Causes of pathology
Pedicled papilloma occurs due to infection with the human papilloma virus. This virus can enter the body in several ways:
- From mother to child through the birth canal.
From person to person through touch or sexual contact.- By household means through personal hygiene items of an infected person, handrails in public transport, swimming pools, etc.
In order for the papillomavirus to penetrate the skin, one condition is necessary - the presence of damage. These include wounds, cuts, scratches and even microcracks that are not visible to humans. Such damage occurs especially often in people with extremely dry or moist skin.
When the human papillomavirus enters the body, it invades the cell nucleus. The further process depends on the human body - with strong immunity, the virus hides and can remain latent for several decades. Many people do not even suspect that HPV is present in their body, and they only find out about it when papilloma growths begin to appear on the body. Thus, the incubation period for each person depends only on his immunity.
What provokes the “awakening” of the virus:
- Hypothermia.
- Infectious diseases.
Inflammatory processes in the body.- Endocrine disorders.
- Hypovitaminosis.
- Malnutrition.
- Alcoholism and nicotine addiction.
- Blood loss.
- Surgical intervention.
- Pregnancy.
- Prolonged stress.
- Frequent physical fatigue.
- Metabolic disorders, obesity.
Any factor affecting the immune system and the general condition of the body can become a trigger for the activation and spread of papillomavirus.
When viral cells are activated under the influence of negative factors, they disrupt the physiological process of cell life.
In a normal state, the cells of the basal layer are not able to divide, but only thicken, and when they reach the surface of the skin, they die. But when the papilloma virus enters the cell nucleus, the basal cells begin to actively divide, forming various growths on the surface of the skin. If infection occurs with type 2, 3, 5, 7 or 9 of the virus, then papillomas appear on the stem.
Treatment of papillomas on the leg
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qtI096p1MIo
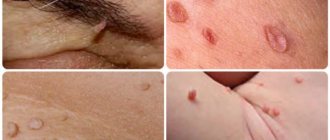
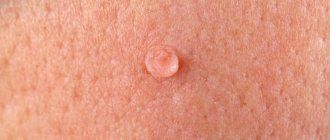
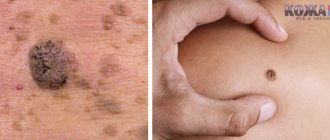
Neoplasms on the stem can be of various types. Outwardly, it is not difficult to distinguish one type from another. Some papillomas have an elastic surface, while others have a keratinized top layer. The growths vary depending on the thickness of the stem. It can be wide or thin.
If you take a closer look at the acrochord, you can note the thread-like composition of the neoplasm. It is located on the surface of the patient's skin. At the initial stage of occurrence, a small nodule may appear. Under the influence of the virus, it grows, not only increasing in size, but also acquiring a full-fledged leg. It can be thick or thin. But a distinctive feature of any leg is its smaller diameter compared to the papilloma itself.
Due to this structure, mobility of the neoplasm can be observed. A person feels discomfort during hygiene procedures or when wearing clothes.
If the papilloma grows, it becomes elongated and oval. In rare cases, a pedunculated neoplasm has a round shape.
Papillomas can appear when HPV enters the body. Therefore, a person needs to protect the body not from the neoplasms themselves, but from viral infection.
Vaccination is the main preventive measure against HPV
Prevention should include:
- observing personal hygiene rules;
- use of barrier methods of contraception;
- avoiding contact with the skin of people infected with HPV.
Modern medicine offers to protect yourself from viral infection during vaccination with Gardasil and Cervarix. Vaccinations begin in adolescence (from 11 years old) for both girls and boys. Adults can also undergo the procedure. However, the age of drug administration is limited to 26 years.
The occurrence of pedunculated papillomas can be avoided if you follow preventive recommendations and start treatment promptly when the virus becomes active.
Filiform papillomas or acrochords are all kinds of pedunculated papillomas.
Friction against clothing leads to injury, inflammation and twisting.
Papillomas on the leg are very typical for relatively young women.
Such neoplasms often occur in women with problem skin:
- with increased sweating;
- with actively working sebaceous glands;
- with moist skin.
When examining the acrochord in detail, we are talking about the thread-like composition of a benign tumor.
Acrochordal papilloma is located in the superficial layer of the skin.
At the beginning of the growth process, the acrochord is marked by a small nodule.
Under the influence of HPV, the papilloma increases in size both its body and leg.
The leg can be thick or thin.
It is smaller in diameter than the body of the papilloma.
This structure of the papilloma ensures its mobility.
Most often, papillomas are elongated and oval, occasionally – round.
Hygiene procedures and clothing cause pronounced discomfort.
Treatment is always necessary as they are very traumatic and cause major cosmetic problems.
They are coagulated using chemical methods at home on their own, essentially “burned.”
Or they are removed by surgical methods - with a scalpel, laser, liquid nitrogen, electrocoagulator or radioelectrode.
Sometimes, the immune response becomes so pronounced that papillomatosis goes away on its own.
They occur in large numbers in one place and are very difficult to remove.
Then the largest ones are removed, and others often self-destruct.
If the appearance of papillomas arose from highly oncogenic types of HPV, then general treatment is necessary - therapeutic, by prescribing immunostimulants and interferon inducers.
Papillomas are very prone to relapse.
This suggests that papillomas often reappear on the skin in the same place or in a completely different place.
Today, vaccination against highly oncogenic HPV types is popular.
Papillomas can change their color, become injured, become inflamed, darken and even turn black, which indicates drying out of the papillomas.
If the papilloma dries out, then there is a possibility that a new papilloma will appear again in the same place.
You need to be very attentive to the visible change in the appearance of papillomas and always respond quickly to this by contacting a doctor for advice.
Clinical picture
The manifestations of such papilloma are difficult to confuse with the symptoms of other diseases. Hanging papilloma forms on delicate areas of the skin:
- on the face;
- neck;
- under the breast;
- in the axillary and inguinal folds.
In such places, the skin is most often injured and subjected to mechanical stress (using peels, scratching, rubbing with clothes), which provokes the virus to enter the skin.
In the axillary and inguinal folds, as well as under the breasts, there is always a moist and warm environment, which promotes the development of tumors. When a pedunculated papilloma forms, initially a small papillary growth appears above the skin, which, as it grows, takes on an elongated shape. If you look closely, you can see that the papilloma rests on a thin or thick stalk, depending on the type of formation. Usually, the growth of papillomas occurs without pronounced symptoms; sometimes slight itching or pain when pressed may occur.
Two types of such neoplasms can be distinguished:
- Thread-like - usually blend in color with the skin, but sometimes they are yellow, brown or dark pink. The sizes can vary from almost imperceptible formations to large growths reaching 1 cm. There are both single papillomas and group ones that merge into large uneven growths.
Finger-shaped - are less common and are formed only on the scalp and along the hairline. They are flesh-colored or pink elongated formations on a thick stalk, which can grow up to 2 cm. They do not have the ability to group, so they occur as single growths.
Unlike other papillomas, hanging papillomas are more prone to injury. Such formations are weakly connected to the skin, and even a slight mechanical impact leads to tearing off part of the papilloma, while the root remains in place. They are constantly rubbed with clothes, torn off with washcloths and combs, and papillomas on the neck are subject to friction from jewelry.
Pedicled papillomas formed on the eyelid cause psychological discomfort to the wearer. In addition, they cause unpleasant symptoms:
- They interfere with closing the eyes, which causes dry mucous membranes.
- They cause discomfort.
- May cause tearing.
- Cause itching.
- Contribute to infection: conjunctivitis, blepharitis.
When a papilloma is injured, bleeding may begin, and an open wound is an entry point for bacteria and fungi. If the papilloma comes off, the wound must be washed with an antiseptic and a fabric-based patch should be applied on top. It is recommended to visit a dermatologist so that he can advise on treatment and tell you when the papilloma can be removed.
Frequent injury leads to infection of surrounding tissues, active reproduction of papillomas begins and their fusion into a large growth of irregular shape. Sometimes new growths begin to change color and structure: they turn black, red, become softer or dry out. This may indicate both an infection and the transition of cells to a malignant form.
Varieties
Papillomas on the back can be of three types:
- flat;
- pointed;
- threadlike.
Externally, a flat papilloma resembles a mole with rounded outlines. The neoplasm has a dark tint, but is lighter than a regular mole. A flat growth can grow up to 1-2 cm.
Single formations can form foci. Itching and soreness may occur when touched.
The pointed form has many processes that unite into one tumor. The size of such a formation can reach 2-3 cm. It is easily injured while wearing underwear or swimming. When injured, the pointed formations quickly become inflamed and begin to bleed. They are distinguished by a dark shade.
Filiform papilloma is a thin thread of flesh-colored or white color. Such a formation may bleed if touched. Sometimes it merges into one large lesion.
Treatment options
Before getting rid of hanging papillomas, you need to visit a doctor, who, after conducting a diagnosis, will make sure that the formation is benign and can be removed. It is best if the papilloma is removed by a specialist, but treatment can also be carried out at home.
The most effective methods of traditional treatment are surgical, which can be performed on an outpatient basis:
- Laser coagulation.
- Radio wave method.
- Electrocoagulation.
- Cauterization with liquid nitrogen.
It should be remembered that the earlier the removal is performed, the less chance there is for re-development of growths and complications. You can remove papilloma yourself using special medications, but only after consulting your doctor. He will tell you which remedy is best for treatment and how to use it correctly. What drugs are effective:
- Super clean.
- Verrucacid.
- Fresol.
- Wartner Cryo.
- Lapis pencil.
- Papilux.
- Collomak.
- Special patches.
For treatment, you can use antiviral ointments, for example Viferon, Acyclovir, Panavir or Oksolinovaya, but they are effective only on new papillomas that have not yet had time to grow and get stronger. In addition, to get rid of HPV, it is necessary to treat the virus from the inside and strengthen the immune system. The most effective drugs:
Isoprinosine.- Cycloferon.
- Panavir.
- Lycopid.
- Immunomax.
- Polyoxidonium.
Methods of infection
There are several ways the virus can enter the blood:
- In direct contact with a sick person: through a handshake, kiss, unprotected sexual contact.
- When using personal hygiene products that were previously used by a virus carrier.
- When visiting places with high humidity: sauna, bathhouse, swimming pool.
Research has established that the virus is able to maintain its viability even outside the human body, remaining on the surfaces of objects and in the air.
Causes and sources of infection
Papillomas on a stalk along the body appear due to the HPV virus. The virus is transmitted both sexually and domestically. Sometimes neoplasms can appear immediately after birth in both the child and the mother.
In most cases, the virus does not manifest itself in any way when it enters the human body. Its activity can be stimulated by decreased functionality of the immune system and increased sweating. After the virus has entered the cell nucleus, it begins to actively multiply, resulting in a growth.
Hanging papilloma (photo) occurs in different types, which differ in appearance:
- keratinized;
- elastic;
- plantar;
- flat wart;
- threadlike;
- genital warts;
- on a thick leg;
- on a thin leg.
Sometimes papillomas do not bother a person, so he is in no hurry to treat them - which is the wrong approach. Black papillomas on the feet often become inflamed and subject to injury, therefore, there is a high probability of their transformation into malignant tumors. The same applies to benign neoplasms in other parts of the body. The appearance of papilloma on the legs - the reasons can be different, including injury to the skin (scratches, cuts), the virus can easily be transmitted from person to person. It is for these reasons that it is important to monitor personal hygiene and constantly stimulate the immune system.
The tumor can appear in different parts of the body
The tumor can appear in different parts of the body:
- on fingers;
- on the face;
- on the genitals;
- on the feet;
- on the neck;
- armpits.
Most often, the virus progresses in the fair sex.
Risk group
Dermatologists say that there is a group of people who are at risk of getting papillomas on the body:
- people living a promiscuous sex life (sexual acts with strangers without protective equipment will ultimately lead to infection with the virus);
- one of the partners is a carrier of HIV;
- frequent diseases that lead to a sharp decrease in the immune system;
- the presence of sexually transmitted diseases: thrush, herpes, chlamydia, gonorrhea;
- drug and alcohol abuse;
- disorders of the vaginal microflora in women;
- frequent visits to swimming pools, saunas, baths, beaches.
Every person must remember that his health is only in his hands. Promiscuity, poor personal hygiene, and inattention to one’s body can cause the virus to appear in the body. A healthy lifestyle, proper nutrition, and a favorable atmosphere will lead to a strong immune system, so such diseases will be avoided.
What threat does
Papilloma on a thin stalk most often does not manifest itself in any way, therefore, if you discover a new growth on your skin, it is important to consult a doctor.
Papillomatosis can cause itching; neoplasms quickly grow throughout the body, forming so-called “islands”. It is worth noting that often touching papillomas can cause bleeding, as a result of which blood poisoning and malignancy of the growth develop.
If the papilloma somehow comes off, it is important to follow the following algorithm of actions:
- stop the bleeding by using hydrogen peroxide and a sterile wipe;
- treat the wound with an antiseptic;
- cover the damaged area with a bactericidal plaster;
- See a doctor for examination, tests and histology.
Sometimes black papillomas on the legs can be interpreted as dried , it is important to understand that this can be a serious and dangerous symptom, therefore, if you notice any change in the papillomas (shape, color, size), you should immediately consult a doctor.
The growths can periodically become inflamed, causing pain and discomfort due to their increase in size.
Appearance of papilloma on the stalk and the place of its formation
The beginning of the development of the pathological process is indicated by the appearance of a small nodule on the skin. It gradually grows and gradually separates. The neoplasm remains connected to the skin only by a small stalk. The growth itself takes on an elongated shape. Sometimes doctors diagnose patients with round papillomas of this type in the legs, arms or other parts of the body.
If you study photos of patients who have papilloma on a thin stalk, you can find out where it is most often localized. Such a neoplasm is usually located in the following areas:
- Neck;
- Eyelids and area around the eyes;
- The groin and the folds that are next to it;
- Armpits;
- The fold that forms under the breast.
Neoplasms of this type appear in these areas for a reason. Experts have found a pattern in this. In places where benign growths are localized, there is very thin skin. They affect areas of skin folds, as they are characterized by high humidity. And these are ideal conditions for the development and reproduction of pathogenic microflora that activates a viral disease.
Diagnosis and treatment
Only a doctor can determine the presence of papilloma on the leg, since visually it can be easily confused with other dangerous neoplasms on the skin. The doctor, before starting treatment, prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures:
Only a doctor can determine the presence of papilloma on the leg
- cytology;
- PCR – study of the DNA of the growth to determine its etiology;
- biopsy;
- histology;
- Digene-Test - to determine the strain of the virus and the oncogenicity of the formation.
Only the correct approach to the diagnostic procedure will allow you to select the correct and effective treatment tactics.
It is impossible to completely remove the papilloma virus from the body, but you can put it into “sleep” mode. If the papillomas are large or numerous, along with therapy they also resort to surgical removal of the growths. How to remove pedunculated papilloma?
Surgery
Removing pedunculated papilloma requires a professional approach. In modern medicine, several effective methods are used to remove growths on the skin and mucous membranes, including:
- Standard surgical intervention is used most often in hard-to-reach places or in the presence of large papillomas. The procedure is painful, and after removal there is always a scar.
- Radiotherapy is a non-contact type of growth removal that leaves no scars.
- Electrocoagulation is the effect of electric current on the papilloma. The procedure is painful and contraindicated for removing formations on mucous membranes and intimate areas.
- Cryodestruction - the procedure involves exposing the neoplasm to liquid nitrogen. This method has its drawbacks: often the roots of papillomas go deep under the skin, and nitrogen allows only the tip to be removed, as a result of which a relapse may occur with a large appearance of growths.
- Laser removal is an effective, painless, bloodless, minimal recovery period, a modern method for which there are practically no contraindications.
Folk remedies
Papillomas can be removed using traditional methods, for example:
Papillomas can be removed using traditional methods
- Celandine juice - freshly squeezed juice from the stem of the plant is applied directly to the papilloma. The application procedure must be repeated two to three times a day. The duration of this type of therapy should not exceed 14 days. It is important that healthy skin must be protected from the effects of the juice, as you can get a serious burn (seal with a band-aid or spread with a thick cream).
- Garlic juice - the principle of use is the same as that of celandine juice. Just apply the juice to a gauze bandage, which is attached exclusively to the neoplasm, avoiding healthy areas of the skin for at least 5-6 hours. Course duration is from 10 to 14 days.
- Iodine compresses - apply iodine with a cotton swab directly to the tumor 3-5 times a day until the papilloma disappears on its own.
Important: any actions in relation to neoplasms on the skin must be carried out after consultation with a doctor, since papilloma can be easily confused with other malignant skin neoplasms by its external signs.
If a leg remains after removal of the papilloma, you should urgently consult a doctor in order to prevent the possibility of infection.
Removal of papillomas
Stationary removal methods
In cases where drug treatment does not produce the desired effect, the papillomas are removed. There are the following methods for getting rid of tumors:
- Liquid nitrogen /cryotherapy/. The papilloma is instantly frozen. As a result, the growth cells die.
- Radio waves /radiosurgery/. The cutting is done using radio waves. At the same time, healthy skin cells are not injured, burns and the possibility of infection are excluded.
- Laser beam /laser therapy/. It is the most popular and painless method.
- Electric current /electrocoagulation/. Removal is carried out using electric power. If necessary, anesthesia is used.
- Surgical method. Used quite rarely. The growth is cut off with a scalpel using local anesthesia. After the operation, scars and scars remain.
- Chemical cauterization. Removal /burning/ using salicylic acid and cantharidin.
Despite the favorable prognosis, after completing a course of treatment, it is worth considering that even if the papilloma is removed, HPV continues to exist in the body, and relapse is possible at any time. You cannot get rid of papillomas on your own. Self-medication usually leads to infection and other serious consequences.
A practicing dermatovenerologist will tell you about the intricacies of removing papillomas:
Video
How to treat papilloma virus? Removal of condylomas, papillomas, warts
Pedicled papilloma is a type of benign formation caused by the human papillomavirus.
Popularly, such growths are considered a sign of aging.
Indeed, you won’t find them in children, but older people have them almost without fail.
- All information on the site is for informational purposes only and is NOT a guide to action!
- can give you an ACCURATE DIAGNOSIS !
- We kindly ask you NOT to self-medicate, but to make an appointment with a specialist !
- Health to you and your loved ones!
Women react especially emotionally to their appearance, which is not surprising - a wart located on an open area of the body or on the face does not add any charm at all.
But how many people know that a cosmetic defect is not the only trouble that papillomas can cause?
Modern removal methods
Modern medicine has developed various methods for treating papilloma on the human back. Each method has its own effectiveness and contraindications, so you should see a specialist. The most advanced procedures for combating warts:
- Laser. Within 15 minutes, a professional can get rid of a medium-sized growth. This will leave no scars and the patient will not experience pain. The laser cauterizes the capillaries, so this method does not cause bleeding;
- A liquid nitrogen. The essence of the procedure is the local application of liquid nitrogen. This leads to instant freezing of damaged tissues and their death. It is not recommended to use if the growth is deep;
- Chemical treatment. Various remedies are used to get rid of the problem: cantharidin, salicylic acid, podofilin or podofilox. Preparations based on celandine juice are often prescribed;
- Surgical intervention. Local anesthesia is administered and the papilloma is excised using a scalpel. This technique is used in extreme cases, for example, when removing large warts. After the procedure, scars remain. There is a risk of incomplete removal of the damaged area, which is why there is a possibility of relapse;
- Electrocoagulation. As with laser burning, this method is bloodless. Using high-frequency current, the tumor is removed. If the wart is large, a local anesthetic is used;
- Radio wave removal. The safest method, since there is no contact with the skin, the penetration of infections into the blood is excluded and no burns remain after the procedure.
Reasons for appearance
The occurrence of any papilloma is a consequence of infection of the body with papillomavirus (HPV).
- It can penetrate the body in different ways: sexually, through the birth canal, and through everyday life.
- In the case of pedunculated papillomas, infection occurs by contact through microdamages of the skin.
- Increased sweating, oily or wet skin increases the risk of infection.
Thin or wide pedunculated warts are caused by certain subtypes of HPV - types 3, 5, 8 or 9. Once in the body, the virus gains strength for some time (incubation period) and waits for the right moment to become active.
This moment comes with a decrease in immunity, which can happen due to various reasons, for example, another disease.
Having penetrated the epithelial cell, the virus begins to actively multiply, and the person notices the appearance of a growth on the skin.
Causes
The reasons for the appearance of pedunculated papillomas are not entirely clear, since they are formed from blood vessels and collagen present under the skin.
Mast cells increase in number in many skin diseases. They influence T lymphocytes and B lymphocytes, keratinocytes, fibroblasts, Langerhans cells and endothelial cells, due to a variety of cytokines, chemokines and growth factors.
Their presence in acrochordons may play a role in fibroblast proliferation and collagen deposition, as well as in epidermal acanthosis. They are known to enlarge in the dermis in areas subject to repeated friction (a form of trauma) and irritation.
On this topic
- Papillomas
The most effective methods for treating papillomas
- Inna Viktorovna Zhikhoreva
- September 27, 2021
Mast cells have been shown to accumulate at the site of injury as an initial response to injury and increase tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α).
Preformed or newly synthesized TNF-α, as well as other mediators, are then released by them, which at least partially causes several histological changes found in neoplasms. Etiopathogenesis can be initiated similarly to other forms of skin trauma.
Detection of enlarged mast cells is consistent in cases such as:
- obesity and overweight;
- diabetes mellitus type 2;
- insulin resistance
- dyslipidemia;
- pregnancy;
- genetic predisposition.
Predisposing factors include skin irritation and exposure to ultraviolet rays. Neoplasms can serve as a signal for people who have impaired carbohydrate metabolism.
Studies have shown the possible role of human papillomavirus (strains 6 and 11) in the pathogenesis of acrochordon. In rare cases, it may be associated with Gardner's disease, the autosomal dominant disorder known as Burt-Hoag-Dube syndrome and Milroy syndrome (lymphedema), acromegaly, and polycystic ovary syndrome.
Acrochordons are typical for older people.
What is this
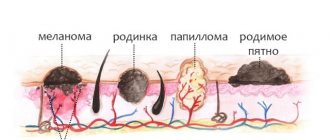
Papilloma - what is it?
- The appearance of such a growth may vary depending on its type.
- These can be soft, elastic or keratinized warts.
- Some of them are attached to the skin on a thick or thin stalk, as if growing from a skin cell.
- Others are a flat but rather dense formation.
Some warts coexist with a person from the moment of their appearance and throughout his entire life, without disturbing their owner in any way.
Others become inflamed and can even become malignant.
But every papilloma is skin cells that have been captured by a virus, and therefore always poses a potential health threat.
Kinds
The international classification of the disease has recorded more than 100 varieties of human papillomavirus. The type of strain affects what the formation looks like and what symptoms it brings. Thus, the growths vary in color; there are gradations from flesh-colored to dark brown. There are different sizes, in some cases the papilloma grows in diameter up to 20 mm. Warts have a thin stalk or a wide base.
The most common types of papillomas on the back are:
Surgitron device: principle of operation and areas of application of the radioknife
- Vulgar or simple. These skin growths look like a small bump with a keratinized surface. They can occur not only on the back, but also on other parts of the body;
- Flat. Round formations have clear outlines and most often have the same color as the skin. In some situations, several growths appear in one place, then the papilloma acquires uneven boundaries. Such formations usually cause itching and pain;
- Thread-like. Papillomas often appear in the armpit area. Most of these papillomas are yellow. They appear in mature people over 40 years of age and are not always caused by a virus; sometimes the cause may be age-related changes in metabolism.
What types of growths are there?
Different strains of HPV are manifested by specific growths and localization:
- simple (ordinary, vulgar) papillomas are small round-shaped formations, slightly rising above the surface of the skin. Sometimes they merge, forming irregularly shaped tubercles. Their surface is keratinized and rough. Most often it can be found on the hands in the area of the fingers or knees. Usually found in children;
- flat warts are small round formations that may rise slightly above the skin (by 1-2 mm). They cause considerable anxiety to the owner. You can often notice that such a wart is inflamed, red, and itchy;
- thread-like formations (acrochords) are soft and elastic, attached to the skin with a thin or wider base - a stalk. Favorite places for their localization are the face, neck, groin area, armpit;
- plantar warts (spikes) - form on the soles of the feet, have a round shape and a dense, rough structure. Unlike calluses, the edges of the formation are slightly raised, and pain occurs when walking;
- genital warts are white-pink formations that appear in the genital area when infected with papillomavirus. They have a cone-shaped shape and can grow, resembling a cauliflower or cockscomb. The route of infection by them is exclusively sexual, therefore they are found only in the genital area, around the anus, and during oral sexual intercourse - in the mouth.
Varieties of papillomas are clearly identified even in photographs, but only a specialist can make a final diagnosis.
Filiform
Photo: filiform papilloma
Filiform papillomas (acrochords) are so named because of their appearance.
- Under high magnification, they resemble a broken thread or even a whole bunch of them.
- They also grow in length, stretching to a size of 5-6 mm.
- They are attached to the skin on a thinner base, the so-called stalk.
Most often they can be found on the neck, in the crease of the groin and under the armpit.
- Here they are quite often injured, rubbing against clothes, underwear or when shaving.
- As a result, they can become inflamed, bleed, and cause discomfort.
Therefore, filamentous papillomas can be considered quite dangerous formations.
Drug treatment of papilloma on the back
At an appointment with a doctor, the patient will be able to learn not only about why papilloma appears in men or women, but also about methods of treating it. Before considering them, it is necessary to mention one important rule. Under no circumstances should you try to remove a benign tumor from the skin on your own. These actions have very dire consequences for the HPV carrier. Papilloma must be treated and only with the method suggested by a competent doctor. Today in pharmacies you can buy drugs that help destroy papilloma. In addition, they well strengthen the body’s protective function, thereby protecting it from relapses of the disease.
If a person has a papilloma on his back, he may be prescribed treatment, which includes the following drugs:
- Antiviral;
- General strengthening;
- Immunomodulatory;
- Burners.
Drug therapy is aimed at burning out the existing growth on the body and preventing the occurrence of new papillomas. Medicines that will be recommended by a dermatologist have a negative effect on neoplasm tissue. Because of them, the growths dry out and fall off safely.
For similar problems with the skin and immune system, the following medications are prescribed:
- "Viferon";
- "Podophyllin";
- "Immunomax";
- "Inosiplex";
- "Genferon";
- "Verrukacid";
- "Ferezol";
- Allokin-alpha."
The mainstay of therapy is usually immunomodulatory drugs. They must be taken wisely. It is very important to prevent an overdose of medications in this category that stimulate the body’s defense system. It is also advisable to take those products that are ideal for a particular patient. Without special knowledge, a person will not be able to choose the right medicine. He will have to go to the clinic and undergo a series of mandatory tests. Based on their results, the doctor will determine the optimal drug for the patient.
To prescribe the right medicine, you need to undergo a number of mandatory tests at the clinic.
If a person still intends to self-treat with a drug purchased at a pharmacy, he must carefully study the instructions that come with the medicine. It indicates the exact dosage of the medication, the rules for taking it and the desired duration of the course of therapy.
Locations
Each strain of HPV prefers to develop in certain areas of the human body.
But, in general, these neoplasms can be found on almost any of them.
- Most often on the neck, face, armpit, groin area, hands and fingers, soles of the feet.
- Some strains of the virus prefer mucous membranes; they can be found in the mouth, throat, and genital mucosa.
- A special type of papillomas appears in the intimate area, called condylomas. They are localized on the labia minora and majora, the head of the penis, around the anus, and in the vagina.
- They can also be found in the uterus, or rather, on its cervix, where they quickly lead to erosive lesions.
On the neck
On the neck, pedunculated papillomas are most often found (the photo reliably illustrates this fact).
Photo: hanging growths on the neck
Moreover, they occur more often in women than in men, which makes women experience psychological discomfort.
Perhaps this preference is given to women because they more often touch the neck and décolleté area with their hands, adjusting a collar, scarf or jewelry and, at the same time, introducing the papilloma virus to this area.
Scientifically, the localization of filamentous papillomas can be explained by thin, delicate skin and increased humidity or sweating in this area.
Why is it dangerous?
In most cases, such neoplasms are benign and do not pose a threat to human life.
However, there is always a risk of oncogenic degeneration and the formation of a malignant neoplasm.
The likelihood of developing cancer depends on the strain. It can only be determined during a diagnostic examination.
Growths on the back are not as dangerous as papillomas on the mucous membranes. There is a risk of injury to the formation on the back. This can happen while simply changing clothes.
Diagnostics
It is not always possible to diagnose papilloma on your own with a high degree of accuracy, because this neoplasm can be externally confused with similar ones.
Therefore, even the specialist you contact is unlikely to immediately diagnose and prescribe treatment. Indeed, in the case of HPV, many factors must be taken into account that affect the prognosis of the disease.
Photo: patient examined by a specialist
Therefore, the doctor prescribes additional diagnostics:
- cytological analysis - assessment of cellular structures in order to determine the benign or malignant nature of the neoplasm;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction) - allows you to detect the DNA of the virus in the material being studied;
- biopsy - collection of several cells for detailed analysis;
- histological analysis - examination of the papilloma after its removal to confirm its benignity;
- The Digene test is the most accurate test to date that allows you to identify the virus itself, its subtype, degree of oncogenicity and concentration in tissues.
Possible complications
More often, papillomas exist without manifesting symptoms and are discovered by a person by chance.
But some varieties cause significant inconvenience: they itch, become inflamed, cause burning and even pain.
Such signs should not be taken lightly. And after taking the first emergency measures, you should consult a doctor.
If the papilloma on the leg comes off
It happens that the papilloma comes off completely. This is not uncommon for pedunculated warts.
If possible, you should save the torn fragment until your visit to the doctor, placing it in a container with saline solution.
Photo: the tumor came off completely
Bleeding often occurs at the site where the papilloma is torn off.
- It can be stopped with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
- Then the wound needs to be treated with an antiseptic, preferably one that will not stain the tissue.
- Cover the wound with a bactericidal bandage and schedule a visit to the doctor in the near future.
Consultation with a specialist is necessary to find out whether the papilloma has been completely removed. If not, you should do so.
Other warts may need to be removed at the same time, as well as HPV treatment.
If it turns black
If the papilloma has darkened, turned black, or dried out, this may be an alarming sign.
Photo: blackened tumor
Typically, such symptoms accompany exposure to the wart in order to remove it. Eventually it should dry out and fall off on its own.
But if such actions have not been taken, then you should consult an oncologist.
This may be one of the signs of its degeneration into a malignant tumor, but it may not indicate such serious health problems.
Only a doctor can figure this out.
Inflammation
Inflammation often accompanies papilloma injury.
- It manifests itself in redness and pain.
- The wart may also increase in size.
What are the causes of papilloma in a newborn? Find out here.
Treatment consists of removal of the inflamed papilloma, antiviral and immunocorrective therapy.
Prevention
As a preventive measure it is recommended:
- Support your immune system with proper nutrition and an active lifestyle.
- Give up bad habits and fast food.
- Avoid contact with infected people.
- Do not use other people's personal hygiene items: towels, scissors, soap, clothes.
- Have a regular sexual partner, avoid unprotected sex.
Since a strong immune system can independently overcome the virus, the main goal of prevention is to minimize contact with a sick person and promote health. The main route of transmission of HPV is sexual intercourse, so you should avoid promiscuity.
If papilloma hurts on your back, you should immediately consult a specialist and get diagnosed. Otherwise, the virus will continue to progress, invading new areas of the back and body. Only an integrated approach to treatment will solve the problem. Removing a wart is not a therapy. Only a comprehensive impact on the virus will allow you to completely get rid of the disease.
Removal
Removal of papillomas is the main condition for the fight against HPV.
There are several options for removing warts. Among them are medical methods, methods of self-removal using pharmaceutical products and traditional medicine recipes.
What methods exist
Doctors advise contacting medical institutions to remove any tumors.
Photo: removing growths with liquid nitrogen
Here you will be offered the following methods:
- removal of papillomas using chemicals. Basically, these are acids that burn off warts. The method is currently not very common, since after its use the formation of rough scars is possible;
- surgical method - cutting out the papilloma with adjacent tissues. It is usually used when wart degeneration is suspected, since a noticeable scar forms at the site of the operation;
- radio wave is a good alternative to the surgical method. The wart is also removed along with adjacent tissues, but the method itself is non-contact, prevents infection and shortens the rehabilitation period;
- electrocoagulation – removal of papillomas using targeted electric current. It has contraindications; it is not used on particularly sensitive areas, as it is quite painful;
- cryodestruction - freezing the wart with liquid nitrogen. When using cryodestruction, it is difficult to control the depth of exposure, therefore it is not suitable for all types of formations;
- laser method - it is preferred as the safest method with a short recovery period after surgery. It has virtually no contraindications and is used even on difficult areas of the body.
Each method has specific indications, so you need to consult your doctor which method is preferable in your case.
There are ways to remove a wart yourself. The pharmacy sells special products for this: Cryopharma, Solcoderm, Superchistotel.
It is important to be careful here and the following rule: if the effect is not achieved the first time, then it is better to consult a doctor.
Removal with folk remedies
Photo: using celandine juice
Treatment with folk remedies can also be effective in getting rid of warts:
- celandine juice. For this method you need to use fresh plant stems. When picked, a drop of juice appears at the site of the rupture, which should be applied directly to the wart. It is better to lubricate the skin around it with a rich cream first. The juice is very hot, it is recommended to carry out the procedure 2-3 times every other day until the effect is achieved;
- garlic. You can use a small plate or crush a slice in a press and use the resulting pulp. The surrounding skin is lubricated with a rich cream, garlic is applied to the wart, and secured with a band-aid for 5-6 hours. The procedure is repeated daily until the wart dries;
- onion juice It is used like garlic, only the duration of treatment will be longer;
- Castor oil. Rub into the wart and the skin around it twice a day;
- propolis tincture. Purchased at a pharmacy. A small cotton ball is moistened in the tincture and attached to the papilloma for 2 hours daily;
- iodine. Lubricate the papilloma with iodine daily, avoid contact with the skin around it.
There are many other folk methods.
If the condition of the papilloma worsens (inflammation, redness, increase in size), you should immediately consult a doctor.
ethnoscience
Some experts recommend removing papillomas on the leg using traditional medicine recipes. Any of the chosen methods must be agreed with your doctor. Among the most popular recipes are the following:
- Celandine. Celandine juice has long been used in the fight against various types of warts. To achieve the desired effect, you need to use fresh juice obtained by breaking the stem of the plant. To avoid burns, it is better to pre-smear the skin with a nourishing cream. The course of treatment should consist of 5-6 procedures, which are performed every 1 day.
- Garlic pulp. To prevent burns, you need to lubricate the skin around the formation with a nourishing cream. The prepared garlic paste is applied to the patch and attached to the papilloma for 5 hours. The course of treatment will be completed when the formation disappears on its own.
- Onion juice or its pulp has the same property. In practice, this method affects papilloma much longer than the garlic method.
- Propolis tincture can be applied to the papilloma as a compress for several hours.
- A healing bath helps get rid of formations well. For it you need to brew 0.5 buckets of chestnut leaves and leave for a day. The strained broth is added to the collected bath. The course of treatment is 14 days, baths should be taken every other day.
- A tincture of dandelions and triple cologne removes papillomas. To prepare it, you need to take dandelion heads and stuff them tightly into a bottle of cologne. The tincture is stored for 2 weeks in complete darkness, then used as compresses.
- A popular folk method is to tie a thread over the wart. Take a silk thread and tie knots over the papilloma. The string is then placed into a cut potato and left in a dark place to allow the vegetable to rot.
- Iodine has the same effect as propolis. But there are disappointing statistics: papillomas that were removed with iodine did not disappear, but problems with the thyroid gland appeared.
- The same reviews can be heard about the healing monastery tea. It will never rid the body of papillomavirus, since the set of medicinal herbs is not conducive to this.
Rehabilitation period
The rehabilitation period is very important to prevent complications and achieve a cosmetic effect.
Photo: crusts after removal of tumors
Therefore, at this time you need to adhere to the following rules:
- do not wet the surgical site with water until the crust falls off the wound on its own;
- do not cover the wound with a band-aid to prevent the greenhouse effect underneath;
- avoid exposure to the sun, especially 2 weeks after the scab falls off, to prevent unwanted pigmentation;
- the wound must be treated with antiseptic or other agents prescribed by the doctor;
- There is no need to apply creams or decorative cosmetics to the area of the wound or recently fallen off crust.
What to do if the crust comes off
- If the crust comes off from the wound for some reason, you need to immediately treat the area with an antiseptic. It is better to use a colorless product (for example, chlorhexidine hydrochloride) to immediately notice signs of inflammation.
- If there is blood when tearing off the crust, you should first stop the bleeding with a solution of hydrogen peroxide.
- If, after tearing off the crust, you notice, despite regular treatment, redness of the surrounding tissues and pain, then consult a doctor immediately. You may have been unable to avoid infection.
How is the recovery period after removal of papilloma on the head? Find out here.
How to deal with papillomas on the body? Read here.
Pedicled papilloma, despite its small size and asymptomatic existence, can still cause health problems and dissatisfaction with one’s appearance.
Therefore, do not be lazy to consult a doctor and undergo a course of treatment for papillomavirus, and also remove it in a timely manner. Your health will only benefit from this.
Rehabilitation period
After removal of the papilloma, a rehabilitation period begins, which includes taking medications aimed at eliminating pain and strengthening the immune system. Medicines used include:
- Viferon, Anaferon - contain interferon molecules that stimulate the immune system.
- Analgos, Nurofen - reduce pain after wart removal.
- Interferon in the form of injections strengthens the immune system.
- Oxolinic ointment – has an antiviral effect, strengthening local immunity.
Viferon - used during the rehabilitation period.
Treatment usually does not require hospitalization. The exception is large papillomas that have a high degree of oncogenicity.
It is recommended to treat wounds after removal of papillomas with an antiseptic in order to reduce the likelihood of developing an inflammatory process. After the scab leaves, new cells form in place of the papilloma.