Papillomas on the chest are one of the manifestations of the disease caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV). Correct diagnosis and timely treatment will help get rid of unpleasant symptoms and prevent relapse.
Today, patients often consult a dermatologist with papilloma on the chest - this is a viral disease that causes skin changes. Externally, the neoplasm resembles a small limited nodule, sometimes prone to peeling and itching.
The disease itself, HPV (human papillomavirus), does not cause trouble for 90% of people who do not even suspect that they are infected. In the remaining 10%, the disease lasts a long time, most often throughout their lives.
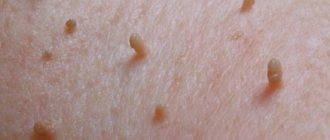
The disease manifests itself in the formation of flesh-colored, yellow and brown growths consisting of epidermal cells and blood vessels. The latent period lasts from a month to six months.
Sometimes it lasts for several years. Before the appearance of papilloma, the place where the tumor grows begins to burn and itch. Most strains do not pose a health hazard, but some types of viruses can lead to cancer.
Favorable conditions for the occurrence of symptoms are a weakening of the body’s immune defense.
Papillomas on the chest appear due to:
- stressful situations, nervous overstrain;
- abortions;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- absence of pregnancies in women over 40;
- microtraumas;
- wearing tight, tight or strange underwear;
- the existence of bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking);
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- menopause, puberty;
- excessive physical activity;
- excess weight, sweating:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- chronic, venereal, frequent colds.
Women are more susceptible to hormonal imbalances, depression, and are more likely to develop papillomas than men.
The virus is localized on the chest:
- on the nipple and areola;
- in the milk ducts (cystadenoma);
- under the chest.
In the first case, the structure of the growths is granular. Papillomas come in round and pointed shapes. When injured, they multiply quickly, capturing the entire nipple, areola and surrounding areas.
The intraductal type consists of single or group cystic growths. The size varies from 3–5 mm to several centimeters.
The disease is identified by discharge from the nipple and treated surgically. Women with mastopathy after 40 years of age are most susceptible to the disease.
There are folds under the breasts and increased sweating, which creates favorable conditions for HPV. Papillomas are pedunculated or broad-based, with no skin pattern.
Mainly they create aesthetic inconveniences. If the growths are injured, a secondary infection may occur.
Papillomas in the chest area are caused by strains of viruses with low oncogenicity.
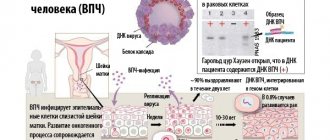
HPV infection occurs in several ways:
- Sexual contact, even protected. The virus can penetrate the epithelium if the integrity of the skin on any part of the body is damaged.
- During childbirth from mother to child.
- Household method. Through a handshake, dishes, using other people's personal hygiene products.
You can become infected while shaving or epilating if a person is a carrier of the virus.
Why do they arise?
Often in women, neoplasms called papillomas form under the breasts. Benign growths do not cause significant discomfort, and therefore their owners do not attach any importance to this. But this is a misperception of this problem.
Such a place of concentration raises suspicions of the presence of cancer. It is in this area that papilloma often degenerates into a malignant tumor, which requires other specific therapy.
The formation of such can be caused by the influence of the following predisposing factors:
- tight underwear worn by a woman (skin chafing);
- groin warts;
- long-term therapy with antibiotics and other potent drugs;
- Promiscuous sexual activity, constant unprotected sexual intercourse;
- increased sweating in the area under the breasts;
- papillomas on the penis;
- injury to the skin in the area under the breast;
- insufficient content of vital vitamins in the body;
- hormonal imbalance;
- frequent stressful situations.
Papillomovirus can enter the body accidentally, due to slight injury to the skin and untimely treatment of the wound.
The appearance of characteristic symptoms occurs during a decrease in protective forces and when exposed to provoking factors.
Breast diseases
First of all, we are talking about intraductal papilloma in the chest area. Synonyms: Mintz disease, bleeding mammary gland, intraductal papilloma. The tumor can reach several centimeters and is located in the lumen of the duct.
The patient experiences copious discharge from the nipple, sometimes bloody. The disease is local, the formations are located either inside the ducts or intracystically. The tumor can be microscopic and reach 5-7 cm in diameter.
The danger of the disease is that papilloma is an obligate precancer that requires surgical treatment. One form of the disease is cystadenopapilloma. The tumor originates from the milk ducts, outwardly it looks like papillae located in the dilated duct; similar growths can be found in a mammary gland cyst.
This disease is classified as mastopathy. The first and important symptom is pathological discharge from the nipple. They may be whitish, bloody, or greenish. In some cases, the patient herself detects the tumor by palpation. Typically, the tumor is localized in the peripapillary zone.
Diagnosis of the disease is not particularly difficult. First of all, a cytological examination of discharge from the nipple is carried out. Atypical cells confirming the presence of papilloma are valuable.
Additionally, ultrasound and mammography are performed. The methods do not allow one to accurately differentiate the disease, but they make it possible to distinguish it from other pathologies. The method of ductography, or galactography, has great informative value.
A contrast agent is injected into the duct, after which pictures are taken in two projections. The method makes it possible to assess the location of the tumor, since MRI and mammography do not have such capabilities.
Ductography is indicated only for those women who complain of brownish, green or bloody, whitish discharge from the nipples. In nulliparous women, discharge from both glands may indicate a side effect of hormonal drugs or a pathology of the pituitary system.
Source: kozhatela.ru
What types exist
Papilloma is formed from epithelial cells of the excretory ducts. The base can be wide or “pedaled”, soft or hard.
Neoplasms can be of several types:
- Flat papilloma. More often diagnosed in young people. Flat papillomas are flesh-colored or yellowish in color. They occur due to hormonal imbalance and go away on their own as it normalizes.
- Senile papilloma. It is of non-viral origin. They appear after the age of 40 and have the appearance of neoplasms devoid of pigmentation. Shape – round, flat or protruding.
- Filiform papilloma. This type of neoplasm occurs against the background of changes in the hormonal system. In this regard, papillomas form during pregnancy and menopause, in older people, people who are obese or have diabetes. They have the appearance of acute cell growths.
The type of tumor can be determined by undergoing appropriate diagnostics. Based on its results, treatment is prescribed.
Forms of papillomas
Three types of growths can appear in the chest area: thread-like - appear with age, although they can occur under the influence of hormonal imbalances and excess weight, during pregnancy, diabetes and menopause. They grow up to four centimeters.
In cases of frequent injury, there is a high risk of degeneration into a cancerous tumor; senile - occur after forty years, do not have a viral nature of origin, and are often colorless.
They are also called keratomes; flat in shape - appear most often in childhood and adolescence, have a pale color, and disappear with age under the influence of changes in hormonal balance. Removing papillomas under the mammary glands on your own can have negative consequences and is therefore undesirable.
The virus easily enters the blood, the growths begin to multiply and increase in size at high speed. You should be careful not to accidentally injure the warts, which is very easy to do in this area.
Source: kozhatela.ru
Diagnostics
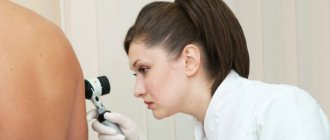
A mammologist will be able to detect papillomas under the breast. If necessary, the person is referred for consultation to an oncologist.
The correct diagnosis can be made based on the results of the following studies:
- ultrasound diagnostics and mammography (can detect intraductal papillomas);
- X-ray diagnostics using a contrast agent (helps determine the exact location of the tumor and its size);
- laboratory diagnostics - analysis of exudate released from the nipples (allows us to exclude oncological pathologies);
- laboratory diagnostics - blood test (allows you to determine the type of tumor).
If you promptly diagnose a viral infection at an early stage, you can prevent its further spread throughout the body.
Possible complications and precautions
The danger of human papillomavirus infection is the development of serious complications of the disease. These include the following conditions:
- Bleeding from papilloma under the breast occurs after damage to the formation.
- Tight underwear and mechanical combing provoke a violation of the integrity of the growth.
- Injured formations are an easy target for bacterial and viral flora. Suppuration of the growth is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms: pain, itching, local increase in body temperature.
Preventive measures help prevent infection with papillomatosis:
- Daily body hygiene prevents the colonization of the skin by viruses.
- Timely treatment of wound defects with antiseptic agents prevents HPV from entering the body.
- Treatment of chronic and acute diseases in the early stages prevents weakening of the immune system.
- Taking vitamin supplements as recommended by a doctor increases the body's resistance to infectious agents.
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Basic treatment
What to do if the diagnosis has been confirmed based on research results, only a doctor can determine. If the diagnosis is “papilloma virus”, immunomodulatory drugs and agents with antiviral effects are first prescribed. Diet adjustments and lifestyle changes are required.
A cosmetologist will tell you how to get rid of tumors under the breast using a radical method, especially if they are small and there are many papillomas. There are many methods for getting rid of growths.
Some of them:
- Laser removal. It is considered the most popular treatment method. There is no pain during the procedure, and no postoperative traces remain.
- Removal using electric current. Anesthesia is used during the procedure. After removal, a scar remains.
- Removal by freezing (cryodestruction). The procedure is carried out using liquid nitrogen.
- Removal using a radio knife.
- Removal with a regular scalpel. The technique is used for extensive damage to the skin.
- Removal with special chemical solutions. The growth is cut out along with the stem and root.
Additional treatment
You can treat growths using folk remedies. This is a sour apple (its juice) or rowan (also its juice). The new growths are wiped with products every day until they fall off.
- An ointment made from garlic and cream is effective. A clove of garlic is ground to a pasty state and mixed with a small amount of cream. The resulting mixture is applied to the growth and left for 20 minutes. Repeat the procedure daily.
- New growths can be treated with castor oil. Repeat the procedure 4 times a day until it falls off on its own.
- The treatment uses an infusion of dandelions. It is prepared as follows: grind the flowers, add 1:1 diluted alcohol, leave to infuse for 12 hours. Wipe the growths with the resulting product twice a day.
- You can use celandine juice, which is effective in treating papillomas, warts, and other growths. If other means can be used independently, then such a procedure requires supervision by a specialist.
What is the danger
New growths under the breasts bring not only aesthetic, but also physical discomfort. When clothing rubs against such growths, they become injured. In this case, the risk of deeper germination into the gland and degeneration into a malignant neoplasm increases.
Of all types of neoplasms, the most dangerous are intraductal ones, which in 50% of cases degenerate into malignant tumors. Symptoms include inflammation in the mammary gland, cloudy nipple discharge, burning sensation and chest pain.
Physical methods for removing growths.
Electrocoagulation
Papillomas are exposed to high frequency electric current. After cutting out the tumors, the edges of the incisions are sealed, which protects the patient from bleeding and infection from entering the bloodstream.
Cryodestruction
Papillomas are treated with low temperature liquid nitrogen. In less than a minute, the frozen cells are destroyed. Rehabilitation lasts up to a month, healthy tissues are affected.
Laser technology
The targeted impact of a carbon dioxide laser allows you to reach growths even on deep layers of tissue. The procedure is painless, leaves no scars, and excludes infection.
Radio wave destruction
Non-contact method of exposure to a beam of high-frequency radio waves. The papilloma is cut off in a gentle manner, and the incision is disinfected during the operation. The procedure is bloodless. Due to coagulation of nerve endings, it eliminates pain.
Surgical method
Used when other methods are ineffective. Performed under intravenous anesthesia. Used when cutting out an area of the mammary gland affected by intraductal papillomas. Disadvantages include a long recovery period and scars.
To prevent the disease, preventive measures are used in the form of vaccination, periodic medical examinations, and visits to the gynecologist.
You need to have one sexual partner, maintain personal hygiene, and wear comfortable underwear. Avoid physical contact with strangers and skin injuries.
Prevention of formation
The main preventive method for papillomas and oncological pathologies in the chest area is a systematic visit to a mammologist (at least once every 12 months).
You can increase the body’s protective function and reduce the risk of infection by normalizing your diet and enriching it with useful vitamins and microelements. It is recommended to harden the body, attend sports clubs, and walk in the fresh air every day.
Researchers have developed specific vaccines that reduce the possibility of infection entering the body. These include Cervarix, Gardasil, etc.
Risk factors
The occurrence of papilloma can be caused by a combination of one or more reasons that provoke hormonal imbalance in women of different ages:
- Puberty;
- Menopause;
- Pregnancy;
- Long-term use of hormonal contraceptives;
- Obesity;
- Problems with the ovaries (dysfunction, polycystic disease);
- Experienced stress.
Any of these factors not only affects the production of female hormones, but also leads to a weakened immune system. This increases the risk of contracting HPV. Wearing tight, uncomfortable clothing and frequent visits to public baths and swimming pools are also causes of infection.
Source: venerologiya.com
Symptoms of papilloma on the nipple
The growth of papillomas on the chest, near the nipple, is associated with the activation of the virus. Once in the body, it can remain dormant for a long time; the following factors can “awaken” the virus:
- Injury to the mammary gland: bruise, inaccurate shaving (a common cause of the growth of papilloma on the nipple in men), hair removal;
- Skin lesions, microcracks, which may be a consequence of a lack of vitamins and nutrients. They often provoke the growth of papillomas on the nipple circumference;
- Violation of hygiene rules;
- Hormonal imbalance. Papilloma on the papilla in women can occur during pregnancy, menopause, and puberty.
The manifestations and type of formations depend on their location:
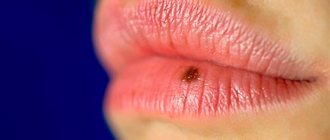
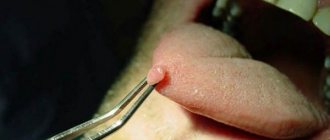
The growths on the nipple have a slightly elongated shape, are supported by a wide stalk, and can be dark brown in color.
Pain occurs when a wart is injured;
Papilloma on the areola of the mammary gland is characterized by small size and lack of pain;
Papillomas on the mammary gland are based on a thin stalk and have a cone-shaped shape. Associated manifestations are as follows:
- Increased breast sensitivity;
- Itching;
- Tingling.
How is the HPV virus transmitted?
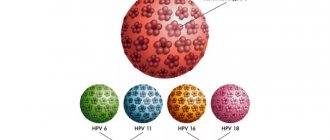
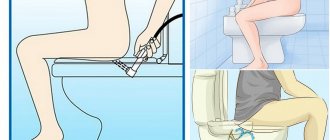
An infected person infects others without noticing it. There are three main routes of transmission of Human Papillomavirus:
- contact household, if people use common washcloths, towels, soap;
- from mother to newborn (98% of cases), when the fetus passes the birth canal;
- infection during unprotected sexual contact.
The mammary glands are not the only place where papillomas are located in women. Often rashes, individual or in colonies, appear in the armpits, neck, and face.
What is this
The disease manifests itself in the formation of flesh-colored, yellow and brown growths consisting of epidermal cells and blood vessels. The latent period lasts from a month to six months. Sometimes it lasts for several years. Before the appearance of papilloma, the place where the tumor grows begins to burn and itch. Most strains do not pose a health hazard, but some types of viruses can lead to cancer.
Favorable conditions for the occurrence of symptoms are a weakening of the body’s immune defense. Papillomas on the chest appear in the following cases:
- stressful situations, nervous overstrain;
- abortions;
- ovarian dysfunction;
- absence of pregnancies in women over 40;
- microtraumas;
- wearing tight, tight or strange underwear;
- the existence of bad habits (alcohol abuse, smoking);
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- menopause, puberty;
- excessive physical activity;
- excess weight, sweating:
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- chronic, venereal, frequent colds.
Women are more susceptible to hormonal imbalances, depression, and are more likely to develop papillomas than men.
The virus is localized on the chest:
- on the nipple and areola;
- in the milk ducts (cystadenoma);
- under the chest.
In the first case, the structure of the growths is granular. Papillomas come in round and pointed shapes. When injured, they multiply quickly, capturing the entire nipple, areola and surrounding areas.
The intraductal type consists of single or group cystic growths. The size varies from 3–5 mm to several centimeters. The disease is identified by discharge from the nipple and treated surgically. Women with mastopathy after 40 years of age are most susceptible to the disease.
During pregnancy
While expecting a child, women undergo hormonal changes in their bodies, which reduce immunity and give impetus to the growth of tumors. Significant deformation of the skin is observed in the second and third trimester, so HPV symptoms appear more often during this period. In most cases, papillomas disappear after childbirth. During pregnancy, you should not take radical measures to remove growths if they do not bother you or become inflamed.
Recommendations for pregnant women:
- Examine your breasts and get tested for HPV before conceiving a child to exclude the possibility of transmission of infection during childbirth.
- Avoid tight clothing and underwear to avoid chafing and chafing of the skin.
- Dress according to the weather, protect yourself from infectious colds.
- Watch your weight. Avoid eating fatty and spicy foods.
Medicines are not used for treatment. The doctor selects a vitamin complex to maintain the body’s immune defense. Removal of growths is carried out in isolated cases, if there are significant indications. The procedure is performed without anesthesia in the first three months, since tumors grow faster in later stages.