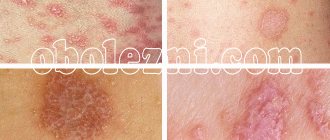
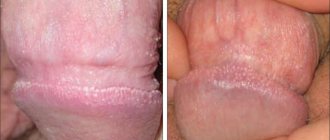
Folliculitis is a pathological process of infectious origin, which affects the hair follicle, its middle and deep areas.
An infectious lesion provokes the development of inflammatory and then purulent processes.
The disease occurs in all parts of the human body where there are fragments of hair.
One of the options for the development of pathology is folliculitis on the penis, which is quite common in many men.
The prevalence of this disease is explained by an impressive number of triggers.
In medical practice, the etiology of penile folliculitis is divided into:
- viral
- fungal
- bacterial
- parasitic
In the area of the follicle affected by pathogenic microorganisms, a pustule is formed, from the center of which hair grows.
Such formation can be single (localized damage to one follicle).
And multiple (when, under the influence of unfavorable factors, a network of nearby follicles becomes infected).
Over time, an ulcer forms from the pustule, oozing, with signs of weeping, and painful.
As the ulcer heals, a scar remains in its place.
Folliculitis of the penis is dangerous in the absence of adequate treatment, which is explained by the localization of the pathological process.
The disease is accompanied by extremely unpleasant symptoms, causing a man a lot of inconvenience and suffering.
In the absence of adequate treatment, serious complications from the genital organs are possible.
Folliculitis on the penis
Folliculitis is a pathological process of infectious origin, which affects the hair follicle, its middle and deep areas.
An infectious lesion provokes the development of inflammatory and then purulent processes.
The disease occurs in all parts of the human body where there are fragments of hair.
One of the options for the development of pathology is folliculitis on the penis, which is quite common in many men.
The prevalence of this disease is explained by an impressive number of triggers.
In medical practice, the etiology of penile folliculitis is divided into:
In the area of the follicle affected by pathogenic microorganisms, a pustule is formed, from the center of which hair grows.
Such formation can be single (localized damage to one follicle).
And multiple (when, under the influence of unfavorable factors, a network of nearby follicles becomes infected).
Over time, an ulcer forms from the pustule, oozing, with signs of weeping, and painful.
As the ulcer heals, a scar remains in its place.
Folliculitis of the penis is dangerous in the absence of adequate treatment, which is explained by the localization of the pathological process.
The disease is accompanied by extremely unpleasant symptoms, causing a man a lot of inconvenience and suffering.
In the absence of adequate treatment, serious complications from the genital organs are possible.
Symptoms of folliculitis
Clinical manifestations vary depending on the origin of the disease.
Most types of folliculitis are acute.
Inflammation begins quickly, manifests itself violently, but after treatment it completely stops.
The person recovers and no longer suffers from folliculitis, unless he has an immunodeficiency, or the patient does not become infected again during sex.
But two types of folliculitis can become chronic:
- staphylococcal
- fungal (dermatophytes)
Regardless of the cause of inflammation, the patient has no significant complaints.
Sometimes he feels slight soreness or slight itching.
Occasionally, there is an increase in inguinal lymph nodes.
Acute staphylococcal folliculitis
Classic folliculitis has a staphylococcal etiology.
Its symptoms are identified more objectively than felt subjectively.
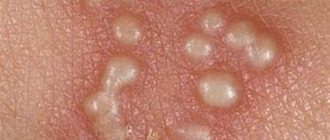
Upon examination, the doctor discovers a rash.
Pustules are multiple, located separately.
There is a hair in the center of each pustule.
There is usually no pain at rest, but on palpation the formations can be quite painful.
The pustules are surrounded by a rim of reddened skin.
Gradually they open up.
Small ulcers form, which immediately become covered with crusts.
If a person has suffered superficial folliculitis, after the crusts come off, no traces remain.
Only slight post-inflammatory pigmentation is possible, which goes away on its own in a few weeks or months, gradually matching the color with the surrounding skin.
The marks usually remain red on white skin, light on dark skin.
The greatest danger is deep folliculitis.
This is a phenomenon in which the inflammatory process of staphylococcal or other etiology spreads below the funnel of the follicle.
It requires antibacterial therapy.
In its absence, the immune system is not always able to fully cope with the infection.
Therefore, against the background of sycosis, a boil, abscess or phlegmon may develop, depending on the intensity of purulent tissue damage.
Deep folliculitis itself can be quite painful.
The skin over it swells, becomes hot and red.
Nearby lymphatic vessels and nodes may enlarge and become painful.
After suffering sycosis, cicatricial alopecia is possible.
The follicle on the penis dies.
Hair no longer grows in this area.
Symptoms of chronic staphylococcal folliculitis
As we have already said, staphylococcal folliculitis can be not only acute.
It often becomes chronic.
This is possible if:
- the patient is not receiving treatment
- predisposing factors for the development of infection remain (lack of adequate hygiene, regular hair removal, sweating, diabetes, etc.)
There are usually no subjective symptoms.
The patient only complains of constant rashes on the penis.
Upon examination, the doctor discovers elements of the rash that are standard for folliculitis.
In this case, evolutionary polymorphism is observed.
This is the name for the phenomenon in which different morphological elements are visible on the skin at one point in time.
And this is due to the fact that they are at different stages of development.
Some elements of the rash are in the papules stage, others are pustules, others look like erosions, and others look like crusts.
Post-inflammatory pigmentation is also detected in places where there was previously folliculitis.
Symptoms of other folliculitis
If the disease is caused by the fungus Pityrosporum, the disease is accompanied by itching.
It develops most often in hot climates, against the background of sweating or fever, and increased production of sebum.
The rash usually looks the same.
Papules and pustules form at the mouths of the follicles.
Due to constant itching, the man scratches the skin of the genital area.
Therefore, during the examination, the doctor may perform excoriation.
Severe scratching may result in a bacterial infection.
Folliculitis caused by Pityrosporum differs from ordinary acne in the absence of comedones (sebaceous plugs).
Illness caused by pseudomonas infection is usually mild.
Inflammation of the follicles is mild.
Small papules appear.
After a week they disappear even without treatment.
Read also: What sexually transmitted diseases can occur in the mouth
Gram-negative folliculitis often develops during antibiotic therapy.
There are many bacteria in the human body.
Many of them live on the skin.
All these bacteria compete with each other.
As soon as antibiotics destroy some microorganisms, others that are not susceptible to these drugs grow more intensively.
This may be gram-negative flora (Escherichia coli).
Quite often this form of folliculitis is complicated by abscesses.
With dermatophytosis, the doctor may detect gray spots on the skin of the groin area.
Areas of baldness appear.
In place of the follicles, purulent foci sometimes form.
As a rule, against the background of dermatophytosis, penile folliculitis is the least of the patient’s problems.
It may even remain undetected because other symptoms are more significant.
Against the background of fungal folliculitis, Trichophytosis granuloma of Majocchi sometimes develops.
This is a rupture of the follicle against the background of deep inflammation.
A large knot appears in its place.
Multiple such nodes are detected on the penis and groin.
Folliculitis due to candidiasis is usually associated with immunodeficiency conditions.
It can also occur during the use of hormonal ointments.
Large ulcers appear.
At the same time, nearby skin is affected.
You can find red spots, papules, erosions, cracks, and white plaques on it.
Herpetic folliculitis is manifested by transparent bubbles with liquid, which are permeated with hair in the center.
There are many such elements appearing.
They are painful.
They arise almost instantly, a week after infection during sex.
At the same time, the lymph nodes become enlarged and painful, and systemic symptoms may appear.
A viral infection is often complicated by a bacterial one.
In this case, the blisters become purulent.
Herpetic folliculitis may recur after several months.
With syphilis, red papules appear in the follicle area.
There is usually no pain or itching.
With syphilitic folliculitis, hair falls out, but then grows back.
With demodicosis, papules and pustules appear in the area where the follicles are located.
The skin around them is red and peeling.
A bacterial component of inflammation is often associated.
Folliculitis on the penis: causes and predisposing factors
The main reason for the development of folliculitis is the penetration of pathogenic pathogens into the follicle cavity.
Based on the fact that the disease can be viral, bacterial, fungal or parasitic in nature, in each case a separate group of pathogens is identified.
Most often, they contribute to the occurrence of the pathological process.
Bacterial origin of folliculitis on the penis is the most common.
The most common pathogens in this case are:
- staphylococcus;
- pseudomonas;
- spirochetes (Treponema pallidum - the causative agent of syphilitic infection);
- gonococci (Neisseria gonorrhoeae - provokes the development of gonorrhea);
- other bacteria.
If we are talking about a viral form of penile folliculitis, in most cases the following pathogens are implied:
- molluscum contagiosum;
- herpes viruses (especially shingles and simplex).
The development of a pathological process of fungal origin occurs when the follicle on the penis is damaged by the following fungal life forms:
Parasitic forms of the disease are much less common in developed countries.
Their main pathogen is considered to be a microscopic mite of the genus Demodex.
Depending on what pathogen caused the development of the pathological process, the follicles on the penis are divided into parasitic, viral, fungal, and bacterial.
A separate group is syphilitic.
In each case, dermatologists note separate clinical signs indicating the nature of the lesion.
In addition to the above reasons for the occurrence of folliculitis on the penis, dermatologists were also able to identify a number of predisposing factors.
Their confluence significantly increases the risk of pathology.
If several such factors are combined simultaneously when exposed to a pathogenic pathogen, penile folliculitis is almost inevitable.
Viral diseases
Some sexually transmitted diseases can also manifest as pimples and bumps on the penis and scrotum. These are usually condylomas and herpes. These viral infections can be transmitted through all types of sexual contact and cause a lot of inconvenience to both sexual partners. Genital herpes is treated with drugs containing acyclovir or valacyclovir (Valtrex), and condylomas are burned off with chemical drugs (for example, containing podophyllotoxin, Condilin) or removed surgically. Molluscum contagiosum is also a viral disease. In this case, only surgical treatment, thermal destruction or destruction with liquid nitrogen is effective, although molluscum contagiosum can disappear without any treatment.
With frequent use of latex (rubber) condoms, pimples and bumps may appear if there is an individual intolerance or allergy. Stopping the use of condoms in this case helps get rid of acne on the penis. The use of antiallergic drugs may speed up recovery.
Some may develop so-called pearlescent papules along the edge of the glans penis. These small wart-like growths are usually harmless, cause no discomfort, and do not require treatment. If desired, they can be removed surgically or by cauterization.
Folliculitis on the penis due to rubbing
One of the main factors predisposing to the development of pathology.
Chafing on the penis can occur due to a number of accompanying factors:
- while walking or running;
- due to wearing uncomfortable underwear or tight clothing;
- with rough or too frequent sex;
- due to scratching (due to itching, sweating);
- commitment to masturbation.
In each of the mentioned cases, folliculitis of the penis due to chafing occurs due to abrasion of the skin.
In this case, the hair follicles may be injured, which will allow access to pathogenic pathogens inside.
Folliculitis on the penis after sexual intercourse
The development of penis folliculitis after sex is possible in two scenarios, in each of which sexual intercourse takes place:
- During friction (during vaginal, anal or oral sex), swellings may form on the penis, which will allow pathogenic pathogens access to the follicle cavity. This probability increases significantly if there is insufficient production of pre-ejaculate (lubricant produced during sexual arousal) or the use of low-quality condoms.
- Infection of the follicle with sexually transmitted sexually transmitted infections. This is possible even when having sex with a regular partner, if the latter is a latent carrier. But the chance of infection is many times higher in cases of promiscuity and neglect of contraception.
Folliculitis on the penis due to enlarged sebaceous glands
Anatomically, hair follicles are associated with endocrine glands.
Some representatives of the stronger sex experience an increase in sebaceous glands.
This anatomical feature caused by increased production of sex hormones is called hypertrophy.
Folliculitis of the penis with enlarged sebaceous glands occurs due to the increased secretory function of the latter.
As a result, the follicle becomes clogged with sebaceous secretions and epithelial cells.
An artificially created isolated environment promotes the development of pathogenic microorganisms that provoke the occurrence of folliculitis.
This factor occurs especially often among young men who have increased synthesis of androgens.
They stimulate the function of the sebaceous glands, causing hypertrophy and increasing sebum production.
Folliculitis on the penis with diabetes
This pathological process of a systemic type disrupts the functioning of many organs and systems in the body.
Folliculitis on the penis in diabetes mellitus develops due to disruption of blood circulation and tissue innervation.
Such pathological changes in the body negatively affect the state of the immune system.
With a decrease in immunity, an uncontrolled growth of the population of opportunistic microorganisms present on the skin begins.
Under such conditions, the risk of follicular damage increases significantly.
Enlarged sebaceous glands
Sebaceous glands may be more visible on the penis or scrotum, since the skin in these areas is thin and contains little subcutaneous fat. The function of these glands is to lubricate the skin and keep it soft and elastic.
Clogged and enlarged sebaceous glands resemble white pimples, as they may appear as slightly raised white or yellow bumps of varying sizes. While taking a shower or hot bath, they may increase.
In Sweden, treatment is carried out only in case of inflammation of the sebaceous glands with antiseptic ointments, solutions or antibiotics, and in some cases, when the bumps reach large sizes, their surgical removal is necessary under local or general anesthesia. In some cases, long-term lubrication of the skin with products such as Skinoren and Differin helps get rid of them.
Folliculitis on the penis due to allergies
Allergic reactions are not capable of causing the development of folliculitis in any of its manifestations.
However, allergy manifestations on the surface of the skin of the penis are possible.
Such allergic reactions are accompanied by a rash and itching and can be caused by the following factors:
- wearing underwear made of synthetic or low-quality materials;
- individual intolerance to personal hygiene products;
- allergy to powders and rinses used in washing underwear;
- individual reaction to the use of certain contraceptives.
To combat such forms of allergies, creams and ointments are often used, which are applied to the skin of the penis.
Such topical preparations can clog pores and hair follicles.
This disrupts secretory functions and promotes the development of anaerobic bacteria, provoking the occurrence of folliculitis of the penis due to allergies.
Some local antiallergic drugs contain topical glucocorticoids.
These medicinal substances reduce immunity at the local level, provoking an increase in the population of opportunistic bacteria that can provoke the development of folliculitis.
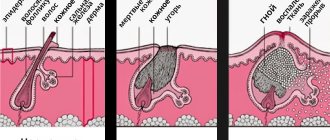
Hair follicles - definition
What are hair follicles? These are the channels from which hair grows. Hair and fat glands protect the skin from damage (lipid coating) and ensure its gas and heat exchange.
When the follicle is damaged, for example, by aggressive cosmetics or during depilation, microbes enter the base of the follicle and multiply there. The body begins to defend itself against bacteria, and this is how inflammation occurs. Those. folliculitis is an inflammatory reaction to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria or substances dangerous to the body.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis on the penis due to poor hygiene
The most common factor contributing to the development of folliculitis on the penis.
Obviously, the likelihood of penile folliculitis due to insufficient intimate hygiene is many times higher than for people who regularly take care of themselves.
Poor hygiene also leads to the development of other pathological processes of infectious origin.
The main factor for folliculitis in this case is irregular washing, bathing or showering.
The skin on the genitals quickly becomes contaminated; this is facilitated by a number of physiological processes:
- urination;
- secretory functions;
- increased sweating in the intimate area;
- having sex and so on.
If a man showers irregularly, the chances of developing folliculitis increase significantly.
Since a favorable environment is created for the development of pathogenic microorganisms.
Another factor related to hygiene is wearing underwear for more than 1-2 days, which happens especially often.
In addition, it is important to select suitable personal hygiene products (body gels, soaps, etc.), without neglecting their regular use.
Compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene allows you to eliminate pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic bacteria from the surface of the skin, controlling their population.
It also removes sebum, cleanses pores and layers of dead cells that feed bacteria.
The use of hygiene products dries out the skin, creating an unfavorable environment for the life of various microorganisms that love moisture.
Intimate hygiene also includes removing hair from the groin area and directly from the body of the penis, which is increasingly used by men today.
This is a useful procedure from a hygiene point of view, but it is important to carry it out correctly, preferably in a trusted salon.
Otherwise, especially when removing hair on your own, there is a high probability of damage to the follicles, which can cause folliculitis.
Prevention of penile folliculitis
To prevent the development of a pathological process or prevent its relapse, prevention is important.
Following a number of simple recommendations can reduce the likelihood of follicle infection:
- compliance with the rules of intimate hygiene, regular washing with hygiene products;
- wear comfortable underwear made from natural materials, change your underwear regularly;
- dress according to the weather - overheating in the groin area leads to increased sweating, provoking the occurrence of folliculitis;
- lead a healthy lifestyle to maintain immunity (healthy eating, exercise, etc.);
- avoid promiscuous sex or regularly use condoms;
- in case of relapse due to depilation, refuse to remove hair in the groin area.
If folliculitis appears on the penis, contact the author of this article, a venereologist in Moscow with many years of experience.
Clinical picture of folliculitis on the penis
The clinical picture of the development of the pathological process is clear and characterized by rapidity.
Most of the symptoms cannot be missed, as they cause significant discomfort, especially when folliculitis is localized in the groin area.
In dermatology, the symptoms of penis folliculitis develop in the following sequence:
- In the area of the affected follicle, a distinct hyperemia of the skin occurs with noticeable traces of infiltration. At this stage, most patients experience severe itching; scratching can aggravate the pathological process and provoke complications.
- The area of hyperemia increases in diameter; in place of the follicle (at the base of the hair), a pustule is formed, filled with serous or whitish purulent contents. This formation also itches, but when touched it responds with strong painful sensations.
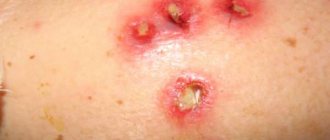
- After spontaneous, accidental (when scratching, rubbing on clothes) or intentional (it is recommended to do this only at a doctor’s appointment) opening of the pustule, pus flows out of it (or is cleaned out by a doctor). At the site of the pathological formation, an ulceration remains, covered with a purulent-bloody crust.
Subsequently, upon receiving adequate treatment, the crust comes off, and a scar remains at the site of ulceration.
When the entire body of the follicle is affected, the scar is more pronounced, and traces of hyperpigmentation may be present.
Before any signs of the disease appear, patients often experience itching and soreness at the site of future development of folliculitis.
It is noteworthy that even in the area of the penis, on the body of which there is a small number of hairs, folliculitis has a multiple course (in most cases).
Folliculitis on the penis – which doctor should I contact?
The disease is characterized by pathological damage to various layers of the skin; accordingly, diagnosis and treatment are carried out by specialists associated with dermatology.
If the disease is caused by poor hygiene, chafing and other everyday causes, even a dermatologist can help.
If we are talking about factors related to sexual activity and STDs, you should contact a venereologist.
However, the best solution to receive complete treatment would be a visit to a dermatovenerologist.
In some cases, it is possible to prescribe treatment after the initial examination.
If a severe form of the disease is suspected, for example, provoked by a syphilitic infection, a full diagnosis is required, on the basis of which drugs are selected.
Folliculitis - what is it?
The content of the article
Folliculitis is a form of staphylococcal infection. Its symptoms are papules and pustules on the arms or chest, formed, for example, after shaving. Folliculitis can be associated with a superficial or deep infection caused by bacteria.
Dermatologists warn: you cannot ignore the skin rashes that often appear after shaving. If left untreated, this can lead to the formation and rupture of a boil.
Features of diagnosing folliculitis on the penis
Diagnosis of folliculitis involves undergoing a number of diagnostic measures, the first of which is an initial examination at an appointment with a dermatovenerologist.
Based on the results of the examination, the doctor decides what tests to take for penile folliculitis and gives a referral.
The main importance is to determine the degree of damage to the follicle and identify the pathogen.
For this purpose the following studies are carried out:
- Dermatoscopy using optical or digital equipment to enhance visualization during the examination.
- Folliculitis on the penis requires culture for bacteria; for this, a sample of purulent contents is taken from the pustule.
- If there is a suspicion of the development of an STD (folliculitis on the penis is similar to herpes or syphilis), biomaterial is collected for PCR research and RPR test.
Principles of treatment of folliculitis on the penis
Treatment of penis folliculitis is conservative, based on drug therapy.
Drugs are selected based on diagnostic results.
The key factor in choosing medications is the etiology of the disease and identification of the pathogen.
So, for fungal infections, antifungal agents are used, for bacterial ones, antibiotics are used.
In the early stages of development of the pathological process, local drugs are prescribed.
How to anoint penis folliculitis, there are different variations:
- Bacterial etiology, for example, common staphylococcal infection - penis folliculitis is treated with antibiotic ointments. One option would be to use Zinerit to treat penis folliculitis.
- Fungal infection - drugs with a wide spectrum of antifungal activity are prescribed (Terbinafine, Fluconazole).
- Herpetic form - acyclovir-based products are used.
- Demodicosis - the best option is to use Parmethrin cream.
Examples can be given for a long time; it is important that each medication is prescribed by the attending physician.
In severe cases of the disease, with deep damage to the follicle, systemic therapy is added to local therapy.
The doctor will answer what antibiotics to take for penis folliculitis.
Most often these are drugs of the erythromycin or tetracycline series.
In order to reduce the spread of infectious lesions to nearby tissues, doctors recommend the auxiliary use of boric alcohol.
The solution is used to treat the affected and surrounding areas of the skin.
In some cases, physiotherapy using ultraviolet radiation is performed.
Folliculitis - treatment
Antibiotics are used to treat folliculitis (locally - ointments or systemically - orally). In addition, the skin in the area of the boil and above the inflammation itself should be frequently disinfected and periodically moist warming compresses should be applied to it to promote spontaneous emptying of the lesion. However, the boil should not be squeezed or punctured, as this can cause the infection to spread, including blood poisoning.
ONLINE REGISTRATION at the DIANA clinic
You can sign up by calling the toll-free phone number 8-800-707-15-60 or filling out the contact form. In this case, we will contact you ourselves.
If you find an error, please select a piece of text and press Ctrl+Enter
Possible complications of folliculitis on the penis
Lack of timely treatment or disruption of the immune system, for example, with HIV, threatens the development of serious complications of penile folliculitis.
There are several possible complications:
- With advanced folliculitis of the penis, a carbuncle appears - a pathological purulent formation, consisting of several boils, requiring surgical intervention.
- An even more severe form of complications is penile folliculitis that progresses into an abscess. This term characterizes an even more severe form of the inflammatory process, accompanied by tissue necrosis. Treatment is also surgical in combination with systemic drug therapy. To cure such penile folliculitis, the purulent elements are opened, cleaned out, and then massive doses of antibiotics are taken.
When it comes to immunodeficiency, penile folliculitis is accompanied by frequent relapses.
In such cases, it is necessary to find out the main cause of relapses, strengthen the immune system, and carry out prevention.