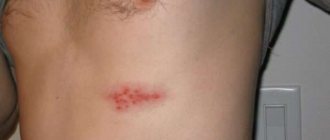
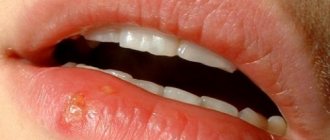
The herpes virus has more than a hundred varieties. But to date only eight of them have been studied. The first type of virus, the so-called herpes simplex, occurs in ninety percent of the population of our planet. For most, it can remain dormant for quite a long time and will not appear throughout life. But under certain conditions, it begins to actively develop and cause severe complications and serious illnesses. Fortunately, this number of people does not exceed the five percent barrier.
Let us consider the main reasons for the penetration of a simple type of virus and the consequences of its impact on the body. It appears as a blistering rash that forms on the lips, in the nose and on its outer surface, on the outer skin, mucous membranes and internal organs. Herpes blisters cause redness, burning, itching and pain. When the first warning signs of the disease appear, it is necessary to immediately begin treatment and block further development of the virus. This article will tell you in detail about why herpes appears in the nose, symptoms and treatment, as well as what the consequences of this disease may be.
How does infection occur?
When we talk about herpes in the nose, we mean that the infectious agent for this type of disease is the herpes simplex virus type 1. It is well known that this type in most cases is introduced into the human body during childhood. However, there are also exceptions.
For reference. If a person, having reached a working age, has not yet “had the opportunity” to acquire the herpes virus (which is rare), then it should be taken into account that infection is expected through close contact with the carrier. By close contact we mean hugs and kisses.
Let us recall that the concept of herpes simplex refers to herpesvirus type 1 and herpesvirus type 2. So, only HSV-1 relates to the topic of herpes in the nose. An analysis of articles on Internet sources showed that some of them indicate HSV-2 as the causative agent.
According to WHO ( https://www.who.int/ru/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/herpes-simplex-virus ), herpes virus type 2 (HSV-2) is transmitted only through sexual contact and causes genital herpes.
Of course, close contact with a carrier does not imply intentional infection. Perhaps the carrier does not even assume that the “cold in the nose” or rash on the lips that he has is an infectious disease. Or rather, the active phase of this disease. Since in “sleep” mode the transmission of an infectious agent is unlikely.
Of course, you should be careful and not use other people’s personal hygiene items (towel, lipstick). Because you may not be able to see that the carrier is in an active phase of virus reproduction and has left infectious material on these objects. Naturally not intentionally.
Herpes in the nose - causes
Let us recall that HSV-1, as a viral agent, cannot live outside the cell . The main “place of residence” for it are nerve cells (ganglia). In them and only in them the herpes virus takes root, introducing its genome into DNA.
In relation to the “herpes in the nose” option (herpes under the nose and herpes on the nose), we have the localization of the entrance gates for the virus - the eyes, mouth and nose. Accordingly, their mucous membranes are the most convenient tissues for penetration into nerve cells.
For reference. It is the eyes, mouth and nose, as parts of the body with functions of communication with the external environment, that have a large number of nerve endings entering their structures. That is, easy access to the injection site.
But in a normal (latent or dormant) state, introduced herpes simplex viruses may not appear throughout the life of the carrier.
When favorable conditions occur, HSV-1 can become active and begin to reproduce intensively.
These conditions include:
- skin damage (including microscopic) - open wounds on the surface of the skin;
- contact with the mucous membrane of the carrier;
- weakening of the immune system.
Nerve cells infected with the herpes virus descend to the nearest mucous tissues and begin to actively reproduce the virus. Accordingly, the places where cells with the multiplying virus settle become inflamed.
Inflammation manifests itself in the development of symptoms of herpes labialis (colds in the nose and lips).
Attention. Taking medications incorrectly, particularly antibiotics, weakens the immune system. As a result, the herpes virus is activated.
This situation often happens after an illness, especially after an infectious disease. We are often not warned that after taking antibiotics it is necessary to restore the microflora, which is part of the immune system. And antibiotics kill it.
Also, the impetus for the activation of the herpes virus can be:
- unhealthy diet
- overheating or hypothermia of the body,
- existence in environmentally unfavorable conditions,
- transfer of any respiratory pathology.
Stages of herpes in the nose
Activation of HSV-1 reproduction most often first becomes noticeable in or around the mouth. Then the inflammation is transferred to the nose area. Transfer is standard: dirty hands, personal hygiene items.
The process of disease development from inflammation to healing of the rash can last from one week to a month. The timing depends on the capabilities of the immune system. Naturally stimulated by drugs.
It is customary to consider four stages of disease development:
- precursor (prodromal period): during the first one or two days, an uncomfortable state is observed in the nasal area (tingling, itching, tingling, sometimes pain). The area affected by the herpes virus turns red;
- rash: by the end of the second or third day, the nose (under the nose or on the nose) is covered with herpes blisters. The rash is accompanied by pain. Pimples gradually grow and fill with fluid;
- erosion: this stage is the most uncomfortable. The rash develops into small ulcers. The process is accompanied by pain. Cosmetic defects are clearly visible;
- healing: the longest and most uncomfortable stage. The healing of wounds is accompanied by itching, but scratching is strictly forbidden. Scratching will lead to the spread of infection over a larger area with the resumption of the inflammatory process. The crusts dry out and you can’t pick them off either.
Attention. During the period of virus reproduction, the carrier becomes the most dangerous to others.
What to do if a sore under a child’s nose does not go away
When a sore under a child’s nose does not go away for a long period, it is necessary to adjust the treatment provided for its speedy healing.
When a cold occurs, parents often treat their children themselves, but the formations between the lip and nose may not go away due to the chosen treatment measures.
1. It is very important, if there is a sore under the nose, to explain to the child that you cannot touch it with your fingers and do not try to “pick it out.” This can be quite difficult, due to the fact that babies automatically pull their hands towards their faces.
2. Another, more serious reason why they can “pick” their nose, doctors consider the presence of psycho-emotional complications. But such a factor should only be treated by a specialist.
3. For long-lasting pain, after an appointment at the clinic, the doctor must prescribe a course of antibiotics, based on how old the child is. It is recommended to smear the resulting boils with brilliant green, supplementing the therapy with ointments that have a healing effect.
4. When a child has a weak immune system, the sores under the nose do not go away for a long time. During such a period, the area where they formed is constantly injured, which can lead to a chronic form. In this case, after getting rid of them, the sores form again.
Herpes in the nose - symptoms
Due to its location, herpes in the nose manifests itself differently than in other parts of the body. This is due to the characteristics of epithelial cells.
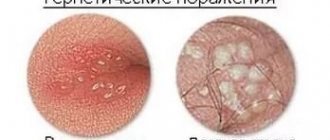
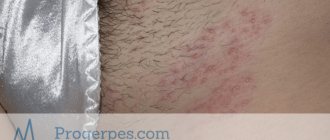
A cold in the nose externally looks like a rash with a smooth bottom of a red hue (sometimes light pink), soft to the touch. Rash blisters up to 1-4 mm in diameter. They appear over and over again in the same place. Sometimes there is one rash, sometimes there are many small ones, which then merge.
The effect of the herpes virus on the nasal mucosa can only be detected at the stage of visual appearance of the rash, since tingling and mild itching during the ripening process can be ignored.
But already the first bubbles that appear cause quite strong pain (the pain is felt stronger than with a rash on the lip). Externally, the vesicles are slightly different from a rash on the lips - the surface of the vesicle is covered with a denser layer of cells, and the vesicle itself resembles an abscess.
Physiological symptoms are added to the visual symptoms:
- body temperature rises;
- headache appears;
- general malaise;
- The skin in the nose area swells noticeably.
Attention. It is important to prevent the spread of the rash in a timely manner, otherwise the virus will expand the already captured areas. In addition to herpes on the nose, lesions on the lips and around the nose will become noticeable.
Clinical manifestations
Manifestations of the disease depend on the accumulation of HSV and the state of immunity. The following signs of herpes are distinguished:
- the appearance of characteristic bubbles with a clear liquid containing the virus under and inside the nose;
- low-grade fever (increase in temperature in the morning to 37.5 degrees, decrease in the evening);
- itching, redness, swelling of the skin around the rash;
- If left untreated, the blisters burst, forming erosions or ulcers.
Symptoms of the disease depend on the state of the immune system and the causes of herpes. The more a person suffers from colds, ARVI, flu, infections, the more often herpes is activated, causing the appearance of symptoms. With immunodeficiency, rashes form constantly and cannot be controlled.
Complications of herpes in the nose
Despite the apparent simplicity of the disease, herpes in the nose can cause significant trouble in the future.
Among the consequences we highlight the following:
- frequent appearance of rashes. These manifestations of herpesvirus activity are associated with weakened immunity. This weakening is especially dangerous for HIV-infected people. But for any person it will be an unpleasant surprise with each new manifestation of increasing areas of inflammation.
- secondary infection. Dispersal of newly formed viral agents by scratching the inflamed area. This is especially true for children.
- damage to nerve cells. Each subsequent activation of the herpes virus contributes to the capture of more and more nerve cells for implantation. It is logical to assume that the risks of neurological diseases increase.
- damage to the organs of vision. The high degree of innervation by the nerve cells of the organs of vision makes it possible for herpes viruses, when activated, to descend to them and cause harm.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is based on the clinical picture. An anamnesis is collected, with special attention paid to relapses.
An external examination of the patient is enough to conclude that there is an inflammatory process. Based on the appearance of the rash, it is possible to draw a preliminary conclusion that the lesion is caused by a herpes virus.
However, herpes in the nose requires differential diagnosis. Laboratory tests are used for this:
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) – capable of identifying the pathogen in the early stages;
- ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) - allows you to detect the presence of antibodies specific to a particular virus;
- Immunofluorescence analysis (IFA - fluorescent antibody method) - allows you to detect herpesvirus antigens in the blood;
- serodiagnosis – allows you to evaluate the body’s immune response to the introduction of a pathogen into the body;
- Cytology analysis is the most informative for determining viral changes. Repeated tests show the degree of increase and change in antibodies.
Diagnosis is best made when there are obvious external signs of the disease. Of course, it is possible to detect the virus with or without tests. But in this case, tests will need to be carried out almost every day. Which is not very logical.
Differential diagnostics
Herpes is differentiated from impetigo, bacterial infection and a number of other diseases. If necessary, the doctor may prescribe additional examinations.
In its simplest form, herpes in the nose is truly diagnosed unambiguously.
However, although not often, there are combination options. Let's say some bacterial disease (more precisely, its treatment with an antibiotic) partially activated the herpes virus, which turned out to be closer to the nose area. As a result, a herpetic rash appeared in the nose.
It is customary to distinguish colds in the nose and lips from other similar diseases:
- herpes zoster (shingles). This disease is accompanied by fever and fever. The rash does not necessarily appear on the mucous membrane of the nose or lips. But this is possible.
- boil of the nose. There is a difference in color from herpetic vesicles. On the 3-4th day, a white-yellow “cap” with pus forms on the boil. Sometimes the disease is accompanied by fever and enlarged lymph nodes.
- sycosis. The disease is characterized by inflammation of the hair follicle of the vestibule of the nose. Unlike herpes, the affected area is larger and there is necessarily hair in the pustule.
- thrush or candidiasis. It is difficult to isolate specific vesicles in this disease; it manifests itself in a whitish coating that occupies a significant area of the oral mucosa, and less commonly, the nose.
For reference. Differential diagnosis is especially important in controversial cases for the correct prescription of treatment.
Brief characteristics of antiviral agents
What medications should be used for herpes? As mentioned earlier, it is impossible to completely get rid of this infection. If external manifestations of the disease occur, doctors recommend using ointments, tablets and injection solutions that have an antiviral effect. They successfully suppress the activity of the disease and promote rapid healing of wounds. The most effective antiviral drugs for herpes are Acyclovir, Penciclovir, Famciclovir, Docosanol, Valaciclovir, Tromantadine, Panavir Gel, etc.
- The most common antiviral drug prescribed for all types of herpesvirus infection is Acyclovir (analogues of Zovirax, Herperax). The drug is available in the form of ointment, tablets and powder for injection. To obtain a positive therapeutic result, its use should be started at the first signs of the disease, without waiting until fluid-filled blisters appear on the skin. Acyclovir is an immunostimulant. It suppresses the activity of the virus in diseased cells without affecting healthy ones. Available to most patients due to its low price.
- Penciclovir is used to suppress the manifestations of recurrent herpes type I. It is a cream for external use. Penciclovir has a depressing effect on cells affected by herpes virus infection and helps to quickly suppress the exacerbation of the disease. Widely used to treat patients in Western countries.
- Farmciclovir is an analogue of Penciclovir, available in tablet form. Used to suppress the primary manifestation and recurrence of herpes simplex.
- Docosanol is a relatively new and quite effective medicine prescribed for herpes localized on the lips. Available in the form of a cream. An analogue of Docosanol is Erazaban.
- Valacyclovir is used in the fight against all known herpes viruses. Produced in tablet form. The use of Valacyclovir allows you to eliminate the external manifestations of the infection and suppress its biological activity in the body. Taking the drug significantly reduces the risk of transmission of the virus through contact of an infected person with healthy people. Popular analogues of Valacyclovir are Valtrex, Valmir.
- Tromantadine is a herpes remedy available as an ointment. Prescribed for all types of infection. When applying the ointment to problem areas during the first few hours after the appearance of the rash, it is possible to stop the virus and prevent its further spread.
- To treat herpes, you can use Panavir Gel, a herbal antiviral drug based on potato shoot extract. The medicine is available in the form of a white homogeneous mass and is intended for external use. Recommended for suppressing herpes viruses types I and II. Panavir Gel is not inferior in effectiveness to Acyclovir, but is considered a safer drug.
Only a doctor should select antiviral drugs for herpes for a patient.
Each of the remedies described above has its own characteristics of use and contraindications, so their use without the advice of a specialist may lead to a deterioration in a person’s condition and the occurrence of adverse reactions.
During treatment with antiviral drugs, experts often recommend that patients take vitamins C and E for one to two weeks. They will help strengthen the immune system, which plays an important role in the fight against herpes.
But you should not try to get rid of the manifestations of infection with the help of antibiotics, since they have no effect on viruses.
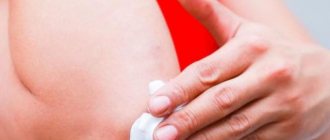
Herpes in the nose - how to treat it
a doctor locally to clarify the technique for treating herpes in the nose .
For reference. Ulcers on the mucous membranes heal faster than on the skin. For effective treatment of herpes in the nose, ointments, creams, and gels are best suited.
The ointments or gels used should not be rubbed in. They must be gently slammed with the pad of your finger. Do not injure the damaged tissue, as the wound will begin to bleed and cause pain.
If you do not start the disease, then healing of the mucous membrane with continuous therapy may end within a few days. This is important to prevent further spread of the herpes virus. And also to exclude the possible addition of a bacterial infection.
Drug treatment of herpetic rashes in the nose involves the prescription of systemic and local drugs. Depending on the severity of symptoms, treatment can be carried out comprehensively or medications can be prescribed separately.
At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, local therapy with Zovirax, Levomekol, and Acyclovir can be used. They affect the active form of HSV-1, causing the cessation of DNA synthesis.
Fenistil Pencivir cream can also be used, costing an average of 400 rubles.
The drug Erazaban prevents the development of complications. 5% ointment costs from 55 rubles, 10% from 226 rubles.
For reference. The best option would be to use a weak drug at the initial stage, so that with the further development of the disease, it will be possible to enhance the therapeutic effect by increasing the strength of the drug.
So, it is more logical for Erazaban to first apply 5%, and in case of a weak reaction, switch to 10%. It would be better to stop the inflammatory process with a 5% composition.
We recommend considering the use of Panavir ointment. A small tube (3 grams, which is enough for several activations of the herpes virus) is sold at a price of 145 rubles. This drug will help cope with even an advanced form of herpes, relieves pain, has an anti-inflammatory effect, and also helps increase local immunity.
Viferon gel works well for the treatment of herpes in the nose (herpes on the nose and herpes under the nose). The price of a tube is from 200 rubles. Usually, when applied 3-5 times a day, herpes goes away in 5-6 days.
When prescribing treatment, tablets with an antiviral effect are usually added to ointments and gels.
These drugs include:
- Famvir,
- Valaciclovir,
- Acyclovir,
- Valtrex.
For reference. The advantage of the tablets is that they stop the formation of viral DNA and also stimulate the immune system, helping to quickly cope with the disease.
Zinc or tetracycline ointment will be useful during the healing stage of ulcers. These fairly cheap, domestically produced ointments help prevent the spread of infection to nearby areas of the face.
If the disease becomes more complicated, Paracetamol or Ibuprofen can be added to the treatment regimen.
To assess the effectiveness of treatment, it would be good to take tests before and after the course of treatment.
To treat herpes under the nose, systemic antiviral agents are used, taken in the form of tablets. They have an effect on the entire body. They drink them when rashes occur frequently and the immune system is weakened.
To treat persistent manifestations of herpes under the nose, the latest generation of products are used. They are effective for immunodeficiency. Strong antiviral agents are Foscarnet and Brivudine. The only contraindication is intolerance to the components of the drug.
Treatment of herpes in pregnant women
For reference. The difficulty of treating herpes in the nose during pregnancy is that many anti-inflammatory and antiviral drugs are prohibited due to their possible harmful effects on the fetus.
Therefore, you should consult your doctor before using any medicine.
Most often during pregnancy, the doctor prescribes local antiviral ointments. The safest during this period is Panavir, as well as tetracycline, oxolinic, and zinc ointments. Acyclovir and Zovirax are prescribed only in the first and second trimester of pregnancy.
In this case, it is advisable to use rosehip and sea buckthorn oils, as well as aloe juice.
Herpes in a child's nose
For reference. In the case of treating herpes in a child’s nose, the prescription of drugs should be approached very carefully. It is important to consult your doctor. It’s better to work with a pediatric infectious disease specialist.
This is important because, for example, acyclovir-based drugs are not recommended for children under 12 years of age.
It is good to use Viferon in suppositories (Viferon suppositories). This drug is approved for the treatment of children from the first years of life.
A complex approach
For persistent herpes with frequent exacerbations, treatment should proceed in two directions:
1. It is necessary to transfer the disease from the rapid stage of development to a “dormant” form, to suppress its activity. 2. Increase the body's defenses.
The first task is accomplished by plants that have an antiviral effect: Kalanchoe juice, calendula, pine resin, leaves and buds of birch, eucalyptus, St. John's wort, celandine, plantain, string, and sweet grass.
Immunity is increased by plants such as eleutherococcus, Rhodiola rosea, aloe, lemongrass, and echinacea, which are widely used in folk treatment.
The drug alpizarin was created from the aerial part of the yellowing kopek plant, which is used to treat the skin, mucous membranes, and genitals. Therefore, kopeck is widely and justifiably used in the treatment of this disease.
A comprehensive approach involves external, local treatment of the rash, as well as taking various decoctions and infusions to suppress the virus and increase immunity.