What are the types of acne in children?
Acne on the face and head of newborns, as well as in school-age children, varies, but they can all be divided into four categories:
- Open acne. The rashes are inflamed and filled with pus, and usually appear on the surface of the skin.
- Closed acne. They are located deep in the skin layers. Such acne on the face of newborns occurs quite often and disappears on its own.
- Purulent rashes are acne in a child over 3 years of age that appears due to staphylococcus.
- Watery red pimples in children about 7 years old indicate streptococcus has entered the body.
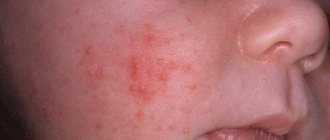
Open rashes are characterized by blisters that resemble herpes and chickenpox in appearance. Small red pimples in a 5-month-old baby are a sign of heat rash, and when the skin peels, it is atopic dermatitis.
Acne in babies
Blackheads and acne in babies, caused by blockage of the sebaceous glands, usually appear on the chin and cheeks (singly or in a group). There are no effective means of combating such pimples on the face and head of newborns, so it is better to wait until they disappear on their own (this will not affect the child’s health).
White dots on the nose of an infant in the first weeks of life will soon disappear on their own
Sometimes in the second or third week after birth, small reddish pimples appear on the neck and back of babies. This is the result of the formation of the hormonal background of a small organism, so the neoplasms will go away on their own.
Often, acne in a 9-month-old child or even younger appears due to allergic reactions to certain irritants:
- improper nutrition of a nursing mother;
- plant pollen;
- pets, etc.
We have already talked about heat rash above, but you also need to remember that it does not appear immediately on the face, but forms first on the neck (this is the main sign by which pediatricians diagnose heat rash).
The next common cause of acne in a child under 7 months is dysbacteriosis, which is easily diagnosed: the baby becomes restless, colic appears and stool is disrupted.
... but if your child has pimples and his cheeks are red, the cause may be a food allergy
Why might a rash appear on a child's forehead?
If a child has a rash on the forehead, this symptom can be either physiological, for example, associated with an allergic reaction of the body, or pathological, that is, arising against the background of the development of a specific disease. It is on the basis of what source provoked such rashes that their most effective treatment is determined.
Why rashes appear: physiological and pathological sources
Often the cause of a physiological rash on a child’s forehead is an allergic reaction to a certain external irritant. For example, it could be:
- any food product (nuts, apricots, chocolate, oranges, etc.);
- pet hair;
- synthetic fabric for casual wear;
- any cosmetic product (cream, gel, lotion, etc.);
- detergent;
- medicinal product, including antiseptics;
- plant pollen;
- No less rarely, children develop allergies to sunlight, wind or cold;
- a bite of an insect.
Rash on forehead
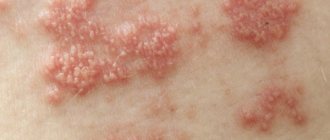
In such cases, small pimples appear, and less often, blisters, the contents of which are liquid. After opening them independently, symptoms of irritation on the skin are observed, namely, redness and itching.
Also, the skin on the forehead may peel, swell, and acne, spots, and blisters often form on it, which indirectly indicates the development of contact dermatitis, eczema, urticaria, neurodermatitis and other diseases.
Other sources of rashes on the skin of the forehead include:
- the development of a disease of one of the organs such as the liver, gallbladder, pancreas;
- pathologies of rheumatoid etiology;
- hormonal imbalances;
- endocrine diseases;
- pathologies of the digestive tract;
- helminths present in the body; skin diseases;
- low-quality products that the child eats.
As for newborns, rashes on the forehead often occur for physiological reasons. For example, one of these is the individual reaction of the body to the consumed formula or breast milk. Due to the fact that during lactation all the vitamins and microelements contained in the food consumed by the mother are transferred to the child, her diet should be complete and healthy. At best, a woman should adhere to a certain diet:
- with the exception of fatty, fried, salted, smoked foods;
- with limited consumption of allergic foods: chocolate, citrus fruits, red vegetables and fruits, nuts, sweets, condensed milk, honey, etc.
It is also important to introduce complementary foods correctly, starting with a small volume of a particular product, gradually increasing if an allergic reaction is not observed.
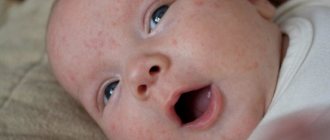
Erythema toxicum
Erythema toxicum in a newborn
The disease can have both toxic and physiological etiology. If the latter form of pathology is not treated in a timely manner, erythema can become toxic. Often this occurs as a primary disease, which occurs against the background of excessive production of specific substances in the body - transmitters of allergic reactions. This process, in turn, has the following etiology:
- occurs after the mother suffered toxicosis during pregnancy;
- develops as a result of a woman taking medications during pregnancy;
- hereditary predisposition is an equally rare provoking factor;
- harmful professional activity that the pregnant woman was engaged in;
- the mother has diabetes mellitus, obesity, ovarian or thyroid pathologies;
- if the baby was infected during the prenatal period or was exposed to hypoxia.
The development of toxic erythema can be suspected by such signs as slightly compacted red spots on the forehead, as well as in other areas of the body, in the center of which there are yellow tubercles. Itching syndrome also occurs. The child becomes restless. Most often, erythema toxicum occurs in children who are breastfed.
As such, treatment of the disease is not currently provided, because erythema of a physiological and toxic nature can go away on its own without causing the formation of scars. To quickly stop the process, it is recommended to follow some rules:
- Daily bathing of the child (a decoction of string, chamomile, and potassium permanganate can be added to the baths).
- Frequent change of clothes and bed linen.
- Elimination of overheating.
- Systematic air baths.
- Use baby cream if the skin becomes flaky.
In case of protracted and complicated course of the disease, drug therapy is prescribed, namely the use of antihistamines, vitamin preparations, as well as drugs that help maintain intestinal microflora.
Sweating
Taking into account the fact that the skin of the face is especially delicate, heat rash often occurs in this area. The reason for this is excessive insulation of the child’s head. In addition to the forehead, the rash can also appear on the cheeks, as well as the chin, neck, and other parts of the body.
Prickly heat in infants
If the heat rash has spread to small areas, for example, only on the forehead, treatment can be limited to folk remedies, for example, herbs or powder. The following decoctions and infusions can be added to baths when bathing:
- From nut leaves. The product is prepared as follows: pour 3 chalked leaves with a glass of boiling water, cover with a lid and leave to infuse for an hour. After filtering, the finished product can be used to add to baths.
- From oak bark. 50 g of bark is poured into a glass of boiling water and brewed for half an hour, after which it is filtered and used for its intended purpose.
- From bay leaves and tea. Place bay leaves (5 pcs.) and one tablespoon of black tea in a saucepan of boiling water (3 liters), and simmer for 20 minutes. After removing from heat and cooling, the product can be added to baths.
No less effective is powder, which has a drying and soothing effect. If these do not help get rid of prickly heat, the doctor may prescribe medications, for example, the following:
- Zelenka and Fukortsin are drugs that are used to cauterize individual, most inflamed areas.
- Sintomycin ointment, which fights purulent blisters.
- Boric acid, which has a drying effect.
- Depanthenol, which has a restorative effect.
- Zinc ointment, which helps eliminate the inflammatory process and dry out the blisters.
In the event that the miliaria is present on the skin together with a bacterial infection of the latter, the use of antibiotics and antihistamines is prescribed.
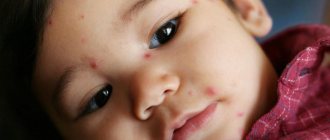
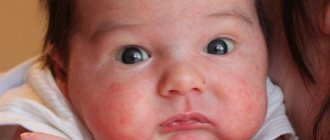
Newborn acne
Symptoms in this case are expressed in the appearance of a small red rash. In the middle of such a pimple, a white purulent dot is localized. In appearance, newborn acne resembles teenage acne. The forehead is not the only possible location for the rash, because it can also appear in areas such as the cheeks, nose, head, ears, neck, and back. As such, the rash does not bring discomfort to the baby. There is no pruritic syndrome.
Acne
The erroneous opinion of many parents is that the cause of acne is improper child care and poor hygiene, but the main source of this phenomenon is considered to be an excess of maternal hormones in the blood of the newborn or inadequate functioning of the sebaceous glands. Such rashes are not contagious, are not transmitted from one child to another, and are not considered infectious or allergic.
There is no treatment for acne as such. Doctors do not recommend using brilliant green, Fukortsin, Chlorophyllipt, potassium permanganate or any other antiseptics to eliminate the rash. In this case, it would be advisable to simply wipe the affected area with a decoction of folk remedies such as string and chamomile. It is also necessary to ensure that the skin is always dry and clean. To dry pimples faster, you can purchase Bepanten ointment, which must be used to treat the corresponding areas.
Important! Doctors strictly prohibit squeezing out purulent pimples on your own. In this case, it will not be possible to get rid of the pathology faster, but you may end up with an intensification of the inflammation process, thereby causing a secondary infection. In those places where the pimples were localized, scars will remain.
The disappearance of acne in newborns is observed only after the mother’s hormones are completely removed from the body and the baby’s hormonal levels return to normal. The duration of such periods can vary from 2 weeks to 2 months, because each body is individual and reacts differently to such processes. After the acne disappears on its own, there will be no traces left on the skin.
Even though the rash does not require treatment, it is still necessary to visit your pediatrician for a follow-up examination. Only a doctor will be able to correctly determine the nature of the rash on the forehead of a baby and, if newborn acne occurs, give the necessary recommendations for caring for the skin. Differential diagnosis is carried out with a pathological condition such as allergies, which requires specific therapy. The main differences between acne and allergies are:
- Appearance of the rash. When an allergic reaction occurs on the skin, large red spots or a small red rash appear. There is no purulent crown on the pimple. In the case of acne, pimples appear that are red on the bottom and white on the top.
- Presence of itching syndrome. An allergic reaction is manifested by itching, which becomes a cause of anxiety for the baby. Acne does not bother the child in any way, because the rash does not itch.
- Area of localization of the rash. Acne usually occurs on the face and scalp. Allergic rashes can form in any part of the body.
- Symptoms of intoxication. Acne of newborns, apart from the characteristic rash, does not manifest itself in any way. In the case of allergies, disruption of the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract may occur with the occurrence of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. The cheeks may also turn red.
As has already been clarified, rashes on a child’s forehead are not always a physiological phenomenon that does not require therapy. In any case, if pimples appear in such an area, it is recommended to visit a specialist who will find out their nature and prescribe the most effective treatment (if necessary).
Dr. Komarovsky is available about childhood rash:
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.
♦ Category: Children's diseases.
kakzdravie.com
Drug treatment of acne in children
Do not buy facial acne products from pharmacies for children 9 years of age and younger without a prescription if they are intended for teenagers. Such ointments and creams are too harsh on the sensitive skin of babies.
To treat acne in a child under 9 years of age, use only what your doctor prescribes. For example, this could be a light 1% hydrocortisone cream or a silver colloidal ion solution.
Severe forms of acne in children under 8 years of age may be accompanied by itching, dryness and soreness of the skin. The above-mentioned hydrocortisone, which slows down the production of fat by the sebaceous glands, allows it to be calmed down.
Silver colloidal ion solution has a milder effect compared to hydrocortisone, but effectively fights bacteria growing in skin pores and relieves itching.
When acne on a child’s body, similar to mosquito bites, causes discomfort and pain and does not go away within a month, doctors prescribe mild ointments against acne. Retinoid cream consisting of tazarotene, adapalene and tretinoin is highly effective.
Pimples on a child’s face – causes, treatment and prevention
11.10.2016
As it turns out, pimples on the face of an infant are a fairly common phenomenon that causes great concern for many parents. Such rashes can be red, white, black, small or large in size, single or multiple. What is the cause of acne on a child’s face and what should be done when it appears? You will learn about this from this article.
Causes of rashes on the face of infants
The most common reasons that newborns develop a small rash on the face include the following factors:
- Hormonal changes.
- Allergic reactions.
- Climate change.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Prickly heat.
Hormonal changes. This condition does not require special treatment and, as a rule, goes away on its own within three to four, sometimes up to eight to nine, months of the baby’s life. The rash occurs suddenly due to hormonal changes, but it does not cause discomfort to the baby.
Allergic reactions. Small pimples on the face of a month-old baby may appear due to an allergic reaction. If you are breastfeeding, you need to pay special attention to your diet. When you see at least one pimple on your baby’s face, try to remember what exactly you ate before and, if necessary, change your diet. In a bottle-fed baby, rashes may occur when choosing the wrong formula. Recently, allergies have increasingly occurred to creams, powders, washing powders and various cosmetics.
Climate change. In children under the age of nine to ten months, acne on the face may appear when climate conditions change, as well as after a long walk during severe frost.
Dysbacteriosis. The next common cause of pimples on the face of a month-old baby can be dysbacteriosis. In this case, the baby will experience frequent (up to nine to ten times a day) and infrequent bowel movements, and possibly restless behavior. This problem requires targeted therapy to help normalize the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
Prickly heat. If the skin at the site of the rash turns red, then most likely it is prickly heat. As a rule, it is observed on the face, in the area of the neck folds, on the arms and back. Often, prickly heat appears in the hot season in babies under the age of five to seven months, while they still move little.
Diseases that cause pimples to appear on a child’s face
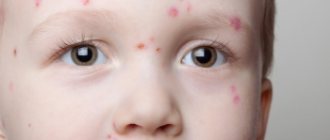
Rashes may appear on the baby’s face, which indicate the presence of certain ailments. These include:
- Vesiculopustulosis. Watery white pimples on a child's face may be a symptom of this disease. They occur throughout the body and greatly disturb the baby. The cause of their appearance is considered to be staphylococcal bacillus. Such rashes are treated with brilliant green and require special treatment.
- Measles, scarlet fever or rubella. Such childhood diseases are also accompanied by a rash on the face and other parts of the body.
- Furunculosis. Small red pimples with a white tip are a symptom of furunculosis.
- Herpes or chickenpox are infectious diseases accompanied by the appearance of watery, vesicular pimples on a child’s face. In childhood they are tolerated without any complications, but after eight to ten years the likelihood of a severe form of the disease increases significantly.
We do not recommend self-medication for these diseases. The child needs complex medications, which can only be prescribed by an experienced pediatrician, so we advise you to immediately call a doctor at home or take the patient to the nearest medical center for medical care.
Treatment of pimples on an infant's face
In most cases, rashes in infants disappear on their own over time, without treatment. But we must not forget that the skin of children, especially newborns, is vulnerable to various infections. Therefore, we remind you once again that if you notice even a minor rash, consult a doctor immediately. He will examine the skin rashes - red, white, black, watery - and then prescribe treatment.
However, there are still general recommendations that will help you treat acne on a child’s face:
- During bathing, you need to thoroughly wash off any cosmetics from your baby. When performing water procedures on a newborn, we do not recommend using soap frequently (2-3 times a week is enough). Children older than one year can be bathed with soap more often - up to 5-6 times.
- It is advisable to wash small children with boiled water at least two to four times during the day.
- For bathing infants, we recommend using infusions or decoctions of herbs (chamomile, string) or a weak solution of manganese. This recommendation will be especially relevant when prickly heat appears.
- All kinds of dirt and food debris on the child’s face must be carefully removed using special wet wipes (not alcohol wipes). This will help prevent the development and spread of infection.
We also note that pimples on a child’s face cannot be treated with gels, creams and other products that are intended for adults. It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out blisters that appear.
Preventing acne in children
To prevent pimples from appearing on a child’s face, parents need to know some rules for preventing rashes. For example, try to give your baby air baths as often as possible (at least once before water procedures and twice when changing a diaper). Also pay attention to your child's nutrition. If the baby eats exclusively mother's milk, then she needs to monitor her diet and the quality of the products she eats.
If formula is used to feed a small child, it should be chosen together with a pediatrician, because just one component in its composition can provoke an unwanted allergic reaction.
When washing dishes and washing children's clothes, use only special hypoallergenic products. Usually the age from which they are allowed to be used is written on the packaging.
Rate this article:
Home remedies for acne in children
To get rid of acne in children under 9 years of age, mild baby soap can be used to wash the baby’s face. You should not do this more than once a day, since excessive washing will cause irritation on the skin, and the work of the sebaceous glands will intensify, and the situation will worsen.
Do not use greasy creams on areas where your child has acne. Despite the apparent dryness of the skin, adding oil will make the sebaceous glands even more active, and the acne will become inflamed and there will be more of them.
When treating acne in children, you should never squeeze them, as this will not give a positive result, but will only make it worse. The skin becomes irritated when pimples are squeezed out, and the glands will begin to produce even more fat - the number of pimples will inevitably increase.
Be patient, as acne on the skin of children under 7-9 years of age goes away in most cases without outside intervention within a few weeks. If the acne-affected areas look very bad and your child feels discomfort, go to the doctor, who will prescribe specialized treatment.