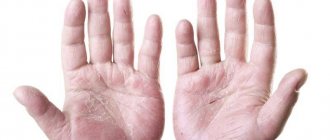
An itchy rash on the hands can be caused by many diseases. At the same time, it is not at all necessary not to adhere to basic hygiene rules. Microorganisms and bacteria, with low resistance from the human immune defense, provoke the occurrence of complex, sometimes dangerous diseases, which, in turn, can develop into a chronic form. Therefore, if the skin on your hands itches and pimples appear, you should pay attention to this factor by seeking professional help from a dermatologist or venereologist.
Formation of pimples with pimples on the hands: reasons
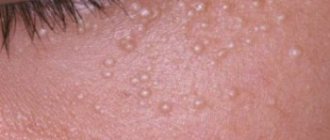
If small pimples appear on your hands and they itch, this may be due to the growth of microorganisms or fungal infections. Self-medication in this situation only aggravates the situation, because “healing” the underlying disease leads to complications, sometimes even damage to internal organs. The main reasons that can be considered by a doctor are:
- allergy. Doctors associate 50% of all diagnosed skin problems and rashes with the body’s local reaction to specific drugs, enzymes, and microparticles. At the same time, it is not at all necessary to suffer from allergies all the time. A severe form of an allergic reaction can be a “cumulative” form, that is, in order for the first signs to appear, it takes several months, or even years, of constant contact with a certain allergen. Treatment in such a situation is to identify the source that provokes the rash and completely protect from any contact;
- fungal mycosis. In turn, such mycotic formations are divided into yeast, saprophytic and dermatophytic subspecies. In the chronic form, damage occurs to the deep layers of the epidermis, less often to internal organs and mucous membranes of the body. Treatment is combined and periodic – antimicrobial;
- scabies mite. The development of this disease can also occur over a long period of time. From the moment of infection (most often in damp places with dense vegetation) to visible signs of the disease, it can take from six months to three years. It all depends on the immune defense and characteristics of the human body at this stage;
- eczema of fingers. Provocateurs can be nervous tension, stress, or infection from a source. Symptoms are accompanied by severe itching, often an unbearable burning sensation in the affected area;
- neurodermatitis is exclusively a manifestation of nervous stress over a long period of time. This condition is aggravated by a lack of vitamins B, A and D. Itching and rashes are characteristic of the elbow, knee joint, chest and neck.
Among the main causes of itching and redness of the skin are diseases associated with the endocrine system (diabetes mellitus, diseases of the thyroid and pancreas).
How to treat allergies
When experiencing skin rashes, many people look at their hands with horror, begin to panic and wonder what to do. There is no need to panic. First of all, to avoid complications, you need to start washing your hands with bactericidal, preferably liquid soap.
Household chemicals often lead to similar phenomena. The skin of the hands is sensitive and cannot withstand the onslaught of chemicals, as well as frequent contact with water. It is better to wear gloves when washing and using powders.
For itching and burning, you can use skin-soothing mash, baths with the addition of chamomile, or string. Baths with peat oxidate and a water temperature of 37°C help well. You need to repeat the procedure for several days. If a scabies mite has penetrated the skin, you cannot avoid treating the skin with Spregal, Benzyl benzoate. In this case, it is necessary to disinfect all things, treat them thermally or even chemically.
Allergies should not be confused with scabies. These are completely different diseases that differ in symptoms and treatment. It is best to seek help from a doctor immediately.
Transparent rash on the wrists itches: causes and clinical picture of the disease
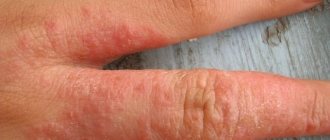
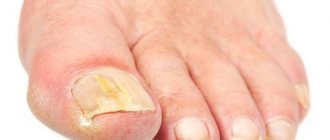
When your fingers itch and pimples appear, this may be evidence of a fungal infection. The habitats of such a provocateur are damp wooden platforms, bathhouses, kitchens, bathrooms with fungal manifestations. At first, such bubbles have a single distribution on the upper part of the hand. After the disease progresses, growths and transparent pimples are already visible on the entire plane of the hands. After a while, the transparent blister-like pimples burst, causing itching and even burning. The treatment is long-term, at least six months. Topical antifungal drugs + antibacterial therapy should be prescribed exclusively by a doctor. If left untreated, joint deformities may occur, accompanied by bulges and constant exacerbations. In the chronic form of the disease, treatment can only reduce unpleasant symptoms, however, it will not be possible to completely get rid of the consequences of fungal infection.
Important to remember
It is worth separately noting two dangerous viral diseases that cause acne on the hands:
- Streptoderma: occurs when the streptococcus microorganism enters the body through scratches. It is characterized by the appearance of small transparent pimples filled with cloudy liquid inside, itching and general weakness. The disease itself is extremely contagious and easily transmitted to healthy people, and if the immune system is weakened, it can lead to damage to the joints and cardiovascular system;
- Neurodermatitis: this is a chronic disease that is neuro-allergic in nature. There are several types of neurodermatitis, which differ in the types of acne and where they spread. The main feature of the disease is its chronic nature: the disease cannot be cured completely; there is always the possibility of remission.
What to do if pimples appear on your hands
When small pimples appear on your hands, the first thing you need to remember is that a dermatologist must make an accurate diagnosis and prescribe treatment. Since most rashes are similar to each other, although they have a different nature, only a professional can make an accurate diagnosis. It is especially important to visit a doctor as soon as possible if we are talking about a child: it is likely that the baby has measles or chickenpox, and he needs competent treatment .
Before visiting a doctor, you must follow certain rules:
- Do not touch pimples or scratch them;
- You can gently cleanse the skin with mild cosmetics, such as exfoliation - this will help remove dirt and cleanse pores;
- Check for other signs of illness: fever, weakness, chills.
It is also worth trying to determine for what reasons acne on your hands could appear:
- First, it is necessary to exclude nervous disorders and hormonal problems: for example, during stress, this is the most likely cause of rashes. However, during pregnancy, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible: if acne does not appear due to hormonal imbalances, the doctor will be able to choose the most gentle and optimal treatment.
- Then you need to check for the possibility of an allergic reaction. One of the signs of contact allergies caused by the use of cosmetics or household chemicals is the concentration of inflammation in one place. If in the coming days you have used any new products, worn jewelry or synthetic clothing, you need to remove them for a while and wait a few days.
It is also necessary to exclude harmful foods with dyes and preservatives from the diet, and remove the most likely allergens.
- If pimples between the fingers and on the palms are accompanied by fever or weakness, most likely the cause is a viral disease. The likelihood increases if you have had contact with sick people in the near future.
- It is necessary to adjust your diet by adding vitamins to it.
- You should not use cosmetics with aggressive ingredients (alcohol or acid): this can cause acne to grow.
First aid
If you can’t see a doctor, you can use some folk recipes. They will help reduce inflammation and itching, but they will not be able to get rid of the cause.
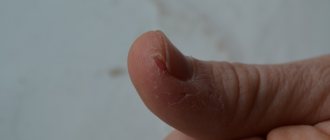
Subcutaneous acne
Most often they occur with hereditary Darier disease. If this is not the problem, you can use the following remedies:
- Wipe acne with a solution of the juice of half a lemon in a glass of water;
- Make hand baths with sea salt;
- Target the affected areas with iodine or ichthyol ointment: they have an antimicrobial effect and relieve inflammation.
Dry acne
Such rashes may appear immediately or form in the final stages, when the pus has dried. Usually, to remove them, it is enough to carry out a course of gentle cleansing of the skin from dead cells and moisturizing it.
Red pimples
They are often accompanied by painful itching and inflammation. These symptoms can be reduced with calendula tincture, salicylic acid solution or aloe juice. Ichthyol ointment and Vishnevsky ointment will also help relieve inflammation. They must be applied pointwise, strictly on pimples.
Purulent and watery pimples
White pimples on the hands filled with pus should never be treated independently. Before visiting a dermatologist, you can lubricate them with aloe or celandine juice, as well as chamomile infusion - this will help remove irritation and reduce the activity of bacteria. You can read more about watery acne here.
Any appearance of acne on the hands indicates a disturbance in the body's functioning: this may be a reaction to a virus or fungus, a consequence of hormonal disorders or a lack of vitamins. Treatment of inflammation should be carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist. A specialist can draw up a complete treatment program only after conducting all the necessary tests and long-term observation.
If pimples and inflammation suddenly appear on your hands, the first step is to determine the cause.
Red rash between fingers: causes and treatment
If the rash on the inside of the arm itches and periodically burns, and flaky areas of the skin are also characteristic, this may indicate the presence of eczema. Such a disease can be acquired and a consequence of the body’s reaction to certain drugs. As a rule, rashes are provoked by aggressive antibacterial chemicals, as well as psychotropic and tranquilizers. In some cases, patients experience a simultaneous disorder of the nervous system, accompanied by panic attacks and mood swings. Nervous tension, stress and constant emotional overstrain + negative factors from “outside” provoke the occurrence of eczema, which, in turn, requires complex treatment.
Preventive measures
The formation of small pimples on the hands can be prevented if you adhere to basic hygiene standards and do not expose your body to constant exposure to various types of allergens. Doctors note that this problem will almost never affect a person who follows the following recommendations:
- control over the cleanliness of hands, periodically washing them with soap, treating minor injuries with antiseptic solutions;
- maintaining a normal daily routine, providing the body with adequate sleep and daytime rest;
- eating foods enriched with vitamins and minerals, and in the winter season - taking additional vitamin complexes to prevent the development of hypovitaminosis;
- strengthening the immune system;
- high-quality hand skin care using moisturizing creams, nourishing masks, etc.;
- giving up bad habits, which always complicate the course of the underlying disease and increase its relapse;
- avoiding stressful situations and nervous tension;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of diseases of internal organs.
Climatic conditions: why do your hands itch in winter?
Many chronic diseases have such a feature as progression during a period of weakening of the body. Skin diseases and psycho-emotional states of the patient can provoke the formation of external rashes. Redness and itching of the palms, a rash in the chest and upper back, manifestations in the form of blistering transparent rashes, which are accompanied by peeling and coarsening of the upper layer of the epidermis - these are clear signs of winter vitamin deficiency. This condition is aggravated by improper nutrition, excess or, on the contrary, excessively low weight of a person. Treatment is complex, long-term, using antibacterial therapy, as well as individual selection of vitamins. External irritants (itching, burning, flaking) are eliminated with the help of creams and gels with anti-itching and moisturizing effects.
Treatment recommendations
Acne on the feet is often confused with dry calluses, so self-medication is ineffective. To get rid of profuse rashes on the body and legs as soon as possible, it is recommended to adhere to the following rules:
- choose clothes and shoes only from natural fabrics;
- give up heels at least for a while;
- change skincare products;
- if possible, take air baths as often as possible.
It is also recommended to replenish the vitamin balance in the body. To do this you need to take vitamin A and vitamin E
No less important for eliminating dropsy is prevention.
The first thing you need to do is cleanse your body by reviewing your daily menu. Instead of junk food, you need to include in your diet foods rich in minerals and vitamins. It is better to completely exclude fried, spicy and highly salty foods from the diet, as they negatively affect the condition of the skin and the functioning of the digestive system.
We recommend Why does sweating occur between the legs in the groin, and how to deal with it?
Regarding sweets, dermatologists say that they take away beauty. Many studies have proven that people who often eat chocolate and sweets often suffer from acne, acne, clogged pores and other skin diseases.
It is imperative to add fermented milk products to your daily diet. It improves the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, helps cleanse the body, eliminates toxins and speeds up metabolism. As a result, the skin looks more rested and the number of breakouts is significantly reduced.
To prevent the appearance of acne on the feet, as well as corns, it is recommended to regularly cleanse the skin with scrubs, peels, and pedicures. At home, you can use pumice, a heel file, or steaming for this.
Human skin is very susceptible to external and internal irritants. Therefore, if you notice any inflammation, pimples or redness, you need to listen to your body. Perhaps this is just a symptom of a serious disorder or pathology that can be dangerous to human health and life.
Eczema
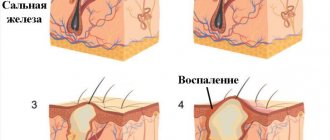
A chronic skin disease affecting the superficial layers of the epidermis is eczema. When the skin of the hands is affected, elements of inflammation and itchy pimples, weeping and painful, appear. Eczema is not transmitted through tactile contact or touching the things of a sick person. The disease develops as a result of damage to the digestive system, disorders of the thyroid gland, genetic predisposition, nervous diseases, and weakened immunity.
Eczema often affects people who are constantly in contact with chemicals, various dyes, formaldehyde, detergents, etc. In addition to itching and burning with eczema, severe peeling of the epidermis on the hands is observed.
The principle of treating this dermatosis is to eliminate the causes of its occurrence:
- if the provoking factor is an allergy, then it is necessary to take measures aimed at reducing the body’s sensitivity to various allergens;
- to remove toxic substances from the body, adsorbent drugs are used, for example, Enterosgel, Polysorb, activated carbon;
- if the symptoms of eczema are aggravated by nervous disorders, then it is advisable to use sedatives such as Novopassit, Afobazol, valerian;
- to relieve symptoms of itching, it is recommended to take anti-allergy medications;
- To speed up recovery from eczema on the hands, various vitamin complexes are prescribed.
It is very important to treat eczema comprehensively and use local therapy products that have antipruritic and anti-inflammatory properties. The most effective are considered to be such agents as podophyllin ointment, ichthyol ointment, resorcinol solution, boric acid.
When eczema affects large areas of the epidermis on the hands, hormonal ointments and creams are prescribed, which quickly and effectively relieve all the symptoms of this pathology.
Rash classification
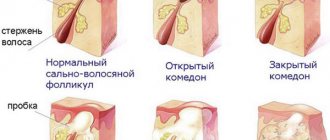
Exanthema (rash) is a discrete pathological formation of the skin, its response to the effects of toxins and metabolites of the pathogen. The primary morphological elements include: spot, blister, nodule, node, tubercle, vesicle, vesicle, pustule.
Secondary morphological elements include: secondary hypo- and hyperpigmentation (secondary dyschromia), scales, crusts, cracks, erosions, ulcers, scars, vegetation, lichinification, excoriation.
A spot (macula) is a limited area of skin of changed color, without changes in its relief and consistency. The spot is flush with the surrounding skin. Spots can be vascular, pigmented or artificial.
Causes of spots - hypopigmentation or depigmentation (for example, vitiligo) and hyperpigmentation - accumulation of melanin (for example, café au lait spot of neurofibromatosis, Mongolian spot or hemosidirin), abnormalities of skin vascular development (for example, capillary hemangioma), temporary dilatation of capillaries . Criteria for the classification of exanthems:
- type of rash elements: roseola, macula, erythema, papule, tubercle, node, urticaria, vesicle, pustule, bulla, petechiae, ecchymosis;
- sizes: small - up to 2, medium - up to 5, large - over 5 mm in diameter;
- shape: regular, irregular;
- uniformity of rash elements: monomorphic (all elements belong to the same type and have the same size); polymorphic (rash elements vary sharply in shape, size, or there are elements of different types);
- localization of elements: symmetrical and asymmetrical, mainly in one or another area of the skin;
- abundance of rash: single (up to 10 elements), sparse (elements can be counted) and abundant (multiple);
- metamorphosis of the rash: the appearance of an element, its development, often with the transition of an element of one type to another, and the extinction of the rash;
- timing of appearance: early - 1-2nd, medium - 3-4th and late - after the 5th day of illness. When characterizing the rash, indicate the background of the skin (pale, hyperemic).
Erythema, or hyperemic, is a spot caused by temporary expansion of capillaries. The size of the spots varies from 1 to 5 cm or more in diameter. An erythematous spot up to 1 cm in diameter is called roseola (for example, syphilitic roseola). With diascopy, the hyperemic spot disappears.
Spots formed due to the release of red blood cells outside the vessels are called hemorrhagic. Small hemorrhagic spots are called petechiae, large ones are called ecchymoses. A nodule (papula) is a primary bandless surface morphological element, characterized by a change in skin color, consistency and resolving without scar formation.
Papules usually protrude above the surface of the surrounding skin and can be palpated. The surface of the papule can be smooth (for example, lichen planus) or covered with scales (for example, psoriasis). Nodules can be inflammatory or non-inflammatory.
In a number of dermatoses, peripheral growth of papules or their fusion and the formation of larger elements - plaques (for example, mycosis fungoides) occurs.
Plaque (plax) is a flattened formation, raised above the skin level and occupying a relatively large area. As a rule, plaques have clear boundaries. A tubercle (tuberculum) is a primary non-banded formation that occurs as a result of the development of a granulomatous infiltrate (granuloma) in the dermis. Clinically, it is quite similar to papules.
The tubercle has clear boundaries and rises above the level of the surrounding skin. The diameter of the tubercles is from 5 mm to 2-3 cm, the color is from pinkish-red to yellow-red, copper-red, bronze, and bluish. During diascopy, the color of the tubercles may change (tubercular tubercles).
The tubercles have a dense or doughy consistency. They occur in limited areas of the skin and tend to group (for example, syphilis) or merge (for example, tuberculosis). Unlike nodules, a scar remains at the site of the tubercles (if it disintegrates, with the formation of an ulcer) or cicatricial atrophy (with the resorption of the tubercular infiltrate).
Node (nodus) is a primary non-banded infiltrative formation of a round or oval shape, located in the deep parts of the dermis or subcutaneous tissue.
The node differs from the papule in its larger size (from 2 to 10 cm or more in diameter) and depth. Bubble (vesicula) is a primary cavity formation containing serous or serous-hemorrhagic fluid and rising above the skin level in the form of a hemispherical or round element 1.5-5 mm in size.
The bubble has a wall, a cavity and a bottom. The walls of the vesicle are so thin that the contents—plasma, lymph, blood, or extracellular fluid—can be seen through the peak. Pustula (pustula) is a primary strip morphological element containing purulent or purulent-hemorrhagic exudate. Purulent exudate may be white, yellow or yellow-green in color.
A pustule develops around hair follicles (usually staphylococcal) or on smooth skin (usually streptococcal). The sizes and shapes of pustules vary. A pustule associated with a hair follicle is called folliculitis. A blister (urtica) is a primary, bandless morphological element (papule or plaque) with a flat surface that occurs when the upper parts of the papillary dermis are swollen.
The pathognomonic sign of a blister is its ephemeral nature: they usually last no longer than a few hours and are accompanied by itching and burning.
Blisters may have a flat, smooth surface, round, ring-shaped, or irregular shape. Due to the movement of dermal edema, the shape and size of the blisters quickly change. The color of the element is pale pink.
Source: emhelp.ru