A common problem is itching and redness on the hands, which causes particular discomfort and physical inconvenience. The mechanism of its appearance is not fully understood; the reasons may be varied.
Most often - exposure to allergens, penetration of bacteria (germs) through small cuts, abrasions, injuries. In older people, dry, swollen skin is observed due to decreased function of the sebaceous glands.
Before selecting ointments or creams for treatment, it is important to establish the true causes leading to discomfort on the skin of the hands.
Diseases that may be accompanied by swelling of the limbs
- Enlarged lymph nodes in the armpit (in the absence of wounds on the extremities). In this case, you should immediately contact an oncologist.
What to do if your finger is swollen? If swelling increases, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Itching and redness on the hands of pregnant women
During pregnancy, the female body experiences great changes. Redness and itching on the hands are provoked by hormones, namely high levels of estrogen, leading to the development of telangiectasia.
However, there are other reasons:
- Excessive sweating of hands;
- Stress, anxiety and anxiety;
- Allergenic foods;
- Constant contact with household chemicals and water;
- Skin dermatitis, fungal infection;
- Increased bilirubin in the blood.
Women can get an allergic reaction to external irritants if their skin is excessively dry.
It is important to identify and eliminate true triggers or allergens at an early stage. Otherwise, the constant nervousness and irritation of the expectant mother can negatively affect the health of the newborn.
Treatment
Polyarthritis. The main goals are to relieve pain, reduce swelling, and maintain joint mobility. You can do the exercises yourself: clench and unclench your fingers, stretching them. Make circular movements with your thumbs straight. Repeat the exercises every day. Use alternating cold and hot compresses to reduce pain.
Felon. In the initial stage of the disease, keep your finger in a warm bath with manganese for 5 to 7 minutes. Hot saline solutions will help. Apply a bandage with Dioxidin or Levomekol. Vishnevsky ointment gives a good effect. In advanced stages, surgical intervention is indicated. The doctor removes the nail using local anesthesia. Finds out why fingers swell. Then he prescribes dressings, antibacterial and drug therapy depending on the cause of the disease.
Bites of insects, animals and humans. The wound should be washed immediately with soapy water. A solution of furatsilin and hydrogen peroxide are also used to wash wounds.
Drug treatment for itching and redness on the hands
Let's consider what drugs can be used to treat itching and redness on the hands due to a particular disease.
Itching and redness due to temperature changes
The basis for the treatment of cold or sun allergies is antihistamines with antifungal properties.
Most popular:
- Sinaflan is a glucocorticosteroid to relieve itching, allergies, and inflammatory reactions. Contraindications: precancerous conditions, psoriasis, acne. Use for children from 2 years of age, not for long. Average cost 90 rubles ;
- Advantan is a non-halogenated corticosteroid medication. Indicated for atopic dermatitis and eczema. Rub into skin 2-3 times a day. Can be used by infants from 1 month. The course of treatment is no more than 4 weeks. Average cost 350 rubles ;
- Hyoxysone - to provide an anti-inflammatory effect. Prescribed for carbuncles, furunculosis, frostbite. Apply by applying a thin layer to the affected areas 1-3 times a day, applying sterile gauze on top, securing with a bandage. The course of treatment is 7-10 days. If the lesions are extensive, it is not recommended for use in children under 12 years of age. The average cost is 50 rubles .
Sinaflan Advantan Hyoxysone
Itching and redness from insect bites
Most prescribed drugs:
- Dimexide is an analgesic anti-inflammatory medication. Apply applications to the affected areas, moistening a napkin with the solution and applying for 30 minutes. The course of treatment is 10-15 days. Apply ointment 1-3 times. Use for children from 12 years of age. Average cost 60 rubles ;.
- Tavegil is an antiallergic, antipruritic drug, a histamine receptor blocker. Release form: tablets. Do not use during pregnancy, lactation and bronchial asthma. For children under 1 year of age, the acceptable form of use is syrup, solution. Tablets only from 6 years of age. The average cost is 180 rubles .
Dimexide Tavegil
Itching and redness during an allergic reaction
The basis of treatment is antihistamines with antipruritic, antifungal, antibacterial effects, to relieve hyperemia, itching, burning and redness.
The most effective drugs:
- Psilo-balm is a local anesthetic with a cooling effect. Use in a dose of 2-3 g up to 3 times a day. Children - from 2 years old, pregnant women - with the permission of a specialist. Average cost 300 rubles ;
- Levomekol - with antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory effects. Can be used during pregnancy and for children over 2 years old. Apply in a thin layer. Average cost 110 rubles ;
- Skin cap - with antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects. Process up to 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 3-4 weeks. Can be used by children from 1 year of age. Average cost 780 rubles ;
- Elidel - with anti-inflammatory effect. Treat skin areas up to 2 times a day until symptoms are completely eliminated. Can be used from 3 months. The average cost is 960 rubles .
Psilo-balm Levomekol Skin-cap Elidel
Itching and redness with eczema
When treating eczema on the hands, antihistamines with antipruritic and sensitizing effects are used:
- Hydrocortisone ointment - apply twice a day for 14-20 days. Apply dressings for hypertrophic ulcers every 24-48 hours. Can be used in children from 1 year of age, but without using occlusive dressings. The duration of treatment is no more than 2 weeks. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Elokom - with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory effect. Treat the affected areas once a day, for children only from 1 year. In severe cases of the disease - from 6 months under the guidance of the attending physician. Average cost 160 rubles ;
- Beloderm - with antiproliferative and vasoconstrictive effects. Treat twice a day, for children from 6 months. The course of treatment is 4 weeks. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Flucinar is an anti-exudative drug with treatment of skin areas twice a day, applying no more than 2 g. The course of treatment is 2 weeks. Contraindications: pregnancy up to 12 weeks and children under 1 year of age. Average cost 260 rubles ;
- Triderm - with antifungal and vasoconstrictor effect. Treat skin areas twice a day (morning, evening). During pregnancy, use with the permission of a doctor, for children from 2 years of age. The average cost is 450 rubles .
Itching and redness with scabies
When your hands are affected by scabies mites, the following medications help:
- Sulfur ointment - before use, wash and dry the affected areas. Apply in the evening before bed. The course of treatment is 5 days. Use for children over 3 years old. Average cost 30 rubles ;
- Benzyl benzoate - apply in the evening during the period of mite activation on dry skin of the hands, evenly distributing the composition and rubbing into the affected areas. The course of treatment is 3 days. Use for children from 1 year of age. Average cost 230 rubles ;
- Spregal is an aerosol for suppressing subcutaneous parasites. Spray onto the affected dermis every 12 hours, keeping the can at a distance of 30 cm from the body. Use for children from 6 years of age. The average cost is 940 rubles .
Sulfur ointment Benzyl benzoate Spregal
Itching and redness with lichen ruber
Effective ointments for treating rashes:
- Fenistil - with an antiserotonin effect. Apply the composition 3 times a day. Use for children from 1 month. Average cost 400 rubles ;
- Salicylic ointment - with an antiseptic, keratolytic effect. Apply a thin layer and place a sterile bandage on top. Dose 4-5 ml per day. Suitable for children from 2 years old. Average cost 30 rubles ;
- Zinc ointment - with a drying, astringent effect. Apply a thin layer to previously cleansed skin areas up to 3 times a day. Can be used for infants from 1 month. The average cost is 40 rubles .
Fenistil Salicylic ointment Zinc ointment
Itching and redness due to skin fungus and candidiasis
To eliminate fungal infections on the hands, systemic remedies are prescribed:
- Fluconazole - to suppress microbial stearin synthesis. Children use from 1 month. Apply once a day. The course of treatment is from 2 weeks to 0.6 months. Average cost 60 rubles ;
- Terbinafine is an antifungal drug in tablets to suppress infections on the skin and nail beds. Use for children over 3 years of age and weighing at least 20 kg. Average cost 140 rubles ;
- Ketoconazole - take 1 tablet for up to 7 days. The drug is contraindicated for children under 18 years of age. It is acceptable to take it with the permission of a specialist if you weigh over 30 kg. Average cost 130 rubles ;
- Nystatin - apply to fungal-infected skin areas, rubbing up to 3 times a day. Single dosage – a strip of ointment up to 0.5 cm in length. Duration of use is 3 weeks, including 10 days of treatment after the symptoms subside. Use for children from 2 years of age. The average cost is 130 rubles .
Fluconazole Terbinafine Ketoconazole Nystatin The following
are used to treat candidiasis:
- Lotrimin - perfectly destroys all types of fungal infections and some forms of bacteria. Treat the skin of the hands together with the nail plates up to 3 times a day, rubbing in with massaging movements. The duration of therapy is 2-3 weeks, depending on the severity of candidiasis. After symptoms pass, continue therapy for up to 2 weeks. Before handling, wash your hands with soap and warm water. Use for children from 1 year of age. Average cost 170 rubles ;
- Canesten - apply and rub a thin layer into the affected areas of the dermis, especially between the fingers. A single dose of 4-5 mm of ointment column in length. Duration of treatment is 4 weeks. Use for another 14 weeks for preventive purposes. For children only in consultation with the pediatrician. Average cost 320 rubles ;.
- Clotrimazole - Wash hands with soap and dry before use. Apply a thin layer, lightly rubbing 2-3 times a day, covering nearby healthy areas of skin. A single dose for treating the palm is 5 mm strips of ointment. Pregnant women can use the drug only from the 2nd trimester, children - from 6 months. The average cost is 70 rubles .
Lotrimin Canesten Clotrimazole
During treatment it is important:
- Maintain personal hygiene;
- Do not use rough pumice stones or washcloths;
- Gently wash the folds with liquid baby soap to relieve itching;
- Do not wet your hands during treatment;
- For dry skin, use natural formulations with propolis, calendula and chamomile.
ethnoscience
Used to assist drug treatment.
For arthritis, when your finger is swollen, try this recipe: mash a burdock leaf until the juice comes out. Apply the smooth side to the sore spot and bandage. When the sheet is dry, change it. Repeat everything three times. Then apply a bandage with a paste made from golden mustache. Everyone knows the power of this plant. This medicine is made like this: grind a leaf of golden mustache in a meat grinder and pour in vodka (1:1). Leave for two days, gently squeeze. Walk with this bandage for several hours, then apply ointment at night: add 50 ml of camphor oil to 100 g of alcohol (70%), stir, add 50 g of mustard (powder). Beat two egg whites and mix with the prepared mixture. Repeat for several days (up to three weeks).
If the patient has bruised her finger (the swelling is minor), it is recommended to make a compress for several hours with an infusion of chamomile, aloe juice (you can apply a leaf and bandage it) or from raw potatoes grated.
Prevention
- Splinters should be removed immediately.
- Treat wounds with an antiseptic (alcohol, brilliant green, iodine).
- For acute respiratory infections and infectious diseases, do not neglect bed rest to avoid inflammation of the joints.
- Move more, play sports, toughen up.
- Do not abuse alcoholic drinks or smoking.
- Reduce your sugar and salt intake.
Why can your fingers swell?
To know exactly what to do if your finger is swollen, it is important to find out the cause of such an unpleasant symptom. Unfortunately, there are many causative factors for swelling of one or more fingers and it is quite difficult to find out the truth on your own. In this case, it is important to seek specialized medical help in time, because this swelling may indicate serious health problems.
Let's look at the main reasons why fingers swell, and how you can suspect something is wrong and recognize a severe pathology.
Itching and redness on the hands of children
Reasons that cause unpleasant reactions on the skin of the hands in children:
- Hives;
- Neurodermatitis;
- Chapping of the skin;
- Lack of personal hygiene;
- Atopic dermatitis;
- Measles, chickenpox, scarlet fever and rubella;
- Allergies to food and household chemicals;
- Miliaria, leading to severe itching and scratching of the skin until it bleeds;
- Vitamin deficiency, especially lack of vitamin B in the child’s body;
- Endocrine and nervous system disorders;
- Long contacts of the child with the ground.
In addition to severe itching, the following symptoms may occur in childhood:
- Lethargy and apathy;
- Temperature increase;
- Decreased appetite;
- Skin cracking;
- Swelling of the fingers;
- Swelling of the upper lymph nodes.
Signs of itching and redness on the hands of children are specific and depend on the irritant. Children usually immediately begin to scratch the rashes, thereby provoking an increase in unpleasant symptoms.
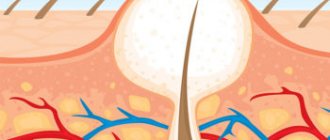
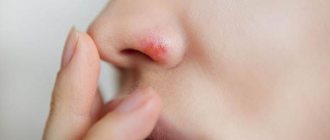
Felon
This is perhaps the most common cause of swelling and redness of the finger. This type of inflammation is infectious in nature and is often accompanied by the formation of pus in the soft tissues of the phalanges. Infectious agents, and most often these are staphylococci, streptococci, enterococci, penetrate into the tissues of the finger through minimal damage to the skin (abrasions, cuts, splinters, needle pricks, pulling out hangnails, injuries during manicure, etc.). Sometimes you can prick your finger when cutting fish. Very often, the entrance gates of infection go unnoticed, and patients complain that their finger is swollen for no reason.
Due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure, purulent inflammation does not spread over the surface area of the skin, but deep into the soft tissues and can be complicated by damage to the tendons, muscles, joints and bones of the phalanges.
Panaritium is accompanied by a number of characteristic symptoms:
- sore finger, not only swollen, but also painful;
- the pain is tugging, bursting in nature, disturbing not only when moving, but also at rest;
- the skin over the affected area turns red, in some cases begins to turn blue, becomes smooth, as if stretched, shiny and hot to the touch;
- sometimes a person’s general well-being suffers, weakness appears, and body temperature rises;
- in the center of the redness you can see white pus; in some cases, pus accumulates and is visible under the nail plate;
- As a rule, only one finger is involved in the inflammatory process (index, little finger, etc.) - the one that has become the entry gate for infection.
Depending on the depth of inflammation and the severity of the condition, the following types of panaritium are distinguished:
- cutaneous – only the skin is affected;
- subcutaneous – inflammation is localized in the subcutaneous fatty tissue;
- tendon – the tendons of the finger muscles are involved in the pathological process;
- articular – purulent lesions of the interphalangeal and/or metacarpophalangeal joints;
- subungual - pus accumulates under the nail bed, such panaritium most often develops due to a splinter getting under the nail or due to the bad habit of biting nails;
- periungual (paronychia) - inflammation of the periungual ridge of the finger, the main cause is pulling out hangnails;
- bone - the bone tissue of the phalanges of the fingers is involved in the pathological process; it develops infrequently and, as a rule, as a complication of the subcutaneous form of panaritium.
What to do if your finger is swollen due to felon? Treatment includes a complex of conservative and surgical techniques. The patient must be prescribed anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and painkillers. Surgical treatment of the purulent focus is also performed. The felon is hidden, the pus is eliminated, and the wound is drained and washed with antiseptic solutions.
It is important to know! When panaritium develops, any warming procedures, compresses and ointments are strictly prohibited. Such “treatment” is likely to lead to deeper and more extensive purulent tissue damage and the development of complications, for example, the bone or tendon form of the disease.
If a child’s finger is swollen, then most likely the reason lies precisely in the development of felon, because children, like no one else, are prone to the habit of biting off hangnails and biting their nails.
Treatment of itching and redness on the hands during pregnancy
For pregnant women, many drugs are prohibited. The main goal of treatment is not to harm the baby’s health and not lead to negative reactions within the body.
Drugs approved for use during pregnancy:
- Fenistil - average cost 400 rubles ;
- Radevit - average cost 420 rubles ;
- La-kri - average cost 360 rubles ;
- Uniderm - average cost 250 rubles ;
- Bepanten - average cost 500 rubles ;
- Pantestin Darnitsa - average cost 260 rubles .
Joint diseases
In second place among the causes of swelling of the fingers are diseases of the small joints of the hands.
Arthritis
If the joint on your finger is swollen, you need to rule out the development of arthritis. In the case of a single lesion, you need to think about a simple infectious inflammation of the joint, but if several joints swell at the same time, most likely the person has one of the rheumatological diseases, for example, rheumatoid arthritis.
With rheumatoid arthritis, several joints of the hands are simultaneously affected, as well as other joints in the body (knees, ankles, wrists, elbows, etc.). The pathological process is symmetrical, that is, the joints on both upper extremities suffer and swell at the same time. Uncharacteristic locations of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis are the distal interphalangeal joints, the metacarpophalangeal joint of the thumb, the proximal interphalangeal joint of the little finger, the sacroiliac joints and the lumbar spine (the so-called “exclusion joints”).
Rheumatoid arthritis is characterized by pain. The joints hurt both at rest and with movement, the pain intensifies with palpation and transverse compression of the joints. Morning stiffness of the injured fingers is typical, which goes away after a few hours.
The disease has a long course, with periods of exacerbation and swelling of the joints of the fingers followed by remission and subsidence of all symptoms. Over time, specific deformations of the hands are formed, which often cause loss of performance and disability, especially in children with the development of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
If the joints on the fingers are systematically swollen, the cause may be other forms of arthritis, for example, inflammation of the joint due to gout, psoriasis, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, dermatomyositis and other systemic connective tissue diseases.
Arthrosis
Another common cause of swelling of the joints on the fingers is deforming osteoarthritis. This is a degenerative lesion of intra-articular cartilage with further destruction of other components of the joint and the development of severe deformation of the joints. From time to time, arthrosis is aggravated by the development of reactive synovitis (inflammation of the joint capsule); it is during this period that swelling of the small joints of the hands occurs and pain increases during movements.
Over time, more and more joints are drawn into the pathological process, which are destroyed and lead to typical deformities. Nodular formations appear on the fingers - Bouchard's and Heberden's nodes.
A rheumatologist knows how to treat joint diseases. It is he who should be contacted if such a problem develops.
Traumatic injuries
This is also a fairly common cause of swelling of the index and other fingers. Mostly, finger injuries are in the nature of bruises, dislocations and fractures. For differential diagnosis, radiography is used, with which you can accurately determine the type of injury and prescribe appropriate treatment.
If the cause of joint swelling is an injury, then the swelling appears immediately after exposure to a traumatic factor, at the same time there is pain and the inability to make active and passive movements because of it. The finger may turn red or blue. In this case, a cold compress will help relieve the swelling, which will also reduce the intensity of the pain.
Treatment of itching and redness on the hands of children
For excessive skin sensitivity, the following will help:
- Special emollient creams with a softening, moisturizing effect, for example, Mustela cream, the average cost of which is 600 rubles ;
- Non-hormonal ointment Gistan - average cost 170 rubles .
Mustela Gistan
You should only consult a doctor to select medications for the treatment of unpleasant symptoms in children.
The best baby creams containing panthenol, herbal extracts and vegetable oils.
The safest ointments and creams:
- Panthenol can be used for children with various dermatitis and diaper rash from birth. Average cost 40 rubles ;
- Skin-cap - use for children from 1 year of age with psoriasis, atopic dermatitis and weeping eczema. Average cost 780 rubles ;
- Protopic - can be used by children from 2 years old. It is not advisable to use 0.1% cream before the age of 16. Average cost 900 rubles ;
- Fenistil gel - to relieve itching and irritation on the hands. Use for infants from 1 month. The average cost is 400 rubles .
Panthenol Skin-cap Protopic Fenistil
If the disease is severe, children are prescribed hormonal compounds:
- Advantan - for treating skin with atopic or allergic dermatitis, true and microbial eczema on the hands of children from 4 months. Average cost 680 rubles ;
- Elokom - for use in children from 2 years of age. The average cost is 430 rubles .
Advantan Elokom
Hormonal formulations based on hydrocortisone are prohibited for children under 18 years of age - Loracort, Diprospan, Celestoderm Triderm, Sinalar, Diprosalik.
Neoplasms
Neoplasms on the fingers are not very common, but it is simply necessary to be aware of this possibility. Tumors can be either benign or malignant (cancer); they can affect both the soft tissue of the finger and bones.
The most common tumors of the skin of the fingers (basal cell carcinoma, melanoma). Among soft tissue neoplasms, sarcoma, lipoma, chondroma, and chondrosarcoma should be mentioned. The bone of the phalanx of the finger may be damaged due to the development of osteosarcoma, as well as metastatic tumors.
Erysipelas
Erysipelas is an infectious lesion of the skin and subcutaneous tissue, which is caused by the entry of beta-hemolytic streptococcus into the soft tissues through microtrauma. This is a contagious disease, which is treated by an infectious disease specialist, and in case of complications, by a surgeon.
Important! Erysipelas is treated only in a hospital; home therapy is not recommended.
Characteristic signs of erysipelas of the finger (erysipeloid):
- general malaise – headache, nausea, vomiting, fever;
- redness of the affected skin (erythematous form of erysipelas), which has clear boundaries and differs sharply from healthy areas;
- the shape of the redness is irregular, reminiscent of “tongues of flame” or a “geographic map”;
- the inflamed skin is swollen and rises above healthy areas;
- the hyperemic area is very itchy and painful;
- in the case of the development of the bullous form, serous or serous-purulent blisters appear against the background of hyperemia;
- if there is a phlegmonous form, purulent melting of the superficial soft tissues of the hand is observed;
- gangrenous - the most severe form of erysipelas, in which necrosis (death) of the skin and sometimes subcutaneous fatty tissue is observed.
Why do itching and redness occur on the hands?
Many factors can cause itching and redness on the skin of the hands:
- Exposure to household chemicals , cosmetics;
- Dry indoor air with humidity less than 30%;
- Dehydration;
- Wearing tight, synthetic clothing in hot weather;
- Constant contact of hands with hot water , leading to vasodilation and increased itching;
- Abuse of strong tea , coffee, drugs, alcohol, and some medications;
- Food intoxication in case of taking products containing additives (dyes, vitamin A, E);
- Diseases of the liver , gall bladder due to the accumulation of bilirubin and bile (strong irritants of nerve endings) under the skin;
- Skin diseases - atopic dermatitis, eczema, urticaria, neurodermatitis, psoriasis, eczema, scabies;
- Hereditary factor and diabetes mellitus;
- Nervous overexcitation , frequent stress, leading to irreversible changes in the structure of the skin;
- Insect bites;
- Fungal skin infections - lichen ruber, candidiasis.
Tenosynovitis
This is an inflammation of the tendon of the finger and/or its synovium (tendon sheath). The finger flexor tendons are most often affected. Externally, tenosynovitis manifests itself as pain, especially when trying to move, swelling and swelling of the finger, and limitation of the motor function of the diseased phalanx.
The causes of the pathology are numerous. Among them, it is worth knowing about such as complications from panaritium, injuries, arthritis, autoimmune lesions, brucellosis, tuberculosis, constant injury and overload of the tendon in people with certain stereotypical work (seamstresses, typists, programmers, etc.).
Wearing rings
Sometimes wearing jewelry such as rings can cause your finger to swell. Very often, after hard physical work, in hot weather, with increased drinking, after alcohol abuse, with obesity, during pregnancy, people's fingers become prone to swelling. If the ring is not removed beforehand, it will begin to compress the soft tissues and blood vessels of the fingers, causing the condition to worsen and the swelling to increase.
As a rule, to get rid of such a symptom, it is necessary to remove the jewelry. If this cannot be done right away, you need to rest a little, give the limb an elevated position, hold your hand in cold water, and lubricate the skin with a rich cream. As a rule, this is enough to get rid of the ring. But sometimes it has to be cut to free the finger.
If your fingers are swollen for no known reason, you should definitely seek help from a doctor. After all, such a symptom may indicate the development of serious diseases of the heart, kidneys and other organs. Therefore, you cannot hesitate to contact a specialist. A timely correct diagnosis is the key to successful treatment.
Preventing itching and redness on the hands
To prevent itching and redness on your hands, you should follow these tips:
- Wear rubber gloves when in contact with water , soap, powders, detergents and disinfectants;
- patients are prone to food allergies,
- When going out into the cold, wear gloves and treat the skin of your hands with a rich cream;
- Carry out wet cleaning in the room more often , ventilate, wipe off dust.
Why do my fingers swell? 7 Possible Reasons
Swollen fingers cause particular discomfort. Clenching your palms is difficult, and your senses are weakened. If we also have jewelry on our fingers, swelling can pose a serious threat. Check out what are the most common causes of swollen fingers.
Fingers swell for many reasons – most of them are harmless. It is, however, worth knowing why this happens in order to reduce the risk of this unpleasant symptom, and yet it is better not to reduce this symptom. Especially if it is accompanied by pain. In such a situation, swelling may indicate very serious health problems.
Swollen fingers and fever
When it's really hot outside, the blood vessels dilate, which ultimately causes swelling. Signs of this will increase when we are physically active or doing heavy work and using our hands (eg digging in the garden, chopping wood).
Swollen fingers and excess salt
Dishes with a high salt content cause water retention in the body. This may manifest itself as swelling of the hands and lower extremities. Typically, benign swelling caused by salty foods goes away spontaneously within one day, but may last longer, depending on how much sodium we have in our bodies. If you reduce the amount of salt and the swelling persists, you should go to the doctor.
Swollen fingers and lymphedema
Lymphatic fluid transports waste, bacteria and viruses from the body. When the entire lymphatic system does not work properly, swelling can occur. Lymphedema causes swelling in the extremity area and is a condition that requires a visit to the doctor. Sometimes accompanied to treat another disease, such as radiation therapy in the fight against cancer.
Swollen fingers and joint diseases
If swelling occurs mainly in the morning, the cause may be arthrosis. As a rule, the swelling is also accompanied by pain and problems with mobility within the affected joint. Osteochondrosis often appears with age because it usually occurs due to wear and tear of the shock-absorbing tissues that form the joints.
Swollen fingers and median nerve
When the nerve that runs from the forearm to the palm is compressed at the height of the wrist, discomfort, pain, and even swelling can occur. Swelling is usually accompanied by burning, tingling or numbness of the hands and fingers. These symptoms develop slowly but make normal functioning significantly more difficult.
Swollen fingers and preeclampsia
Leg swelling is common in the later stages of pregnancy when a woman spends a lot of time standing. However, if swelling occurs on the face and palm area, the pregnant woman should go to the hospital as soon as possible. You should also be concerned about high blood pressure, oliguria, and abdominal pain.
Regardless of the reason for the swelling of the fingers, it is necessary to remove jewelry (rings, bracelets) as quickly as possible so that there are no serious complications as a result of ischemia.
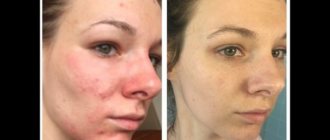
Itching and redness on the hands due to contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis is a general concept for a group of diseases with an acute or chronic course that can occur on the skin upon contact with irritating substances that cause inflammation.
Causes of contact dermatitis:
- Irritants (chemical, medicinal);
- Burns or frostbite;
- Exposure to sunlight;
- Household chemicals (washing powders, paints, emulsions);
- Decorative cosmetics (creams, ointments).
Symptoms of acute contact dermatitis:
- Redness and swelling;
- The appearance of small nodules and bubbles with the formation of crusts;
- Necrosis of areas;
- Severe burning and itching;
- Feeling hot and sore.
Symptoms of chronic contact dermatitis:
- Compaction and thickening of the epidermis;
- Hyperkeratosis with the development of infiltration;
- Erythema in the form of violet-bluish papules;
- A kind of scab followed by the appearance of erosive ulcers.
With contact dermatitis caused by an allergic reaction, symptoms usually develop more slowly.
What to do if your finger is swollen?
For elevated temperatures, you can take antipyretic drugs, and for severe headaches, painkillers. But what to do when your finger swells? After all, this unpleasant phenomenon causes a lot of discomfort to a person. It is impossible to bend the phalanges; there is a constant aching or tugging pain. But for an active person this is a big problem. So what to do if your finger is swollen? And in order to answer this question, you first need to find out the reason why this disease may occur.
Itching and redness on the hands due to an allergic reaction
Hand allergy is a process of sensitization when the human body comes into contact with allergens, which begin to produce antibodies.
Allergic reactions on the hands can be caused by:
- Consumption of allergenic foods - citrus fruits, honey, nuts, chocolate, milk;
- Use of medications leading to side effects;
- Overheating or hypothermia of the body , as well as exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- Contacts with chemicals and cosmetics;
- Excessive excitability of the nervous system and the development of a viral or infectious process in the body;
- Prolonged stay in environmentally unfavorable areas.
Local signs of allergy:
- Peeling, burning, dryness and blanching of the upper layer of the dermis;
- Non-healing wounds , cracks and bursting blisters, accompanied by itching;
- Urticaria-type burns , swelling and redness;
- Pustular rashes , itching, burning, swelling from contact with water;
- Dry cough , redness of the conjunctiva of the eyes and tearing;
- Digestive disorders in the form of vomiting and nausea;
- Sore throat , sneezing, runny nose and nasal congestion.
During the acute course of an allergy, angioedema, laryngeal stenosis and anaphylactic shock can occur.
Causes of swollen fingers
In most cases, swelling of the finger on the hand is observed due to traumatic injury. This can be either a slight bruise or a fracture. The latter is characterized by symptoms such as:
- finger swelling;
- sharp pain;
- subcutaneous hemorrhage;
- hyperemia, etc.
Such an injury requires urgent contact with a specialist (traumatologist). He will conduct an X-ray examination and apply a cast, which will promote proper fusion of bones and cartilage.
You can get a finger injury in various situations. For example, in case of a fall, impact, careless work with hard objects in the garden or garden, etc. Therefore, if you have swelling of your finger, then analyze your recent actions. Perhaps it is trauma that is the main cause of swelling.
It is worth noting that in case of traumatic injury, swelling of the finger is almost always accompanied by pain. In this case, the skin on the damaged phalanx may differ from healthy fingers in increased temperature.
Joint diseases
When swelling of the fingers is observed for no apparent reason, it is likely that in this case there is a joint disease. For example, arthrosis or arthritis, which is characterized by the development of an inflammatory process in the joints and nearby tissues. It is worth noting that in addition to swelling of the skin, other symptoms are observed with such diseases:
- sharp pain in the joints when bending a finger;
- convulsions;
- redness of the skin;
- increased skin temperature in the damaged area, etc.
If such signs appear, you should also immediately contact a specialist. Since joint diseases develop very quickly, they are practically impossible to treat. If the problem is detected in time, then there is a chance to “freeze” the development of the disease.
Abrasions and cuts
Cuts and abrasions are a common thing for us, because we are always in a hurry to get somewhere. And in a hurry, you can get this kind of injury very quickly. And even if the injury is minor, it still cannot be left without proper attention, as there is a risk of infection entering the open wound. All this can cause the development of a purulent process, which greatly complicates treatment.
The main symptoms when receiving a cut or abrasion are as follows:
- redness of the skin;
- pain when bending a finger;
- swelling of tissues;
- the appearance of a tingling sensation when water penetrates the wound.
It is worth noting that if you often cook in the kitchen, you may also feel pain when salt and other spices come into contact with the wound. In this case, the pain goes away instantly when you wash your hands in warm water.
Therefore, if you receive a cut or abrasion, immediately treat the damaged surface with antiseptic agents.
Splinter in the finger
If your finger is swollen, carefully examine it and make sure there is no splinter in it. If you have one, be sure to carry out the procedure to remove it. Otherwise, the finger will continue to swell, a tugging pain will appear, and the process of rotting will begin.
Remember to use sterile instruments when removing a splinter. This is necessary in order to eliminate the possibility of infection.
Wearing rings
Wearing rings that are incorrectly sized can lead to poor circulation and stagnation of blood in the phalangeal vessels, which causes swelling of the finger. In this case, severe swelling may be observed when trying to remove the ring.
However, the finger can increase in size even with a properly selected ring. As a rule, this phenomenon is observed in people who lead a sedentary lifestyle, eat a lot of salty foods, and also suffer from obesity.
In these cases, one can observe not only swelling of the finger, but also impaired functionality of the respiratory and cardiovascular systems. And this can lead to the development of numerous diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to immediately take any measures to eliminate the cause of the swollen finger.
Methods for eliminating swelling in the fingers
There are many reasons why a finger may swell. In any case, this phenomenon is not considered normal and may even indicate the development of various pathological processes. Therefore, this symptom should never be ignored. And if you are unable to independently determine the cause of its occurrence, seek help from a doctor.
If the cause of swelling on the finger is an injury, then before you start treating it at home, you should make sure that there is no fracture. To do this, an x-ray should be taken. But before that, you should give yourself first aid. Take a regular pencil and secure it with a bandage to your finger. This will help avoid possible complications.
Cuts and abrasions
If the cause of the swollen finger is a cut or abrasion, then you should thoroughly treat the wound with special antiseptic agents that will prevent the development of a secondary infection. If you do not have such remedies at hand, you can resort to the help of traditional medicine.
In this case, a gruel made from grated raw potatoes gives a good effect. Take a potato and grate it on a fine grater. Treat the damaged surface with the resulting slurry, and wrap your finger on top with a cabbage leaf washed under running water and secure it with a bandage or plaster.
This compress should be left for 10-12 hours, so it is better to do it at night. In the morning, remove the cabbage leaf and treat the wound with hydrogen peroxide or furatsilin solution.
If you have a weeping wound on your finger, you can treat it with 1 tablet of streptocide. Grind it to a powder (if you have ready-made powder, use it) and sprinkle it on the wound.
Joint diseases
Well, if the cause of swelling of the fingers is a joint disease, then you must first establish the cause of the disease. And for this you will need to visit a specialist and undergo a special examination.
If the swelling is severe, you can eliminate it at home using any external ointment that contains the active substance heparin. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and helps improve blood circulation.
In addition, you can again resort to the help of traditional medicine. The most effective in this case is a compress made from natural bee honey. In order to make it, you need 1 tbsp. mix honey with ½ tbsp. wheat flour. As a result, you should end up with a thick paste, which you need to apply to the damaged finger and secure with a bandage.
This compress is applied for 3-6 hours. Afterwards, you need to remove it, prepare a new “portion” and apply it again. After a few days, the swelling should completely go away.
If there are inflammatory processes in the joints, you can take anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs to help relieve inflammation and pain. However, they should only be taken as prescribed by a doctor. Since the course of their administration and dosage are prescribed in each case individually.
Swelling for no known reason
If the finger on your hand is swollen just like that (you have not been injured and do not suffer from joint diseases), then do not touch it and give it complete rest. If you urgently need to relieve swelling, then you can use simple methods - raise the hand on which the finger is swollen up and hold it there for 5-10 minutes, or apply a cold compress to the swollen phalanx for the same time.
If you choose the second method, remember that you cannot hold the compress for more than 10 minutes, as this can lead to poor circulation, which will cause even more swelling and frostbite.
Hot weather
Quite often, the cause of swelling of the upper extremities is provoked by hot weather. With prolonged exposure to the sun, our body gets tired, which is shown in this way. To eliminate such a symptom in this case, good rest is required. And to speed up the process of eliminating swelling, you can place your hands in cold water and then raise them up for 10-15 minutes.
Wearing a ring
When your finger becomes swollen due to wearing a ring, in order to eliminate this symptom, you will need to first eliminate the cause, that is, remove the ring. Naturally, not everyone wants to cut their favorite decoration. Therefore, we advise you to use the following methods.
Lather your hands thoroughly with soap in warm water, then carefully and slowly try to remove the ring. If this method fails to solve your problem, then use something greasy and slippery, such as vegetable oil or Vaseline. After treating your fingers with these products, begin to slowly pull the ring off your finger.
Do not make sudden movements, this can only aggravate the current situation. If none of these methods helped you, then there is nothing left to do but cut the ring. To do this, you need to see a doctor.
Also often the cause of swelling on the fingers is an insect bite. In these cases, it is necessary to immediately wash the damaged surface with a soap solution or furatsilin.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis if you have persistent itching, flaking, or redness on the skin of your hands, you should consult a dermatologist or therapist.
Steps to carry out diagnostics are step-by-step:
- Examination of the skin;
- Taking anamnesis;
- Redirection for testing - blood, urine, feces.
- Skin scraping for subsequent histological examination;
- Colonoscopy;
- Fibrogastroduodenoscopy;
- Ultrasound, ECG for suspected diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, endocrine, nervous, cardiovascular systems.