Children's love for animals in some cases leads to negative consequences, since microsporia is often found among the diseases that can be contracted from cats and dogs. Another name for this disease is ringworm; it affects the scalp and is the most common infection. According to statistics, children are more likely to suffer from this disease than adults.
Etiological factors of microsporia in children
The cause of microsporia in adults and children is a fungus from the genus Microsporum. It is divided into three types: anthropophilic, zooanthropophilic and geophilic.
The most common is an anthropophilic pathogenic fungus that parasitizes the human body. Infection occurs from a sick person, through household objects and through household contact.
The carriers of the zooanthropophilic species are cats, dogs, guinea pigs, and hamsters. The infection spreads to a person through contact with a sick animal or things that have the fur of a sick animal on them.
The third type of microsporia are geophiles that live in the soil. These mushrooms are very resistant and can survive in the soil for more than three months. They are easily transferred to animal fur and household items.
Diagnosis of microsporia
A dermatologist may suspect microsporia already during a clinical examination of the patient, confirming the fact of contact with animals indicated in the anamnesis, and prescribe adequate treatment. When a person is infected with microsporia, one can detect mycelium and changes in hair and skin characteristic of mycoses. This is determined using dermatoscopy and scraping microscopy. But these laboratory research methods only confirm the presence of a fungal disease, but do not help establish an accurate diagnosis.
A more informative method is cultural diagnostics microscopy by seeding with subsequent identification of the pathogen, determining its type and genus. The study helps to select the most effective drugs for treatment. However, this method takes much more time.
Fluorescence testing allows for a quick examination of the patient and his contact persons. This method is used for:
- pathogen identification;
- identifying affected hair;
- determination of infection or carriage in animals;
- control over persons who had contact with the patient;
- assessing the results of therapy.
The green glow is a sign of fungal mycelium, but the cause of the phenomenon has not yet been studied. In the early stages of the disease, there may be no glow at all, since the hair is not yet affected.
Provoking factors
In medical practice, there are several factors that can trigger infection in children. Some of them:
- environmental influence,
- lack of vitamins, poor nutrition,
- decreased immunity,
- non-compliance with sanitary standards in children's institutions,
- a large number of abrasions, wounds on the skin,
- violation of personal hygiene rules.
Treatment and prevention of microsporia
To treat microsporia, general or local antifungal therapy is used, depending on the severity of the lesion. Emulsions, sprays, ointments and creams containing antifungal drugs (Terbizill, Termicon, etc.) are used as local therapy. This takes into account the patient’s age and physiological condition. You need to know that there are contraindications for pregnant and lactating women. Such drugs should be used with caution. The advantage of ointments with antifungal components is the fact that modern rubbing does not leave greasy marks on the skin and clothes, allowing patients to feel comfortable throughout the course of treatment.
Combination drugs containing antifungal and hormonal components are used in case of a pronounced inflammatory reaction. A good therapeutic effect is achieved by alternating applications with ointments and treatment with iodine solutions, provided there is no skin damage.
The use of Triderm ointment gives excellent results in the treatment of microsporia complicated by secondary infection. Preparations containing dimexide are used for deep skin lesions.
Prevention of microsporia consists, first of all, in maintaining personal hygiene, limiting contact with stray animals and regularly examining children in child care institutions to identify patients. You also need to pay special attention to the issue of purchasing animals for keeping at home. Without a veterinarian's examination, such a purchase can cause an intrafamily outbreak of microsporia.
Routes of infection
Pathogenic microsporia fungi spread easily in the external environment. Therefore, you can become infected with this disease everywhere in the following ways:
- with constant contact with the soil,
- through microtrauma of the epidermis,
- due to dry skin,
- when in contact with stray animals,
- if there is a failure in the secretory function of the sebaceous and sweat glands.
Attention! A child can become infected from a sick adult or in a children's group.
When it turns out that microsporia has been detected in a children's institution, it is quarantined and disinfected.
Advice from Dr. Komarovsky
When confirming the diagnosis, the famous pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky recommends adhering to the following approach to treatment:
- Observe the rules of hygiene, periodically wiping the wet surface of the skin (in the affected areas).
- Do not self-medicate under any circumstances (since microsporia is a serious disease that is difficult to treat) and if you suspect an infection, immediately contact a medical facility.
- Use folk remedies only as a complement to the main treatment.
- Use antifungal ointments and oral medications prescribed by your doctor, without exceeding the permissible dosage.
- During illness, protect the child from contact with other children and adults (since there is a high risk of transmission of infection).
Following these recommendations will speed up the healing process.
Symptoms and signs of microsporia in children
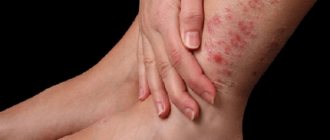
At the initial stage, this disease manifests itself in the form of a red spot with clearly defined boundaries at the site of penetration of the fungus. It protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin and becomes larger over time. A roll with a small rash forms along the edges and gradually becomes like a ring.
The development of microsporia is accompanied by itching. If a child begins to scratch the source of infection, the infection begins to spread throughout the body. Places where lichen is often concentrated are the neck, limbs, face, shoulders.
Types of disease
In medicine, it is customary to distinguish several types of microsporia:
Bestiality, the source of which is animals or household items and clothing that have come into contact with saliva or fur of an infected pet. To become infected, it is enough to pet an infected animal. The incubation period lasts from 5 to 8 days.- Anthropotic, the source of infection in which is a sick person. Infection can occur even when there are no signs of microsporia on the patient’s body, but he is a carrier of the fungus. The incubation period in this case will be much longer - from 4 to 6 weeks.
- Geophilic - infection occurs through soil or sand, where fungal spores are stored in their original form for a long time. After contact with the skin, do the spores penetrate inside through cracks? and the development of the pathological process begins. It is also not possible to recognize this type of disease at an early stage - the incubation period can reach one and a half months.
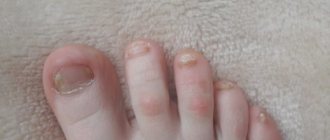
The fungus most often affects smooth skin or the scalp, but cases of damage to the nail plate are known.
Consequences when a large amount of rash appears
- a general painful state occurs,
- body temperature rises,
- the body becomes weak,
- possible enlargement of lymph nodes,
- sleep is disturbed
- loss of appetite.
The spots increase to 5 cm and all have the shape of a ring.
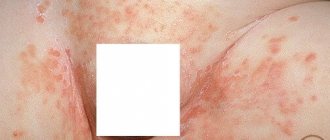
The center exhibits a pale, scaly appearance. The edges are clearly bordered by many bubbles filled with liquid. Bursting, the bubbles form small lesions on the skin, which later become covered with crusts. If microsporia spots are severely inflamed and swelling is visible, the child suffers from constant itching. Ringworm on the scalp in children usually occurs between the ages of 6-12 years. Peeling begins, and as a result, ring-shaped spots appear. At the initial stage, the fungus is very difficult to notice, since it chooses a location at the roots of the hair. Parents should pay attention to the fact that the child’s head is constantly itching. Microsporia is mainly concentrated on the crown, temples and parietal part of the head. It subsequently spreads along the entire length of the hair, which becomes brittle and dull. The skin in these places takes on a grayish tint.
A characteristic sign of the disease is the appearance of three large lesions, around which there are many small bald patches. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, complications may arise in the form of suppuration. This can subsequently lead to large bald spots where hair stops growing.
Microsporia of the nail plates is very rare. It is characterized by the development of faint spots on the nail, which after some time become white. The nail in this area can be very fragile and soft and becomes damaged over time.
Forms of microsporia
The types of microsporia are classified taking into account the depth of skin damage, the prevalence of lesions, the method of infection, and the course of the disease.
Superficial
The surface layer of the skin is affected, on which red scaly spots appear on the body and head, where the hair breaks off, forming bald spots with short stumps.
Exudative
Affects the deeper layers of the epidermis. Bright red spots are visible on open areas of the body, on the surface of which small bubbles with liquid inside form. There is weeping and itching. Serous discharge permeates the skin scales, they stick together, forming a dense crust. Underneath there is erosion, similar to a burn.
Infiltrative-suppurative
Affects the skin to its full depth. It usually appears on the scalp as a raised, dense, painful infiltrate, which gradually softens with the formation of purulent contents. When you press on the node, pus is released from the openings of the hair follicles. Accompanied by fever, intoxication, and enlarged lymph nodes. At the site of the infiltration, a scar or areas devoid of hair are formed.
Sometimes it takes the form of kerion Celsi (honeycomb of Celsus), when the pus flows like honey from a honeycomb, thick and light yellow.
Chronic
Another name is recurrent. It develops with untreated or undertreated microsporia, when the fungus makes itself felt again.
Anthroponotic and zoonotic
If a child becomes infected from an animal, then this form of microsporia is called zoonotic. It is the most common. Anthroponotic is much less common. It is transmitted from person to person or through the patient’s belongings.
Both forms of microsporia manifest themselves with the same symptoms and are treated according to the same regimen.
Atypical forms
They run smoothly and disguise themselves as other skin diseases. Their classification is based on similarities with other diseases.
- Trichophytoid microsporia. Forms many small, vague foci without signs of inflammation. The hair is broken off close to the head. Gradually covers the entire hairline with the formation of bald areas. Often becomes chronic.
- Seborrheic causes severe hair loss and flaking of the skin with the formation of many scales resembling dandruff.
- Rosacea-like appears on the body in the form of pink spots with clear boundaries and slight peeling, reaching very large sizes.
- Psoriasiform. Reminiscent of psoriasis - plaques covered with silvery scales.
Differential diagnosis
Microsporia should be differentiated from the following skin diseases:
- Trichophytosis is a fungal disease that affects the hair roots, and black dots appear in place of lost hair. Sometimes the wounds can fill with pus and bleed.
- Favus - the disease is now rare. The fungal spores do not completely affect the hair, so in patients with favus they do not break off. And they fall out because the hair follicles become necrosis.
- Seborrhea differs from microsporia in that foci of infection are localized on the face and hair, in places where the sebaceous glands are concentrated.
- Psoriasis is a non-infectious skin disease. The disease is not accompanied by itching, the red dry spots of which have clear outlines and sometimes peel off.
- Alopecia areata – can occur suddenly on the skin, mainly on the scalp and face. There are a small number of small round bald spots. These spots can enlarge, coalesce and lead to complete baldness.
Main symptoms of the disease
All types of the disease have both common symptoms and signs, as well as individual features that are characteristic of a particular type of disease. One of the first symptoms is the appearance of small red spots on the body or scalp. It is also possible for plaques to form in the eyebrows and eyelashes.
A few days after the main plaque appears, it changes its color to pale pink, and dry skin flakes begin to form in the center. If the hair is affected, the strands begin to break off at a height of a few millimeters from the head, creating the appearance of a short haircut. The hair becomes discolored and becomes whitish. Thus, small bald spots are clearly visible on a person’s head, which are covered with dry skin flakes.
In rare cases, microsporia is not accompanied by hair breaking. A large number of dry scales appear on the head, which are mistaken for unexpected dandruff. Even more rarely, the disease manifests itself as a small gray spot and a complete absence of hair on it .
When smooth skin is affected, a pink-colored maternal spot forms on its surface, along the edges of which a ridge protruding above the healthy epidermis is clearly visible. This roller, as it were, limits the area of spread of infection. Often, inside the main spot, another one of the same type appears, only smaller.
Gradually, the affected areas increase in size, taking on the shape of an oval or circle, while their size reaches 10 cm. When several lesions are located nearby, they can merge with each other. Often the formation of spots is accompanied by severe itching, but there are cases where there was no unpleasant sensation at all.
If there are a large number of lesions on the face and body, the patient may have a fever and enlarged lymph nodes. An inflammatory process often develops against the background of infection. In this case, the areas affected by microsporia swell and pus collects in them .
Drug therapy
To treat microsporia, the doctor prescribes antifungal drugs. In the morning you need to start treating the affected areas with fucorcin, 2% iodine solution, 10% dimexide. After this, antifungal ointments are applied.
Salicylic ointment
This is an excellent remedy for wounds and burns. Salicylic ointment is prescribed for diseases of eczema and pityriasis versicolor. You must use the product with extreme caution, carefully reading the instructions, as it can cause an allergic reaction. Also, the ointment should not be used by people who have kidney problems. It is not recommended to apply to moles and warts. The course of application is from 7 to 10 days.
Sulfuric ointment
The drug copes well with microsporia. This has long been a well-known remedy for combating scabies and lichen. Ointment (10%) quickly heals wounds and has a soothing effect on the skin. The product (33%) is able to loosen the upper layers of the skin and instantly absorb into it. It helps perfectly in the fight against lichen that has managed to penetrate deep into the skin. No side effects of this ointment have been identified. Treatment takes no more than 10 days. It is enough to apply the ointment once a day.
Tar ointment
It has a broad therapeutic effect, during which it disinfects and fights parasites. Method of application: in the morning, the affected areas are lubricated with iodine, then tar ointment is applied. The procedures should be repeated for three weeks.
Along with traditional ointments, treatment can also be carried out with modern drugs. These include: Clotrimazole, Terbinafine, Iconazole, Mycozolin, antimycotics. Lamisil, which is available in pharmacies in the form of creams or sprays, has a good antifungal effect. Of the many tablets for fungal infections, the following are prescribed:
- Ketoconazole, which stops the spread of mycosis and adversely affects fungal cells.
- Preparations containing Griseofulvin inhibit the development of fungal cells and affect the DNA of its spores. This is one of the effective treatments for microsporia in children. Should be taken every day 4 times with meals along with 1 tsp. vegetable oil, which will help dissolve this drug faster and increase the degree of its effect. Children under three years of age are prescribed this remedy in liquid form.
- Terbinafine. One tablet 1 time per day. Well tolerated by children's bodies.
Methods for treating microsporia
Therapy is carried out under the supervision of a dermatologist and usually does not require hospitalization.
Comprehensive treatment is indicated, this will allow you to quickly get rid of the causative agent of the disease and prevent relapses. After therapy, a consultation with a cosmetologist may be required.
Be sure to read:
Types and treatment of lichen in humans: differences between the disease in children and adults
General recommendations
- Shaving hair. For microsporia on the scalp, once a week you need to carefully shave the hair 0.5-1 cm from its edge.
- Washing the skin . Wash the skin around the affected area several times a day to remove dirt. The contact of water with the resulting lesions should not be frequent.
- Limiting physical activity.
- Vitamins (proper nutrition, taking vitamin-mineral complexes).
- Personal hygiene products. The patient must have his own personal belongings - washcloth, towel, comb, etc.
It is also not recommended to allow the skin to become overcooled or expose it to direct sunlight; take a bath (it’s better to limit yourself to a shower).
All family members should undergo a preventive examination by a dermatologist.
Taking antifungal drugs by mouth
Antifungal agents in tablet form must be prescribed:
- Griseofulvin . It is advisable to take it with fatty foods (milk, butter), so it is better absorbed.
- Terbinafine . The course of treatment is about 8-12 weeks.
The dosage for adults and children is selected by the doctor.
The listed medications stop the growth and development of fungi, and also have a direct destructive effect. They are the basis of treatment.
Folk remedies
Many people consider it safe to treat microsporia in children with folk remedies. However, this opinion is wrong. Various herbs, tinctures and many other remedies should be used in combination with basic drug treatment.
Treatment of fungal diseases with folk methods is based on treatment with medicinal plants that have antifungal and antimicrobial effects. An excellent treatment for microsporia is calendula. A tincture is used from flowers, which needs to be soaked into the diseased areas 3 times every day. Onions and garlic are also suitable for external use. You need to prepare a paste from these ingredients and lubricate the affected areas 2 times daily.
A tincture of birch buds and medical alcohol is also another gentle remedy for treating a child with ringworm. They are mixed in proportions: 2 tsp. birch buds to 250 ml of alcohol and infuse for about two weeks. Used for external use, 4-5 times daily.
Attention! If the disease is advanced, then traditional medicine must be combined with drug therapy.
Diagnostics
To diagnose microsporia, the following research methods are used:
- Luminescent
- Microscopic
- Cultural
The luminescent method is based on the fact that hair affected by the microsporum fungus exhibits an emerald green glow when exposed to a Wood lamp (a lamp emitting in the “soft” ultraviolet range). Examination under a Wood's lamp makes it possible to assess the extent of fungal damage and subsequently serves to adjust therapy, determining its effectiveness.
During microscopic examination, hair scales are taken from the lesions. And with microsporia of the scalp - hair fragments. Under a microscope, filaments of mycelium, spores on the surface of the hair, and disturbances in its structure are visible.
A cultural study consists of inoculating the fungus in a nutrient medium and serves to accurately determine the pathogen. Hair scales or fragments are also used as material for sowing. Results usually appear on the third day after sowing.
Prevention methods
Everyone knows that it is better to prevent any fungal disease than to treat it later. This primarily applies to microsporia, the prevention of which does not require much effort. The most important rule to follow is to teach your child to wash his hands and not allow him to have contact with stray animals. But if this happens, and the child pets a sick animal, then you need to wash your hands with soap. Tar or laundry dark soap is suitable for this.
Strict adherence to your doctor’s prescriptions will help you quickly cope with the infection, and following normal hygiene rules will prevent infection.
Classification
Depending on the manifestations, microsporia is divided into types:
- mycosis of the skin;
- scalp;
- nail plates.
Forms of the disease from the source of infection:
- zoonotic – transmission from animals;
- anthroponotic – owner – sick person;
- geophilic - the pathological process begins after contact with the ground without protective equipment.
Classification is necessary for epidemiological disinfection measures, which prevents further spread of the fungus.
Types of microsporia by type of lesion:
- superficial – formations on the skin or hair;
- exudative - with the release of fluid;
- purulent - lesions penetrate deep into the outer integument, and an infection joins them;
- nail;
- chronic – with constant exacerbations and remissions.
Quarantine in kindergarten and school
Since microsporia in children is highly contagious, the risk of transmitting the fungus from a sick child to a healthy one is quite high. That is why, if a pathology is detected in one of the kindergarten students, the group is quarantined. To do this you need:
- submit an application to SANPiN with the relevant requirements. In this case, you should describe the problem;
- exclude the sick child from attending the group until complete recovery;
- Conduct daily examinations of children.
Microsporia quarantine lasts for 45 days. If no new cases of the disease are recorded during this time, the quarantine will be lifted. If new cases are discovered, the quarantine will be extended for another 45 days.
If your child has had contact with other infected children, you must:
- wash it using fungicidal soap. At the same time, attention must be paid to all parts of the body, including the head;
- change the clothes he was wearing in the garden. Dirty laundry must be washed at high temperature and ironed thoroughly;
- Visit a dermatologist a week after contact. During this time, the fungus should have time to manifest itself. The first symptoms may not be noticeable to parents, but the doctor will see them;
- In case of infection, the child must be given a separate towel, comb and other hygiene items. The children's room must be ventilated regularly. If there are other children in the family, it is important to monitor their condition and minimize contact.