Keratoma is a benign process that forms a neoplasm that affects the epidermis. In this case, compaction of skin cells occurs, followed by keratinization. The growth on the skin is made up of horny tissue made from keratinocyte cells.
The disease rarely occurs in young people. The risk group includes middle-aged, elderly and senile people. The peak incidence is observed at 60-63 years. The pathology is diagnosed in women and men with equal frequency.
Sometimes keratoma is confused with papilloma. Neoplasms are different, because papilloma appears due to damage to the human body by HPV.
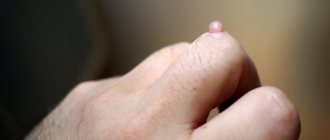
Skin keratoma looks like a hard, dark-colored mole. The contours are clear or faint. A small tumor may disappear on its own. However, after an indefinite time it will return to its original place.
The disease belongs to other epidermal seals according to ICD-10 code L85. The tumor is made up of healthy cells.
Causes
Why do keratomas appear? The main reason for their occurrence is considered to be pathological modification and uncontrolled growth of previously normal cells.
The most important risk factor is excessive sun exposure. Among the victims of keratosis are many lovers of solariums and beach holidays. Light-skinned and blue-eyed people, descendants of Scandinavians, are especially prone to the disease.
However, the sun's rays are far from the only culprits of neoplasms. There are other causes of keratomas:
- constant mechanical damage to the skin in one place;
- endocrine disorders in the body;
- chemical burns of the epithelium;
- decreased immunity;
- hormonal imbalance.
The last point most often becomes the cause of the development of tumors on the body in women.
Some medical sources indicate a genetic predisposition to keratomas. In this case, the disease is diagnosed through the male line and develops in older people with dry skin and numerous moles.
The danger of some types of keratomas lies in their ability to quickly turn into cancerous tumors. Therefore, such changes in the epithelium cannot be ignored.
Symptoms
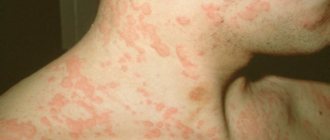
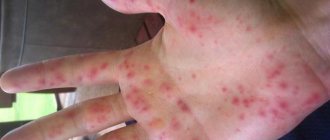
Typically, a skin keratoma develops as a small, vague spot of light brown or gray color that soon begins to peel off. Gradually, the plaque increases in size and rises above the skin, resembling a nevus. The color of the spot becomes richer, and a dense crust grows on the surface. When it is torn off, the keratome becomes inflamed and bleeds.
Such symptoms in themselves are not terrible. The tumor becomes dangerous if the growth swells and hurts. This may indicate degeneration into a malignant form, although it is difficult to predict the likelihood of such a transformation.
Keratoma on the skin has several manifestations:
- pigmented spots;
- scaly plaques;
- nodules;
- skin growth.
Such keratinization of cells causes significant aesthetic discomfort to patients. Women are especially affected by keratomas.
Clinical picture
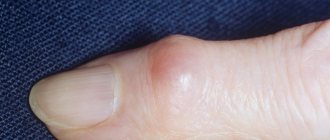
In appearance, a keratome resembles a small formation formed on the surface of the skin. In the initial stages of its development, it has a grayish or pale coffee color.
The formation protrudes slightly above the surface of the skin, and its surface may peel off.
Over time, it increases in size, and a compaction forms on the surface, which is then covered with a dense crust. It can come off on its own due to constant friction with clothing or mechanical damage. This process causes pain.
When the growth is injured, bleeding is also observed. Keratoma can form one at a time or in groups.
Kinds
Modern medicine classifies keratoses based on the causative factor. Since each type of disease has its own symptoms and localization, we will give brief descriptions of them separately.
Senile
Senile keratoma (another name is seborrheic or senile keratosis) develops in people after 55 years of age and is multiple in nature. In this case, plaques and age spots, resembling warts and moles, are found on closed areas of the body - the back, chest, abdomen and thighs. Often the keratoma is localized in the forehead or cheeks.
When the epithelial tissues on the head become keratinized, the hair follicles become clogged. This leads to the formation of flaky brown growths and a noticeable deterioration in the condition of the hair, up to patchy baldness.
Senile keratoma occurs over a long period of time and very rarely degenerates into oncology. In some cases, plaques soften and fall off on their own.
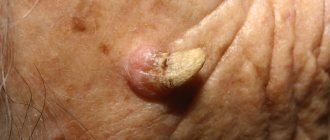
Horny
Horny keratoma is also called cutaneous horn. The growth has a dark color and an elongated, conical shape, noticeably rising above the surface of the epithelium. This tumor develops on any part of the body, including the scalp, but especially prefers the forehead and eyelids. It can be either single or multiple. Moreover, there are often cases when several horny keratomas grow from one place.
The surface of the conical growth may be smooth or flaky, and the color may be dark brown. To the touch, the keratome has a dense consistency. A feature of this form is its frequent degeneration into a cancerous tumor. The signal for the onset of the pathological process is inflammation and swelling of the skin at the base of the horn.
In medical practice, there are cases of conical keratomas appearing at the site of sutures. Scar tissue, by its nature, differs significantly from ordinary epithelium and contains a lot of pathological structures with impaired blood circulation and the ability to change. All this contributes to the development of keratosis.
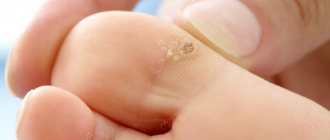
Follicular
Follicular keratoma is rare and in most cases occurs in the fairer sex. The disease is manifested by the formation of growths of pinkish-brown or gray color, often reaching 1 cm in circumference.
Most often, the keratoma is located above the upper lip, forehead or under the hair and is accompanied by blockage of the hair follicle. This leads to redness and inflammation of nearby tissues, itching and swelling.
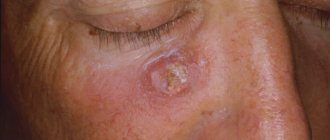
Solar
Solar or actinic keratoma is usually a precancerous form of keratosis. The disease affects people over 45 years of age and is localized in open areas of the body.
With this form, multiple pinkish spots appear on the skin of the face, arms, chest and back. Gradually they darken and begin to peel off. The surrounding tissues become red and inflamed, the patient complains of pain and itching.
The disease progresses slowly and, if left untreated, develops into oncology. This characteristic of the most dangerous type of keratoma should prompt the patient to immediately consult a doctor.
Localization
Since keratoses originate from the cells of the upper layer of the epithelium, they can only appear on the skin. Moreover, the place of their localization does not depend on the type of growth. Especially often, neoplasms are observed in areas of the body accessible to ultraviolet irradiation and much less often in the area of the legs and ankles.
It is because of the constant exposure to UV rays that the majority of keratoses (70% of cases) are keratomas on the face. As a rule, it is singular in nature and manifests itself with the same symptoms as on the body.
Comments
- megan92 () 2 weeks ago
Has anyone managed to get rid of papillomas in their armpits? They really bother me, especially when you sweat.
- Daria () 2 weeks ago
I have already tried so many things and only after reading this article, I was able to get rid of papillomas in the armpits (and on a very budget). PS But I’m from the city myself and didn’t find it on sale here, so I ordered it online.
- megan92 () 13 days ago
Daria, post a link to the article! PS I'm from the city too))
- Daria () 12 days ago
megan92, that’s what I wrote in my first comment) I’ll duplicate it just in case - a link to the article.
- Sonya 10 days ago
Isn't this a scam? Why do they sell on the Internet?
- Yulek26 (Tver) 10 days ago
Sonya, what country do you live in? They sell it on the Internet because stores and pharmacies charge outrageous markups. In addition, payment is only after receipt, that is, they first looked, checked and only then paid. And now everything is sold on the Internet - from clothes to TVs and furniture.
- Editor's response 10 days ago
Sonya, hello. This drug for the treatment of papillomavirus infection is indeed not sold through pharmacy chains and retail stores in order to avoid inflated prices. As of today, you can only order on the official website. Be healthy!
- Sonya 10 days ago
I apologize, I didn’t notice the information about cash on delivery at first. Then everything is fine if payment is made upon receipt.
- Margo (Ulyanovsk) 8 days ago
Has anyone tried traditional methods to get rid of warts and papillomas?
- Andrey A week ago
I tried to burn off a wart on my head with vinegar. The wart really went away, only in its place there was such a burn that my finger hurt for another month. And the most annoying thing is that after a month and a half, two more warts popped up nearby ((
- Ekaterina A week ago
I tried to burn out the papilloma with celandine, but it didn’t help, it just turned black and became so scary (((
- Maria 5 days ago
I recently watched a program on Channel One, they also talked about this PAPIFEX. Many doctors recommended for treatment. I ordered it, I use it, and indeed, the papillomas are dissolving one by one, there are only 2 left, the most tenacious ones.
- Elena (dermatologist) 6 days ago
Maria, soon these two will disappear too!
- Alexandra (Syktyvkar) 5 days ago
A good product, completely worth the price. I have never seen any analogues.
- Maxim Today
Has anyone tried to reduce papillomas with liquid nitrogen?
- Tatyana (Ekaterinburg) Today
Yeah, you burn one, after a month three more grow ((I don’t recommend liquid nitrogen, although hospitals often use it
- Elena (dermatologist) 6 days ago
Tatyana, liquid nitrogen is a thing of the past, now PAPIFEX is used in full and there is no need to go to the doctors!
- Mikhail (Moscow) Today
PAPIFEX also helped (I ordered it according to the advice above), it should work, try it
- Vika (Ekaterinburg) Today
That's great! I need to order, otherwise I’m already tormented with these warts! After all, a woman always wants to be beautiful!
- Kristina (Minsk) Today
I had papillomas removed with a laser, quickly and without pain. But it's damn expensive.
Add a comment Cancel reply
| consultations by email mail, individual production of medicinal ointments and lotions tel. mob. (call from 9.00 to 11.00 in the morning and from 18.00 to 20.00 in the evening Keratoma is a collective name for different types of benign neoplasms, in the formation of the structures of which cells of the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) participate. It does not display the specific morphological characteristics of each type of disease, but explains the etiology of the pathological process. When defining a pathology, the name is always specified. For example, seborrheic keratoma is a term that is used to refer to a formation that forms when excess sebum is produced. |
Which doctor treats keratoma?
The formation of suspicious growths, plaques and spots on the skin should not be ignored. If they appear or changes in existing epithelial lesions (warts, moles), it is necessary to urgently visit a dermatologist or dermato-oncologist. If such specialists are not available at your local clinic, you should approach your GP or general practitioner. After an initial examination and a preliminary diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe treatment or refer the patient to a specialist. If previous tumors have spontaneously disappeared, you should not cancel your visit to the doctor. Keratoma may appear again and in a more serious form.
Surgical removal
Surgical treatment is one of the effective, but traumatic ways to remove tumors, since modern medicine offers more gentle, but no less effective methods. Surgical treatment is prescribed in cases where the keratoma affects large areas of the skin, and there is also a risk of the formation degenerating into cancer. In this case, not only the plaque itself is removed, but also the surrounding tissue. Healing occurs rather slowly; this period requires constant dressings, examination and observation by a doctor.
Diagnostics
During diagnostic procedures, it is very important to differentiate (distinguish) keratosis from other epithelial diseases that have similar symptoms. Therefore, at the first consultation, the dermatologist conducts a visual examination of the stratum corneum of the epidermis and prescribes the patient an additional examination, including:
- histology of growth tissue;
- dermatoscopy (examination of keratomas under magnification);
- biopsy;
- Ultrasound;
- SIAScopy.
The last type of instrumental analysis is the most modern and accurate. It is based on the interaction of light waves of different lengths and the melanin pigment. In a three-dimensional image, you can see the keratoma in great detail and get up-to-date information about its condition. Based on SIAscopy, the doctor makes a decision - to observe the skin formation or to urgently remove it.
Treatment
How to treat keratoma? Modern medicine has two ways to combat keratosis - conservative and surgical. The choice of treatment method is made for each case strictly individually and is based on the size of the growth, its type and existing symptoms.
In the uncomplicated form of the senile type, drug treatment is more often used. The patient is prescribed various ointments for keratomas:
- to reduce the size of the tumor - Retin-A, Colchamine ointment, 5-fluorouracil;
- for disinfection of keratomas - Feresol, Solcoseryl. These remedies are also used if the plaque itself has fallen off;
- for cancer alert - Cyclophosphamide, Bleomycin, Prospidin.
Any local medications are used only under the supervision of a physician.
If conservative therapy for keratosis does not produce an effect and there is a suspicion of cancerous degeneration, the patient is prescribed removal of the growths. The plaque is excised surgically or eliminated using hardware methods.
The first method is rarely used for keratomas, since after the operation a noticeable suture remains. Non-invasive (without compromising the integrity of tissue) intervention methods are much more effective. It is recommended to do this operation in the cold season.
Laser
How to treat keratoma with laser? This is one of the best ways to destroy tumor cells. As a rule, to remove growths, one or maximum two sessions are required, during which pathological tissues are burned out.
The laser beam, aimed precisely at the keratoma, does not damage healthy skin, which significantly speeds up the recovery period - complete healing of the dermis occurs within 7 days. And since laser destruction does not leave scars and does not require a suture, the procedure is suitable for removing growths from the face.
Radiosurgery
This is the most modern way to destroy keratomas on the skin. Using a radio knife, the doctor makes thin, precise and bloodless incisions, allowing plaques of any size and location to be removed without leaving a trace. The method also does not leave scars.
Destruction of keratomas is carried out on an outpatient basis and does not require special preparation. Accordingly, the patient recovers quickly and easily.
Nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen is often used to get rid of keratomas. Cryodestruction is performed without anesthesia, so the patient may feel slight discomfort in the treatment area.
After exposure to cold, crusts form at the site of the keratoma, which fall off on their own after 5–7 days, leaving behind an area of healthy pink epithelium. Unfortunately, the method injures the skin and does not always occur without relapses.
After removal of the keratoma, there is no need to visit the hospital, perform dressings or observe any restrictions. It is enough to apply healing and regenerating ointments to the affected area: Levomekol, Solcoseryl, Baneocin.
Traditional methods
How to get rid of keratomas using alternative medicine? Unfortunately, folk remedies in this case are not effective enough and rarely lead to recovery. In addition, they can only be used if the keratoma is at rest.
Traditional healers recommend the following remedies to slow tumor growth:
- calcined sea buckthorn oil. They wipe flaky plaques on the skin 3-4 times a day;
- oil infusion of unripe walnuts. The balm is used for application to affected areas of the skin;
- celandine ointment. The product is stored in a cool place and applied to the keratoma twice a day.
Often, medicinal creams for keratosis are prepared from aloe juice or bay leaf mixed with unsalted interior fat.
Mechanism of keratoma formation
The epidermis consists of several layers of keratinocytes - skin epithelial cells. The layers lie on top of each other. The cells of the uppermost layer, the one that is constantly in contact with the external environment, gradually die off and turn into keratinized scales. Normally, they peel off and are removed from the surface of the skin during bathing.
The place of exfoliated scales is occupied by cells of deeper layers. In the absence of pathology, this process is balanced. If it is disturbed, various skin diseases develop. It is due to such dysfunctions that keratomas are formed. The tumor is formed from unchanged cells of the keratinized epithelium. At its core, it is a collection of keratinocytes. There are no atypical elements in it, therefore all keratomas are benign formations.
However, the described skin tumor can transform into cancer. According to statistics, this happens in 20% of cases. Because of such high rates, experts classify keratomas as precancerous conditions. The risks of malignancy increase if:
- the tumor began to grow rapidly;
- its surface is constantly injured and bleeds;
- the growth process is accompanied by severe itching or pain;
- there are signs of inflammation.
If one or more of these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek help from an oncologist.
The danger of keratoma also lies in the fact that it can look similar to various forms of skin cancer. Even an experienced doctor is sometimes unable to distinguish them from each other, which is why it is so important to undergo examinations on time and identify existing risks.