complications, including death. Spreading quickly, Staphylococcus aureus provokes the appearance of new foci of inflammation. Most often, boils are found on the face, back, neck area, ears, and intimate places.
Furunculosis requires treatment:
- when enlargement occurs, enlargement of lymph nodes;
- painful lesions spread over areas of the body;
- when furunculosis develops into a chronic stage;
- when placing abscesses on the cervical, head, and facial areas.
Additional drugs used in treatment include drugs to enhance immunity and vitamins. It is important to adhere to the diet prescribed by your doctor.
It is forbidden to treat inflammation at home on your own. Infection can lead to carbuncles.
Doxycycline-based masks
The best way to fight acne with Doxycycline is to use masks at home.
Standard mask based on Doxycycline and cosmetic clay
Doxycycline is used as an auxiliary component for various masks to reduce the number of acne.
Below is a recipe and method of using a standard product based on this drug and cosmetic clay:
- Take 1 tablespoon of any cosmetic clay and dilute it with water to obtain a thick paste;
- 5 Doxycycline tablets are crushed to a powder and added to the composition;
- The components are thoroughly mixed, the resulting homogeneous mass is applied to the face in even layers;
- You must wait until the mask has completely dried, after which it can be washed off with warm water;
- The course is required for 3-4 weeks, the procedure is carried out 2 times a week.
Cosmetic clay contains a large amount of minerals and substances beneficial to the skin; adding Doxycycline to it increases the antiseptic properties of the product.
Egg mask with the addition of Doxycycline
Egg masks are suitable for treating acne on dry skin. They normalize impaired metabolism and stimulate the natural protective functions of the skin. After using the product, color improves, skin elasticity increases and pigmentation is eliminated.
The recipe for preparing and using such a mask is as follows:
- Take 1 raw chicken egg, which will need to be beaten and then mixed with powder obtained from several capsules of Doxycycline;
- As additional components, use 1 teaspoon of olive or wheat oil, 10 grams of potato starch. After introduction into the composition, the mass is thoroughly mixed;
- The mass is applied in equal layers to the affected area, it can be washed off after 15 minutes;
- Depending on the degree of damage, you can take a course for 3 weeks with 2 procedures per week or a week course, applying masks to the affected areas daily.
The addition of Doxycycline to the composition allows you to eliminate various infections located in the upper layers of the epidermis and provide protection against their reappearance.
Milk mask with the addition of Doxycycline
There are various options for milk masks; the recipe discussed below is suitable for treating acne on oily skin.
The use of the product is recommended if acne occurs due to increased activity of the sebaceous glands, since the mask helps normalize their work.
The effectiveness is enhanced by the addition of Doxycycline, which will provide reliable protection against the addition of infectious microflora.
You can prepare and apply the mask using the following recipe:
- It is necessary to mix 2 ground Doxycycline capsules with 20 grams of flour;
- About 50 ml of milk is added to the dry mixture to make a thick paste; to prepare a mask, it is recommended to choose a product with a reduced fat content;
- At your discretion, you can add a small amount of any essential oil or spices to enhance the effect;
- The thoroughly mixed mass is evenly applied to areas of skin with acne.
- After 8 minutes, rinse off the mask with warm, clean water;
- The procedure can be performed 1-2 times a week, the course duration is 1-1.5 months, depending on the presence of positive changes.
Effect of the drug on boils
Antibiotics for the development of boils are aimed at combating the pathogen:
- relieve redness;
- eliminate Staphylococcus aureus;
- restore soft tissues and skin.
In order for the capsules to work correctly, you will need to choose the right drug. The clinic carries out the following analyzes of the patient’s biological material:
Skin scraping helps to accurately identify the pathogen. Bacteriological culture analysis determines the reaction of pathogenic microorganisms to the antibiotic. Based on the test results, the doctor selects an effective form of the drug. The pharmacy sells antibacterial agents: tablets, injections, ointments. They help cope with the infection and remove pus.
Review of the best antibiotics
Therapy depends on the stage of development of the pathology. For mild cases, ointments, rinses, and lotions are used. At elevated temperatures and boils spreading throughout the body, the patient is given injections and antibiotics are prescribed.
The best antibiotics for eliminating furunculosis in tablets
| Name | pros | Minuses |
| "Amoxicillin" | A semisynthetic drug from the penicillin class, similar to ampicillin. The difference is in the hydroxyl group. When taken, it is better absorbed and penetrates into the tissues and lymph of the body. | Rapid heartbeat, headache, dysbacteriosis, nervousness. |
| "Azithromycin" | The medicinal suspension helps eliminate furunculosis in a child. Kills anaerobes, chlamydia, spirochetes and other pathogenic microorganisms. Bioavailability of the drug is 37%; rapid absorption into the blood; excreted through urine, bile; effective after 3 hours. | Decreased appetite, gastritis; itching, rashes on the body; nervousness, rapid heartbeat. |
| "Tsiprolet" | There is no irritation of the gastric mucosa after taking the drug, affordable. |
Valid for 12 hours. A large number of pathogenic microorganisms remain sensitive to the medication. Effective in combating infection of the body when other medications do not work.
Diarrhea, gastritis, rashes, headaches, irritability.
The drug eliminates: staphylococci, streptococci; Klebsiella, Escherichia coli; clostridia, peptococci. Used in case of chiria, meningitis, sepsis.
Drug treatment is prescribed by a doctor after tests. The physician takes into account the age, type of pathogen, patient’s condition and contraindications for use.
| There are many side effects and contraindications. Allergic reactions, anemia, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea occur. | ||
| "Sumamed" | The medicinal macrolide drug is effective in treating infections of the skin and soft tissues. Fights pathogenic microorganisms at the molecular level. | Do not take if you are sensitive to the drug. |
| "Amoxiclav" | The drug is of penicillin origin and contains amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. It prevents the destruction of amoxicillin and helps destroy bacteria. Approved for use during pregnancy and breastfeeding. | Malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract; diarrhea; gagging; rashes on the body; scabies; anemia; convulsive conditions. |
| "Ceftriaxone" | The medicine is inexpensive in its price category. | |
| Painful administration of the drug. Cannot be used in case of individual intolerance, renal or liver failure. | ||
| "Ciprofloxacin" | An antimicrobial agent is often used in the treatment of infections of the skin and soft tissues. Often used for immunocompromised patients. | Prohibited for use during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and children under 18 years of age. |
| "Nitroxoline" | The drug is quickly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and excreted in the urine. Eliminates fungal bacteria, gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Often used for cystitis, prostatitis, tolerated normally. | Nausea, allergic reactions. staining urine saffron yellow. |
| "Erythromycin" | An effective erythromycin drug from the group of macrolides, it is used for purulent processes on the skin, gonorrhea, and diphtheria. | Cannot be used in case of liver failure. Side effects: convulsions, hallucinations, diarrhea, tinnitus, nephritis, palpitations. |
| "Unidox Solutab" | Often used for skin infections and acne. Eliminates infections in the respiratory tract and urinary tract. Recommended for the fight against pneumococci and gonococci. Well absorbed and excreted through feces. | Should not be taken for liver pathology or for children under 8 years of age. Pregnant and nursing mothers are prohibited from taking it. |
| "Doxycycline" | Inexpensive drug, used for skin infections, pneumonia; eliminates staphylococcus; gonorrhea; syphilis. | Not for children under 12 years of age, pregnant or breastfeeding women. Possible side effects: tachycardia, nausea, diarrhea, dizziness. |
| "Cephalexin" | A group of cephalosporins helps eliminate strains of staphylococcus and bacteria. The effect occurs after 60 minutes. Pregnant and nursing mothers are allowed to take it. | Gastrointestinal tract malfunction, muscle weakness, trembling hands. |
| "Flemoxin Solutab" | The tablets dissolve easily and are used in the treatment of chiryaks. Amoxicillin trihydrate acts as a barrier against gram-positive gram-negative bacteria. There is excellent absorption of the product into the blood. Low percentage of negative reactions among medications. | Cannot be used if you are intolerant to the components. |
| "Tsifran" | A broad-spectrum antibiotic that fights bacteria, viruses, syphilis pathogens, and fungal spores. Often used for cystitis. Does not cause side effects on the gastrointestinal tract, is affordable. | Children under 12 years of age and during pregnancy and lactation should not be treated with the drug. Sometimes a rash, allergic reactions, and headaches appear. |
| Location of the boil, patient’s age | Name, effectiveness |
| Pubic area | "Mupirocin", "Fuzidine sodium". Promote the rapid release of abscess contents in the intimate area. |
| Face | “Doxycycline” and “Sumamed” help get rid of lesions on the face so that the infection does not penetrate further into the blood and tissues. |
| Children | Vishnevsky and Heparin ointments are applied after the abscess breaks. Vancomycin and Erythromycin tablets are used for abscesses on the facial part of the skull. |
| Pregnant women |
The use of antibiotics for babies and pregnant women is controlled by a doctor.
Top 10 drugs from the pharmacy
The top ten includes antibiotics from different groups. For the treatment of furunculosis, preference is given to broad-spectrum drugs that act on several pathogenic microorganisms at once.
"Amoxicillin"
Antibiotic from the penicillin group for furunculosis in tablets for adults and children. Available in the form of granules, capsules and tablets of 250-500 mg. Quickly eliminates infection during furunculosis, stops the growth of purulent abscesses. The effect of the drug is 12 hours, does not have a harmful effect on the mucous membranes of the digestive system. For furunculosis, the drug is administered intravenously by drip or stream.
Dosage regimen:
- 2-5 years – 125 mg 3 times a day;
- 5-10 years – 250 mg three times a day;
- over 10 years old - 250-500 mg at a time, 3 times a day (the dosage can be increased to 1000 mg).
The duration of treatment is 7-14 days. Side effects include dysbiosis, tachycardia, diarrhea, nausea and headaches. Contraindications: pregnancy, breastfeeding, renal failure. If prescribed to children under 18 years of age, the drug should not be taken together with metronidazole. The cost of Amoxicillin is 50-140 rubles.
"Erythromycin"
Included in the group of macrolides. Available in the form of tablets, ointments, bottles of powder (for injection). Suitable for any age category. Advantages – minimal risk of side effects.
In newborns it can cause pylorospasm, dyspeptic disorders, and sometimes provokes allergic reactions. For furunculosis, it is prescribed to fight infection in soft tissues and skin.
Dosage regimen:
- Adults are prescribed 200-400 mg, up to 4 times a day, with an interval of 6 hours. If necessary, the dosage can be increased to 4 mg. The drug is taken one hour before meals or 2 hours after it.
- Children are prescribed 30-40 mg/kg per day. The dosage is divided into 2-4 doses.
The duration of treatment is 7-10 days. Side effects - diarrhea, rash, headaches. The drug is contraindicated during lactation, pregnant women, people with liver and kidney failure. The cost of “Erythromycin” is 50-120 rubles. depending on the release form and dosage.
"Azithromycin"
Included in the group of macrolides. Another name for the drug is “Sumamed”. Available in the form of tablets, capsules, syrup and powder for suspension. It is not administered intramuscularly or into veins. A broad-spectrum drug. Suppresses protein synthesis, slows down the proliferation of bacteria, and acts intracellularly on infectious agents.
Dosage regimen:
- Antibiotics for furunculosis in tablets for adults are prescribed one tablet (500 mg) per day (can be before or after meals).
- Elderly people and children over 12 years of age (weighing more than 45 kg) for the first 3 days – two capsules of 250 mg once a day. Then - twice a week, 250 mg.
Duration of treatment – 9 days. Side effects include allergic manifestations, gastrointestinal disorders, arrhythmia, tachycardia. You may experience dizziness and tinnitus. Not recommended for kidney and liver diseases, during lactation, up to 12 years. Take with caution when taking ari - 50-300 rubles. depending on the release form and dosage.
"Levomekol"
Available in the form of an ointment for external use. The drug is made on the basis of the antibiotics methyluracil and chloramphenicol. Quickly destroys a wide range of pathogenic bacteria, stimulates the immune system, and starts the process of tissue regeneration.
The ointment is used to treat opened or burst boils. This helps prevent the spread of infection and promotes rapid healing.
Scheme of drug use:
- before using the product, the boil or wound is treated with an antiseptic;
- the ointment is applied once a day, changed daily;
- the drug can be injected into the purulent cavity through a drainage tube or syringe (pre-heat the product slightly).
Possible side effects are rash, swelling, burning and itching. Not recommended during lactation and pregnancy. Contraindications – psoriasis, fungal pathologies, eczema, individual intolerance to the active components of antibiotics. The cost of "Levomekol" is 130-180 rubles.
"Bactroban"
Available in the form of an ointment. Another name for the drug is Mupirocin. A broad-spectrum drug. It helps well with skin infections and lesions of Staphylococcus aureus. The active component is a new generation antibiotic (mupirocin calcium). Destroys most pathogenic agents, therefore it is often prescribed for furunculosis.
The ointment is applied to boils up to three times a day - under a bandage. The duration of treatment is no more than 10 days. If after 5 days there is no improvement, change the drug to another antibiotic or supplement the drug for oral administration.
Possible side effects are allergic reactions in the form of swelling or rash. Sometimes there is burning, itching, dry skin. Contraindications – renal failure, individual intolerance. The cost of “Baktroban” is 1700-3100 rubles.
"Baneotsin"
Available in the form of ointment and powder. This is a combination drug consisting of two antibiotics – neomycin and bacitrocin. Blocks protein synthesis and the cell membrane of bacteria.
The drug is prescribed for purulent-inflammatory processes (in particular for furunculosis). Quickly destroys strains of Staphylococcus aureus. However, it may cause an allergic reaction. Prescribed starting from one month of age.
Drug treatment regimen:
- Apply a thin layer to boils 2-4 times a day, under a bandage.
- Local application. For children under 18 years of age, no more than 200 g of powder per day.
Duration of treatment is a week. Side effects are rare - allergic manifestations. Contraindications: individual intolerance to the active components of the drug, extensive skin lesions, and simultaneous use of aminoglycoside antibiotics. With caution - in case of renal and heart failure, neuromuscular pathologies. The cost of “Baneotsin” is 170-490 rubles.
"Lincomycin"
Available in 250 mg capsules, solutions, ointments. The active ingredient is lincomycin hydrochloride. Children can be prescribed from the age of one month. It has a powerful bacteriostatic effect due to its broad spectrum of action. Prescribed for purulent skin lesions, furunculosis. The onset of action is 2-3 hours after administration.
Dosage regimen:
- Solutions. Adults are administered intravenously 600 mg with 250 ml of saline 2-3 times a day. In advanced cases, intramuscular injections are given twice a day (600 mg each). Children under 14 years of age are administered 10-20 mg/kg at intervals of 8-12 hours.
- Antibiotics for furunculosis in tablets for adults are prescribed 500 mg 3-4 times a day. The maximum dosage is 1-1.5 g. Children from 3 to 14 years old are given the drug daily at 30-60 mg/kg.
- The ointment is applied in a thin layer 1-2 times a day. If there are relative contraindications, the amount of the drug is reduced.
Lincomycin in ampoules
The drug is taken before meals and washed down with plenty of water. Side effects include allergic reactions, nausea, vomiting. Headaches may appear in the hypochondrium area and pressure surges. The drug should not be taken by nursing or pregnant women, young children, or people with kidney and liver pathologies. The cost of "Lincomycin" is 70-120 rubles.
"Cephalexin"
Antibiotics for furunculosis in tablets for adults are available in the form of tablets and capsules of 250 mg. The powder is intended for children. The active active substance is cephalosporin. It has a powerful effect on the causative agents of furunculosis, in particular Staphylococcus aureus. The onset of action of the drug is one hour after administration.
Dosage regimen:
- Adults are prescribed 1-4 g per day, with an interval of 6 hours. Take 30-60 minutes before meals, wash down with water. If necessary, the dosage is increased to 6 g per day.
- For children it is given in the form of a suspension. Daily dose (child weight less than 40 kg) – 25-50-100 mg/kg, 2 to 4 times a day. When calculating the frequency of administration, the degree and severity of the disease is taken into account.
The duration of treatment is 7-14 days. Side effects include disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, hand tremors, dizziness and general weakness. Pregnant and lactating women can take the drug only after consulting a doctor. Contraindications – individual intolerance. Prescribed with caution during pregnancy and lactation for children under six months. The cost of Cephalexin is 80-100 rubles.
"Amoxiclav"
This is a combination product based on penicillin and clavulanic acid. This helps to quickly destroy the causative agents of furunculosis. Available in tablet and powder form. The drug is active against aerobic gram-positive bacteria. Can be prescribed for furunculosis.
Amoxiclav - an antibiotic for furunculosis
Dosage regimen:
- For adults, one tablet is prescribed, dissolved in 100 ml of water. Or drink plenty of liquid. The interval between medication doses is 8 hours. The tablets are taken before meals.
- For children under 12 years of age, the dosage is calculated individually, taking into account current diseases, body weight, and individual characteristics of the body.
The duration of treatment is 5-14 days. Side effects - disruption of the gastrointestinal tract, allergic manifestations, convulsions, anemia. Dizziness and insomnia may occur.
Contraindications include liver pathologies and individual intolerance to the components. Use with caution during breastfeeding and pregnancy - only after consulting a doctor. Not recommended for children under 12 years of age. The cost of “Amoxiclav” is 70-470 rubles.
"Fuzidin"
Available in tablet form. The active ingredient is fusidic acid. The antibiotic is low-toxic, quickly copes with staphylococci that cause furunculosis and agents that are resistant to other drugs. Available in tablet form.
Dosage regimen:
- Adults are prescribed 0.5-1 g three times a day, after meals. Take the tablets with water or milk. The interval between doses of the drug is 8 hours. For the treatment of severe furunculosis, 2-3 g per day is prescribed, then the dosage is reduced to 1-1.5 g.
- Children from 3 to 4 years old are given 40-60 mg/kg, in three doses. After 4 years, 20-40 mg/kg is prescribed 3 times a day.
The course of treatment is 7-10 days. Possible side effects are nausea, vomiting, rash, abdominal pain. Contraindications – individual intolerance to the components of the drug, children under 3 years of age. Prescribe with caution to patients with chronic renal failure. The cost of “Fuzidin-sodium” is 330 rubles.
Treatment with antibiotics for furunculosis in tablets for adults and children should be carried out under the supervision of doctors. Drugs are selected depending on the causative agent of the disease. It is possible to determine the causative agent of furunculosis only after examining samples of the contents of abscesses in the laboratory.
Treatment regimen for furunculosis with antibiotics
The doctor prescribes a regimen to eliminate the disease:
- Ultraviolet irradiation is used in the presence of purulent infiltrate.
- Painkillers: Novocaine + antibiotic. Medicines are selected based on the sensitivity of the infectious agent to the antibiotic.
- When pus is present, a lotion with silver nitrate (1%) is used.
- The abscess is opened surgically using a scalpel. The rod inside the lesion is removed.
- The cavity is rinsed with 3% hydrogen peroxide and a sodium chloride bandage is applied to clear the wound of pus.
It is forbidden to squeeze the rod out with your hands. With such manipulation, it is possible for foci of infection to multiply throughout the body. The surgeon removes the abscess. The doctor prescribes bandages with gels and antibiotic therapy.
After the autopsy, the doctor prescribes treatment with antibacterial ointments, according to the instructions:
- Levomekol ointment is used topically. Chloramphenicol kills pathogens. Methyluracil restores tissue. You will need to soak the bandage and close the outbreak. Change the fabric every day or go to the nurse to change the dressing. Sometimes allergies occur.
- Bactroban ointment eliminates staphylococcus. You will need to apply the contents 1 to 3 times in 24 hours. The duration of treatment is 7-10 days. Rarely does a rash appear.
Strong antibiotics Cephalexin or Lincomycin are often prescribed to treat adults:
- Take Lincomycin tablets 3 times 24 times, 500 mg each, before meals. The course of treatment is up to 14 days.
- The drug “Cefalexin” should be taken from 1 to 4 grams per day, depending on the course of the disease, and consumed after an equal amount of time. Course – 7-14 days.
It is forbidden to use antibiotics for more than 10 days.
For the best effect, intramuscular antibiotic therapy is used at a prescribed injection dose.
To restore the body, the doctor prescribes drugs to boost immunity and vitamin complexes. It is important for children and adults to adhere to the diet during the course of treatment:
- Use natural products.
- Eat fresh vitamins.
- Use kefir, yoghurts without dyes and low calorie content.
- Supplement your diet with oatmeal, buckwheat, and rice.
- Avoid baked goods and sweet foods.
For the treatment of furunculosis in a child, the following suspensions are suitable: “Zinnat”, “Klacid”, “Azithromycin”.
Take 100 mg for children from 6 months to 12 months. Older children are prescribed a dosage of 10 mg per 1 kg of child weight.
The duration of the appointment is determined by the doctor. Standard scheme: 3-5 days.
Alternative treatment of acute furunculous otitis
Acute furunculous otitis media should be treated with unconventional methods with extreme caution. An incorrectly selected remedy can lead to the development of multiple furunculosis and other complications.
Treatment methods:
- A purulent abscess will open faster if you apply a cut Kalanchoe leaf to it.
- Aloe turundas, which need to be inserted into the ear canal of the affected ear for 1 hour, help well.
- If the boil in the ear has already opened, then you need to use a saline solution of sea and table salt at the rate of 1 tbsp. spoon per glass of water. You can add 2-3 drops of iodine.
- Place 3 drops of freshly squeezed onion juice into the affected ear.
- Take a spoonful of grated laundry soap and 2 tablespoons of water, melt in a water bath. Use for compresses.
- Dissolve 1 teaspoon of salt and 1 teaspoon of grated laundry soap in a glass of water. Moisten compresses and cotton pads in the resulting solution.
- Apply a compress with castor oil. It will be more effective if in 100 ml. oil, infuse 2 cloves of garlic.
To strengthen the body's defenses, it is useful to brew medicinal plants - wormwood, St. John's wort, yarrow, oak bark and oregano. Take half a glass orally after meals.
In what cases is antibacterial therapy contraindicated?
Antibiotic therapy is contraindicated if:
- renal, liver failure;
- allergic reactions to the drug;
- fungal diseases of the skin.
Use with caution during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and childhood. Antibiotics for illness will bring the desired result when the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, does not exceed the dosage, and adheres to proper nutrition.
Source coriummed.ru
Antibiotics in purulent surgery have long become a necessary and main means of treatment. The ways of introducing them into the body are varied. There are products for topical use in the form of ointments, gels, solutions, there are capsules and tablets, you can administer them intramuscularly, intravenously and even in suppositories. Antibiotics for boils and boils (which are the same thing) can be in any of these groups - it all depends on the stage and severity of the process, the age of the patient, and concomitant pathology.
Every patient with furunculosis wants to use an antibiotic that “definitely helps.” Obviously, a doctor will help you choose which antibiotics to take for boils. Patients, with their careless attitude towards these powerful pharmacological agents, unauthorized use due to their availability in pharmacies, and non-compliance with treatment courses over a long period of time, have led to resistance of microbes to treatment on the one hand and sensitization of the human body on the other.
Despite this, the doctor has a way to select an effective antibiotic for boils on the body and face. To do this, it is necessary to culture the purulent discharge and determine the sensitivity of the pathogen to a whole range of antibiotics.
Causes of a boil in the ear
The reason for the formation of a boil (popularly known as a boil in the ear) is infection by bacteria of the hair follicle of the outer ear and the sebaceous glands located next to it. Most often, inflammation is caused by staphylococci. Other causes of boils are as follows:
- Constant microtrauma to the skin of the external auditory canal (especially when cleaning with chopsticks).
- Prolonged contact with water.
- Constantly wearing headphones (vacuum), hearing aids (not the right size).
- The presence of dermatoses with itchy skin, which lead to scratching of the ear.
- Immunodeficiency conditions, hypovitaminosis, concomitant endocrinological and oncological diseases.
- Frequent stressful situations.
- Concomitant pathologies of the ear - otitis, labyrinthitis, tubo-otitis of various etiologies.
Also, the cause of a boil can be irregular adherence to personal hygiene rules or complete disregard for them.
Causes of furunculosis
There are many reasons for developing a common form of boils in one or another area of the human body. The variety of external and internal risk factors creates favorable conditions for the main causative agent of furunculosis, Staphylococcus aureus, to transform into a pathogenic form. 97-98% of all cases of furunculosis owe their occurrence to it. That is why bacterial culture is not done for everyone, but is performed when there is no result from the therapy.
2-3% of the causes are due to other pathogens. Among them:
- beta-hemolytic streptococcus;
- pseudomonas;
- Staphylococcus epidermidis;
- mycobacterium;
- fungi.
Antibiotics according to the mechanism of action on the pathogen are divided into:
The fundamental difference between them is that bactericidal antibiotics cause the death of microbial cells, while bacteriostatic ones suppress their reproduction in the patient’s body.
Bactericidal include:
- beta-lactams (penicillin, amoxicillin);
- fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin);
- aminoglycosides (kanamycin).
- tetracycline group;
- chloramphenicol.
When choosing an antibiotic for furunculosis that effectively affects the pathogen, preference is given to broad-spectrum antibiotics. This means that the drug is active against several types of microorganisms (ciprofloxacin).
The main subgroups of antibiotics for boils and boils are discussed below.
Subgroup of macrolides
Medicines in this group are divided into natural (erythromycin) and semi-synthetic (azithromycin).
General characteristics of the subgroup:
- bacteriostatics;
- active against staphylococci and streptococci, as well as chlamydia;
- concentrated in tissues higher than in plasma;
- low toxic;
- there is no cross-allergy with penicillins.
The first representative of macrolides is Erythromycin. Minimal adverse reactions make it one of the safest antibiotics. Dyspeptic disorders and pylorospasm in newborns, allergic reactions may occur.
- pills;
- ointment;
- bottles with powder for dilution and intravenous infusion.
Indications for use include infections of the skin and soft tissues, which confirms the validity of the use of Erythromycin for furunculosis.
Azithromycin is better known under the trade name Sumamed. Azitrox is also Azithromycin.
It has a number of advantages over Erythromycin:
- maximum accumulation in tissues of all macrolides;
- the half-life is longer, which means you can reduce the number of doses to 1 time per day and the course to 5-7 days;
- higher tolerance.
The combination of Azithromycin with lactulose is called Azithromycin eco or Ecomed.
There are capsules. tablets, syrup and powder for preparing a suspension. It is not injected into a vein or into a muscle.
Macropen is a semi-synthetic macrolide with improved pharmacokinetics. It is particularly important because it is active against staphylococci resistant to other macrolides.
Available as tablets and powder for suspension.
Tablets for boils
As mentioned above, antibiotics are an effective cure for boils. These drugs make up a huge group of drugs, which are divided into small groups depending on their effect on the bacterium and the effect on a specific type of pathogen.
Since staphylococcus is a common causative agent of boils, therapy is carried out against the background of groups of antibiotics that act specifically on this pathogen. Therefore, you need to know exactly which pills to take.
Photo 45 - A boil appears due to staphylococcus
You can give several examples of names and antibiotic treatment regimens for boils. Depending on which tablets you take and how you should treat furunculosis using a conservative method using antibiotics:
- cephalexin tablets 4 times a day;
- amoxicillin: tablet 3 times a day (10 days);
- Macrolides are prescribed if you are allergic to penicillins:
- erythromycin - ethyl succinate: 3 times a day orally (10 days);
- Clarithromycin: orally 2 times a day (10 days);
- azithromycin: 1 time per day (5-7 days);
- clindamycin: orally 4 times a day (10 days).
Many people who are faced with this question are interested in whether it is possible to take diclofenac tablets as an anti-inflammatory drug. Yes, they are used, including for purulent skin diseases.
Photo 46 - Diclofenac
Injections for boils are used quite rarely, since the result of treatment is expected to be better. Doctors use vancomycin intravenously, but due to the large number of side effects, it is used only in rare cases.
Photo 47 - Injections are rarely used
They also use ointments that have antiseptic, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory effects:
- Antiseptic ointments. At the initial stages of boil development, antiseptic ointments are used, as they have the effect of “pulling out” pus. These include ichthyol and heparin ointments. Ichthyol ointment is quite cheap and works great on affected skin. Heparin ointment, in addition to its antiseptic effect, has an anti-inflammatory and analgesic effect due to its specific composition.
- Antibacterial ointments. These include levomekol, tetracycline ointment. They also have an anti-inflammatory effect, help remove pus from the lesion and cleanse the skin lesions from bacteria.
- Anti-inflammatory ointments. Vishnevsky ointment and zinc ointment have a purely anti-inflammatory effect. These ointments relieve swelling and hyperemia, and also double wound healing.
Brewer's yeast for boils
In addition to the official treatment of such ulcers, there are also folk methods. The most common of them is the use of brewer's yeast. There is a lot of controversy about them: “Does brewer’s yeast help with boils?”
Photo 53 - Brewer's yeast
To understand this, you first need to understand what common causes lead to the formation of boils. There are two of them: metabolic disorders (diabetes mellitus) and decreased immunity.
Photo 54 - Brewer's yeast cleanses the skinBrewer's yeast perfectly improves metabolism and cleanses the skin. They consist of protein complexes that are necessary for our body. Yeast contains vitamins: B, E, PP, H, nucleic acids, which compensate for the lack of various microelements in the body.
Photo 55 - Brewer's yeast consists of protein complexes
Most often, brewer's yeast is used together with the main therapy (antibiotics). How to drink them? Brewer's yeast is used twice a day, half an hour before meals. With water or milk. Adults can drink one tablespoon, children a teaspoon. Brewer's yeast is safe for children and has no side effects.
Photo 56 - Brewer's yeast is taken with antibiotics
Due to the fact that yeast contains a huge amount of nucleic acids, it is not advisable for people with old age or kidney disease to consume it.
Photo 57 - Do not consume brewer's yeast if you have kidney disease
In conclusion, let us recall that a boil is an infectious disease that most often occurs due to poor hygiene, with a certain skin structure (usually with oily skin type).
Photo 58 - A boil may be due to increased oily skin
Subgroup of penicillins
Penicillin is the progenitor of the entire group of antibiotics. Since its discovery by A. Fleming in the forties of the last century, hundreds of new, more active and safe drugs have entered the market.
According to the modern classification, penicillins belong to beta-lactamase antibiotics. Impairment of bacterial cell wall synthesis is a common mechanism of action for this subgroup.
The subgroup includes natural (penicillin) and semi-synthetic, which in turn are divided into:
- antistaphylococcal (Oxacillin);
- extended spectrum (Ampicillin, Amoxicillin);
- inhibitor-protected (Amoxiclav);
- combined (Ampiox)
Long-acting penicillins - Bicillins.
There are antipseudomonas penicillins, but they are not applicable for furunculosis.
General properties of the subgroup:
- bactericidal activity;
- cross-allergy within a subgroup;
- wide range of dosages;
- low toxicity.
Staphylococci have developed resistance to this subgroup due to the production of beta-lactamase enzymes that can destroy antibiotics.
Penicillin is a natural parent, but the drugs are called Benzylpenicillin (potassium and sodium salt). These antibiotics are not used in the treatment of furunculosis.
Augmentin, Ecoclave and Medoclav are varieties by trade name. Each of them is based on the semi-synthetic Amoxicillin and clavulanic acid. Adding it to Amoxicillin made it possible to bind and inhibit beta-lactamases produced by staphylococcus, and therefore prevent microbes from developing resistance to the drug. Antibiotics - amoxiclaves are very effective for boils.
Ecoclave and Medoclav are available in the form of tablets of various dosages. These antibiotic tablets are the drugs of choice for furunculosis.
Augmentin is sold in the form of long-acting tablets and powder for the preparation of a suspension or solution for parenteral administration.
Oxamp is a combination antibiotic and consists of Ampicillin and Oxacillin. It is active against staphylococci and is used in the treatment of infections of the skin and soft tissues. Tablets are available in a prolonged form; a suspension or parenteral administration can be prescribed.
Subgroup of cephalosporins
Cephalosporins, by their origin and action, also belong to beta-lactamase inhibitors, like penicillins.
In this subgroup there are 4 generations of antibiotics. As the generation grows, the spectrum of antimicrobial activity of cephalosporins expands.
General characteristics of the subgroup:
- bactericidal nature of the effect on the microbial cell;
- wide range of activities;
- cross-allergy with beta-lactam antibiotics;
- low toxicity.
Cefazolin and Cephalexin are representatives of the first generation of cephalosporins. Compared to subsequent generations, they are inferior in the spectrum of activity to drugs of the fourth generation, but they also retain differences between them.
The parenteral antibiotic Cefazolin is more active compared to Cephalexin, available in tablets. The first generation of antibiotics of this subgroup is not a sufficiently effective treatment for complicated furunculosis, but in mild forms it is possible to treat the boil with antibiotic tablets or capsules for internal use.
Cefuroxime Cefuroxime axetil is a second generation oral cephalosporin. They have a more pronounced effect on gonococci, but in the treatment of infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue their use is justified.
Ceftriaxone and Cefotaxime are the third generation. They are not intended for oral administration but are administered parenterally. They can be prescribed for severe forms of chronic furunculosis and septic complications.
Cefepime is a fourth generation cephalosporin. It is administered parenterally for severe mixed infections with complex forms of resistance.
To summarize the rationale for the use of a subgroup of cephalosporins for furunculosis, it can be noted that for adults it is advisable to recommend Cephalexin tablets in a dose of 2 to 4 grams per day.
Subgroup of fluoroquinolones
Ciprofloxacin, a representative of the second generation quinolones, is indicated for the treatment of skin and soft tissue infections of varying severity. It is considered to be the “gold standard” among this subgroup.
It has a bactericidal effect on a variety of microorganisms, including gram-positive coccal flora, which includes staphylococcus.
Among the large number of side effects, it is necessary to note the negative impact on the development of cartilage tissue of a growing organism, therefore, use for pregnant and lactating women is contraindicated. It is prescribed to children only in special cases.
Increased physical activity while taking Ciprofloxacin can cause rupture of tendons and ligaments.
Another important point to remember when treating furunculosis with this antibiotic. Taking Ciprofloxacin together with a group of NSAIDs increases neurotoxicity, and the development of seizures is possible.
Release form: tablets, ampoules for parenteral administration and eye drops.
Local antibiotics for furunculosis
In the treatment of any boils, one cannot do without prescribing antibacterial ointments. The goal is to combat the infectious agent in the wound, relieve inflammatory reactions, cleanse the wound and accelerate healing.
Levomekol is one of the frequently used ointments. It is based on 2 components:
- chloramphenicol (the familiar Levomycetin);
- etiluracil.
The antibiotic acts bactericidal, killing the infection in the wound. The addition of methyluracil enhances local immunity and enhances regeneration.
The structure of the ointment is such that it allows it to penetrate deep into tissues without destroying biological membranes.
The advantage of the ointment is that it is capable of destroying several types of microorganisms, and also that it has no contraindications, with the exception of individual intolerance.
For boils, apply it to the affected area or apply a napkin soaked in Levomekol. Cover the top with adhesive tape. The dressing is changed 1-2 times a day.
Synthomycin liniment is an ointment based on the antibiotic chloramphenicol. The difference between ointment and liniment (there is also synthomycin ointment) is in a different base. The ointment is created on a fat basis, while liniment is created on a water basis.
The method of using the ointment for furunculosis is the same as for Levomekol.
Levomethyl is the same Levomekol from a different manufacturer.
Netran - oddly enough, it is the same Levomekol, with the same chloramphenicol and methyluracil.
Levomekol, with all its advantages, is a pulling ointment with an antibiotic for boils.
How to treat boils with external medications
Antibiotics are selected for the treatment of boils depending on the location and severity of the purulent-necrotic process. For small single lesions on the body, the doctor may choose topical antimicrobial drugs and recommend concomitant restorative therapy.
External antibiotics for treating the affected skin area include ointments, gels, creams, suspensions, and mash.
These drugs differ not always in the active substance, but also in consistency and percentage of fat content. Some dosage forms penetrate quickly into the layers of the skin and dry out. Others, on the contrary, moisturize the surface of the body for a long time, saturating the epidermis with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial components.
- For small boils on the face, antibiotics are recommended, which are gentle on delicate skin. You can use Levomekol gel, which is based on the antibiotic chloramphenicol. The composition contains methyluracil, which helps accelerate skin regeneration. The gel base allows for quick absorption and does not leave any spots or shine on the face.
- Zenerit cream has a light consistency and is used for minor ulcers and pimples on the face. Zinerit contains the antibiotic erythromycin, which affects many bacteria, including staphylococcus.
- For deep purulent lesions on the body, ointment-based antibiotics are used. For example, Tetracycline ointment. It contains a broad-spectrum antibiotic – tetracycline. The ointment consistency allows you to preserve the active substance on the surface and in the layers of the skin for a long time. For convenience, applications are used, that is, you need to squeeze the ointment onto a napkin, distribute it on the boil and fix it for 2-4 hours.
- The best remedy for skin abscesses and boils is Ichthyol ointment. Its active ingredient is ichthyol, which is obtained by distilling natural minerals and resins. As a powerful antiseptic, Ichthyol ointment helps fight many viruses, bacteria on the skin and in the wound, ensuring a reduction in the inflammatory response and healing. There are known cases in practical medicine when, when using Ichthyol ointment, purulent wounds with an area of 2-4 cm healed.
- If furunculosis appears on the butt, antibiotics must be absorbed as quickly as possible, otherwise the skin will become wet, which will provoke increased inflammation. Antibacterial gel and non-greasy ointments work quickly on the thigh or buttock. In this localization, it is recommended to rub in Gentamicin ointment or Gentaxan; they contain the antimicrobial gentamicin. Such ointments and gels have a pronounced antimicrobial treatment, reduce the work of the sebaceous glands, and dry the skin around the abscess.
- To treat boils in the groin, antibiotics and antiseptics are used, such as Ichthyol ointment, Vishnevsky liniment, Levomekol, Tetracycline ointment. All of them have a pronounced antimicrobial effect and quickly destroy the cause of inflammation. In this localization, the healing process can be lengthy due to poor hygiene, so it is important to systematically maintain the cleanliness of the skin in the genital and groin area.
- When choosing which antibiotics to treat a boil under the arm, the doctor is guided by the characteristics of this location. There are many sweat and sebaceous glands in the armpit area, so the active ingredients must penetrate as deeply as possible into the tissue. To treat furunculosis in the armpits, ointment-based preparations containing antibiotics are used: streptomycin, chloramphenicol, syntomycin. The prescription of Ichthyol ointment and Vishnevsky's balsamic liniment is justified.
It is safe to treat boils yourself with topical antibiotics only for minor skin lesions.
At the first signs of an increase in the inflammatory process, the presence of tissue necrosis, or the appearance of pustules in new locations, the help of a medical specialist is required. The doctor will determine the correct methods of therapy, because local treatment for diffuse skin lesions is sometimes not enough. Elimination of a deep boil is based not only on the effect at the source of inflammation. Antibiotics are also prescribed that affect the entire body.
Antibiotics for furunculosis in children
Dicloxacillin is a semi-synthetic from the penicillin subgroup and belongs to a narrow-spectrum antibiotic. It is aimed at Staphylococcus aureus and therefore the drug is suitable for the treatment of boils and other skin infections. There is cross-intolerance with penicillins and cyclosporines.
For children, the most acceptable form of release is in the form of a suspension. This makes it possible to calculate the dose for a child depending on body weight.
Vancomycin is an antibiotic active against staphylococcus, but is intended to treat infections in the gastrointestinal tract. It is poorly absorbed into the blood and has no systemic effect, so its use for furunculosis is unjustified.
Erythromycin is effective in the treatment of furunculosis, dosed depending on weight, age and severity of the disease. Older children can be given tablets; if swallowing is difficult, a suspension can be used.
Antibiotics for boils on the face
A feature of boils on the face is the need to use antibiotics not only locally in the form of ointments, but also systemically. This is due to the close proximity of the brain and large vessels.
Ciprolet is the same as Ciprofloxacin, a subgroup of fluoroquinolone. One of its advantages is the slow development of microbial resistance to its administration. It is quickly and well absorbed and penetrates into tissues. Easily tolerated. Not for pregnant women, lactating women, children and adolescents.
In adults, the dose is 1 gram per day in 2 divided doses. We must remember that taking Tsiprolet disrupts concentration, so you must be careful when driving a car.
Sumamed is easy to use. The package contains 3 tablets, which must be taken over 3 days, one per day.
Doxycycline is a semisynthetic antibiotic from the tetracycline subgroup. Broad spectrum of action, blocks protein synthesis in microbial cells. Contraindicated in children under 8 years of age, pregnant women from the 2nd trimester, breastfeeding women and those with severe liver diseases. Oral and parenteral administration.
Doxycycline based chatter
In the treatment of acne, a mash based on Doxycycline and Dimexide is highly effective.
Thanks to the combined action of these drugs, the following results can be achieved:
- Elimination of pathogenic microbial and bacterial microflora;
- Reducing inflammation;
- Elimination of pain;
- Acceleration of healing of damaged tissues;
- Less pronounced fibrinolytic effect.
Instructions for preparing and using mash are described in detail below:
- 20 Doxycycline tablets are crushed to a powder;
- The powder is dissolved in a liquid mixture - 150 ml of distilled water or injection solution and 50 ml of Dimexide in the form of a solution;
- Mix the resulting product thoroughly ; it is recommended to keep it in a transparent container;
- Before the first use, the mixture should sit for 24 hours ; the container should be shaken periodically;
- The mash is used to treat areas of skin with acne 2 times a day , in the morning and evening hours;
- After each use of the product, the skin must be treated with a cream with a moisturizing effect;
- The duration of the full course is 3 weeks , after which you must take a break.
Prevention of furunculosis
If we are talking about the prevention of furunculosis with the help of antibiotics, then we can give the following advice. If irritation, burning, slight itching and redness occur at the site of abrasion, abrasion or wound, treat the area of skin with an antiseptic, apply antibacterial ointment, and apply a bandage. This will prevent the infection from spreading.
Source www.dermatit.net
Furunculosis is an inflammatory process localized in the hair follicles and surrounding tissues. The causative agent of the disease is considered to be various microorganisms, which, after entering the skin, can cause furunculosis.
In most cases, furunculosis affects the groin area, face and neck, as well as the back. Antibiotics for boils in the groin and antibiotics for furunculosis on the face should be prescribed by a doctor ; it is not recommended to select medications on your own.
Possible analogues
In some cases, when the use of Doxycycline is impossible, one of the following drug analogues may be prescribed:
- Unidox Solutab - produced in Holland, available in the form of tablets based on doxycycline. The cost is 300-350 rubles ;
- Vibramycin
- has a similar composition; the concentration of the substance in tablets can be 100 and 200 mg.
The average cost of the drug is 530 rubles .
Unidox Solutab Vibramycin
All analogs of the drug, like Doxycycline, can be purchased in pharmacies only if prescribed by your doctor. Self-prescription of the drug is not allowed.
Furunculosis
The disease occurs when staphylococcus enters tissue . The process of activation of the bacterium lasts several days, after which the patient’s skin becomes covered with boils. People call purulent abscesses “boils.” It looks like a large pimple with greenish-yellow contents. A single boil that appears on the skin may be a consequence of hypothermia.
Treatment of boils with antibiotics is usually prescribed when numerous rashes appear in the neck, back, face and head. The greatest discomfort for the patient is caused by boils in the groin area.
In people whose immunity is weakened, furunculosis can develop into a chronic form, which is extremely difficult to treat. Taking antibiotics helps to weaken the course of the disease, helps localize the source of spread and prevents re-infection. Which medicine or ointment should I choose to treat boils?
Indications and contraindications
Antibiotics for furunculosis (treatment with systemic antibacterial drugs) are an integral part of complex therapy. Antibiotic drugs are especially effective in cases where boils affect the head and neck area.
Systemic therapy is prescribed by a doctor for:
- the presence of a large number of boils;
- purulent inflammations complicated by inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- location of ulcers on the neck, head and face;
- chronic course of the disease.
Treatment must be comprehensive. In addition to antibiotics, the patient needs to take immune-strengthening drugs and vitamins.
Antibiotics for medicinal purposes have a number of contraindications . These include:
- individual intolerance to individual components of the drug;
- pregnancy and breastfeeding;
- kidney and liver pathologies;
- bronchial asthma;
- intestinal diseases;
- fungal skin diseases;
- open form of tuberculosis;
- heart and vascular diseases.
Interaction and incompatibility with other drugs
The simultaneous use of Doxycycline and the following drugs with which it interacts undesirably is prohibited:
- Antibiotics belonging to the tetracycline group;
- Medicines with an alkaline environment or an environment with reduced stability;
- Any medications that contain magnesium, iron or calcium.
Other drug interactions are described below:
- When taking retinol-based drugs, the risk of changes in intracranial pressure increases;
- When taking drugs based on methoxyflurane, the risk of renal dysfunction increases; there is a threat of death;
- When taking drugs based on rifampicin or containing ethanol, the effectiveness of Doxycycline is reduced;
- Reduced effectiveness of antibiotics based on penicillin or cephalosporin.
Simultaneous use with indirect anticoagulants requires additional coordination with the attending physician; due to the nature of the effect, individual dose adjustment is often necessary.
Choice of antibiotics
Several types of antibiotics are used to treat the disease . The source of spread when a single boil appears can be localized using a special antiseptic ointment. Tetracycline ointment includes a broad-spectrum antibiotic and is used as a wound healing and anti-inflammatory agent.
The local medicinal product is approved for use for boils on the face, groin, and neck. Available in the form of an ointment, packaged in special tin tubes.
If there are a large number of ulcers, especially if the disease has spread to all parts of the body, it is recommended to administer medications intramuscularly, for example, ceftriaxone. When administered intramuscularly, the drug affects the entire body as a whole.
The medicine is available in the form of a powder for injection. It is recommended to dilute with novocaine. It is administered intramuscularly.
Amoxiclav is prescribed for furunculosis. This is a combination medication that contains amoxicillin. The active substances in amoxiclav destroy pathogenic bacteria. Available in tablet form or as a suspension. The recommended dosage is 3-4 tablets per day (every 7-8 hours).
Main symptoms
It is difficult to achieve a positive result in treatment if you do not know the exact diagnosis. Since there are similar diseases, furunculosis can be confused with atheroma, phlegmon, lymphadenitis. You need to know the following signs of furunculosis:
- The number of boils does not constantly decrease, but increases.
- Ulcers appear on the face and head.
- Boils affect the neck.
- A possible complication is inflammation of the lymph nodes.
- Rashes appear regularly.