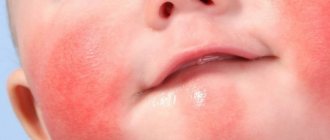
What is dermatitis called?
This is an acute inflammation of the skin, the result of exposure to irritants of various natures. Causes of dermatitis include:
- Individual predisposition. The specifics of metabolic processes, reactions from the immune system, skin type are transmitted from parents to the child, but not the disease. The development of dermatitis itself is provoked by allergens, toxins, stressful situations, exposure to low temperatures and other factors. This dermatitis is not contagious.
- Disturbances in metabolic processes. The condition of the skin worsens under the influence of even those factors that are not directly related to it: pathological conditions of the endocrine system, excess or deficiency of vitamins, metabolic disorders.
- Excessive sensitivity to certain substances. When in contact with certain proteins, the body actively secretes immunoglobulins, which are designed to remove the foreign protein. Penetration of dangerous substances into the bloodstream or their contact with the surface of the body causes an inflammatory process. Obviously it is not contagious.
- Impact of a physical nature. As a result of friction and compression, microtraumas are formed. Extreme temperatures also have a negative impact on skin cells.
- Effect of irritating chemicals. These are acids, alkalis, toxins, household chemicals. Their exposure causes inflammation of the skin or contact dermatitis.
- Contagious diseases (infectious origin) also cause dermatitis.
- Stress. If there is a predisposition to skin manifestations, it provokes diseases, the symptoms of which are rashes.
Accordingly, of the 7 types of dermatitis, only one can be infectious to others. Infections (contagious viruses, fungi, bacteria or parasites) can be transmitted through contact. But not always. Even a specialist cannot always determine the cause of dermatitis only by the appearance of the lesion.
Why does the disease appear?
The causes of dermatitis are divided into two main groups: internal and external.
The internal (endogenous) factors that provoke pathology include the following situations:
- hormonal dysfunction;
- avitaminosis;
- scleroderma;
- metabolic dysfunction.
External causes of dermatitis are contacts with any external irritants: mechanical, physical, biological, chemical.
Against the background of irritation, external signs of inflammation appear. Dermatitis in adults manifests itself with varying degrees of intensity. It depends on several factors:
- type of stimulus;
- characteristics of the patient's skin;
- duration of exposure of the harmful agent to the epidermis.
Is dermatitis contagious?
The main symptom is a rash, the appearance of which is unpleasant. This skin condition raises a natural question: is it contagious? Unless there is a noticeable wet rash or scabs, there is usually nothing to worry about. But it is better to always try to reduce contact with the patient if the nature of the pathology is not known. If you discover that you have dermatitis, you should definitely consult a doctor for a diagnosis.
Allergic
This is a consequence of exposure to a specific external factor on the skin. Allergens include:
- latex;
- nickel;
- skin care cosmetics;
- materials from which clothing and shoes are made;
- pet hair and much more.
The degree of allergenicity of a factor does not depend on its chemical composition. The influence is exerted by the individual sensitivity of the body to the substance. It also matters how direct the contact was. The exposure time does not matter.
Without eliminating constant contact with irritants, treatment is unsuccessful. Most cases of allergic reactions at work, in agriculture, and at home are associated with ignoring basic skin protection measures.
The allergic form of dermatitis is a specific reaction from the immune system. Most often, it occurs predominantly without the participation of antibodies. They are replaced by specific immune bodies. Therefore, this dermatitis does not pose any danger to others; it is not contagious.
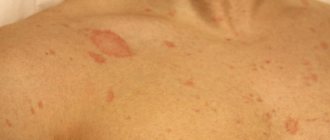
Clinical manifestations are similar to the acute phase of eczema. At the initial stage, the skin is covered with large red spots. They then turn into small bubbles. There are quite a lot of them. As they develop, the swellings burst. In their place, defects (superficial, wet) are formed. Another scenario is also possible - the appearance of small scales and crusts.
The allergic form affects the entire body as a whole. Subject to repeated contact, the emergence of an infectious process, or a stressful situation, secondary foci of inflammation appear. But even in this case, the bright skin symptom is not contagious.
Contact
It is often confused with an allergy, but in this case the symptoms are caused by substances that are equally dangerous for any person. Not everyone experiences them through skin rashes. Predisposition to the disease is determined at the genetic level. Speaking about whether dermatitis of this type is transmitted by family, we can say that it is not. Only the tendency to illness is inherited. Accordingly, this type is not contagious.
Simple contact dermatitis is activated due to direct contact with irritants, and allergic dermatitis occurs only in those patients who are hypersensitive to specific allergens upon contact.
Experts distinguish the following varieties:
- Simple contact. It develops if the cause of the rash is a caustic substance: household chemicals, acids, alkalis.
- Phototoxic contact. A rare pathology that occurs when exposed to ultraviolet radiation. Quite difficult to diagnose.
Both varieties manifest themselves through:
- red mark on the affected area of skin;
- swelling and itching;
- the appearance of bubbles filled with a clear liquid.
During the remission stage, when the symptoms subside, the skin recovers in an unusual way. It becomes covered with specific yellow crusts.
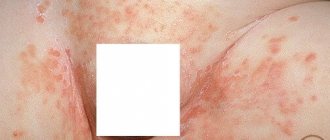
Atopic
Chronic inflammatory lesion, during which phases of remissions and exacerbations are observed. It manifests itself as dryness, increased irritation of the epithelium, and severe itching. The condition causes the patient physical and psychological discomfort. Due to itching, the skin becomes scratched, and signs of secondary infection appear.
It is considered a hereditary disease. This explains the prevalence of the condition among close relatives. Again, it is not the dermatitis itself that is transmitted, but atopic hypersensitivity. The disease is not contagious.
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic, non-contagious inflammatory skin lesion that occurs with periods of exacerbations and remissions.
90% of clinical symptoms appear in the first five years of a child’s life. Provoke the atopic form:
- unfavorable environmental factors;
- failure to maintain a healthy diet;
- neuropsychic overload due to study or a stressful situation at home;
- infections;
- constant contact with allergens.
In young children, the provoking factor is:
- weakened immune system due to insufficient breastfeeding or lack thereof;
- early transfer to artificial feeding and lack of certain microflora components;
- violation of the diet by a woman during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
Almost half of the cases of atopic rash in children occur during breastfeeding.
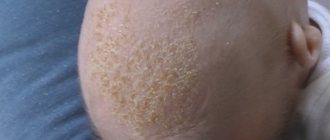
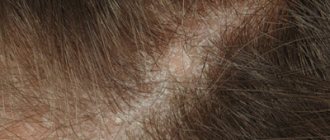
Seborrheic
A pathological and contagious process caused by a fungus. Develops in areas where there are many sebaceous glands. It gets worse in the cold season. In summer, all signs disappear.
The human body can control the growth of fungi. However, due to weakened immune defenses, frequent stressful situations, endocrine disorders, and nervous diseases, this natural ability is lost. Yeast-like fungi begin to grow and multiply.
The disease occurs:
- on the face;
- on the scalp, eyelashes and eyebrows.
The postauricular area, interscapular area, chest, and skin folds are rarely affected.
Manifests itself in the form of dandruff and acne. The most characteristic symptom is specific scales. Seborrheic infection is transmitted from person to person. Skin particles affected by fungus are contagious. But the development of the disease begins only in the presence of provoking factors, for example, weakened immunity.
Infectious
The clinical picture is determined by the disease due to which the infectious form developed. The rash that occurs against the background of measles is localized on the face on the first day. It then spreads to the body. Other infections have their own symptoms.
You can prevent the likelihood of contracting this type of dermatitis with medication. For this purpose, vaccination against such diseases is carried out. It guarantees almost one hundred percent protection against the disease.
Regarding whether it is possible to become infected with this type of dermatitis, experts note: the infectious diseases themselves pose a danger. Whether a particular patient will experience skin symptoms depends on the individual characteristics of the body.
At the doctor
Allergies must be treated, since even the most minor manifestations can develop into severe chronic diseases such as bronchial asthma. If symptoms of dermatitis appear, you should consult an allergist or dermatologist. In addition, it would not be superfluous to consult a gastroenterologist and nutritionist.
The doctor will conduct a full examination and prescribe the necessary tests. It is very important to identify which allergen and related factors caused such a reaction on the skin. After this, it is necessary to completely eliminate the allergen from contact.
Therapy consists of antihistamines, sorbents that help quickly remove allergens from the body, and agents that eliminate local manifestations of allergies. In order to reduce redness and itching, ointments or gels that have an anti-inflammatory effect are used. They do not penetrate the blood, so they can be used even by small children and pregnant women.
Timely treatment of the disease will reduce the risks and protect yourself from relapse.
Hereditary factor
People experiencing dermatitis are worried that the disease may be contagious to their children, that is, transmitted. Such concerns are true only for one type - atopic. The genetic basis of its appearance has been confirmed by numerous scientific studies. According to their results, among patients diagnosed with atopic disease, about 42% of close relatives also have a history of the disease. In addition, in 35% of cases, manifestations of allergies of various natures were recorded. Taking this into account, the thesis of whether atopic dermatitis is inherited appears to scientists to be correct.
Pathology such as a predisposition to skin lesions is transmitted through the maternal line. Experts attribute this to changes in the mother's immune responses during breastfeeding. Therefore, it is the woman’s body that will have a greater impact on the baby’s health.
Despite the evidence of a genetic factor, it is true to talk about a predisposition to dermatitis, but not about the inheritance of the disease itself. Therefore, the child always has a chance to live without unpleasant skin symptoms.
Prevention methods
Specific actions are determined by the type of disease and whether it is contagious or not:
- With the contact type, it is important to exclude contact with the factor that caused the specific reaction. If this cannot be avoided, the surface of the skin is washed with running water, then sent for medical help. Even for healthy people with well-functioning internal organs and strong immunity, it is dangerous to interact with toxic substances for a long time.
- Atopic is most often associated with disorders of the gastrointestinal tract, nervous or endocrine system. Preventive measures are aimed at eliminating the underlying disease. A diet that excludes the consumption of foods with a high allergenic titer will be mandatory.
- Infectious dermatitis is contagious only if the rules of contact with patients are violated. For example, sharing bedding and dishes increases the risk of infection. When in direct contact with an infectious patient, use a mask and gloves. The state of immunity and the presence of vaccinations are also important.
Preventive measures prolong the period of remission and prevent the development of pathology if there is a predisposition.
Diagnostics
Infectious dermatitis can also be identified by clinical signs. But the cause of skin changes is reliably determined based on the results of additional methods:
- General blood tests (leukocyte count, ESR).
- Serological tests (antibodies to microbial agents).
- Studies of discharge from skin elements (microscopy, culture, PCR).
To clarify the diagnosis, consultation with an infectious disease specialist is indicated. In case of systemic disorders and damage to internal organs, there is a need for a corresponding expansion of the range of diagnostic measures.