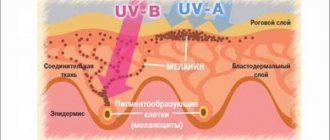
The first single moles on the human body can most often be noticed in preschool age, but the majority of them appear in adolescence during hormonal changes in the body.
But there are children who are born with moles on their bodies. The number of pigment marks, as the first moles in newborns are also called, as well as the type, shape and size, can vary. In most cases, these tumors are safe and benign tumors. Their number may increase and decrease with age.
Why do nevi appear?
To date, scientists have not been able to study the exact mechanism of the appearance of birthmarks on a child’s body. There are only a few theories that consider the possible causes of such skin changes. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Genetic predisposition.
- Gender, that is, sex. According to statistics, nevi are diagnosed more often in girls than in boys.
- Premature birth. Birthmarks are more common in premature babies.
- Hormonal disorders in the body of a pregnant woman.
- Sexual infections, diseases of the genitourinary system.
- Intoxication of the body.
- Excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation.
In addition, the appearance of a nevus can be preceded by an unfavorable environmental situation and a sharp change in climate.
Either one of the above factors or a combination of them can provoke the appearance of a birthmark on a baby’s body.
Causes of birthmarks in newborns
These include: damage to the baby’s arteries, veins, and capillaries. At this stage, scientists have identified two causes of birthmarks in newborns:
- Genetic embryonic failure
- Another reason for the appearance of birthmarks in a newborn is the excessive production of vascular endothelial growth factors.
Also, birthmarks in newborns can appear due to the following phenomena:
- changes in hormonal levels in the body of the expectant mother;
- the presence of infection in the genitourinary system;
- radiation of a woman during pregnancy.
All these phenomena are considered inaccurate, since they have not been proven by anyone, these are just supposed guesses.
Initially, birthmarks in newborns can change color and shape and even grow. But after half a year they disappear by themselves, as if nothing had happened in this place.
Such spots do not harm the child and are absolutely not dangerous.
We also recommend reading: When teeth start cutting
There are folk signs that help you understand why birthmarks occur in newborns.
These are the signs:
- It is believed that if a girl, being in an “interesting” position, becomes very frightened of something, then the baby will be born with a birthmark.
- A girl who is carrying a baby will suddenly see a fire and look at it, then the baby will be born with a fiery spot on her body.
Changes in hormonal levels during pregnancy, as well as climate change, for example, if a woman lived in warm countries and then moved to the north, then such a sudden change will cause the appearance of birthmarks in the newborn and infection.
There are a couple of types of birthmarks that require removal at the first opportunity. These include:
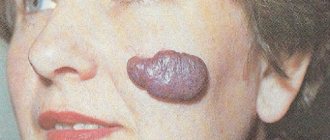
Giant congenital nevus . It reaches 15 cm in size. It belongs to the group of melanoma-dangerous nevi. It is dark in color, may be covered with hair, and if no action is taken, such a spot will turn into a malignant form.
However, if the size does not allow for surgery, then the patient is required to undergo regular examinations by specialists. The operation consists of extensive excision of the damaged area, which involves not only the entire nevus, but also a small area of healthy skin located near the edges of the formation.
In some cases, it is not possible to remove a nevus at once, then specialists resort to a gradual effect on the spot. After excision, a skin grafting procedure is performed.
Only such examinations will help to identify in time a possible deformation into a malignant tumor. The occurrence of melanoma can occur due to the fact that the nevus is affected in some way.
For example, a person may hit the area of the body where the nevus is located, or expose this area of skin to “solar or radiation.” Any damage of a chemical nature is also strictly contraindicated.
Warty nevus - it is rare in young children, but it also requires removal at the age of two years. It has several names - keratotic, epidermal, verrucous, linear or ichthyosiform. The female half has a greater predisposition to warty nevus than the male half.
We also recommend reading: How to treat heat rash in a newborn baby
If birthmarks in newborns do not bleed, do not itch, and do not grow very quickly, then there is no point in being nervous about them. If on the contrary, then you should contact an oncologist.
Types of birthmarks
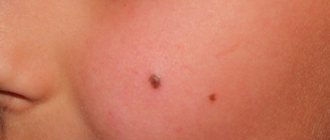
Genetic predisposition, as already mentioned, plays an important role in the formation of nevi. Often in children such formations appear in the same places as in their parents. If, at first glance, the baby was born with clear skin, this does not mean at all that he does not have birthmarks. They are often very light in color, making them almost invisible. Clear and immediately noticeable nevi occur in one percent of children out of a hundred. If at first the birthmark was light, then by 3-5 years it may darken and acquire clearer boundaries.
There are two types of skin formations on the body of children. Let's look at them in more detail:
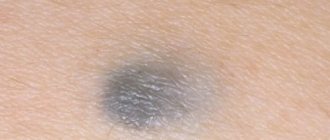
- Pigmented birthmarks. They usually have a brownish or blue-black tint.
- Hemangiomas and angiomas are red spots or birthmarks characterized by a purple, violet or pink hue.
It is by the color of the formation that doctors can guess which cells were involved in the process of formation of the nevus. A black or brownish tint indicates that melanocytes, which are actively dividing, took part in the formation of the birthmark.
A red or pink tint is characteristic of spots formed from vascular cells.
Types of pigmented nevi
There are several types of pigmented birthmarks in newborns. Their appearance is explained by the accumulation of large amounts of melanin pigment in small areas of the dermis. In the table we consider the types of such formations on the body of children.
You might be interested in: Molluscum contagiosum in children
| Name | Characteristics |
| Mongolian spot | This is a benign formation on the body of children whose genotype contains Mongoloid genes. This spot appears in the lower back. Such a nevus does not pose a threat to the life of a child and completely disappears from the body by the age of five. |
| Dysplastic birthmark | These spots, as a rule, have an irregular shape, blurred boundaries, different color intensity and diameter. Sometimes a dysplastic nevus is the result of several point elements |
| Mole | Small spots with varying color intensities. Such formations appear in different parts of the body |
| Congenital birthmarks formed from pigment cells | It is easy to diagnose such a formation in a child by the presence of hair in the area of the nevus. The color ranges from light brown to black. The diameter is usually large |
Pigmented nevi are benign and do not develop into malignant formations.
If the stain is located on open areas of the body, for example, in the face, it can be removed if desired. This is not hazardous to health.
Vascular birthmarks
Such nevi are clearly visible on the body of a newborn from the first days after birth. Nevi of this type are a consequence of active division of blood vessels, which occurs against the background of changes in the structure of small capillaries. These spots grow for up to 12 months, after which there is regression in the process. The nevus becomes smaller, paler, and then disappears. In this case, no treatment is required.
The reasons for this process remain unclear to this day. There is an assumption that such formations develop against the background of damage to small vessels located in the subcutaneous tissue. This process is provoked by dysfunction of collagen fibers. They are responsible for the strength of the walls of hollow tubes. The described birthmarks have different diameters and irregular shapes. Experts believe that they are not life-threatening and often disappear on their own without any intervention.
According to medical statistics, hemangiomas are more often diagnosed in infants born with low body weight.
Spots on a child
Babies are often born with spots on their skin that we call “birthmarks.”
Babies are often born with spots on their skin that we call “birthmarks.” They can occur later, and at any age. Doctors distinguish many types of such formations, which may consist of cells with pigment or overgrown vessels. Some of them are harmless, while others can harm the child.
- Vascular spots are actually benign tumors. The doctor must monitor their development, and there are clear indications that will require their removal.
- Age spots should be seen by a doctor if they grow, change shape, or become unevenly colored.
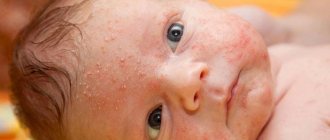
- An allergy rash can be spotty. It quickly appears and disappears in the absence of an allergen.
Types of hemangiomas
The described formations can appear in the baby on various parts of the body, in particular, on the face, head, leg, arm, back, chest, in the eye area, and so on. Doctors distinguish several types of such spots.
Stork trail
Such a nevus appears in the baby in the area of the back of the head, forehead, bridge of the nose, and cheeks. The birthmark has a rich pink tint.
Often one large formation consists of several small elements.
Flaming nevus
The name flaming nevus is given to a birthmark characterized by a bright pink or red color. With age, the color intensity intensifies.
This formation does not pose a health hazard, but, from an aesthetic point of view, it causes a lot of inconvenience.
Kiss of an angel
This interesting name has a nevus located on a large part of the face. Its hue is usually yellowish. During physical activity or the baby's crying, the birthmark tends to change its color and becomes darker.
You might be interested in: Diaper rash in a baby
This skin formation is not dangerous for the health of the baby.
Strawberry spot
Some babies are born with a small pink spot that rises above the surface of the skin and looks very much like a strawberry. Immediately after birth, the nevus grows along with the baby, but around the age of three, this process begins to regress.
If we try to answer the question at what age this formation completely disappears, then we can say that this period usually coincides with the first hormonal changes in the child’s body, that is, puberty. Sometimes a barely noticeable scar remains at the site of such a nevus.
Star birthmark
The nevus received this name because of its shape, reminiscent of the ends of a star. Another name is spider nevus. It is explained by the similarity of the formation with the spaced legs of an insect.
By the time of puberty, the spot, as a rule, disappears from the child’s body without a trace.
Cavernous hemangioma
If such a formation appears in your baby, it will have blurred boundaries and a different shade. With age, the nevus constantly grows and changes. Externally, the stain resembles a seal.
There may be several such formations nearby. If you place your palm on such a hemangioma, you will feel the temperature difference. In the area of vascular compaction it will be higher.
Expert opinion
Ksenia Dunaeva
User experience expert and comment moderator. Higher medical education and more than 5 years of actual practice.
Ask Ksenia
When various birthmarks appear on a baby’s body, the parents’ task is to closely monitor these neoplasms. It is important to exclude injuries to this area, as this can lead to serious complications. When red spots form near the eyes, nose, and ears, you should pay attention to whether they have regressed by the age of two. If the nevus continues to grow and change, it is important to consult a specialist.
Regressive vascular spots of newborns
Congenital pathological formations of blood vessels located in the forehead, upper eyelids, bridge of the nose, and the back of the head are defined as regressive vascular spots of newborns. Various terms are used to describe this type of pathology: cutaneous vascular anomaly of the newborn, “salmon spot”, “stork’s kiss”, vascular marks, nevus of Unna, nevus simplex, nevus flammeus neonatorum, etc. The disease is detected in 25–40% of newborns.
The reason for the appearance of these formations has not yet been established. It is believed that vascular spots in newborns are caused by dilation of capillaries. A number of researchers attribute this to the mechanical impact on these areas of the skin and the resulting temporary hypoxia during childbirth and the passage of the child’s head through the birth canal. This theory is supported by typical localization - the back of the head, forehead, eyelids, bridge of the nose, nose, upper lip.
Very rarely, such formations are localized in other areas of the body. Among the theories of the appearance of “vascular marks”, a hereditary nature with an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern is also considered. The family-hereditary nature of the disease often manifests itself in several generations. According to another theory, the cause of the appearance of lesions lies in the insufficiency of perivascular nervous tissue, which is responsible for regulating vascular tone.
Data obtained using confocal microscopy show an inverse relationship between the density of nerve endings and the diameter of blood vessels in the affected area.
Vascular lesions are detected immediately after birth
Vascular lesions are detected immediately after birth. They are not accompanied by any symptoms, but can lead to aesthetic problems. Less commonly, dermatological diseases (seborrhea, psoriasis) develop in the area of vascular spots. Clinically, the formations are spots of irregular shape, with clear boundaries, not rising above the surface of the skin, with an enhanced vascular pattern, elongated or diffusely occupying the entire affected area (back of the head, eyelid). The favorite localization of vascular spots is the back of the head, forehead, nose, eyelids, lips. In the forehead area they are often V-shaped. They turn pale when pressed. Palpation is painless, no changes in tissue consistency in the area of formations were detected.
Over time, pathological formations fade within the original boundaries, especially in the upper eyelids. Spots in the area of the nose and back of the head are more persistent. Lesions involving the wings of the nose and upper lip are especially resistant to spontaneous regression. According to our observations, vascular spots are detected in almost 20% of cases in children with hyperplasia of blood vessels.
The main presumed factor in the occurrence of these two diseases is hypoxia, but the compensatory mechanisms in these two cases are different. With hyperplasia of blood vessels, restoration of tissue nutrition is achieved due to excessive growth of the endothelium and enlargement of capillaries, while with vascular spots of newborns - due to expansion of the lumen of the capillaries.
Differential diagnosis must be made from stable blood vessel malformations (non-regressive) and blood vessel hyperplasia. Anamnesis data testify in favor of vascular spots in newborns - with this disease, a hereditary predisposition is observed much more often.
Computer capillaroscopy helps to establish an accurate prognosis and course of the disease.
The absence of a rapid increase in the area and volume of the lesion also indicates a vascular spot in the newborn. From this position, observation for a month is appropriate. During this period, hyperplasia of blood vessels, as a rule, is clearly manifested by rapid growth and an increase in the volume of the lesion.
It is more difficult to differentiate spots from non-regressive malformations. In these cases, localization in atypical places helps to make a diagnosis. The diffuse nature of the spots, in contrast to the island nature in children with vascular spots of newborns, also testifies to the malformation. Damage to the skin of the back of the head can also be considered a relatively pathognomonic sign.
The color intensity of a stable malformation increases slightly in the first months of life. The appearance of purple and bluish tints and a slight increase in volume are characteristic. Elevation above the skin surface also indicates a stable malformation. Computer capillaroscopy helps to establish an accurate prognosis and course of the disease. Capillaroscopy reveals superficial, tortuous, dilated capillaries. The density of the capillary network is not increased, the interstitium is transparent. The arrangement of capillaries is structured.
Changes in the capillary network in the area of the vascular spot, diagnosed using capillaroscopy, may be due to increased capillary permeability during hypoxia during childbirth, which, in combination with pressure, leads to persistent paralysis of the vascular bed. In contrast to congenital hyperplasia of blood vessels, there is no endothelial proliferation.
The second important differential feature is the absence of tumor-like growth. This may be evidenced by the blanching of the vascular spot with age without a decrease in its area, while the involution of the focus of hyperplasia of blood vessels is always accompanied by a decrease in its size.
Treatment is usually not required. In the first two years of life, these formations usually disappear in 80% of newborns. In the area of the back of the head, the spots are more persistent and can remain for life. The ability to regress is even less pronounced in spots in the lumbosacral region. If the spots create aesthetic problems, treatment methods recommended for stable capillary malformations of blood vessels are used, primarily laser photocoagulation.
Diameter of birthmarks or what to pay attention to
Benign formations have a certain size. In medical practice, a special classification is used:
- A nevus diameter of up to 7 cm is considered small. They do not pose a threat to the life and health of the child, so there is no need to get rid of them.
- Birthmarks ranging in size from 7 to 12 cm should be closely observed. It is important to prevent their injury. If signs of rapid growth or discoloration appear, it is important to contact a specialist immediately.
- The so-called giant nevi, whose diameter is more than 1 cm, require special control.
It is very easy to control the size of the formation. To do this, measure it with a ruler or cut out the outline of the nevus on paper, after applying it to the neoplasm and drawing the edges.
Later, you can apply this mock-up to the spot and compare how much it has increased in size. This simple method will help you easily control the growth dynamics of a birthmark.
be careful
If any formation is detected on the skin of a newborn, parents need to bring it to the attention of the attending pediatrician, and if there is a noticeable growth or change in the structure of the birthmark, the appearance of inflammation, additional rashes around it, or an increase in the intensity of the color, they should definitely contact a pediatric oncologist. The doctor will be able to determine which of the above formations this birthmark resembles and whether it is a manifestation of any disease or syndrome.
In any case, it is advisable to trace the detected formation on tracing paper immediately after birth and monitor its further growth.
Mom should also pay attention to ensuring that the birthmark is not constantly irritated by tight-fitting clothing, which can lead to its growth or damage with subsequent infection.
Sources:
- https://www.childface.ru/rus/content/330/regressiruyuwie_sosudistye_pyatna_novorozhdennyh.html
- https://www.eurolab.ua/skin-problems-and-treatments/2544/2545/19141/
- https://deti.mail.ru/baby/1-6/pyatna-u-rebenka/
- https://www.7ya.ru/article/Rodimoe-pyatno-kosmeticheskij-defekt-ili-opasnyj-simptom/
Indications for removal
Benign birthmarks do not pose a threat to the child’s health, so their removal is usually not required. But in some situations there are still indications for the so-called removal of moles. This is necessary if the following symptoms appear:
- Changes in the structure and diameter of the spot. In this case, the nevus begins to rise above the skin, increases in size, and changes color.
- Redness and swelling in the area of the tumor.
- The color of the birthmark changes sharply to darker or lighter.
- The edge of the spot becomes torn and changes its boundaries.
You may be interested in: Differential diagnosis of rash in a child
Even if even one of the above-described signs is present, it is worth excluding the transformation of a benign neoplasm into a malignant one. To do this, you need to seek medical help. A pediatric oncologist deals with the diagnosis and treatment of various neoplasms in children.
If negative signs of a nevus appear, you should go to the hospital immediately, since skin cancer is a rapidly progressing and very dangerous pathology.
And it's not dangerous
The small pigment spots that most of us have are only minor cosmetic defects and are not dangerous. But those who have large pigment spots measuring more than 5-10 mm should not actively sunbathe or go to the solarium. This applies more to those with multiple spots.
Pigment spots, as mentioned above, are accumulations of melanocytes, and a hemangioma, despite its benign quality, is still a neoplasm, therefore it is extremely undesirable to expose both pigment spots and hemangiomas to ultraviolet irradiation (under the sun or in a solarium), since increased insolation can provoke malignant degeneration of benign neoplasms.
Pigment spots with intense irradiation, in addition to the production of melanin and darkening, can also begin to actively divide, thus degenerating into a malignant tumor - melanoma. True, it is rare in young children.
Methods for removing nevi in children
If indicated, the birthmark can be removed in one of the following ways. To do this, you should undergo an examination by a specialist who will help you make the right decision about the upcoming operation. Here, such features as the diameter of the formation, its growth dynamics, type, etc. are taken into account. If there are no signs of the spot transforming into a malignant neoplasm, laser therapy can be used. If there are alarming symptoms indicating oncology, the operation is performed using a scalpel.
Use of medications
This therapy involves the introduction of special medications into the area of the birthmark, which help achieve the death of overgrown pathological cells.
The advantage of this type of treatment is that it is painless and can be performed on an outpatient basis. The disadvantage is that the patient is allergic to the active components of certain products.
Laser therapy
This technique is considered effective and safe and does not require long-term rehabilitation. In this case, pathological cells are cauterized with a laser beam. The disadvantages include the fact that such equipment cannot be used on all areas of the body.
It is almost impossible to cauterize nevi in hard-to-reach areas.
Freezing with cryotherapy
This means freezing pathological cells of formation using low temperatures.
Nitrogen is often used for this purpose. This method of therapy is usually used to remove small birthmarks.
Surgical treatment
If it is impossible to use other methods, treatment with a scalpel is used. In this case, the doctor excises unnecessary tissue with a special instrument. Disadvantages: pain, prolonged healing, and the need for anesthesia. In addition, various complications often arise.
Many parents are interested in what age is best for removal. It all depends on the growth dynamics of the spot. The time of the operation is selected by the doctor. A specialist knows best when to perform this procedure.
Prevention of complications
If a child has birthmarks on his body, no matter how many there are, one or several, whether they are white or red, parents should carefully monitor such skin formations. Do not expose this area to prolonged exposure to direct sunlight or cold. It is strictly forbidden to try to remove nevus on your own using various folk recipes. It is important to try to avoid injury and friction with clothing. This can be extremely dangerous for the baby's health. Simple rules of prevention will help prevent complications and maintain healthy baby skin.