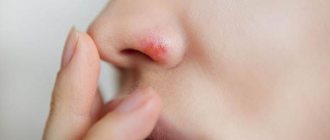
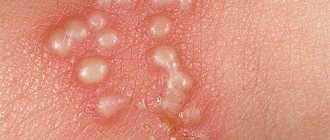
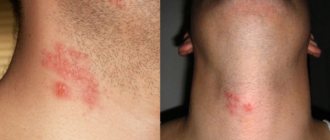
There is a blister in the ear and it doesn’t hurt
Our skin is the first barrier that protects the body from the harmful effects of the environment. Negative processes occurring in the body also affect the condition of the skin. The skin may become red, flaky, rash, and blistered.
Blisters are perhaps the most unpleasant phenomenon of all of the above. They not only spoil the aesthetic appearance, but cause discomfort in the form of itching, and can even cause pain.
It is especially unpleasant when a blister appears on the ear, pinna or on the thin skin behind it. In this case, even touching the pillow can cause pain and discomfort.
It's like bubbles are bursting in my ears
Tinnitus is a symptom characteristic of both pathological processes occurring in the ear and diseases not related to this organ. At the same time, the nature of the noise can be described by patients in different ways. This could be the rumbling of a motor, the buzzing of a saw, crackling, gurgling, or humming. Some patients describe this symptom in such a way that it is as if bubbles are bursting in the ear, or there is a feeling that the sea is splashing.
The most common diseases that may be accompanied by such symptoms are
Among diseases of the ENT organs, the presence of noise in the ear is most often caused by the development of eustachitis, inflammation of the auditory tube.
In this case, this symptom occurs quite acutely and is permanent, which distinguishes it from noise caused by vascular disorders. The pulsating character is atypical for him. There is an increase in noise in a horizontal position, especially with a lowered head edge, which is due to the anatomical structure of the auditory tube and its angle of inclination. When moving to a vertical position, the noise intensity decreases.
Most often, eustachitis is a consequence of acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, or laryngitis. An important factor contributing to the diagnosis of this condition is the presence of catarrhal symptoms, nasal congestion, and runny nose, which appeared several hours before the development of noise in the ear.
The diagnosis can be reliably clarified using otoscopy, which allows one to identify a retracted eardrum.
Such changes are caused by a decrease in pressure in the tympanic cavity, resulting from a violation of the drainage function of the auditory tube.
An effective method of treating eustachitis is the use of vasoconstrictor nasal drops. Their use helps reduce swelling of the auditory tube, as well as reduce the amount of mucus formed. This effect leads to improved patency of the Eustachian tube and, therefore, reduces symptoms.
Reduction of noise in the ear can also be achieved by applying warming procedures to the parotid area. These can be physiotherapeutic procedures, UHF, electrophoresis with anti-inflammatory solutions, wet and dry compresses. A similar effect can be expected from the use of heated ear drops containing boric or camphor alcohol, solutions with an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory component. Improvement should occur within the next few hours.
Untimely implementation of therapeutic measures can lead to the spread of infection to the middle ear and the development of first catarrhal, and possibly exudative otitis media.
In this case, an increase in symptoms and a deterioration in general condition are characteristic. Added to the unpleasant sensations in the ear is severe pain. Otitis media often occurs with an increase in temperature to 38 -39 degrees. The development of this condition requires immediate consultation with an otolaryngologist, whose task is to clarify the nature of the inflammation and prescribe appropriate treatment.
Causes of blisters on and behind the ear
Blisters on the ears can be either independent formations on the skin or symptoms of serious diseases. The causes of blisters (single or multiple) can be:
- allergic reaction of the body;
- insect bites;
- burns (including sunburn);
- taking individually inappropriate medications or non-compliance with their dosage;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- skin fungus;
- viral infection;
- inflammatory processes in the body.
Blisters from sunburn or insect bites are not particularly dangerous, except that in rare cases they can lead to skin infections.
Bubbles that appear as a result of infection with viruses or the formation of a focus of inflammation in the body carry a much greater danger and require special attention from the sick person.
The appearance of blisters, just like any other neoplasm on the body, is a reason to seek medical help, especially in cases where it is impossible to determine the cause of their occurrence on your own.
If you know for sure that you could not be bitten by any insect or you have not eaten anything that could cause an allergy,
Is it okay to scratch blisters?
If you want to scratch an itchy blister, it is worth remembering that such a mechanical effect on the blister can lead to its rupture. In this case, a scar may remain after healing, and in the worst case, an infection can be introduced into the resulting wound or the process of suppuration can begin.
What to do if you find a blister on your ear
The first step is to contact a qualified dermatologist to find out the causes of the formation and prescribe treatment. Self-medication, especially when it comes to a child, is not recommended.
If you cannot go to the doctor, and the pain from the blister does not give you peace, you can alleviate the condition by following these steps:
- Wash the affected area of skin with warm water and soap.
- Disinfect the area with the blister with alcohol or iodine.
- Using a sterilized needle, make punctures along the edges of the bladder and thus open it.
- Completely remove fluid from the blister.
- Apply a bandage with antibacterial ointment.
What not to do with blisters on and behind the ear
Whatever the root cause of the blister, it should never be:
- press;
- rub;
- allow moisture (sweat) to accumulate behind the ear, thereby creating favorable conditions there for the development of pathogenic bacteria.
Prevention is the best cure
To avoid the recurrence of blisters on the ear, you must:
- watch your diet;
- maintain a healthy lifestyle;
- observe the temperature regime (do not overheat or overcool);
- avoid unprotected sex (in case of herpes);
- promptly and completely treat viral diseases.
This video will tell you how to get rid of fungus without causing blisters:
And do not forget about observing the rules of personal hygiene
- wash your ears every day;
- When taking a shower or washing your hair, do not forget to rinse your ears, the area behind the ears;
- get rid of the habit of picking your ears with dirty hands and objects not intended for this (matches, hairpins, pins);
- When using cotton swabs to clean the ear, be careful not to damage the eardrum and ear walls.
Of course, maintaining hygiene will not prevent the appearance of blisters, which are symptoms of allergies or viral and infectious diseases, such as chicken pox, erysipelas, shingles or herpes and others
Hygiene is quite capable of preventing the appearance of acne on the auricles, in the ears and behind them.
What to do if bubbles seem to burst in your ears
Often, with various diseases, there is a sensation as if bubbles are bursting in the ear. Many do not understand what this is connected with and suffer for a long time, unable to get rid of the annoying feeling. In this case, it is recommended to consult an otolaryngologist and find out what’s wrong.
Possible reasons for this sound
An unpleasant symptom in the ear, when you hear noise, crackling, an incomprehensible sound, or something is clearly bursting (like “bubbles”) provoke a variety of diseases. This is due to inflammatory processes, damage, a foreign body or sulfur plug.
The reason may also lie in disorders of the vestibular apparatus, the temporomandibular joint, and even the cardiovascular system. The sensation of something like small bubbles bursting in the ear is usually caused by influenza or secretory otitis, otosclerosis, or blockage of the eustachian tube.
Additional sensations
Sometimes, in addition to the feeling that a dozen small bubbles are bursting in the ears, additional signs of a specific disease are added. This:
- Pain;
- Ear congestion;
- Clicking, ringing and other noise;
- Sometimes there is something tickling in the ear canal.
More serious manifestations are also possible: hearing loss, systematic dizziness and deterioration of coordination. All this manifests itself in varying intensity in certain situations, for example, when flying, hiking in mountainous areas, sudden changes in body position, certain postures, chewing, swallowing, tilting the head, blowing the nose and sneezing.
How to do?
Before taking any measures, you should consult a specialist. Perhaps the situation is much more serious than it seems. Only a doctor can reliably determine why something is “bursting” in the ears and evaluate the accompanying symptoms.
The choice of treatment methods depends on the nature of the disease.
Since there are so many possible causes, there are no fewer treatment options.
Therefore, it is extremely important to make a correct diagnosis. Experienced professionals will first check to see if the ear is inflamed and whether it is due to a cold or infection.
If fears are justified, a course of treatment with antibiotics and other possible methods is prescribed. If inflammation is caused by allergies, antihistamines are used. But if the process is complicated by chronic ear diseases, such medications are not recommended. In this case, you need to protect yourself from any contact with a possible allergen. Review your diet and lifestyle in general. In case of poisoning with drugs or the body does not accept one of them, the doctor is obliged to identify the culprit and replace it with a similar drug, without side effects.
If nothing serious was found, you can use witchcraft recipes and try instilling propolis tincture into the ear, after mixing it with vegetable oil or juice squeezed from a baked onion or yarrow. You can mix honey and viburnum juice - the effect is similar. A blockage of the Eustachian tube is possible, then inside the ear, it feels like dozens of bubbles are bursting. If it is not possible to immediately go to the doctor, then simple techniques will help. They will alleviate the symptom or get rid of it altogether. You can push the lower jaw forward and vigorously move it in different directions - it helps with ear congestion. It is also recommended to inhale, cover your mouth and nose with your palm, and then exhale through pinched nostrils - a characteristic click should occur inside the ear and the airlock will disappear.
What not to do
Some, not knowing the simplest safety measures or trying to treat themselves, cause irreparable harm to themselves.
List of precautions:
- You should not try to remove fluid from the ear using earwax removers - it can only cause harm.
- Do not drink cold liquids.
- Avoid hypothermia of the head.
- Do not use ear and nose sprays for more than a week after opening the bottle.
- Do not apply hot compresses without first consulting your doctor. For purulent otitis media and similar forms of inflammation, this is prohibited!
Conclusion
If bubbles appear to be bursting in your ear, you need to pay attention to additional symptoms that may indicate the root cause. Sometimes you need to wait a few days - the phenomenon may disappear on its own
Sometimes you need to wait a few days - the phenomenon may disappear on its own.
But if everything remains the same, and even more so, new signs of an unknown pathology appear, you need to immediately contact an otolaryngologist and identify the source of discomfort.
How to treat if the appearance of a blister still cannot be avoided
To properly treat a blister, you need to know its origin. Therefore, if the cause of the formation is unknown, it is more appropriate to talk about pain relief, itching and swelling.
Modern pharmaceuticals and traditional medicine recipes come to the aid of the sick.
Medicines to combat illness
Broad-spectrum antimicrobial ointments such as Tetracycline, Erythromycin, Levomekol ointment, the root cause of the appearance of a blister is unknown, because they act on almost any group of bacteria.
Furacilin solution will help disinfect the surface of the skin.
Treatment of blisters caused by the herpes virus
Antiviral ointments are used to treat blisters caused by the herpes virus. They act precisely, reach the source of inflammation faster, and many of them have healing properties.
The most commonly prescribed are Oxolinic ointment, Viferon, Zovirax, Cycloferon.
Treatment of blisters - signs of allergies
In case of an allergic reaction, it is possible to use Suprastin, Zodak tablets and other antihistamines. For topical use, Fenistil gel is usually prescribed; herbal-based Gistan cream is also suitable.
Help with blisters formed at the site of a burn
Panthenol foam cream has proven itself to be effective in the treatment of blisters from burns; it has a light texture that allows you to apply the product without increased friction of damaged skin.
The well-known balm Rescuer, made from natural ingredients, helps to accelerate the restoration of the protective properties of the burned area of the skin.
OzhogovNet and Appolo gels are also effective; they not only have antiseptic properties, but also have a wound-healing and analgesic effect.
Possible routes of infection
You can become infected with the herpes virus:
- By airborne droplets. The virus can easily be transmitted by talking, sneezing, coughing, or kissing. The infection spreads through mucous membranes and microtraumas of the skin.
- Through contact and everyday life. Infection can occur through the use of household items of an infected person. Usually these are towels, cutlery, cosmetics, toothbrushes, etc.
- By transplacental route. In this case, the fetus becomes infected through the mother's umbilical cord.
Causes of ear herpes
The human body is a single balanced system. In case of weakening of the body as a whole or damage to its individual organs, the risk of pathogenic viruses entering the circulatory system increases.
The causes of herpes may be:
- Pregnancy. During pregnancy, a woman’s body is weakened due to the processes occurring in it. Weakened immunity opens the way for many pathogens.
- Prolonged hypothermia. This factor is the cause of many diseases, including herpes.
- Overheating in a bath or in the sun. Extreme temperatures disrupt the nervous and immune systems, which weakens the body.
- Nervous overload. Stress speeds up the heart rate and leads to improper metabolism.
- Menstruation, during which internal processes in the reproductive system change.
- Sexual contacts during which contraception is not used.
- Communication with a sick person.
- A previous viral disease that has weakened the immune system.
- Consumption of alcohol or drugs that interfere with the normal functioning of internal organs.
Through the skin or mucous membrane, the virus enters the circulatory system and spreads throughout the body. As soon as it hits the nerve endings, the first symptoms begin to appear.
All about the infectious agent
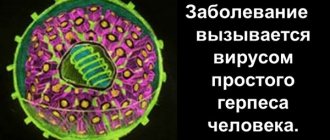
Herpes is a viral infectious disease characterized by the appearance of vesicular blisters on the affected area of the body.
Herpes in the ears can be caused by one of two types of virus:
- Type 1 virus. This is a herpes simplex virus, which is most often localized on the lips, less often on the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, the surface of the ear, and neck. It is present in the bodies of most people. People are first infected with the virus in childhood and remain carriers of this infection forever. It may not manifest itself for a long time, but if the immune system is weakened, its manifestations will not take long to appear.
- Virus type 3. It is also called Herpes Zoster. When it first enters the body (usually in childhood), it causes chickenpox. At an older age, when the immune system is greatly weakened, in a person who has had chickenpox, the virus will manifest itself in the form of shingles.
When the virus gets on a person’s skin or mucous membrane, it gradually begins to move to the internal organs. Then the herpes reaches the nerve endings, where it remains for some time until it disappears.
Symptoms of the disease
As a rule, the first signs of the disease appear within a day after infection.
The symptoms of herpes are as follows:
- appearance of general malaise:
- fever and headache;
- sensation of noise and pressure in the ears;
- constant dizziness and lack of coordination;
- redness of the ears and edges of the nasal passage;
- the ear is very swollen;
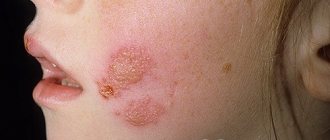
- the appearance of small blisters on the ears, accompanied by itching;
- after 1-2 days, the bubbles on the ears open, yellowish liquid oozes from them;
- over time, the wounds heal and become covered with a brown crust, which disappears after 2-3 days;
- in case of complications, a rash also appears inside the ear canals, which is accompanied by severe pain that periodically occurs in different parts of the head;
- in especially severe cases, hearing is impaired.
Causes of the disease
A total of 8 herpes viruses found in humans have been found.
The cause of rashes in the ear area can be herpes simplex virus type 1 (the one that causes “cold sores”), and the zoster virus type 3 (which also causes chickenpox and a more serious disease, shingles).
Infection with the first type of herpes simplex is estimated to be up to 100% of the world's population, and if it caused an ear sore, the disease will be quite mild.
The vesicles will stay with you for no more than 7 days (with a large area of rash - up to 2 weeks). The bubbles are concentrated at the edge of the auricle, the outer edge of the ear canal.
At the same time, bubbles can also “jump up” on the lips or nose.
If the outbreak is caused by herpes zoster, it means that the virus has attacked the geniculate ganglion (nerve ganglion) of the facial nerve.
This condition is called geniculate ganglionitis. There is a “shooting” in the ear: the pain with such a lesion is severe and can radiate to the face or back of the head, neck.
Vesicles are localized on the external auditory canal, on the eardrum, and can spread to the tongue and palate.
The duration of the uncomplicated form is several weeks. Numbness of the facial muscles, dizziness, and tinnitus may be felt.
Complications from the herpes zoster virus in the ear can be very serious. One of the possible complications is Hunt's syndrome, which causes headaches, ear pain, and facial paralysis.
Herpes in the ear photo
Methods of treating the disease
Treatment of the disease does not require surgery and is carried out exclusively with medication.
In all cases, you must consult a doctor who will prescribe the necessary medications and monitor and adjust the treatment process.
It is carried out in the following sequence:
- Since the disease is contagious, the patient should be isolated. It is advisable if he stays at home until complete recovery.
- Painkillers are taken. Depending on the severity of the lesion and the severity of the pain, analgesics are used in the form of injections, powders or tablets.
- Increased nutrition and consumption of foods and medications that strengthen the immune system are necessary. These are fresh fruits and vegetables, honey, cheese and milk (more details here).
- Antiviral drugs are prescribed. This may be Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Famciclovir or Tromantadine.
- Medicines are used to restore normal activity of nerve endings and restore hearing.
- Various ointments are applied to the rash. These may be available drugs such as Zovirax and Gervirax. You need to constantly monitor your ear. A fresh coat of ointment should be applied immediately if it has been accidentally rubbed off or absorbed. You can replace ointments with castor or eucalyptus oil.
Acyclovir is an antiviral drug for the treatment of herpes.
You should not prescribe medications yourself. Many of them have serious side effects that can cause significant harm to the body.
The course of treatment must be continued until the rash on the ears completely disappears and the pain syndrome is eliminated.
The crusts formed at the site of the wounds cannot be torn off. They must fall off on their own. To reduce itching, you can moisten them with baby cream - this will make them softer and not bother you.
Symptoms and treatment of herpes on the outside of the ear and inside the auricle
Herpes in the ear is a rare localization of infection and can characterize deep viral damage to the trigeminal nerve, middle ear, and oropharynx. Considering that all organs of the facial structures interact with each other, the risk of widespread spread of the virus increases significantly.
The appearance of blistering rashes on the ear requires close attention, since it is ear herpes that leads to serious complications in the brain, organs of vision and hearing. The appearance of herpes in the ears in children is often explained by a primary infection, and in adults - by a recurrence of herpes zoster or chickenpox.
Timely and correct treatment will avoid negative consequences and maintain health.
Infectious agents
Ear herpes is an infectious disease of a viral nature. Experts count several hundred types of virions that affect the appearance of a characteristic blistering rash in various parts of the body: lips, genitals, palms, and oral cavity.
Herpes in the ears and on the outside of the ear is caused by viruses such as HSV 1 and Varicella Zoster. There are known cases of such localization of the disease from other types of virus. The main features of pathogenic microflora are the following:
- the herpes virus is always a chronic infection (once it enters the body, the infection will accompany the person throughout life);
- high degree of contagiousness (in almost 95% of all clinical cases, infection occurs in a healthy person).
The first lesion usually occurs through sexual, contact-domestic or ascending methods. The ear localization of the herpes virus can be caused by inoculation (infection from the lips or genitals to the ears). After entering the body, viruses spread along nerve fibers, causing characteristic herpes rashes on the earlobes, along the edges of the auricle, and inside the ear.
Overview of Herpes Virus Infection
Treatment of herpes on the ear
Herpes on the ears is treated comprehensively using local or systemic medications. Properly organized treatment helps to get rid of the activity of viral microflora and increase the body's protective resources.
For herpes simplex
When treating herpes in the ears, hospitalization is not necessary. Acyclovir is used as the main treatment for herpes simplex. The drug is sold from pharmacy chains in tablets or ointments. Analogues of the drug are Tromantadine or Valacyclovir. The course of antiviral therapy usually does not exceed 14 days, but if necessary it can be extended.
In the absence of a therapeutic result, injection therapy with drugs with antiviral components is prescribed. For topical use, Gervirax, Zovirax, and treatment of rashes with eucalyptus oil are sufficient. Before treatment, it is important to apply a water-based antiseptic solution (Miramistin, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin).
To strengthen the protective forces of the immune system, drugs based on interferons (Leukinferon, Isoprinosine, Viferon) are prescribed. When bubbles become wet, it is important to observe special hygiene and protective regime.
Viferon and Acyclovir
1 2
For herpes zoster
There are no special features in the treatment of herpes infection. Treatment is aimed at relieving pain, restoring lost functions of the nerve roots, eliminating herpes behind the ear, inside and on the surface of the auricle. There are several main groups of drugs against herpes zoster:
- painkillers (Ibuprofen, Ketoprofen, injection analgesics, depending on the severity of the symptomatic course);
- drugs that restore nerves and hearing (“Dibazol”, “Proserin”, B vitamins);
- antiseptics (green solution, methylene blue solution, Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, in which case the product is applied pointwise without affecting healthy areas of the skin);
- vitamins to strengthen immunity.
Shingles in adults usually occurs as recurrent chickenpox. In children, the disease is much milder than in adults. The total period of active infection lasts up to 14 days, so taking antiviral drugs should not be less than 2 weeks.
The classic treatment regimen for infection usually includes the following medications:
- "Acyclovir" in tablets and ointments to destroy the Herpes Zoster viral infection.
- "Gervirax" to prevent the spread of foci of infection to other parts of the face.
- "Reaferon", "Viferon" to increase the body's immune resources.
- "Tromantadine" for the relief of painful manifestations and itching in the localization of rashes.
- "Proserin" to restore auditory reflexes.
- "Dibazol" to improve hearing and reduce tension in the facial muscles.
- “Ibuprofen”, “Ketoprofen”, “Efferalgan” to reduce the intensity of pain in the affected areas.
- "Devirs" to reduce swelling, stimulate the regenerative functions of the skin and mucous membranes, and prevent the inflammatory process.
All these drugs must have an adequate combination, so any prescription must be agreed with the attending physician or infectious disease specialist. Treatment must be long-term, without interruption and in compliance with all medical recommendations.
At the time of therapy, you should refrain from alcoholic beverages and aggressive foods. When the temperature rises, it is enough to take drugs based on paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Treatment of herpes zoster
Possible complications
After an infection, patients should follow a protective regime and maintain immunity in order to avoid a new relapse. Complications from herpetic infection are always individual and depend on the patient’s immunity and clinical history. The main complications are:
- Facial asymmetry. For inflammation of the facial or trigeminal nerve.
- Hearing loss. Ear herpes often causes hearing problems.
- Headache. With a prolonged course of the disease, migraines may develop.
- Chronic rashes. Activation of herpes infection occurs even with minor exposure to various negative factors.
Paralysis and irreversible damage to innervation and nerve sensitivity are considered serious complications of herpes.
The disease requires mandatory treatment according to symptomatic manifestations. Traditional treatment is usually sufficient. During the neonatal period, herpetic infection can be fatal. If an atypical rash appears, you should consult an infectious disease specialist.
Source: https://herpes.center/lokalizaciya/gerpes-v-uhe-i-na-uhe
Prevention of herpes
The occurrence of this rather unpleasant disease is easy to prevent. To do this you need to follow a few simple rules:
- Healthy lifestyle. You need to move a lot and strengthen your body.
- Proper nutrition. Consuming the required amount of proteins, carbohydrates and vitamins will strengthen the immune system sufficiently to successfully resist infection.
- Getting rid of bad habits. Alcohol and smoking significantly reduce the body's resistance to disease.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules. Clean hands and protection during close contacts can save a person from many troubles.
- Maintaining the desired temperature in the room. Don't get too cold outside in winter.
- Consult a doctor promptly at the first signs of viral diseases. It is mandatory to complete the entire prescribed course of treatment. Do not self-medicate.
Constant prevention will allow you to forget about herpes for a long time. Proper treatment will help you get rid of it quickly.
Herpes on the nose - what to do? Herpes on the face
How to diagnose?
Infection of the ear with herpes requires immediate medical attention. The patient should contact a general practitioner, who, if necessary, will refer him to an infectious disease specialist, immunologist and dermatologist.
Diagnosis of herpes can be divided into 2 stages:
- medical examination;
- carrying out relevant laboratory tests.
To accurately determine the diagnosis, you cannot do without testing. Laboratory tests will help determine the type of virus, its concentration and phase of activity.
Classic laboratory diagnostic methods for determining herpes:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The simplest type of analysis that allows you to detect the virus even at the slightest presence in the body.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) . This analysis helps to calculate the presence of IgM and IgG antibodies and identify their concentration and determine the phase of the disease.
- Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) . With this method, the biomaterial is treated with a special substance, under the influence of which the antigens begin to emit light, in which virus particles can be identified.
Blisters on the ear: causes
Blisters are inflammations in the upper layer of the skin, which are characterized by clearly defined swelling, red or pinkish color, and the shape can be either blurry or clear.
The appearance of blisters can be caused by any irritation, friction, the body's reaction can be caused by taking medications, failure to comply with hygiene rules, or infection.
Multiple vesicles - blisters, very similar to pimples, but with transparent contents, appear during an allergic skin reaction. But there are many more reasons when one or more blisters appear behind the ear:
- Insect bite: mosquito, midge, flea and others cause a slight swelling when bitten, which itches a lot
- Fungus: Fungal infections often cause a rash; if the infection occurs in the skin behind the ears, which is not uncommon, blisters and itching are likely.
- Miliaria: as on the fingers, in the armpits, behind the ears, where the skin often sweats under a warm hat, dyshidrosis can manifest itself.
- Friction: Sometimes a blister appears after intense rubbing of the skin behind the ear.
- Dermatitis: After contact with an irritating substance, contact dermatitis can appear behind the ear, where the skin is very delicate.
- Allergic reaction: hives after dyeing hair or changing shampoo or detergent appear and disappear within a few hours.
- Infection: chicken pox, measles, rubella and other infectious and highly contagious diseases occur with a rash in the form of blisters.
- Seborrhea: This disease can also affect the part of the scalp that is not covered with hair.
- Scrofula: many have not heard of this disease, meanwhile, grayish formations behind the ears, itchy and flaky - one of the most common diseases, it is caused by the tubercle bacillus, affects people (often children under 10 years of age, but sometimes adults), with a tendency to tuberculosis, weakened immune system.
- Neoplasms: often what a person mistakes for a blister does not go away for quite a long time; dense contents appear inside it, which keeps increasing, eventually forming not just a blister, but a huge “bump.” Such a blister may ultimately turn out to be either an epidermal cyst (benign tumor) or a malignant skin lesion.
- Otitis: inflammation can be both external and internal; itching and the appearance of a blister in the ear can also be the initial stage of otitis.
Important. Sometimes irritation and blisters behind the ear can indicate herpes, pemphigus (an autoimmune disease that is difficult to treat), problems with the gastrointestinal tract, nervous exhaustion, neurosis, which is also fraught with many unpleasant consequences if the problem is not found and treated in a timely manner.
How to recognize and treat herpes in the ear?
The appearance of a small rash in the ears may be a symptom of the development of ear herpes. The disease can cause serious complications, as it is located near the organs of vision, hearing and brain. Immediate treatment will help avoid serious consequences.
All about the infectious agent
Herpes is a viral infectious disease characterized by the appearance of vesicular blisters on the affected area of the body.
Herpes in the ears can be caused by one of two types of virus:
- Type 1 virus. This is a herpes simplex virus, which is most often localized on the lips, less often on the mucous membrane of the nose and throat, the surface of the ear, and neck. It is present in the bodies of most people. People are first infected with the virus in childhood and remain carriers of this infection forever. It may not manifest itself for a long time, but if the immune system is weakened, its manifestations will not take long to appear.
- Virus type 3. It is also called Herpes Zoster. When it first enters the body (usually in childhood), it causes chickenpox. At an older age, when the immune system is greatly weakened, in a person who has had chickenpox, the virus will manifest itself in the form of shingles.
When the virus gets on a person’s skin or mucous membrane, it gradually begins to move to the internal organs. Then the herpes reaches the nerve endings, where it remains for some time until it disappears.
Possible routes of infection
You can become infected with the herpes virus:
- By airborne droplets. The virus can easily be transmitted by talking, sneezing, coughing, or kissing. The infection spreads through mucous membranes and microtraumas of the skin.
- Through contact and everyday life. Infection can occur through the use of household items of an infected person. Usually these are towels, cutlery, cosmetics, toothbrushes, etc.
- By transplacental route. In this case, the fetus becomes infected through the mother's umbilical cord.
Risk factors
The manifestation of herpes can be provoked by:
- hypothermia;
- overheating;
- pregnancy;
- menstruation;
- being under constant stress;
- alcohol abuse;
- public facilities;
- immunodeficiency states (HIV, AIDS).
Symptoms
Despite some similarities in the clinical picture, herpes viruses types 1 and 3 have characteristic differences in symptoms.
For herpes simplex virus
When the ear is affected by a simple type of herpes, the disease does not bring any particular trouble, passes without pain or complications, and the person feels well.
Herpes appears on the outer parts of the auricle, in the territory of the external auditory canal. Along with inflammation on the outside of the ear, infection can appear in the nose and lips.
The main symptoms of the herpes simplex virus:
- the affected area turns slightly red and swells slightly;
- itching appears;
- the skin of the ear becomes covered with small blisters filled with clear liquid;
- after a couple of days, the bubbles burst and then become covered with a dry crust, which falls off quite quickly, leaving no traces behind.
For shingles
The virus manifests itself not only on the outside of the ear, but also inside the ear canal. Severe pain in inflamed areas of the skin indicates that the nerve ganglia of the facial nerve are affected by the virus.
After opening the watery blisters, noticeable ulcers form in their place, and after healing, deep scars remain.
Shingles is more painful than the simple herpes virus:
- shooting pains appear at the sites of the rash;
- the person feels general malaise;
- body temperature rises;
- lymph nodes enlarge;
- herpes spreads to other areas of the skin.
If the disease proceeds without complications, then herpes zoster goes away in 1-2 weeks. Without proper treatment, the virus can progress to the next stage, which is called Ramsay-Hunt syndrome.
With this syndrome, the herpes rash spreads to:
- face;
- neck;
- tonsils;
- soft palate;
- eardrum;
- back;
- the back of the head.
Characteristic symptoms during the development of Ramsay-Hunt syndrome:
- dizziness and noise in the ears;
- hearing becomes dull;
- mild cramps appear;
- coordination of movements is impaired;
- there is excessive salivation;
- paresis of the facial muscles develops.
Treatment of the disease may take up to 1 year.
How to diagnose?
Infection of the ear with herpes requires immediate medical attention. The patient should contact a general practitioner, who, if necessary, will refer him to an infectious disease specialist, immunologist and dermatologist.
Diagnosis of herpes can be divided into 2 stages:
- medical examination;
- carrying out relevant laboratory tests.
To accurately determine the diagnosis, you cannot do without testing. Laboratory tests will help determine the type of virus, its concentration and phase of activity.
Classic laboratory diagnostic methods for determining herpes:
- Polymerase chain reaction (PCR). The simplest type of analysis that allows you to detect the virus even at the slightest presence in the body.
- Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) . This analysis helps to calculate the presence of IgM and IgG antibodies and identify their concentration and determine the phase of the disease.
- Immunofluorescence reaction (RIF) . With this method, the biomaterial is treated with a special substance, under the influence of which the antigens begin to emit light, in which virus particles can be identified.
How to treat herpes in the ear?
Proper treatment will prevent the spread of the virus, alleviate symptoms and speed up the healing process. Therapy should begin immediately after the first signs of the disease appear.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies will help relieve symptoms and, in combination with medications, will contribute to a faster recovery:
- The areas where herpes is localized are wiped with essential oils of fir, lemon, tea tree, and eucalyptus.
- Aloe and Kalanchoe juice is effective. To do this, simply cut off the leaf and wipe the problem areas with it.
- To increase immunity, it is recommended to drink tinctures of echinacea purpurea and eleutherococcus.
- You can make antiseptic lotions from onion or garlic juice and apply to the ear until the liquid dries.
- Steam baths made from nettle and yarrow are effective.
Is herpes in the ear contagious?
Herpes is a highly contagious infection. A carrier of herpes simplex simply needs to sneeze to infect nearby people. 90% of the inhabitants of our planet are carriers of this virus.
Herpes type 3 is transmitted primarily by contact. The danger is liquid from bursting bubbles. The virus poses a threat only to people who have not previously had chickenpox.
Duration of the disease
The disease caused by the herpes simplex virus lasts on average 5-7 days, maximum 2 weeks.
Shingles lasts at best 1 month, on average 3-6 months, and in severe cases - up to 1 year.
If the case is advanced and cannot be treated at home, it is necessary to resort to the services of a hospital, where you will need to stay until complete recovery.
Complications
Herpes simplex is not dangerous, but herpes zoster can cause a number of complications:
- hearing loss;
- facial asymmetry due to severe inflammation of the facial nerve;
- musculoskeletal disorders (most often older people suffer from this);
- the addition of a bacterial infection - streptococci and staphylococci, which can cause pneumonia and inflammatory skin diseases.
Prevention methods
To prevent the risk of contracting herpes or to prevent the virus already in the body from becoming active, you should follow simple rules:
- lead a healthy lifestyle, move a lot;
- adhere to a proper, balanced diet (eat enough proteins, fats, carbohydrates, vitamins);
- get rid of bad habits that reduce immunity;
- observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- beware of hypothermia and overheating (dress appropriately for the weather);
- avoid stressful situations;
- treat all emerging diseases in a timely manner.
Compliance with these prevention methods will relieve many diseases for a long time and strengthen the immune system. In this case, it will be difficult for the virus to attack the body.
It is almost impossible to completely protect yourself from the herpes virus entering the body, but taking good care of your health will help reduce the risks of contracting this disease and ensure a speedy recovery and absence of complications in case of infection.
Source: https://kozh-med.com/kozhnye-bolezni/gerpes/v-uhe.html
What to do if it itches, scratch it or endure it?
No scratching, no matter how itchy the skin affected by the blister. A serious risk of infection arises due to the specific location of the irritation.
Constant friction with hair and hats contributes to the introduction of harmful bacteria into micro-wounds; even a tiny scratch heals here very slowly, and dermatitis will have to be treated for at least a week.
When affected by a fungus or infectious disease, the risk of spreading the disease with the liquid contained in the blister increases significantly, so herpes, fungus, and lichen can be “spread” throughout the body.
First aid
One or more blisters that appear behind the ears should not be touched with bare hands, especially without treatment with an antiseptic.
If blisters appear where contact with a bandage, headdress or hair is inevitable, remove these squeezing and rubbing objects, put the hair in a ponytail, pin it up, comb it - do everything to avoid contact.
If you suspect an allergic reaction, remove substances that could cause it away: rinse off the hair dye immediately with plenty of water so that the blister does not develop into Quincke's edema (a life-threatening syndrome, which is essentially an ordinary but giant blister that causes suffocation), Wash off shampoos or gels with plenty of clean water.
- If there is a significant deterioration in health or shortness of breath, take the victim out into the fresh air, into a well-ventilated area.
- Give any antihistamine to relieve an exacerbation.
- Treat the surface behind the ears with an antiseptic.
- If severe itching occurs, apply ice; you can lubricate it with any remedy that relieves this symptom, from soda solution to Finalgon.
- If you feel unwell, call emergency medical help; if you feel well, go to the hospital to find out the cause of the blister.
Important. Any formation on the skin may be the result of a serious life-threatening illness.
When applying symptomatic treatment to relieve itching, we must not forget that only a doctor can provide real help, as well as make a diagnosis. Even if the blister does not cause concern, you should not let the disease take its course.
Blister Treatment Options
If formations on the skin appear unexpectedly, and it is impossible to seek medical help, you need to remember about methods of help at home. You can alleviate the condition both with the help of medications and folk remedies.
Pharmaceutical ointments, plasters
- Having noticed a blister, treat the skin around it with an antiseptic;
- if the blisters are not damaged, carefully apply ointment with a cooling effect to a cotton pad, apply to the skin, and secure with a bandage;
- if the blisters burst, it is enough to lubricate them with anti-inflammatory ointment Solcoseryl, Methylurocil, oxolinic or tetracycline;
- repeat every 4 to 6 hours, carefully monitoring the patient’s condition.
Attention. You should not use patches if they are not medicinal, it will damage the skin and cause additional suffering.
For allergies and burns, you need to use products designed to treat them.
Treatment of blisters on the ear with traditional medicine
A lotion of soda with added water is applied to the affected area for insect bites to relieve itching.
Aloe juice, raw potatoes, carrots will help stop itching and inflammation.
A decoction of chamomile, sage, and birch buds will relieve inflammation and itching.
- Mix 1 tsp. dry herbs and buds.
- Boil 1 l. water, add raw materials.
- Boil over low heat for 3 minutes.
- Cool, moisten a disc or gauze in the broth, and apply to the affected area.
- Change every 2 – 3 hours.
This flock will help with burns, dermatitis, and allergic reactions.