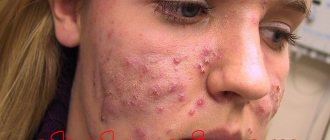
Herpes in the mouth is common and can affect the lips, chin area and oral mucosa. The disease can pass from an acute form to an intractable chronic form, and therefore requires a responsible approach to treatment. The lack of necessary therapy leads to the virus affecting almost all organs and systems.
Herpes in the mouth is common and can affect the lips, chin area and oral mucosa.
Symptoms
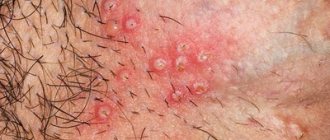
Clinical manifestations resemble herpetic lesions on other parts of the body. Itching and burning appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth, gums, palate, inner cheeks and lips. The affected area appears swollen and red.
At the initial stage of herpes development, symptoms may not appear. Body temperature may remain normal or rise slightly.
Children are often capricious and refuse to eat.
In severe forms of herpetic lesions, characteristic signs of changes in blood composition are detected. Severe swelling of the mucous membranes develops, and blisters form on them. In some cases, ulcers may appear on the gums, which do not decrease with rinsing. Other symptoms of severe herpes infection:
- pain when swallowing or chewing;
- painful sensations in the tongue;
- the appearance of a sharp unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- change in the composition of saliva (it becomes viscous and viscous);
- growth of lymph nodes (cervical and submandibular);
- nausea;
- vomit;
- decreased appetite.
Often a sign of herpes appears, such as bleeding when you press on the gums. And if you palpate the lymph nodes, the patient’s pain may increase.
Bubbles on the oral mucosa have liquid inside. After a while they burst, and in their place ulcers appear. However, even eating can be painful. Subsequently, such ulcers become covered with plaque. There are no scars left at the site of the ulcers.
Some patients may experience a significant increase in body temperature - even up to +40ºС. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate is higher than normal.
The difference between pathology and others
The disease may occur with symptoms that are characteristic of stomatitis. Therefore, when diagnosing, the doctor must be careful to accurately diagnose. To do this, the following must be taken into account:
- With stomatitis, ulcers appear immediately, and with herpes they appear after the blisters burst.
- Herpes can be localized in one area of tissue. With stomatitis, there will be wounds all over the surface of the mouth.
The doctor also needs to pay attention to the affected area. To make an accurate diagnosis, blood tests must be performed.
Causes
The herpes virus can be transmitted by airborne droplets or contact. Often cases of infection occur in adults:
- during kissing and other types of physical contact;
- in cases of poor hygiene (if a person uses a towel, dishes, kitchen utensils or a toothbrush that other people have access to).
Often cases of infection occur in adults through kissing and other types of physical contact.
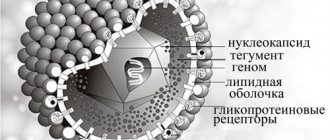
The virus that has entered the human body is able to travel along the trigeminal nerve and reach the oral mucosa. Here it is activated and affects organs.
Provoking factors for the development of herpes:
- stress;
- painful sensations;
- surgical intervention;
- cold;
- increased body temperature;
- irritants - intense solar radiation, wind or low temperature;
- sleep disorders or lack of sleep;
- the beginning of menstruation;
- use of drugs to suppress the immune system.
Why does disease occur in the oral cavity?
It was previously said that 90% of the planet’s population is carriers of the virus. Herpes can remain dormant for a long time and not manifest itself in any way. However, the carrier can infect others without knowing it.
The occurrence of a rash is provoked by a decrease in immunity or any factor that causes stress in the body:
- previous viral or bacterial diseases (flu, colds, sore throat, ARVI, etc.),
- hypothermia or overheating,
- general weakening of the immune system,
- lack of sleep,
- chronic fatigue,
- excessive physical activity,
- menstruation in women (not the most common reason),
- malnutrition,
- bad habits,
- stress,
- direct contact with the patient.
INTERESTING: how are diseases of the oral mucosa diagnosed?
Treatment of herpes in the mouth
Herpetic lesions of the oral cavity must begin to be treated as early as possible. This approach ensures that recovery occurs quickly. If the drugs were prescribed late, the disease will enter the chronic stage, and after the end of treatment, residual traces will be visible. This can also happen in severe cases of the disease.
Treatment for herpes should be started as early as possible.
An integrated approach to the treatment of herpes is of great importance. This means that not only antiviral drugs are used, but also:
- properly selected therapeutic nutrition;
- strict bed rest;
- drinking enough fluid.
All this will help increase the body's resistance to the herpes virus.
Diagnostics
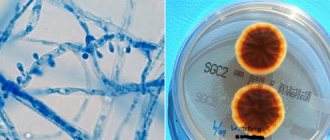
If making a diagnosis is difficult, the doctor prescribes a smear. Further microscopic examination makes it possible to determine the type of herpes pathogen, which greatly facilitates its treatment. An experienced infectious disease specialist can make an accurate diagnosis based on examination.
Drugs
Treatment with antiviral drugs is mandatory. It is recommended to take the tablets from the first days of the development of the pathology. The earlier treatment is started, the better the results and the lower the likelihood of relapse.
The most commonly prescribed drug for herpes is Acyclovir.
Zovirax and Acyclovir are most often prescribed for herpes. The specialist can also prescribe Cholisal, Megosin. Antiviral medicine helps prevent further reproduction of viruses and prevent damage to neighboring tissues and organs.
In addition, immunomodulatory agents are recommended. Thanks to their use, herpes virus infection goes away faster. There are special complex antiviral agents, for example, Imudon. The use of plant complexes to strengthen the body's defenses is shown.
Antipyretic medications - paracetamol and complex medications containing this substance - are prescribed only in cases where the patient is concerned about high body temperature.
Antiviral drugs such as Acyclovir are available by prescription. The patient must carefully follow the regimen for taking such medications.
In mild cases, symptomatic treatment of herpes is carried out. Classification of drugs for treatment:
- antipyretic drugs;
- painkillers;
- immunomodulators;
- multivitamins.
Treatment of herpetic lesions should be carried out by experienced physicians - a dentist, an infectious disease specialist, a therapist or a pediatrician.
The treatment of herpetic lesions is carried out by a dentist, infectious disease specialist, therapist or pediatrician. It is important that the patient enters a state of remission, indicating that all treatment measures are being carried out correctly.
Local therapy
Antiseptics are prescribed as local treatment - Chlorhexidine, Chlorophyllipt, Miramistin, hydrogen peroxide. They do not kill herpes in the mouth. You should rinse your mouth with such solutions to prevent irritation.
To alleviate the condition, ulcers can be treated with Dyclonine solution before meals. Cholisal gel is prescribed to speed up the healing of mouth ulcers.
Ointment for this disease is indicated to relieve pain. Metrogyl Denta gel helps eliminate pain and improve general condition. Local treatment cannot quickly cure herpes, but it is necessary in complex therapy.
Ointment for this disease is indicated to relieve pain. Metrogyl Denta gel helps eliminate pain and improve general condition.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicines do not directly affect the herpes virus. Medicines used at home can only complement the treatment of the disease.
To speed up the healing of affected areas of the mouth, simple and affordable means are used:
- fir or sea buckthorn oil (they need to treat sore spots several times a day);
- aloe juice (it is used topically, and if there are no contraindications, orally);
- infusions of medicinal herbs - lemon balm, chamomile or wormwood - are used as rinses;
- if ulcers form on the lips, you can apply alcohol lotions;
- Chamomile decoction, echinacea decoction or tincture are used as pain relievers.
Echinacea decoction or tincture is used as a pain reliever.
Prevention
To eliminate the risk of contracting herpes in the mouth, you must follow the following rules:
- avoid contact with an infected person;
- Thoroughly disinfect all baby care items. They must be individual;
- traumatic factors should be excluded;
- to prevent the development of herpes, you should eat well, consume the required amount of vitamins and microelements;
- The immune system should be strengthened and all pathologies that contribute to its impairment should be treated.
Proper prevention of herpes helps prevent its recurrence.
Prevention
Since it is impossible to completely get rid of the virus, doctors recommend taking preventive measures. To do this you need:
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- do not use other people's personal hygiene products;
- brush your teeth thoroughly;
- visit the dentist regularly;
- use hygienic lipstick both in winter and summer;
- spend more time in the fresh air and play sports;
- it is necessary to avoid stress;
- Proper organization of the working day with sufficient time for rest and sleep is very important;
- it is necessary to promptly treat all emerging diseases;
- if possible, carry out procedures for hardening the body;
- At the first symptoms of the disease, you should apply an antiviral agent to the itchy area or rinse your mouth.
During pregnancy
The herpes simplex virus is dangerous for a pregnant woman.
During pregnancy, there is a danger of the virus entering the child's body through the placental barrier.
During the period of bearing a child, a woman’s immune system weakens, and the virus additionally affects all organs. A strong immune system is essential for normal fetal development.
During pregnancy, there is a danger of the virus entering the child's body through the placental barrier. The risk of miscarriage increases if the infection occurs in the first trimester. Infection in the third trimester can cause stillbirth or development of brain abnormalities in the baby.
Diagnostics
An experienced doctor will make a diagnosis based on the signs of the disease. However, it happens that the clinic appears too blurred or in an atypical form. Then several laboratory tests are required.
Laboratory methods:
- cultural method (the most time-consuming, costly, but reliable) - growing the virus in tissue culture;
- direct immunofluorescence (DIF) – determination of virus antigens in biological material using a fluorescent microscope;
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) – isolates pathogenic DNA;
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) - detects antibodies to the virus in blood serum.
The immune system reacts to the introduction of the virus by releasing specific antibodies (LgG and LgM), which are identified by the latest research method.
In children
Herpes in children can be much more complicated. The virus can cause severe damage to the nervous system. The manifestations of this pathology are practically no different from those that develop in older age.
Children can scratch the areas affected by herpes and apply their tongue to them. This facilitates the penetration of a bacterial infection and the spread of the virus throughout the body. For treatment, standard drugs are used, the dosage of which is determined individually.
Herpes in children can be much more complicated. For treatment, standard drugs are used, the dosage of which is determined individually.
Complications
Herpes in the mouth can cause serious complications:
- viral stomatitis;
- pharyngitis;
- viral infection of the esophagus;
- viral infection of the digestive system;
- eye diseases - herpetic conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis, keratitis (in the latter case, clouding of the cornea may develop);
- diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system. The most dangerous is viral encephalitis. Involvement of the meninges in the pathological process leads to the development of viral meningitis;
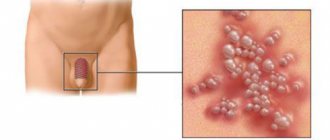
- urogenital pathology;
- herpetic pneumonia;
- viral damage to joints and kidneys;
- generalized viral damage is the most severe complication. In this case, a person develops severe viral damage to all organs and systems.
Herpes in the mouth can cause eye diseases - herpetic conjunctivitis, iridocyclitis, keratitis (in the latter case, clouding of the cornea may develop).
Chronic recurrent herpes
This is the most common type of herpes infection. The disease can manifest at any age. The following factors provoke the disease:
- trauma to the oral mucosa;
- intense sun exposure;
- eating disorder.
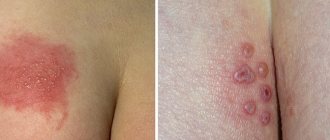
The severity of clinical symptoms of chronic herpes can be much lower than with acute infection. With relapses, small ulcers or rashes appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue or lips. A person feels a slight burning sensation, itching, and sometimes slight pain. If the lesion occurs in the same area, then fixed herpes is diagnosed.
The severity of clinical symptoms of chronic herpes can be much lower than with acute infection. With relapses, small ulcers or rashes appear on the mucous membranes of the mouth, tongue or lips.
This disease must be differentiated from:
- aphthous stomatitis (recurrent);
- allergic stomatitis;
- Streptococcal impetigo.
Treatment of chronic recurrent herpes is carried out using the same drugs as for acute infection. Medicines containing interferon are indicated.
To improve the condition of the body, you should take general strengthening, immunomodulating drugs.
Recurrent herpes requires long-term treatment and compliance with all recommendations, then a sharp deterioration in health can be avoided.