Every adult understands perfectly well that his body is not perfect, and this imperfection is manifested, first of all, by vulnerability to all kinds of diseases. One of the most disease-prone parts of the body, oddly enough, is the throat. A huge number of ailments are associated with this department and the organs that belong to it, while almost each of them has at least several varieties, a number of complications, or can develop into another, more complex disease. In some of these diseases, white spots appear in the throat and similar rashes, the specifics of the appearance of which need to be known at least superficially.
Allergic reaction in adults and children
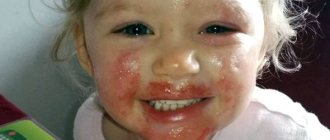
Various rashes in the mouth often accompany allergies. It is usually manifested by the appearance of red dots on the upper palate and other parts of the oral cavity, but it can also be accompanied by the appearance of small pimples or blisters - papules, vesicles.
The appearance of allergic rashes is often accompanied by swelling of the mucous membranes and soft tissues. Inflammation and swelling can quickly spread and cause a life-threatening complication - Quincke's edema. Therefore, even the slightest allergy symptoms cannot be ignored. The appearance of any rash in the oral cavity is a reason to urgently consult a doctor, especially if the allergen that caused such a reaction is unknown.
Photo: red spots on the roof of the mouth
The most common allergens:
- food products;
- chemicals in food products (dyes, flavors);
- plant pollen;
- medical preparations and their components;
- materials for dentures and fillings;
- household chemicals (toothpastes, mouthwashes, fresheners);
- children's toys, teethers, pacifiers and pacifiers made of low-quality materials.
To stop the spread of the red rash and swelling towards the throat, towards the respiratory organs, it is better to take an antihistamine before going to the doctor: Diazolin, Suprastin, Tavegil. You need to act especially quickly if a rash is found in a child’s throat. Many babies are susceptible to allergic reactions in the form of enanthema; any parent should be prepared for this.
The main difference between an allergic rash and an infectious one is that it is not accompanied by fever and general weakness. Red dots on the palate of a child’s mouth, accompanied by a rise in temperature and symptoms of intoxication, indicate an invasion of the body by a viral, bacterial or fungal infection.
Symptoms of herpes in the throat
Herpes in the throat can be difficult to distinguish from other diseases. Throat diseases in children are especially varied. Herpes is often mistaken for sore throat, stomatitis, bacterial diseases
.
Herpes can be identified by the following symptoms:
- acute onset with temperature rising to 40 degrees;
- redness of the throat and other parts of the oral cavity;
- the appearance of vesicles - bubbles with liquid inside;
- soreness, itching, burning;
- salivation;
- enlarged lymph nodes under the lower jaw and chin.
Advice
Herpes in the throat is accompanied by intoxication, nausea and vomiting, headache, fever, and the person refuses to eat.
The main sign of herpes is blisters on the mucous membrane of the throat.
.
They are usually multiple
, often they appear not only in the throat, but also on the oral mucosa.
The bubbles are initially filled with a clear liquid - lymph, containing viruses in high concentration. After two to five days,
the liquid becomes cloudy, the bubbles burst, and bright red ulcers form in their place. They are very painful. Healing of erosion takes up to two weeks.
Pediatric infectious diseases
Many infectious diseases that manifest as a rash on the palate are known as “childhood” diseases. But this does not mean that adults are not susceptible to infection. Having suffered from such diseases once, a person receives lifelong immunity. But if you do not get the same chickenpox in childhood, there is a risk of contracting this infection in adulthood.
Rubella
With rubella, red spots may first appear on the child's palate, and only then on the face and body. Rubella usually resolves easily and without complications in childhood, with the exception of infants up to one year old. These babies endure the disease very hard, so scarlet specks in the mouth, which quickly merge into specks, should alert parents: this may be the first symptom of rubella. This disease is also dangerous for adults who did not have it in childhood, especially for pregnant women.
Measles
As with rubella, with measles a rash in the mouth may appear earlier than on the body - sometimes within a day or two. But the nature of the rash is very different: with measles, the rash looks like dots of white or pale gray color, reminiscent of semolina. Their accumulations on the upper palate, tonsils and back of the throat are surrounded by a pinkish border, this phenomenon is called Belsky-Filatov syndrome.
Chicken pox
With chickenpox, a red rash in the mouth should alert you, as it indicates a complicated course of the disease. Bubbles filled with liquid can shed the gums, tongue, inner surfaces of the baby’s lips and cheeks, and are often found at the top - on the hard and soft palate. Breaking through, they form ulcerations in the oral cavity.
Scarlet fever
With scarlet fever, a small red rash covering the child's body may also appear on the upper palate. The mucous membranes of the pharynx with scarlet fever are bright red, the regional lymph nodes and tonsils are enlarged, the tongue becomes crimson in color and is covered with a white coating - see photo.
Speckled rashes are usually accompanied by a very high fever and vomiting, and in severe forms of the disease - convulsions and clouding of consciousness.
Roseola
Since the disease begins with a high fever, and after a couple of days, when the temperature subsides, a rash appears, roseola is often mistaken for ARVI and an associated allergy to medications. Small red spots and blisters in the throat and palate precede the appearance of similar rashes on the body. Their presence is accompanied by redness of the pharynx and pain when swallowing.
The difference between a rash in the mouth and on the body with roseola and any other is that it disappears when pressed.
Causes of rashes in the throat
As most likely, many have already guessed, the reason why they appear, especially those with a characteristic whitish or yellowish color, is most often infectious diseases. They can be either viral, bacterial or even fungal, but the causes are unchanged; rashes occur as a result of infection entering our body.
All possible infections penetrate and settle in the throat due to the fact that our immune system fails, and the tonsils, located in the throat and acting as a human shield on the path of all diseases, become the first frontier on which all possible consequences of the disease are reflected. Of the most likely ailments that cause a characteristic white rash in the throat, the following are found:
- Chronic tonsillitis.
It is these two diseases that can and are usually accompanied by purulent formations that look either like pimples in the throat (follicles, ulcers, blisters, etc.) or like small white dots that represent a clogged throat. In any case, these symptoms are most often accompanied by unpleasant sensations, have a number of aggravating consequences and need to be gotten rid of. But how to get rid of such troubles should be considered in more detail, touching on the very specifics of the ailments listed above.
Any sore throat is purely infectious in nature, however, the infections that cause this disease are often the same - bacteria such as staphylococci, streptococci or pneumococci. This disease always comes very suddenly, has extremely unpleasant symptoms, and is quite difficult to tolerate, but there is one plus - sore throat is very difficult to confuse with any other disease. In the case of follicular sore throat, diagnosis is even more simplified due to the characteristic formations in the throat. As for the symptoms, the picture emerges as follows:
- Pimples in the throat are the most obvious symptom of follicular tonsillitis. Formations on the palatine tonsil and on the upper wall of the throat, having a whitish tint and clearly filled with some kind of liquid (pus). They are very clearly visible even if you just look at them in the mirror and are accompanied by a strong feeling of pain when swallowing.
- Increased temperature - this symptom is characteristic of any sore throat; body temperature rises very quickly and often reaches almost 40 degrees mercury on the thermometer.
- also occurs, and the throat acquires a bright scarlet hue, soreness begins, drying of the mucous membrane and accompanying pain. If we compare this pain with that which occurs when follicles appear, then it often makes it impossible to eat.
- Another symptom of follicular angina is a general state of weakness and fatigue that accompany the patient throughout the entire period of the disease.
- In especially severe cases, or if we talk about this disease in children, delirium due to fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and headaches may appear.
- If the disease drags on, the patient develops a cough, runny nose and inflamed lymph nodes that hurt on palpation.
If we talk about the treatment of follicular tonsillitis, then there are a number of proven means and techniques, which, of course, should be used in combination. First of all, it is worth remembering that for angina, bed rest and drinking large amounts of fluid are strictly recommended in order to reduce intoxication.
Next, you should take care of rinsing your throat. Chamomile infusion diluted in a small amount of warm water or a soda-salt solution with a small addition of iodine (literally 4-5 drops) are best suited for these purposes. These remedies bring very good results if you gargle at least 5-6 times a day. This way, you will moisturize the mucous membrane, reduce pain a little, but most importantly, the purulent rash in the throat will go away quite quickly.
If the disease has become serious, the person’s condition is really serious, then the doctor will most likely prescribe you a course of antibiotics in order to cope with the infection attacking the body as soon as possible.
Otherwise, the treatment picture is often standard; in combination with an antibiotic, antihistamines are also taken, special lozenges are dissolved, sprays, nasal drops and medications are used to reduce swelling, if required.
How to relieve discomfort from enanthema
Determining by eye what causes the appearance of papules, white or red dots in the throat of a child or adult is not always possible even for experienced specialists. Such a symptom, in addition to infections, may indicate chronic and even oncological diseases of internal organs and systems. Most often, you can find out the true cause of the rash only after taking tests. Therefore, the first thing a sick person should do is consult a doctor.
It is impossible to eliminate rashes in the oral cavity without comprehensive treatment of the underlying disease that caused this symptom, according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. While waiting for a medical examination, you can only try to relieve the pain at home. After all, the presence of a rash on the palate and mucous membranes of a baby’s mouth makes breastfeeding difficult, and prevents older children from thoroughly chewing food, swallowing, and even speaking. It is also difficult for an adult to endure constant irritation on the tongue, cheeks, gums or larynx.
To reduce discomfort in the mouth, you can use rinses and baths with decoctions of chamomile, sage, yarrow or oak bark, treat red pimples and spots with solutions of Furacilin, Chlorhexidine or Miramistin. An antihistamine tablet will help relieve swelling and itching. For herpes, antiviral ointments based on acyclovir come to the rescue. But rinsing, bathing and taking medications does not eliminate the need for urgent consultation with a specialist doctor.
Source
The mucous membrane of the oral cavity in adults and children is sensitive and reacts sharply to even the most minor disruptions in the body. Often a rash appears on it, the appearance of which helps to diagnose the pathology. That is why doctors always examine the throat and evaluate the condition of the soft tissues in the mouth. Doctors call enanthema rashes in the form of red dots on the palate, tongue and inner surface of the cheeks. How dangerous is she? How to treat, what complications can there be?
Conclusion
Based on everything that has been written, a rather simple conclusion follows - any whitish or yellowish formations in the throat, characterized as rashes, indicate the presence of an active inflammatory process there, which is accompanied by local suppuration. There are not many diseases with such symptoms, and the methods of dealing with them are described above, so there is nothing terrible about them, only discomfort and unpleasant sensations for some time.
– a very rare form of the disease. Typically, herpetic blisters appear on the mucous membrane of the mouth - on the palate, cheeks, tongue. This virus can infect literally any part of your body: from the skin of the face, lips and ending with the genitals. It will not miss the mucous membranes - the eyes and the oral cavity. But if characteristic rashes appear in the throat, this indicates a severe form of herpes
requiring serious systemic treatment.
Causes of rashes on the oral mucosa in children and adults
The causes of oral rashes are numerous. Often, the presence of rashes in the mouth indicates dental diseases, dysfunction of organs and systems, and hormonal imbalances. The type of infection can be determined by the nature of the spots and accompanying symptoms. The dentist should make a diagnosis and determine a treatment regimen.
Viral and bacterial infection
Red spots on the palate of a child and a rash on the tonsils are most often caused by viral or bacterial infections. An infectious lesion in a child or adult is accompanied by a febrile state (fever, sore throat, and in some cases chills).
The cause of rashes can be influenza, chickenpox, diphtheria, ARVI, scarlet fever, meningitis and other serious diseases. At a young age, children often encounter stomatitis and herpes sore throat. These diseases are severe, accompanied by acute pain, attacks of nausea and bowel dysfunction.
Fungal infection
Spots that have arisen due to the penetration of fungal agents into the body require special attention. The most common fungal disease of the oral cavity is candidiasis (thrush). Caused by microscopic fungi of the genus Candida. Their activity increases after illness, when the immune system is weakened, when taking certain medications. You can distinguish such a rash in the mouth by a white coating in the oral cavity - on the cheeks, on the mucous membrane, on the tongue. The treatment regimen is chosen by the attending physician after determining the type of pathogen and depending on the patient’s medical indications.
Allergic reactions, poisoning
Enanthema in adults and children is often a consequence of an allergic reaction of the body or intoxication. In both cases, it is presented in the form of small red dots on the palate, tongue, and inner surface of the cheeks. Swelling of the soft tissues is also characteristic, which often leads to bronchospasm and Quincke's edema.
Any rash is a reason for medical examination. For effective treatment and elimination of associated symptoms, it is necessary to identify the allergen that provoked the pathological changes. The most common causes of enanthema of this etiology are:
- material for dental structures and fillings;
- Food;
- toothpastes, mouthwashes, brushes;
- medications;
- teethers, pacifiers.
With an allergic rash, there is no fever or other symptoms of infectious diseases. The rash is located symmetrically throughout the mucous membrane, in some cases it can occur in certain areas of the skin. In case of poisoning, swelling of the soft tissues, an increase in temperature are possible, and sometimes plaque appears on the tongue and the inner surface of the cheeks (on one or both sides).
Rare specific diseases (granuloma, petechiae, sarcoma)
Specks can sometimes indicate the presence of a rare specific disease. In this case, the rash looks like pinpoint red spots or looks like a large spot, located mainly in the throat and palate. The following pathologies are distinguished, characterized by similar symptoms:
- Kaposi's sarcoma. It presents multiple formations on the skin in the form of flat or convex plaques, has a bright purple color with additional shades (red, brown). Quite often it is diagnosed inside the oral cavity (on the palate), on the lymph nodes, and in rare cases - on the internal organs. The disease mainly develops in HIV-infected people.
- Pyogenic granuloma. A benign vascular formation that occurs in areas subject to frequent trauma or affected by staphylococcus. It has a red-cherry hue and looks like a dense rounded nodule. The pathology does not hurt, grows quickly and reaches its maximum size in just a few weeks.
- Palatal petechiae are scattered round spots on the palate or at the top of the oral mucosa (you can see the appearance of the rash in the photo).
Throat rash treatment
Your pediatrician will be able to choose the right tactics for treating a rash in the throat. In diseases of a viral nature, rashes on the mucous membranes do not always occur.
The need to use serious medications depends on the form and severity of the pathology. In most cases, it is quite possible to get by with maintenance therapy, which consists of reducing fever, gargling, taking vitamins, rinsing the nasal passages and other similar procedures. In addition, agents are prescribed to combat the causative agent of the disease, depending on its etiology.
If the treatment was correctly chosen and started in a timely manner, then, as a rule, the rash in the throat quickly disappears along with the cause that caused it. Even such a diagnosis as scarlet fever, with the modern development of medicine, has become harmless, although previously this pathology often led to the death of the patient. However, with modern methods in a hospital setting, it is quite easily cured, leaving no consequences.
Prevention of the appearance of a rash in a child’s throat is, firstly, maintaining the baby’s immune system. In addition, you need to make sure that he is always dressed as the weather conditions require, and try to exclude colds. It is advisable to carry out preventive vaccinations in a timely manner. During the massive spread of infections and epidemics, it is worth protecting the child from visiting public places and reducing the likelihood of contact with sick children. From an early age, a child should be taught to observe the rules of hygiene.
Types and nature of rashes in the oral cavity
A rash in the mouth is a sign of a developing disease. Rashes have different appearances, so it can be quite difficult for doctors to identify their true cause at first glance. The photo below with explanations shows examples of various rashes.
There are several types of rash in the mouth:
- Blisters with serous fluid. Common with herpes and chickenpox.
- Blisters are dense, irregularly shaped formations without a cavity. They appear suddenly and quickly disappear. Itchy blisters often occur with hives or allergies to insect bites.
- Pustules are deep or superficial. The internal cavity of the formations is filled with turbid contents.
- Spots - a change in the shade of the mucous membranes, some areas become lighter or scarlet.
- Ulcers. Formed as a result of the development of pustules and blisters. They deeply affect the mucous membrane.
- Nodules. They look like separate plaques that visually merge into one (for example, with candidiasis).
- keratinization. Observed in hairy leukoplakia of the mouth.
Diagnostic methods
The diagnosis of rashes is made by a local physician, pediatrician, or dentist. It is necessary to contact specialists immediately after identifying the problem, so as not to aggravate the course of the disease. In a number of situations, the attending physician gives a referral for additional examination to an infectious disease specialist, ENT specialist, or gastroenterologist. The following diagnostic methods are used to make a diagnosis:
- visual examination of the patient’s mucosa;
- taking anamnesis;
- taking tests - blood tests, allergy tests, coprogram;
- laboratory examination of a smear from the mucous membrane (if fungal infections are found, fungal micelles are found, if atypical cells are detected, a referral is given for a blood test for tumor markers);
- tests for sexually transmitted diseases, etc.
How to treat?
Treatment of rashes in the oral cavity should be carried out under medical supervision and only after the cause of the pathology has been established. You should not open pustules for yourself or your children, or injure the formations with foreign objects. Any independent intervention can aggravate the course of the disease. Treatment tactics are selected depending on the pathology, medical indications and age of the patient.
In children
A viral rash on the tongue and throat of a child is treated with medications that stimulate the production of interferon in the body, helping it fight pathogens. Viferon, Cycloferon, Acyclovir and other immunomodulatory drugs are recommended. For pathologies of an allergic nature, Erius, Tavegil, Cetrin and other antihistamines are prescribed.
For bacterial infections, antiseptics (Stomatidin, Miramistin), rinsing solutions (Rotokan, calendula tincture) are used. Gels (for example, Kamistad) are used for pain relief and cooling. They rarely resort to antibiotics due to their negative effects on a weakened body. For fever and pain, Nurofen and Panadol are used.
In adults
A red rash in the throat caused by viruses is treated with antiviral medications in adults. These are Zovirax ointments, Herperax ointments, Valtrex tablets. To treat bacterial rashes, the same antiseptics are used that are used for babies. In difficult cases, therapy is supplemented with antibiotics (Augmentin, Cephalexin).
They relieve pain with local anesthetics (lozenges, baby gels that are used for teething) and more effective medications (Efferalgan, Tempalgin). For allergic mouth stains, antihistamines are used. The doctor may prescribe Claridol, Kestin, Suprastin. In this case, the main attention is paid directly to the disease, which caused the unpleasant phenomenon.
Treatment of herpes in the throat
Herpes in the throat is treated comprehensively. The localization of pimples does not allow the use of conventional ointments, so they often use gargles, as well as tablets and injections. To cure herpetic stomatitis, antiviral and immunomodulatory agents are used.
Antiviral therapy
On the throat it differs from the treatment of other types of herpes by using only tablet and injection forms of the medicine, since the use of local agents (ointments, gels) is difficult due to the localization of the disease.
Use antiviral drugs:
- – used in the form of tablets or – in case of severe disease – in the form of injections;
- valacyclovir
, a drug that is converted into acyclovir when ingested and is considered less toxic, is also used in tablet form.
Since herpes in the throat in the vast majority of cases occurs in children, it is not worth talking about other antiviral drugs for the treatment of this disease, since they are very toxic
and are not used to treat children.
The note
Attention: only a doctor should select the antiviral medicine and its dosage!
Antiseptics
Antiseptics will help alleviate the patient’s condition and relieve acute sore throat:
- hexoral
is a drug for the treatment of inflammatory diseases of the throat, it is used to treat fungus in the throat of a child, relieves inflammation in herpes, sore throat, stomatitis, and helps prevent superinfections. - faringosept
- has antiseptic, bacteriostatic and antimicrobial effects. - Septolete
- a drug for the treatment of throat diseases of a fungal or bacterial nature - has an analgesic and antiseptic effect for herpes.
It is impossible to use only antiseptics to treat herpes in the throat
.
They only relieve symptoms, but do not in any way affect the cause of the disease -. Of course, the manifestations of herpes in the throat can go away on their own, but if the infection in the throat is not treated, it will recur again and again, and each next time
the manifestations will be more and more severe.
Concomitant medications
For severe sore throat, painkillers can be used
.
This could be no-spa, nurofen, ibuprofen
.
It is better to bring down a very high temperature with medication. Allergic reactions may occur with the large number of medications used to treat herpes. To prevent them, you can take antihistamines
.
Immunomodulatory agents
An important part of the treatment of herpes in the throat is the correction of immunity. Any manifestation of herpes always signals a decrease in the body’s natural defenses, since a healthy person easily copes with the herpes virus.
To treat herpes in the throat in adult children, use:
- interferon (cycloferon, viferon, kipferon, etc.)
activates the work of the body’s immune cells, allows you to quickly cope with the disease and prevent relapses; - Interferon inducers
are drugs that stimulate the body's production of its own interferon. The following drugs are effective: levamisole, amixin, pyrogenal, kagocel, alpizarin. One course of these drugs should be taken by people suffering from herpes and frequent colds. In addition to course treatment, they are also taken to treat herpes in the throat. In addition to immunomodulatory effects, drugs in this series also have an antiviral effect. It is especially worth noting such complex action agents as Lavomax and Wobenzym, which, in addition to interferon induction, have anti-inflammatory and antiviral effects; - immunoglobulins
– preparations of natural and synthetic origin based on human immunoglobulin containing antiherpetic antibodies.
An anti-herpes vaccine has also been developed.
Its use is justified for frequent relapses of herpes. It is administered once every six months between exacerbations of the disease.
Treatment of herpes in the throat with folk remedies
A red rash in the throat is usually painful. Inflammation of the tonsils can also be treated with folk remedies. To relieve pain and swelling, it is recommended to use rinses:
- infusion of chamomile, sage or linden
- pour a tablespoon with a glass of boiling water and infuse, then gargle often for two to three days;
- a decoction of flax seeds
- not only relieves discomfort in the throat, but also helps ulcers at the site of burst blisters to heal faster; - Sea buckthorn oil, rosehip oil and calendula
are used to lubricate ulcers - this relieves pain and speeds up healing. - tea with mint and linden blossom
reduces sore throat.
In the throat, especially with relapses, it should include natural remedies to increase immunity, such as echinacea, rose hips, leuzea, eleutherococcus
. These natural remedies will help the body quickly cope not only with herpes, but also with any viral diseases.
The note
It is important to remember that if you have herpes in the throat, you should absolutely not use warming, hot compresses, heating pads, or mustard plasters. At high temperatures, the virus, on the contrary, develops and spreads.
When treating herpes, it is important to drink plenty of fluids
To relieve intoxication, warm teas, including herbal teas, with lemon and mint, are best. Since a patient with herpes has difficulty swallowing, it is necessary to exclude rough foods; it is better to prefer pureed dishes during an exacerbation of the disease. It is imperative to exclude spicy foods so as not to irritate the already inflamed mucous membrane.
What complications can there be?
Any rash on the tongue or palate in adults and children requires evaluation by a specialist. In the absence of timely treatment, serious complications may arise due to further development of the disease. Rashes in the mouth can be complicated by:
- meningitis;
- airway obstruction;
- damage to the kidneys and heart muscle;
- intoxication of the body;
- retropharyngeal abscess;
- pneumonia;
- chronic pharyngitis;
- necrosis of soft tissues of the mouth;
- sepsis.
Prevention measures
Prevention of rashes in the mouth is based on compliance with the following recommendations:
- strengthening the immune system;
- giving up bad habits - smoking, alcohol;
- fighting the habit of keeping foreign objects in the mouth;
- exclusion of contact in an aggressive environment;
- use of protective equipment when working with toxic substances;
- protected sexual intercourse;
- a ban on visiting places with large crowds of people during epidemics;
- indoor microclimate control (humidity – 50-70%, temperature – 18-22 degrees);
- maintaining personal hygiene.
A mandatory preventive measure is regular visits to the dentist. In this case, the specialist will be able to cure the developing oral disease in time and give recommendations for daily care. In addition, it is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, monitor your diet and drinking regime. This will help avoid overwork and vitamin deficiency, which lead to decreased immunity.
Source