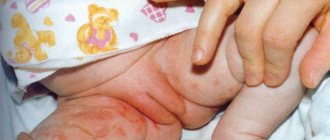
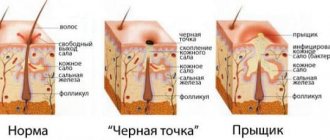
Initially, chancroid was common only in warm countries. Subsequently, the bacteria that causes the disease changed somewhat, and people began to travel more. As a result, the disease has become popular among our compatriots. In some cases, chancroid in men occurs without symptoms, which does not allow the disease to be diagnosed in time. Patients become latent carriers of the infection, actively spreading it among their sexual partners. How does chancroid manifest itself, is it possible to cure this disease and what complications can it lead to?
Syphilis on the lips
Signs of syphilitic infection in women appear mainly in the genital area, since the main method of transmission of the spirochete bacterium is considered to be unprotected sexual intercourse. However, recently, cases of infection entering the mucous membranes of the mouth have become more frequent. Above is a photo of what syphilis looks like in women, in which the symptoms of infection appear on the lips.
Ways of transmission of syphilis
Transmission of syphilis can occur when infected lesions (treponema bacteria) come into contact with the soft skin of the mucous membrane found inside the vagina, urethra, or abrasion during vaginal, oral, and anal sex. It spreads most easily in the first (primary) stage, as symptoms usually go unnoticed.
What does syphilis do to my body?
Syphilis affects the body in stages, each stage has its own symptoms. Previously, we published photos of syphilis at different stages.
Stage 1: initial stage
Sores appear in the genital area (penis or vagina) or mouth within ten days to 3 months after infection.
The sores are usually hard, round, small and painless; it is the painlessness of the ulcer that distinguishes it from other diseases such as stomatitis.
The ulcers should go away on their own, but the bacteria remain in the body (without treatment), and after a few months the disease enters the secondary stage.
Stage 2: secondary stage
If syphilis is not treated, a person will develop a rash photo.
The rash appears as rough, red or reddish-brown spots that are usually not itchy and are located on the palms of the hands and the bottom of the legs.
The person may have rashes on other parts of the body or may have other symptoms such as fever, swollen glands, or hair loss.
Stage 3: hidden stage
If a person does not receive treatment, the infection will remain in his body even if there are no symptoms. The infection is called "latent".
This “latent” stage can last up to 30 years, while affecting human organs every day.
Stage 4: late stage
If left untreated, the bacteria will attack other parts of the body.
Syphilis can affect the brain, heart, eyes, bones, liver, blood vessels, nerves and joints.
Important questions and answers about syphilis that everyone should know.
Syphilis in women photos on the lips
To know how syphilis manifests itself in women, photos, you should take into account the fact that a syphilitic infection today can be transmitted by kissing or oral sex with an infected person. When syphilis is transmitted through a kiss or oral contact, syphilitic chancre appears on the lips and takes the form of cracks or small wounds with a hard bottom.
Varieties of chancre
Soft chancre sometimes presents in its course and clinical picture significant deviations from the just described norm. The benign variety is the so-called diphtheritic chancre. An ulcer that has reached a certain size in the manner described is covered with a firmly seated whitish-gray coating and often remains at this stage for a long time without changes, without increasing. After more or less time, the plaque disappears, clean granulations appear, and the ulcer heals.
Gangrenous or phagedenic chancroid, which occurs almost exclusively in men, is more severe in nature. The bottom and edges of the ulcer turn into a putrid, dirty brown-black mass, the decay progresses rapidly, so that extensive ulcers are obtained that can destroy the foreskin and glans penis over a large area, spread between the cavernous bodies of the penis, leading to partial separation of the glans penis, to exposure of the cavernous bodies of the urethra and penis, to corrosion of the walls of blood vessels and to severe bleeding.
An equally severe variety is serpiginous chancroid. In this form, the ulcerative decay first goes much deeper, penetrating through the entire skin and exposing the subcutaneous tissue, fascia, muscles, but at the same time it has a greater tendency to spread further, so that it passes from the initially affected penis to the pubis, inguinal folds, scrotum , lower abdomen to the navel, on the thighs and even on the lower legs. As a result, extensive and very painful ulcers are obtained, the bottom of which is exposed, often as if dissected soft parts, and the edges are formed by purple, finely jagged, undermined skin. Further spread of the process usually occurs in such a way that near the edge, separated from it for the most part by a bridge of purple skin, 1-2 mm wide, but communicating underneath with the ulcer, an ulcer is formed, the size of a pinhead, which, quickly growing, destroys the bridge , merges with a large ulcer and thereby contributes to its enlargement. The formation of such numerous small ulcers along the entire edge explains its jagged, tortuous shape. Sometimes entire parts of the edge of the ulcer are destroyed. Sometimes the process creeps further in only one direction, while on the other side the edge flattens and scarring occurs.
Syphilis on the legs
IT IS IMPORTANT TO KNOW!
In the question of what syphilis looks like in women in the photo, it is generally accepted that chancre occurs mainly on the genitals. However, in rare cases of transmission of infection or development of the disease, the primary signs of female syphilis photo may appear on the feet and toes.
Symptoms and causes
The phenomenon has pronounced symptoms, which depend on the external varieties of its manifestation.
By some characteristic features, this formation can be distinguished from other types of sexually transmitted diseases:
- The hardness of the surface is explained by the presence of a cartilaginous base, which can be clearly felt when pressing on the edges of this formation.
- The chancre has clearly defined edges; they rise slightly above the entire tip of the wound.
- The hard formation is adjacent to areas of the skin surface, which, without infection penetrating into these areas, are not subject to inflammation and do not ache.
- In the internal space of the chancre, it is not stained bright red, except in situations of obvious infection.
- There is a smooth film on the upper surface of the wound, which can release a certain amount of liquid when pressure is applied to it.
- Usually it is not accompanied by sensations of pain, there is no burning or itching, and there are no provocations of attacks of fever or increased temperature.
As a rule, the cause of chancre in women is transmission of infection through sexual intercourse.
Solid
The formation is characterized by the presence of an outer hard shell and a dense central part. The photo clearly shows its round shape and dimensions up to 3 cm in diameter.
When pressing, there may be pain, but often there is no release of fluid from it.
Treatment is prescribed depending on the external manifestations and mainly involves the use of local medications. It is located mainly in the vaginal and pubic area.
Symptoms of syphilis in men
Each stage of syphilis has its own manifestations. The phase of the disease can be determined by the nature of the skin formations.
First signs
After the incubation period, a subcutaneous hard swelling appears at the site of penetration of the treponema, from which a dense ulcer quite quickly forms - primary syphiloma, or chancre. In 30% of cases there are several syphilomas. Nearby lymph nodes enlarge and lymphadenopathy develops. The symptom is due to the fact that treponema multiplies only in the lymph.
Dermatovenerologist Lenkin Sergey Gennadievich more about the first manifestations of syphilis
What does syphilis look like at different stages?
Below we have provided photos of skin defects that are caused by Treponema pallidum at each stage of the disease.
Development of syphilis
Primary syphilis
Primary syphilis is manifested by the appearance of hard chancre. They can be the size of a millet grain or gigantic, reaching several centimeters in diameter. Small chancrees usually appear in the area of the frenulum of the penis, while giant ones are characteristic of the extrasexual type of infection and are localized on the pubis, thighs, and chin.
Photo:
- The first symptom of male syphilis is a hard, painless lump on the penis at the site of treponema penetration - https://prntscr.com/vlaedp.
- Primary syphiloma on the penis and on the head - https://prntscr.com/vlaf4v, https://prntscr.com/vlafb3, https://prntscr.com/vlafl8.
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the groin in the initial form of syphilis - https://prntscr.com/vlafx2.
- Chancre on the lips (looks like mature herpes) - https://prntscr.com/vlag3n.
- Chancre on the lip - https://prntscr.com/vlagbk.
- Chancroid felon on the fingers – https://prntscr.com/vlagix.
Secondary syphilis
If measures are not taken, then in a few weeks the chancre will heal on its own, and the treponema will multiply throughout the body - syphilis will go into a secondary phase, called generalized. A characteristic sign will be the appearance of a rash, which is often accompanied by additional symptoms. Most often these are fever, muscle and joint pain, swollen lymph nodes, headache, and weakness. The infection is present in all biological fluids; humans are highly contagious. The rash is painless and does not itch. It is usually localized on the palms, soles of the feet and body.
Types of secondary syphilis:
- Fresh, which develops immediately after the primary. The rashes usually disappear after 1.5 months.
- Hidden form. This is the next stage after fresh syphilis.
- Secondary relapse. It appears after a few years. The rash upon relapse is no longer so abundant. Usually takes the form of a ring, garland or arc. The structure of the rashes varies: papules, nodules, pustules, spots, vesicles. Below are photos of some of them.
When secondary syphilis occurs and how it manifests itself, says urologist Sergei Gennadievich Lenkin
This is shocking:
Syphilitic rash and seizures - https://prntscr.com/vlaias.
Papules on the palate and tongue, rash on the back - https://prntscr.com/vlaiwp.
Papular syphilis – https://prntscr.com/vlaj4n.
Syphilitic overgrown papules on the pubis and penis - https://prntscr.com/vlajd4.
Malignant formations in secondary syphilis: papules, rupees and ecthymas - https://prntscr.com/vlajo5.
The secondary phase of syphilis is also characterized by the appearance of weeping mucous areas in the area of the anus, genitals, and mouth. Grayish plaques appear in the armpits, on the inner thighs, under the breasts, and in the navel - Lata condylomas. Hair loss may occur in certain areas of the head.
Small focal alopecia with syphilis - https://prntscr.com/vlajyz.
Tertiary syphilis
In the absence of adequate treatment, syphilis progresses to the tertiary phase immediately or after 3-5 years. Movable hard tubercles first appear on the skin or mucous membranes. Then they begin to transform healthy cells around themselves, fuse with tissues, grow and deepen. As a result, granulomas develop - tertiary syphilides, also known as gummas. Inside there is a viscous transparent liquid with an unpleasant odor, and at the bottom there is a yellow-green rod. Formations can be single or grouped into several pieces.
The development of gumma lasts from 4 to 6 months, after which syphilis goes into remission with periodic relapses. The latter arise due to local activation of infection.
The contents of gummas contain much less treponemes than in ulcers that appear at the secondary stage, but for the body these formations are more aggressive. With weak immunity, they enlarge, disintegrate, compress surrounding tissues and destroy them. Such gummas are called mutilating. If the immune system suppresses the activity of treponemas, the gumma heals, but in its place a deep, disfiguring scar forms.
- Gumma on the finger – https://prntscr.com/vlal19.
- Gumma on the face – https://prntscr.com/vlalff.
- Disintegration of gumma on the nose - https://prntscr.com/vlaloc.
- Gumma on the lower leg – https://prntscr.com/vlalym.
- Gummous infiltration – https://prntscr.com/vlam76.
- Scarring gumma - https://prntscr.com/vlamfk.
How does tertiary syphilis develop?
Along with gummas, tertiary syphilis can cause tuberculate syphilides. Groups of dense, painless bumps form under the skin and mucous membranes, usually more than 10 of them. After a few weeks or months, they disappear, leaving behind dark scars and spots. Locations: forehead, nose, back, elbow bends.
Tuberous syphilides - https://prntscr.com/vlancc.
Mosaic scars after healing - https://prntscr.com/vlasfg.
There are also so-called creeping syphilides, also known as serpening ones. They are pockets of several formations. Those in the center heal or disintegrate, and new ones appear at the edges. The process can take several years.
Creeping syphilides - https://prntscr.com/vlat1z.
Sometimes syphilides appear in the form of a platform, as in the photo https://prntscr.com/vlat9w.
Vegetating syphilide - https://prntscr.com/vlathk.
If left untreated, after 10-20 years, syphilis will enter the fourth stage, at which the treponema will reach the central nervous system. This is fraught with tabes dorsalis and progressive paralysis.
Congenital syphilis
Congenital syphilis is also called transplacental syphilis because it is transmitted to the child through the placenta during fetal development. About 90% of babies die without treatment. Provided that syphilis is treated promptly and adequately before the 19th week, the fetus will not be harmed.
Congenital syphilis can be early, late and latent. In the latter case, the child has no symptoms, but the disease can manifest itself in adulthood.
Transfusion syphilis
Syphilis can be contracted through a blood transfusion or through a needle containing the blood of an infected person. In some cases, with this form of transmission, primary syphilides are absent. After 11 weeks, secondary ulcers appear. This type of syphilis is also called headless or transmissible syphilis.
Chronic syphilis
Chronic syphilis occurs due to insufficient or absent treatment. Treponemas, under the influence of negative factors for them, are transformed into cysts or L-forms. In this form, they are protected from the immune system and antibiotics, and can remain in the lymph nodes or cerebrospinal fluid for a long time. L-forms are not determined by diagnostic methods; tests for syphilis will be negative.
When the immune system is weakened, the infection resumes activity, and syphilis relapses. It may be serological or clinical. In the first case, the activation of the infection is determined on the basis of tests; there are no typical symptoms of syphilis. The clinical form may begin with a latent phase, then a rash appears.
How to treat syphilis in men
Treponemas do not mutate and remain sensitive to penicillin, therefore penicillin drugs are used to treat all stages of syphilis. If the patient is allergic to penicillin, then it is replaced with cephalosporins or tetracyclines, but they are less reliable. The course of treatment for the initial stage of syphilis can take 2-3 months. If efficiency is low, it is repeated.
In outpatient settings, long-acting penicillin drugs called durants are used: “Retarpen”, “Bicillin-1”, “Extencillin”. The regimen also includes the combination drugs Bicillin-3 and Bicillin-5. Durant penicillins are administered intramuscularly once at a dose of 2.4 million units. After this, the drug will remain in the blood for 2-3 weeks. “Retarpen”, “Exensillin” are administered once a week, 3 injections per course. "Bicillin-1" - once every 5 days. Combined drugs are injected 2 times a week.
A few hours after the first administration of the medication, a rash may appear, the temperature may rise, muscle pain, headaches, and vomiting may occur. These are signs of mass death of treponemes. Symptoms are relieved with aspirin.
If you are intolerant to penicillins, high doses of Doxycycline, Sumamed, and Erythromycin are prescribed. Treatment lasts from 14 to 30 days.
In parallel with antibiotics, immunotherapy is used for syphilis:
- Pyrogens: "Pyrogenal".
- Interferons: "Amiksin".
- Stimulators of lymphocytes and phagocytes: “Tactivin”, “Timalin”, “Timogen”.
- Phagocytosis stimulants: “Likopid”, “Polyoxidonium”, “Galavit”.
Auxiliary therapy:
- Vitamin therapy: vitamins B, C.
- Adaptogens: extract of eleutherococcus, Rhodiola rosea, ginseng.
- Biostimulants: “Polybiolin”, “Plasmol”.
Practicing dermatovenerologist Lenkin Sergey Gennadievich talks about methods of treating syphilis
Physiotherapeutic methods include inductothermy, magnetic and electric wave therapy, and laser exposure.
Large syphilides are treated with chlorhexidine, a solution of dimexide with penicillin. Lotions are applied until the scarring is complete.
At the end of the course of treatment, the man is registered. If serological tests are negative, the observation period is 1 year. Control is carried out through RPR testing.
For inpatient treatment of recurrent syphilis, injections of sodium benzylpenicillin, 1 million units, are given every 4 hours. for 20 days. On an outpatient basis, procaine-penicillin is administered once a day, 1.2 million units. If the patient is allergic, inject ceftriaxone 1 g once a day for 10 days.
All sexual partners of an infected person should be tested for syphilis. Treatment is necessary even with negative tests if contact occurred within 3 months before diagnosis.
Complications
With timely treatment of complications, you don’t have to worry too much; the disease simply won’t have time to develop to such an extent as to affect other organs and systems. In the absence of therapy, the following complications develop:
- Serpingia chancroid. The primary symptoms of the disease in the form of spots with purulent nodules begin to increase in size, sometimes merging into large formations.
- Gangrenous chancroid. Pus penetrates deep into the tissues, and inflammatory processes begin. Often the matter ends in thrombosis and blood poisoning.
- Phagedenic chancroid. The purulent process deepens and a scab forms. At this stage, infection becomes almost inevitable unless surgical intervention is performed.
- Lymphadenitis. It manifests itself in the form of inflammation of the lymph nodes throughout the body, which act as the main barrier to the spread of infection throughout the body. This complication almost always leads to sepsis and blood poisoning.
In addition to these complications, the development of other sexually transmitted diseases is often observed. Soft chancre weakens the body's defenses, opening the way for other representatives of pathogenic microflora. The most dangerous of these diseases is syphilis.
Syphilis is an insidious venereal disease. It is dangerous because it is fraught with numerous consequences from different systems and organs. You can find out what complications there will be, and whether there are relapses?
In the future, chancroid, which was not treated in a timely manner, can lead to infertility and disruption of the functionality of some organs and systems (do not forget about purulent processes). In rare cases, death can occur. To avoid these problems, it is enough to monitor your health, give up casual sex, and also strengthen your immunity!
You can also watch a video where a specialist will tell you about chancroid, its symptoms, treatment, and how you can avoid this disease.
Treatment of hard syphilitic chancre
Treatment is possible in outpatient and inpatient settings. Contact with the sick is prohibited. If one partner is diagnosed with hard syphilitic chancre, both should be treated.
The doctor prescribes antibiotic therapy with drugs of the penicillin group in the form of injections. Treponema pallidum is most sensitive to such drugs. Extensillin is used as a base agent, and Erythromycin or Doxycycline tablets are used as an additional agent. It is also possible to use parenteral drugs: Benzylpenicillin and Ampicillin.
On the outside, tissue needs to be restored. This will help to exclude additional infection with another infection and resolve the symptoms of syphilitic chancre. Tissues will regenerate faster if you use solutions of Benzylpenicillin or Dimexide, as well as heparin or levorin ointments.
For the oral cavity, rinse with solutions:
- Furacilina;
- Gramicidin;
- based on boric acid.
The treatment regimen in a particular case is determined only by the attending physician.