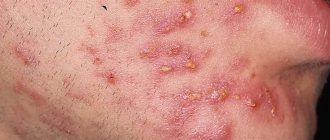
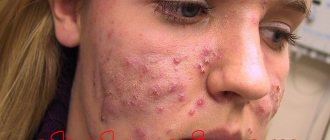
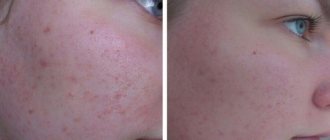
Pimples and blackheads
It is believed that acne is a problem for teenagers who, due to the rampage of testosterone, suffer from oily skin and sebum produced in excess. Sebum (sebum) moisturizes the skin, but if there is too much of it (so that the fat does not disappear after washing with water), the sebum mixes with dead skin particles, forming a kind of crust. A new portion of sebaceous secretion cannot be released - and a yellowish sebaceous plug appears in the pore. Why does it turn black? Under the influence of oxygen.
If you thought that acne was more unpleasant than pimples, you were wrong: bacteria multiply in the sebaceous plug and provoke painful inflammation on the surface of the skin - pimples and even abscesses.
Those with oily skin have enlarged pores and increased sebum secretion. Hence the risk of acne and inflammation. This does not mean that people with dry skin are immune from unpleasant skin conditions. Acne appears on some areas of the face - on the forehead, chin, and rarely on the neck.
Puberty is over, but your face still looks like the surface of the moon? Perhaps it is due to the stimulation of testosterone by other triggers: problems with the digestive tract, kidney disease, thyroid disorders and disruptions in the reproductive system.
Acne
Main goals
- Prevention of new comedones . Includes proper care for problem skin and measures for the overall health of the body.
- Removal of existing comedones . It is carried out using comedolytic drugs and comedo extractors at home or in beauty salons.
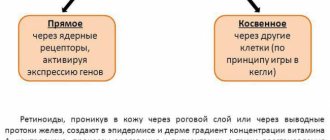
- Reducing sebum secretion . Achieving a noticeable clinical effect is possible when secretion is reduced by 30 percent or more. Drugs of the retinoid group, hormones - estrogens, antiandrogens - are used.
- Relieving the inflammatory process and preventing its spread . It is achieved by using antibacterial drugs externally and internally.
- Reducing the cosmetic disadvantages of scarring . Produced by dermabrasion, laser therapy, cryotherapy.
Complex therapy
- Completing a course of procedures in a beauty salon plus active home care with recommended medications.
- Combined treatment with external agents and drugs with systemic effects (affecting the entire body).
- The use of drugs that affect the entire chain of the mechanism of acne development (hypersecretion of sebum, increased keratinization of hair follicles, proliferation of microbes, inflammation).
- The presence of chronic processes in the body (gynecological, endocrine, gastrointestinal diseases, foci of chronic infection) can interfere with acne treatment and reduce its effectiveness. Therefore, in parallel with the treatment of acne, treatment of concomitant pathologies should be carried out.
A large number of external drugs are currently used in the treatment of acne.
External preparations in the treatment of acne
Benzoyl peroxide has a strong keratolytic and whitening effect, due to which it has been used in dermatology for over 20 years to treat ichthyosis and skin pigmentation. Its ability to “dissolve” dead skin tissue and its pronounced antibacterial effect make it possible to use benzoyl peroxide for the treatment of mild to moderate acne. The combination of benzoyl peroxide with antibiotics, azole compounds, and sulfur preparations in combination preparations significantly increases the effectiveness of its use.
Azelaic acid has a pronounced anti-comedogenic, antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effect, but does not affect the production of sebum.
Tretinoin is a synthetic retinoid, an analogue of vitamin A. It is used externally in the treatment of acne if benzoyl peroxide is ineffective or individual intolerance. Eliminates existing comedones and prevents the appearance of new ones by normalizing the processes of keratinization of the epithelium and reducing the secretion of sebum.
Benzoyl peroxide, azelaic acid and tretinoin
are first-line drugs in the treatment of acne. They are effective with long-term use (3 months or more). Sometimes their use causes skin irritation, which is usually eliminated by reducing the frequency of application to the skin or reducing the concentration. When treating acne with these drugs, the simultaneous use of two or more drugs, as well as temperature changes and active insolation, is unacceptable.
Antibiotics for external use . The external use of antibiotics in the treatment of acne is resorted to in cases of lack of effect from treatment with first-line drugs or combination therapy in the treatment of complicated forms of the disease. The disadvantages of treating acne with antibiotics include the development of an addictive effect and insensitivity of propionic bacteria.
Erythromycin is considered one of the most effective antibiotics against acne. The high antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity of erythromycin is even more pronounced in its combination with zinc. Zinc, in turn, reduces the secretion of the sebaceous glands and loosens the pores, facilitating the local action of erythromycin.
Clindamycin is not addictive to skin microflora and is highly active against propionibacteria and staphylococci.
Systemic antibiotics are used orally in combination with local therapy for moderate acne. Of the tetracycline group antibiotics, minocycline or doxycycline are most often used due to their high antimicrobial activity, rapid absorption and intensive accumulation in the sebaceous glands. Less commonly used in the treatment of acne are clindamycin, erythromycin and drugs of the sulfonamide group.
Treatment of acne with systemic antibiotics involves long-term (at least a month) use. During this period, intestinal and vaginal dysbiosis and persistent adaptation of skin microflora may develop. Other complications from taking antibiotics include ulcerative lesions of the esophagus, stomach ulcers, softening of the nail plates (onycholysis), the appearance of hyperpigmentation on the skin and nails, etc.
The interaction of antibiotics with other drugs should be taken into account so that their effect does not overlap. If the effect of antibiotic treatment is insignificant or prolonged, the issue of changing the drug or prescribing retinoid drugs should be considered.
Antiandrogens. In the treatment of acne in women, a combination of external treatment and hormonal contraceptives containing antiandrogens or an estrogen profile is possible. Severe forms of acne require combined (external and general) treatment.
The absence of a clinical effect from treatment for more than 3 months is one of the indications for the use of Isotretinoin, a synthetic analogue of vitamin A. The advantage of this drug is its effect on all mechanisms of acne (increased sebum secretion, follicular hyperkeratosis, proliferation of microorganisms, inflammation). The course of treatment with isotretinoin ranges from 4 months to a year.
Hardware treatment methods for acne are considered additional and are applicable only at the comedonal stage. These include massage and facial cleansing, superficial cryotherapy, laser therapy, darsonvalization, etc.
Surgical procedures are not widely used in the treatment of acne, as they lead to the formation of rough scars. In the treatment of abscess forms of acne, it is possible to inject purulent foci with corticosteroid drugs.
From the experience of complex acne treatment
As practice shows, the best results are achieved by an integrated approach to treating acne. Since it was previously noted that doctors of many specialties are called upon to solve the problem of acne in the community, the observed patients with acne had to undergo a comprehensive examination by a dermatologist, gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, and gynecologist. The choice of methods and duration of treatment was determined by the severity and severity of acne, taking into account individual characteristics.
On average, the course of acne treatment was 7-8 months. At the first stage, it included external treatment with azelaic acid and metronidazole gel, as well as doxycycline. Additionally, cryomassage and darsonvalization were prescribed. A month later, the course included chemical peeling with fruit acids in gradually increasing doses. At the same time, correction of identified disorders in the endocrine, reproductive, and digestive systems was carried out. A month later, an interim assessment of the effectiveness of acne treatment showed a stable trend towards improvement: the disappearance of pustular rashes was noted in 89%, a reduction in the number of comedones - in 71.2% of patients, and the process of sebum secretion decreased. Subsequently, stable remission was observed.
Acne treatment prognosis
When predicting the long-term results of acne, the following points should be considered:
- Acne is a chronic, intractable disease, since hereditary predisposition or provoking factors can cause a new exacerbation, even if the disease has not recurred for several years. However, knowing the reasons that provoke a new wave of acne, you can clearly control and quickly relieve exacerbations of acne, prevent the development of gross cicatricial changes in the skin (post-acne) and the formation of persistent cosmetic defects.
- If the disease has already occurred, then the changes in the skin are irreversible, and it will not be possible to achieve its previous ideal state.
- A full course of acne treatment is a long process, taking 4 months or more.
- Treatment of acne can occur with exacerbations of the process, especially in the first months, when the mechanisms of disease development are suppressed.
- It is necessary to carry out a full course of acne treatment, without interruptions, even if there is a noticeable improvement. Untreated acne can manifest itself with a new exacerbation at any time.
Despite the fact that adult acne is a disease that will accompany you throughout your life, you should not despair. A modern selection of methods and preparations for external and systemic use can significantly alleviate the course of acne, carry out timely prevention of its exacerbations, and avoid serious complications and destructive changes in the skin. Today, acne treatment is carried out at all stages of the disease, allowing one to achieve good cosmetic results and long-term remission.
Blackheads and acne
If acne is just a small thing, then acne is a real epidemic. People aged 21 to 30 suffer the most from this disease. In terms of symptoms, acne resembles acne, but it consists of entire islands of acne, after recovery of which deep scars are formed in the areas of inflammation - indentations in the relief of the dermis.
Initially, the cause of acne was considered to be hormonal imbalance and bad eating habits. But acne is a multifactorial skin disease that occurs under the influence of viruses in a pathogenic environment. Acne can appear against the background of gastritis, flu, food poisoning due to the active proliferation of harmful bacteria and weak immunity. Subcutaneous mites, fungi of the intestinal flora, staphylococci increase their number, distorting the pH of sebum, converting the acidic environment into an alkaline one. The mouth of the sebaceous gland is expanded and allows any infection into the dermis.
Four main factors cause acne:
- Excessive production of sebum (sebum);
- Hair follicles are clogged with oil and dead skin cells;
- Bacteria;
- Internal inflammation.
Pimples typically appear on the face, forehead, chest, upper back, and shoulders because these areas of the skin have the most oil glands. Hair follicles are connected to the sebaceous glands. The follicle wall may swell and cause whiteheads. Pimples are raised red spots with a white center that develop when blocked hair follicles become inflamed or infected with bacteria. Blockages and inflammation deep inside the hair follicles lead to the formation of cyst-like bumps under the surface of the skin.
Certain things can cause or worsen acne:
Hormonal changes . Androgens are hormones that increase in boys and girls during puberty and cause the sebaceous glands to enlarge and produce sebum. Hormonal changes in midlife, especially in women, can also lead to breakouts.
Some medications . Examples include medications containing corticosteroids, testosterone, or lithium.
Diet. Research shows that eating certain foods, including carbohydrate-rich foods like bread and chips, can make acne worse.
Stress . Stress does not cause acne, but if you already have acne, stress can make the situation worse.
Heredity. Unfortunately, if your parents had acne, then there is a high chance that you will also have the same problem.
Products with BHA acids are one of the ways to solve acne problems
How to treat acne - our advice
There are several things you can try at home to prevent and get rid of acne:
- Cleanse your skin daily with a gentle cleanser to remove excess oil and dirt without drying out your skin;
- Shampoo your hair regularly and keep it away from your face. If you use styling products, try not to get them on your face;
- Don't squeeze pimples, which spread bacteria;
- Avoid touching your face with dirty hands.
Dangerous consequences
Acne can turn into purulent boils, which are extremely painful and difficult to treat. Under no circumstances should you squeeze out blackheads and acne on your face. Think of a tube of toothpaste: you press in the middle and the contents are distributed both ways. Same with skin. Some of the sebum is squeezed out, but some penetrates even deeper inside.
Limit your use of cosmetics. Change sponges and treat brushes to prevent skin problems. Contact a cosmetologist if you suspect you have a rash. In case of acute inflammation, the skin is treated by a dermatologist, who may even prescribe antibiotics.
Your diet is of great importance. For example, in the case of a rash caused by candida fungus, dairy and fermented milk products are excluded from the menu.
Diagnosing acne is an important step towards treatment. Using tests, the doctor determines the reasons for the spread of the rash, prescribes cosmetic and medical preparations, but most importantly, helps eliminate inflammation without damaging the skin or leaving ugly marks on it.
The structure of human skin
It is the largest organ in the body and performs many functions. The first is a protective cover. The upper layers of the dermis protect all other cells from external factors. The second most important function is thermoregulation. With the help of many small pores that evaporate water, the human body does not overheat in extreme heat. And, of course, the skin allows us to sense the world around us tactilely. A person receives most of the information through the organs of hearing and vision. But a significant part is transmitted through the skin.
You might be interested in: What is a front sight? Features of applying permanent makeup
The thickness of the skin varies. It can be 0.1-4 mm in different parts of the body. The skin consists of three layers:
- Deep, which mostly consists of adipose tissue. This is a kind of “safety cushion” and “pantry” of nutrients.
- Average. It is very complicated. It contains hair follicles, sebaceous glands, nerve endings and much more.
- The upper one is the epidermis. This is a constantly renewed cover. The scales of the epidermis constantly die off and are replaced by new cells. In essence, a person “sheds” his skin, but not immediately, but gradually throughout his life.
Difference between blackheads and pimples
How to get rid of skin rashes? Treatment methods will depend on the form and stage of the disease. In fact, this is not a complete classification of skin rashes. They can differ in the degree of inflammation, the causative agents of the infection, the shape of the pimples and various specific reasons that cause their appearance. For example, a separate group of rashes includes inflammation in bodybuilders caused by taking certain drugs (steroid acne). There are inverse ones, the area of appearance of which is limited to the armpits, groin and abdomen. Or juvenile acne, which most dermatologists consider an absolutely normal phenomenon that goes away on its own after puberty.
So what is the difference between blackheads and pimples and how to treat them? In fact, they are practically the same thing. Pimples and blackheads are different stages of blockage of pores on the skin. In some people, this disease takes on relatively harmless forms, while in others it is complicated by concomitant infections.
Treatment
You may be interested in:What are hangnails - causes and treatment of hangnails on the hands
How do pimples differ from acne in terms of treatment? The difference is not so global. The fact is that on your own, without consulting a doctor, you can only try to get rid of comedones, milia, papules and single pustules. Everything else requires more serious drug therapy.
Acne and pimples can be treated using approximately the same medications. But in the first case, it is better to focus on products that cleanse and tighten pores, removing fat from the skin. And in the second case, the drugs must additionally have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory effects.