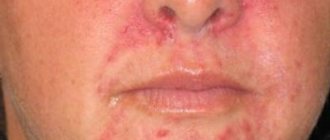
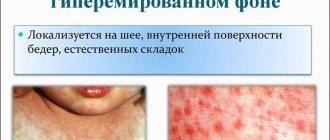
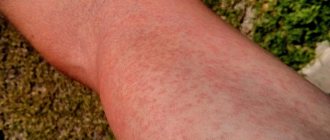
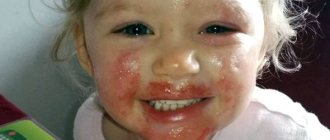
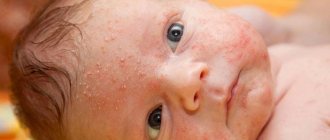
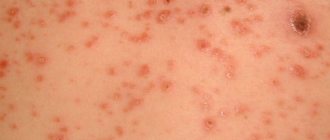
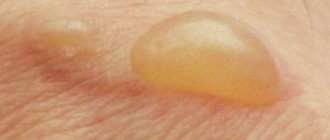
What is vesicle and papulovesicular rash?
vesicles in the photo
This type of rash is always characterized by an acute clinical picture of the course, dense localization in all parts of the body. A striking example of a vesiculopapular rash is acne with chickenpox. The nature of the origin of skin rashes can be very diverse. Most often, temporary damage to the skin is provoked by an allergic reaction, infectious or viral invasion. Much less commonly, vesiculopapular rash has a parasitic etiology.
Erythema nodosum
This type of erythema is an allergic reaction of the body to an irritant. It is characterized by inflammation of the skin and subcutaneous fat cells, which are accompanied by pronounced pigmentation and pain upon physical impact. According to medical statistics, this disease is widespread among the female half of the population.
An erythematous rash in this case appears in the form of spherical nodes, the size of which depends on the severity of the disease.
This symptomatology manifests itself exclusively on the extremities, but despite this, an accurate diagnosis of erythema nodosum requires a full course of examination, on which further treatment will depend, namely:
- examination and conclusion of a pulmonologist;
- X-rays of light;
- passing general tests;
- consultation with a dermatologist;
- examination by a rheumatologist.
The most common causes of the development of this disease are the consequences of such chronic diseases as:
- tonsillitis;
- cystitis;
- otitis and other streptococcal infections.
READ ALSO: Allergic skin rashes in adults and children (photo): rash treatment
Erythema nodosum most often affects people between the ages of twenty and thirty years and, with poor treatment, can regularly worsen in cold seasons.
Causes of occurrence on the skin
Over many decades of medical practice in the field of dermatology, the following reasons have been identified and highlighted, due to the presence of which a vesicular rash appears on the skin of adults and children.
In a child and newborn
The formation of vesicular type dermatitis on the face, palms and fingers in young children most often occurs due to such negative factors as:
Allergic reaction
The immune system of a newborn child, or one in the early stages of its development, is not yet sufficiently formed and strengthened to effectively resist allergens coming from the external environment. The use of synthetic diapers or clothing items made from low-quality fabrics entails the development of vesicular dermatitis of allergic etiology. A characteristic rash may appear on the lip, eyelid and other parts of the baby’s body.
Low level of hygiene
To avoid vesicular rash due to insufficient hygiene, it is necessary to bathe the child at least once a day. Moreover, after each trip to the toilet, the newborn’s skin is washed with warm water and hypoallergenic soap, and then the skin is treated with baby powder and preparations made on its basis to prevent the formation of diaper rash. Failure to follow these simple rules leads to a vesicular rash due to the child's skin being too dirty.
In an adult
The adult body is more resistant to various negative environmental factors, and the skin has a strong local immune system. Despite this, a vesicular rash can affect the epidermal tissues of adults, regardless of their age, for the following reasons.
Parasites
In this case, we are talking about infection of the skin with scabies mites. This parasite penetrates the epithelial layer of the dermis and makes its home in it, laying multiple passages in the subcutaneous layer that resemble an intricacy of labyrinths. The scabies mite is microscopic, so it is impossible for humans to see it with the naked eye. The pathogenic activity of this parasite provokes skin irritation and the formation of a vesicular rash, which most often covers the abdomen, fingers, back and neck. In dermatology, this pathological condition of the skin is called demodicosis.
Infection
Infection of epidermal tissues by pathogenic microorganisms of infectious or viral origin first manifests itself in the form of multiple inflamed pimples, which gradually transform into ulcerative formations. This kind of vesicular rash always resembles small blisters, inside of which there is a clear liquid. The most common culprits of bacterial skin lesions are Staphylococcus aureus and streptococcal infections. It is very dangerous if the rash appears on the penis and is concentrated on the skin of the intimate area. Pathogenic microorganisms can enter the prostate gland through the urethra and cause inflammation.
vesicle virus in the photo
In the future, for men this will result in such an insidious disease as chronic prostatitis. Not often, but still the appearance of rashes in the throat occurs. This is observed if a person falls ill with scarlet fever, the course of which is accompanied not only by inflammation of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity, but also by damage to the epidermal tissues. If the Mantoux test was performed to identify the susceptibility of the immune system to the tuberculosis bacillus, then a mild vesicular rash may also occur. Skin rashes of an infectious and viral nature require careful diagnosis and examination of the entire body.
Vascular diseases
The subcutaneous layer of the epidermis contains a huge number of tiny capillary blood vessels. If an adult has acquired a disease of the cardiovascular system associated with circulatory disorders over many years of life, then some of the capillaries cease to receive blood supply in the volume that they need from a physiological point of view. They become brittle and collapse under even slight static pressure. Because of this, an external skin reaction occurs, expressed in the form of irritation and multiple vesicular rashes.
Regardless of the cause of the appearance of a skin rash in adults and small children, it is necessary to make every effort to establish the pathogenic factor that provokes a negative reaction of the skin, since such severe infectious diseases as secondary syphilis, rubella, measles, roseola, anthrax, skin tuberculosis.
Papular urticaria
The obvious cause of papular urticaria is insect and arthropod bites. The result of such bites is the development of a classic delayed-type allergic reaction. Visually, the pathological process is manifested by the appearance of papular elements on unchanged skin. The essence of the process lies in the body’s atypical response to insect saliva, which, in contact with the surface of the skin, toxically damages dermal cells and provokes the release of histamine, which causes tissue swelling.
If diagnosed and treated incorrectly in the early stages of the disease, any other type of urticaria can transform into papular urticaria. In this case, papules, instead of the usual urticarial rash, appear due to the fact that cellular infiltrate is added to the swelling of the skin, which already exists in a minimal volume. The dermis under the slightly convex urticaria swells, turning it into a papule, noticeably rising above the surface of the skin.
Any exo- or endogenous cause that causes urticaria can trigger the appearance of papules. This requires three conditions: an aggressive antigen, skin hypersensitization and time. Additional triggers for papular urticaria can be ultraviolet radiation, changes in ambient temperature and pressure, and physical activity. The mechanism of development of the pathology is due to the degranulation of mast cells, which are located in the connective tissue of the dermis and mucous membranes, performing a protective function designed to prevent the penetration of antigens into the body.
When they encounter an antigen, mast cells become activated. Lymphocytes secrete IgE, which adheres to the mast cell membrane, merges with it and stimulates the release of histamine, heparin, prostaglandins and other biologically active substances into the dermis. Histamine increases vascular permeability, heparin thins the blood, which leads to tissue swelling and the development of inflammation. Mediators cause itching. An allergic reaction occurs, but mast cells localize it, trapping allergens at the site of their penetration into the skin. Despite the fact that the provoking antigen may continue its contact with the skin, causing the appearance of new papules and itching, the pathological process does not spread beyond the skin.
Classification of papular urticaria
There is no generally accepted classification of papular urticaria in modern dermatology. The most useful for making decisions about adequate detoxification therapy is the following classification, based on the way the allergen enters the patient's body. There are:
- Papular urticaria caused by the venom of Hymenoptera (bee, wasp, bumblebee sting).
- Papular urticaria, provoked by the saliva of blood-sucking insects during bites.
- Papular urticaria, caused by direct contact with the skin of body fragments and waste products of insects.
What do the symptoms and stages of the disease look like?
The symptoms of vesicle formation largely depend on what kind of primary disease was diagnosed in the patient, because the rash itself acts as a sign of the disease.
In general, the general symptoms of vesicular dermatitis are as follows:
- the area of skin located in the area of the future lesion begins to turn red, and a characteristic feeling of discomfort appears;
- small dots form on the epithelial surface, which quickly increase in size and become inflamed;
- a strong feeling of itching develops, and in some cases, depending on the etiology of the disease, pain is also present;
- a red rash of an infectious nature transforms into wound surfaces, and ulcers tend to grow in diameter and deep into the epidermis.
Why does erythema multiforme occur: the main reasons
At the moment, there is no single proven etiological factor for the development of erythema multiforme. It is believed that the pathological process is polyetiological, but has a single development mechanism. Presumably, with erythema multiforme there are genetically determined changes in the immune system, which lead to its hypersensitivity and inadequate response to exposure to antigens. The immune system perceives skin cells damaged by the antigen as foreign proteins and tries to destroy them. This version of the development of the inflammatory process is the most popular today.
Vesicle treatment
Depending on what dermatological disease was identified in the patient, specific treatment is prescribed not only for vesicular rashes, but also for the underlying disease. If the patient does not have such concomitant signs of the disease as a temperature of 38 degrees or higher, fever, weakness, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea, then vesicle therapy proceeds according to the following principle:
- the patient is in bed rest (he needs to be provided with complete rest, close the curtains in the room, create an atmosphere of twilight so that external stimuli do not stimulate the nervous system;
- it is necessary to drink as much warm liquid as possible (herbal teas can be an alternative);
- taking antihistamines in tablet form from the category Aleron, Suprastin, Eden, Ketotifen, Suprastinol (needed to relieve the feeling of itching, as well as to avoid scratching the skin with the introduction of infection into the epidermis along with the subungual contents);
- antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs are prescribed if the course of the vesicular rash is acute and the skin lesion is caused by infectious pathogens (the type of drug is selected individually by the attending physician based on what type of bacteria was cultured during a laboratory test);
- areas of the skin covered with a vesicular rash are treated with external medications in the form of an alcohol solution of brilliant green, iodine, aniline dyes, and alum based on copper sulfate.
As the main cause of the formation of a vesicular rash on the body is eliminated, acne disappears from the surface of the skin, and the condition of the inflamed epithelium stabilizes again. His functional ability is completely restored.
Etiology and classification
Papular rash is characterized by the appearance on the skin of bandless neoplasms of various shapes and sizes. There are no sinuses with fluid in the papules.
Papular rash can occur due to diseases of the liver, gastrointestinal tract, blood, and autoimmune disorders.
The following causes of the development of the disease are also identified:
- 1. Mechanical injury to the skin, leading to rupture of small vessels.
- 2. Overexertion during childbirth.
- 3. Autoimmune pathologies: vasculitis, thrombocytopenic purpura, scleroderma and others.
- 4. Infectious diseases: meningitis, scarlet fever, mononucleosis.
- 5. Chemotherapy.
- 6. Radiation therapy.
- 7. Taking drugs.
- 8. Use of anticoagulants for a long period.
- 9. Hemolytic disorders.
- 10. Hormonal imbalance.
Depending on the size, doctors classify the rash into types:
- 1. Billionary - spherical rashes with a diameter of no more than 1 mm. The elements are located near the hair follicle.
- 2. Lenticular - up to 5 mm in diameter. They can be of various shapes: flat, convex.
- 3. Numular - up to 2 cm in diameter. The papules merge with each other and acquire a coin-shaped structure.
Based on the nature of the rash, the following types of rash are distinguished:
- 1. Maculopapular.
- 2. Erythematous-papular.
- 3. Maculopapular.
To classify neoplasms into a certain group, the doctor takes into account their location on the body, the symmetry of the pattern, the presence of itching and the total number of elements.