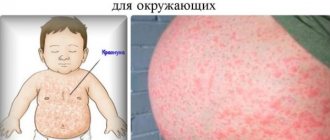
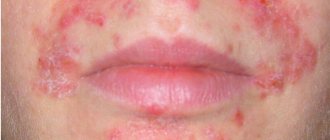
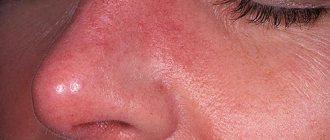
Inflammation of the hair follicle is called folliculitis. This is a disease that occurs in the follicle due to fungal, bacterial, viral and other pathogens.
The cause of the onset of the disease may be a weakened immune system due to hypothermia or a previous illness.
Focal infection of the contents of the hair follicle, which can affect only the upper part of the follicle, or spread to its root, sebaceous and sweat glands.
In this case, first redness around the hair appears on the surface of the skin, and then a blister with pus. In some cases, this phenomenon is single, in others, a person develops many abscesses, and we can talk about a rash.
Causes of the disease
Inflammation of the hair follicles occurs due to bacteria entering them. This may be caused by a minor injury or cut. This most often happens during shaving or hair removal.
The cause of the development of pathology can be wearing tight clothes and underwear. Representatives of the fairer sex face this especially often. In this case, inflammation of the hair follicles in the groin begins.
Elementary lack of hygiene and the use of public saunas and swimming pools can lead to such a pathology. In this case, the microbe can penetrate both damaged skin and a healthy follicle.
Complications of folliculitis
Typically, this infectious disease is mild and does not pose a serious threat to life. But complications may develop. This happens in the absence of treatment, non-compliance with hygiene rules, and a weak immune response of the body.
Among the common complications is a boil, which leads to:
- to hidradentitis and lymphadenitis;
- carbuncle;
- abscess;
- follicular scars;
- dermatophytosis.
Isolated cases are accompanied by nephritis, meningitis and pneumonia.
Symptoms of pathology
Inflammation of the hair follicles on the head or in any other places can be superficial or deep. In the first case, there is slight redness in the hair area and a small abscess, which does not exceed 5 millimeters in size.
With deep inflammation, extensive damage to the upper layers of the skin occurs. The abscess has a size from one to ten centimeters.
The lesion can be either single or multiple. In especially severe cases, pain and itching occurs.
Degree of complexity of folliculitis
The pathogen can penetrate both the upper and deeper layers of the skin. There are several stages of the disease.
Surface
It is characterized by the appearance of single or multiple small ulcers on the skin. Within a few days, a dense crust forms on their surface, which then falls off.
Deep
The infection penetrates into the deep layers of the follicle. Accompanied by the appearance of painful lumps on the body. As the inflammatory process develops, the purulent contents come to the surface, the wound becomes covered with a dense crust (within 5-7 days after the onset of acute symptoms).
Depending on the severity of inflammation, complicated and uncomplicated forms of folliculitis are distinguished. Treatment regimens differ; in the first case, the patient experiences associated complications.
Patients are often diagnosed with a cystic form of folliculitis. In this case, a subcutaneous formation of a benign nature is diagnosed; as a rule, it is hereditary. Subject to surgical removal (laser surgery or conventional incision).
Inflammation of the hair follicle: treatment
It is up to the specialist to decide whether to treat the pathology or not. Contact a dermatologist and get a qualified prescription. In most cases, treatment is performed surgically. This usually does not require the use of anesthesia. Only in particularly severe cases is representative anesthesia of the affected area necessary.
Treatment of inflammation of the hair follicle is carried out using a scalpel or thin curette. The doctor treats the adjacent area and opens the abscess. After this, you need to thoroughly clean the wound from pus and disinfect it. In most cases, the hair growing from a given follicle is completely removed with tweezers.
After such treatment, you need to treat the affected area with special solutions several times a day. A specialist will decide what exactly is right for you. Most often, brilliant green, furatsilin, chlorhexidine or alcohol are prescribed. In especially severe cases, with deep inflammation, it is recommended to use compresses with ichthyol. You need to apply such lotions several times a day until complete recovery.
Known treatments
Timely detection of the problem makes it possible to carry out treatment at home, but you need to take into account an integrated approach. Dermatologists recommend paying attention to the following groups of drugs:
- Topical products – antibacterial ointments. They are suitable for treating the disease at an early stage of development. Effective ointments are Levomekol, Levosin and Gentamicin.
- For systemic use - antibiotics. They are used if the affected area is large, and also if the cause of the disease is a bacterial environment. Experts may recommend Ceftriaxone or Azithromycin.
- Antiseptics in solutions will prevent the infection from spreading. You can use Miramistin, regular hydrogen peroxide, Iodinol and others. Alternative remedies are brilliant green or fucorcin.
- Skin restoration products are also a must. Acnecutane and Roaccutane are good options.
- Antifungal ointments are effective if a fungus is the cause of the disease. The most commonly used are Nizoral or Mycozoral.
- Antiviral drugs are necessary if the herpetic form of the disease is diagnosed. An inexpensive but effective drug is Acyclovir in the form of an ointment.
- Anti-allergy medications. Suprastin or Tavegil relieves swelling and itching well.
You can try to cure folliculitis of the scalp using Ichthyol or Zinc ointment. In order to improve the functions of the immune system, vitamins are prescribed.
Alternative treatment: using medications
Depending on the cause of the inflammation, additional measures may be recommended. If folliculitis is caused by long-term use of hormonal drugs, then they are simply canceled. Of course, the benefits and possible risks for the patient are taken into account.
In addition, doctors prescribe antibacterial agents that act on the microorganism. However, before this, it is worth taking a test to identify sensitivity to certain drugs. Doctors often use the following medications: Metronidazole, Naxogin, Cefotaxime, and so on. Remember that without preliminary analysis, treatment may be ineffective.
What is a hair follicle
The hair follicle is a pore that is the receptacle of the hair root, where the hair shaft is formed and grows outward from there.
It depends on it what the structure, color and length of the hair will be. The hair follicle is located in the dermal layer. Consists of the following parts:
- hair follicle;
- follicular funnel;
- root sheath;
- holding muscle.
Capillaries, sweat and sebaceous glands also communicate with it. Capillaries are responsible for nutrition, and the sebaceous glands are responsible for lubricating the hair with sebaceous secretion, protecting it from aggressive environmental influences. But in the absence of proper hygiene or excess sebum production, it is the activity of the sebaceous gland that most contributes to the inflammatory process.
Ways to prevent the disease
Is there any method to avoid hair follicle inflammation? Absolutely yes. To begin with, you should reconsider your own lifestyle and observe basic hygiene. Cleanse your body regularly using gels and special scrubs. Take a shower at least once a day.
Try not to use other people's towels, scarves and clothes. Avoid questionable ponds, saunas and swimming pools. If you are swimming, the water in the enclosed space should be chlorinated. In this case, its pH must be at least 8.
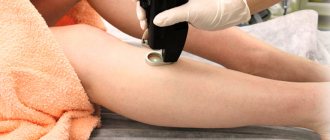
Avoid wearing thick underwear. Avoid strong friction of clothing in the area of skin folds, for example, in the groin area. Always use emollients when waxing and shaving. After the procedure, apply alcohol softening lotions to the skin. They will help disinfect the skin and prevent bacteria from entering the wound.
The main reasons for the development of the disease
Inflammation in the hair follicles develops due to the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms and when the immune system is weakened.
There are external factors that can cause the disease:
- skin irritation, cuts and microtraumas;
- wearing tight clothes made of artificial materials for a long time;
- accidental or systematic hypothermia;
- increased humidity or air temperature.
Often folliculitis can be diagnosed against the background of other diseases:
- diabetes;
- HIV;
- some sexually transmitted diseases;
- pathologies of a chronic nature.
In women and men, folliculitis may appear after depilation of the intimate area. This phenomenon can also occur against the background of thrush.
Treatment of recurrent or advanced forms
Antibiotics are prescribed if the disease is detected already at the stage of sycosis, that is, there are multiple lesions with purulent formations of varying degrees of maturation. In this case, in parallel with the main treatment, sulfonamides and drugs that increase immune defense are prescribed.
When independently applying local remedies to areas with mature or opened pustules, you should not press on the affected area or try to open the formations yourself. This action is carried out only under sterile conditions in the treatment room.
Stages of the disease
In the initial stages, folliculitis manifests itself as a small compaction located on the surface of the affected area. Then a painful nodule with fluid is formed, after which a purulent core forms. Over time, a purulent focus develops (many call it a boil).
The disease can affect all areas where there are hair follicles. A complication is lymphadenitis. In more severe cases, a person is bothered by severe itching of the skin, and hair loss is also observed.
How to treat
Therapeutic measures depend on the nature of the pathogen, the location of the rash and the severity of folliculitis. As a rule, external agents, tablets and physiotherapeutic procedures are used. Comprehensive treatment increases the patient’s chances of a speedy recovery.
Antibiotic ointments
To diagnose the nature of the pathogen, laboratory culture of secretions from skin lesions is performed. If bacterial flora is detected, the patient is prescribed external agents and antibacterial agents.
They have a wide spectrum of action and are aimed at destroying the cell wall of bacteria and suppressing their further development. Erythromycin, Methicillin, etc. are considered popular ointments. The medicine is applied precisely to the affected area and rubbed in gently. The frequency of application depends on the degree of damage (from 2 to 4 times a day). During the treatment period, be sure to follow the rules of personal hygiene, avoid wearing things made of synthetic materials, etc.
Before applying the ointment, the abscess is treated with an antiseptic, opened, the contents are removed and a bandage with antibacterial ointment is applied. The course of treatment and frequency of application is determined individually for each patient. On average, therapy lasts 7-10 days (depending on the severity of folliculitis).
Treatment of children is carried out extremely carefully. Drugs are selected based on age and form of folliculitis. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often used to relieve unpleasant symptoms.
Antibiotics are mainly prescribed from the group of cephalosprorins, penicillins and macrolides. The duration and dosage are selected individually. To treat ulcers, use salicylic ointment, boric alcohol or brilliant green. For multiple formations, treatment is prescribed by a pediatric dermatologist.
In case of frequent relapses, the patient is prescribed antibiotics for oral use, and in parallel, immunostimulants are taken to strengthen the immune system. For deep lesions, compresses with ichthyol ointment are used, which “pull out” the purulent accumulation; severe forms of pseudomonas vasculitis are treated with antibiotics from the ciprofloxacin group.
Delaying the treatment of ulcers increases the chances of developing boils, carbuncles and other complications. In rare cases, the patient develops meningitis, nephritis, etc.
Antifungal drugs
If specialists identify fungal pathogens during culture, the patient is prescribed antifungal drugs. They are taken orally or applied to the affected area (ointments, creams, gels, etc.).
Popular and effective drugs include Terbinafine, Intraconazole, etc. They are applied to the affected areas 2 times a day, the course of treatment is determined individually.
If the pathology is diagnosed at an early stage, then they are limited to treating the affected areas with solutions of brilliant green or fucorcin. It is strictly forbidden to open the ulcers on your own or tear off the crust that has formed on the surface.
Ural Federal District
Ultraviolet irradiation is used as part of complex therapy. Patients are exposed to special lamps that emit rays of a certain wavelength. The number of courses is determined by doctors individually, based on the form and stage of hair folliculitis.
Ulcers in the area of hair follicles are very common. Folliculitis develops with the active action of a fungal, bacterial, viral or parasitic form. The disease is accompanied by a number of unpleasant symptoms and requires mandatory drug treatment. Delaying therapy increases the chances of associated complications and repeated relapses in the future. For prevention, it is recommended to follow the rules of personal hygiene, strengthen the immune system and promptly treat existing diseases.
Use of folk remedies
Home treatment is effective: you can use fucorcin and brilliant green. The affected area can be washed with antibacterial soap. If there is deep inflammation, the doctor prescribes ichthyol ointment (the product is applied no more than twice a day). Folk remedies will help you overcome the inflammatory process faster, but remember: they should not cause allergies.
Chamomile decoction
helps with husks on the head left after purulent wounds.
Dandelion root tincture
- another useful remedy: with the permission of a doctor, it is taken orally. You need to take two large spoons of dandelion and pour 200 ml of boiling water.
You can also use a decoction of burdock
. You need to take a large spoon of this plant and add a small amount of water (50 ml will be enough).
In addition to treatment, prevention is necessary. Any inflammation should not reach folliculitis. Be careful when using a razor and tweezers: try not to injure the skin. You should not use other people's hygiene products, eat a lot of fatty foods, or wear clothes that restrict movement.
In conclusion, we add: you should not treat the disease yourself. To achieve a good result, you should consult a doctor!
A person often encounters various diseases and pathological processes. Some of them go away on their own, while others require proper treatment. This article will discuss what inflammation of the hair follicles is. Almost every person can encounter this pathology. It is worth knowing what a hair follicle is and how the symptoms of its inflammation manifest themselves. We will also find out ways to treat the pathology.
Preventive measures
Preventing the occurrence of hair folliculitis after hair removal is quite simple. To do this you need to follow these tips:
- Regardless of the chosen method of hair removal, it is necessary to carry out antiseptic treatment of the skin before the procedure;
- hair removal must be carried out with strict adherence to technique;
- After shaving, apply a soothing lotion to the skin;
- For the first day after the procedure, it is recommended to avoid bathing, steaming and sunbathing.
Stages of development
Hair follicles can be in a state of rest and growth; these phases alternate with each other with a certain cyclicity. Main stages of development:
- Anagen. Primary growth stage, lasting from 2 to 4 years. In a healthy person, more than 60% of body hair is in the anagen stage.
- Catagen. Transitional stage lasting 2-3 weeks. At this stage, the supply of nutrients to the hair follicle cells slows down, as a result of which they stop dividing.
- Telogen. Dormant stage lasting up to 90 days. At this stage, hair that has stopped growing falls out. After this stage is completed, the cycle begins again.
Important! With the negative impact of external and internal factors, the telogen stage is delayed, which is why the sleeping bulbs do not wake up and baldness begins.
Diagnostics
An experienced dermatologist can identify the disease by its external manifestations, but laboratory tests are required to confirm the diagnosis and select a further treatment regimen:
- taking a smear for Gram staining;
- taking blood to determine sugar levels and determine liver enzymes;
- tank sowing the contents of purulent sacs.
If after these tests the clinical picture is not fully identified, a skin biopsy is prescribed.
Diagnosis and treatment: what do doctors recommend?
If you notice any unpleasant symptoms, you should consult a doctor. The diagnosis is determined by the results of a comprehensive examination. First, an anamnesis is taken, then the results of a blood test are studied.
It is important to study the features and structure of the hair follicle. Next, you need to undergo diagnostics to identify the pathogen. The doctor may order a test to rule out dangerous diseases such as syphilis and gonorrhea.
Treatment does not only involve the use of medications. The patient needs to follow a daily routine and adhere to a certain diet. The doctor prescribes disinfectant ointments. In addition to them, antibacterial compounds may be prescribed.
In the presence of deep inflammation, a surgical opening is required: after this procedure, the skin is treated with a disinfectant composition. Immunotherapy and antibiotic treatment are drastic measures necessary in the case of severe folliculitis.
In any case, try to help yourself in treatment. Follow the rules that will help you recover faster. Do not wet the affected area unnecessarily, and do not use compresses unless recommended.
It is worth noting : the disease can be fought with the help of traditional Vishnevsky ointment: it pushes the pus out, thereby alleviating the symptoms.