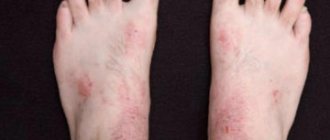
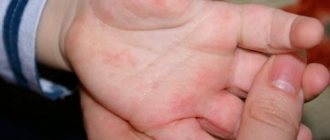
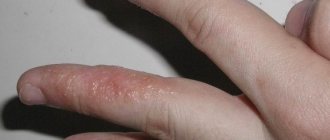
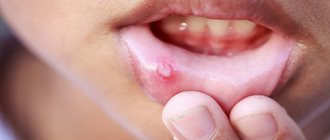
Every year the number of patients with allergic reactions is growing steadily. Moreover, this applies to both adults and children, even the youngest. One of the most unpleasant reactions is ear allergies.
Ear allergies can manifest themselves in several ways:
- rash;
- itching;
- swelling;
- There are often cases when ear allergies are accompanied by fever.
All of this, one at a time and in combination, can significantly complicate the life of any person. However, you shouldn’t give up; allergies can and should be fought.
Photo: Peeling behind the ear
Factors provocateurs
Provocateurs of allergic reactions in the ears are most often chemicals and medications used in everyday life.
These include:
- antibiotics;
- bleaching agents;
- cosmetics for face and body care;
- powders containing phosphates;
- detergents;
- benzocaine and benzophenones;
- substances containing a sulfonamide group;
- para-aminobenzoic acid esters, etc.
Important! The use of almost any inexpensive household chemical can lead to an allergic rash on the ears.
Why does it itch behind the ear?
Itching is a signal from the body that forces you to pay attention to a particular organ. It is difficult to ignore this unpleasant sensation, especially if the scalp, for example, the parotid area, is itchy. Why does it itch behind the ears? This feeling is based on irritation of nerve endings under the influence of various mediators, primarily histamine.
Allergy sufferers are well aware of this phenomenon, since histamine plays an important role in the development of an allergic reaction. But not only allergies cause itching - it can occur as a result of infection, insect bites, contact with irritating chemicals, etc. Itching is characterized by an irresistible desire to rub or scratch the irritated area. Scratching can damage the outer layer of skin. Damage to the skin only increases itching and leads to secondary problems, such as infection, purulent inflammation, scarring, etc. This is why it is very important to treat itching behind the ears while the integrity of the epidermis is not compromised.
“Sudocrem”
The drug has a complex composition. The main functioning element is zinc oxide. The cream softens the skin, relieves irritation, dries and anesthetizes the affected areas of the skin. The medicine helps restore the dermis, disinfects, protects against pathogenic microorganisms and fungi.
The cream is gently rubbed in until a thin film remains on the skin. It is allowed to be used up to 3-5 times a day. Contraindications for use are considered to be personal intolerance to the ingredients of Sudocrem and purulent skin infections. In case of personal intolerance, irritation, a slight rash and redness of the skin are possible.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with the Cause of a small rash on the shoulders of an adult
Allergy symptoms
Manifestations of a negative reaction in the ears are most often the following:
- Intense itching. Many people ask whether their ears can itch due to allergies. The damaged part begins to itch and in the process of scratching, injury to the skin on the ears is likely. As a result, inflammatory infectious processes are likely to occur.
- Congestion in the ears. Lack of timely treatment can provoke purulent otitis media and other diseases of the ear cavity.
- The appearance of nodular redness. Suggests the presence of malignant growths. If such a pathological process is suspected, urgent therapy is necessary.
- A keratinized red area near the ears in adulthood may indicate the formation of actinic keratosis or solar keratosis.
Thickening, induration and swelling on the ears indicate the presence of itchy dermatitis of chronic origin.
Causes of the disease
There are a number of reasons that can cause the body to react to the ears.
The most common of them are:
- animal fur: dogs, cats, rabbits and others;
- pollen of flowering plants;
- ticks and other insects;
- cigarette smoke;
- mold spores;
- hypothermia or, conversely, prolonged exposure to the sun;
- allergies to certain foods;
- bacteria and fungi;
- house dust;
- weakened immune system;
- stressful situations and much more.
Among other things, ear allergies can be caused by damage to the body by microbes and parasites in the intestines, as well as by uncontrolled use of various medications.
Diagnostic methods
To accurately diagnose the disease, an initial consultation with a pediatrician or therapist is necessary. As a result of the survey, the doctor finds out the frequency and severity of symptoms, pulps muscle tissue, performs auscultation of the respiratory organs and on this basis refers to a doctor of narrow specialization: otolaryngologist, dermatologist, allergist.
The otolaryngologist examines the ear canal and eardrum area. To clarify and assess the degree of impairment of auditory functions, audiometry methods, tuning forks or speech are used. Based on the audiogram, the doctor can diagnose diseases of the ear organs and exclude those that are not associated with allergies: otitis media, external and internal, Meniere's disease, labyrinthitis, fungal infections.
If the disease is allergic in nature, then to diagnose it it is necessary to conduct a general blood test:
- The leukocentral formula will show the content of eosinophils in the blood. Their sharp increase is a sign of an allergic reaction or parasitic infection.
- An immunogram will determine the amount of class E immunoglobulins. A high level of antibodies reliably indicates the presence of an allergy.
Carrying out tests and samples will determine the type of allergen.
Skin (scarification) tests are the most common and most accessible visual method for identifying a possible allergen. There are several types of skin tests:
- drip;
- scarification;
- application;
- intradermal;
- prick test.
When conducting provocative tests, the allergen is applied to the mucous membranes of the nasal, oral cavity, under the lower eyelid, or by inhalation.
The elimination method consists of stopping the medication or excluding a certain food product from the patient’s diet.
These tests are not performed for children under three years of age, for diseases of the nervous system, during pregnancy and lactation, for infectious, oncological, autoimmune diseases, exacerbation of allergies and taking antihistamines.
Therapy consists of local use of drugs together with general desensitization of the body. For this, the doctor prescribes the following medications:
- antihistamines to block the production of histamine and alleviate the general condition: cetrin, claritin, suprastin, zodak.
- corticosteroid ointments, creams and gels to eliminate red spots, itching, rashes and irritation on the ears and behind the ears: Elokom, Uniderm, hydrocortisone;
- For rinsing the ears during otitis, a solution of boric acid, hydrogen peroxide, ear drops Otinum, anauran are used to promote tissue regeneration in the area of the eardrum and ear canal;
- nasal, eye drops and sprays to relieve allergic rhinitis and conjunctivitis: taufon, cromoglin, reactin, allergodil, lecrolin;
- the absorption and removal of allergens from the body is facilitated by the use of sorbents: white and activated carbon, smecta, polysorb, enterosgel.
If a secondary infection develops in the ear area, a course of antibiotics is prescribed. The use of any medications must be as prescribed by the attending physician. Incorrectly selected treatment or its prolonged absence can lead to serious complications: paralysis of the facial nerve, atrophy of the eardrum, and the development of cholesteatoma of the ear. In such cases, surgical intervention is performed.
To wash the ear canals during otitis, infusions of chamomile, calendula, rose petals or a decoction of bay leaves are used. Washing with vodka also helps fight suppuration. To ease the course of otitis, infusions of mint, sweet nightshade or horseradish juice will help. These products must be instilled into the ears several times a day, three to four drops. For all forms of allergic otitis, dry heat is recommended.
Characteristic forms of rash behind the ears
- A very itchy, profuse rash of small red spots may indicate lupus erythematosus and sexually transmitted diseases.
- A rash that is very painful when touched indicates damage to the body by amyloidosis, sarcoidosis, or severe viral infections.
- A colorless or translucent rash is a sign of keratosis; a whitish rash is observed with lichen and vitiligo.
- Watery, weeping rashes are characteristic of dermatitis, streptococcal and parasitic infections.
- Dense pimples and acne are observed during puberty, hormonal imbalance, and abuse of fatty foods.
- Small pink pimples in children indicate heat rash.
- A pustular rash can be the result of microbes getting under the skin.
Seborrhea is often the cause of a rash behind the ears in adults.
If a rash is detected on the ears, you must first consult a dermatologist who will make a diagnosis and prescribe adequate treatment. If metabolic disorders in the body are recognized as the cause of the rash, it is necessary to change the diet, introduce foods rich in protein into the diet, and eliminate sweets, salty foods and fatty foods. To determine the microorganism that caused the skin inflammation and the spread of the rash, swabs are taken from the earlobes.
After determining the origin of the pathogenic flora, a course of antimicrobial or antifungal therapy is prescribed. Autoimmune diseases are treated with hormones and immunosuppressants. Physiotherapy is used successfully in the treatment of rashes behind the ears of various etiologies.
Why does a rash occur?
Eating disorder. consumption of foods rich in heavy fats and carbohydrates, sweets, carbonated drinks, fast foods. In this case, the rash occurs not only behind the ears, but also on the face, neck and cheeks. It appears due to malfunctions of the digestive system, which thus signals that the body is overloaded with unnecessary nutrients.
If a child develops a rash behind the ears, prickly heat should be suspected.
Allergic reactions usually appear during the flowering period of plants; in addition to a rash behind the ears, on the face and body, allergies are accompanied by a number of symptoms: lacrimation, sneezing, coughing. These conditions go away on their own if a person avoids encounters with the irritant (pollen or dust). In order to determine the specific allergen that causes the rash, it is necessary to donate blood to detect antibodies to various food and external irritants.
We advise you to read: Causes of rashes on the face
Using inappropriate facial skin care products. Some cosmetic preparations contain components that can irritate or dry out the skin, causing disturbances in its nutrition, and hence the formation of acne on the face and behind the ears, on the scalp. Cosmetic products need to be selected very carefully. Given the characteristics of the skin, it is imperative to conduct a skin test.
Bites from ticks, mosquitoes, bees and other insects. Toxins released by blood-sucking insects can cause skin reactions and small rashes. During their breeding season, after walking and relaxing in nature, you need to carefully examine the surface of the skin of an adult and with special care in children. If a rash appears behind the ears and a tick has been found embedded under the skin nearby, you must immediately go to the emergency room to have it removed by medical professionals.
Skin diseases can cause a rash behind the ears. They have a chronic course with periods of exacerbations and require consultation and treatment with a dermatologist. These are leishmaniasis, erysipelas, vitiligo and other diseases.
Symptoms
The main symptom indicating an allergic reaction to the ears is otitis media, which may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- allergic rhinitis - rhinitis;
- effusion in the middle ear - accumulation of fluid;
- rashes and the ears themselves are swollen;
- swelling of the mucous membrane in the area of the tympanic cavity;
- weeping eczema in the area of the external auditory canal;
- leakage of fluid from the external auditory canal.
Photo: Redness of the ears
In addition to the above symptoms, the patient during the onset or exacerbation of allergies may be accompanied by:
- insomnia or, conversely, excessive sleepiness;
- sweating;
- irritability;
- weakness;
- decreased performance and inability to concentrate.
In advanced cases, mucus and pus begin to secrete from the external auditory canal.
Itchy
During an exacerbation of allergies, the patient may experience itching of the ears. With allergies, the ears itch, and at the same time painful sensations may occur.
Itching in the ears can occur periodically or continue constantly, leading the patient to nervous stress.
Photo: Dry ear
Lays
In addition, the patient may experience hearing problems. According to people who have experienced this disease, many of them had an unpleasant feeling as if their ears were blocked.
The sensation is especially acute when there is a sudden change in pressure.
Swelling
Upon examination, swelling inside the ear can be diagnosed, which is asymptomatic.
Otitis
Allergies aggravated by otitis media, in case of infection, are accompanied by acute shooting pains. However, most often allergic otitis media is asymptomatic.
Allergic otitis media can be either middle or external. It is most often caused by either food allergies or bacteria.
With late diagnosis and treatment, the patient may be at risk of complete or partial hearing loss.
In addition, autophony may occur when the patient hears his own voice too loudly.
Seborrheic dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis is a fungal disease that affects areas of the skin rich in sebaceous glands. If a person suffers from itching specifically in the parotid area, the possibility of this disease should first be considered.
Seborrheic dermatitis develops as a result of an increase in the number of fungi of the genus Malassezia in the skin microflora. It is known that this disease affects people suffering from hypersecretion of the sebaceous glands (the fungus feeds on the lipids that make up the sebum). Malassezia is considered an opportunistic fungus, meaning it is present on the skin of most healthy people. When immune defense is reduced (for example, due to hormonal imbalance, sudden climate change, treatment with antibacterial drugs, etc.), the amount of fungal microflora increases significantly. As a result, the following violations develop:
- peeling skin behind the ears;
- dandruff;
- itching;
- oily skin and hair;
- the appearance of a rash (“irritation”) as a result of inflammation of the sebaceous glands;
- decreased skin resistance to infectious and chemical irritants.
Some symptoms are caused by the influence of fungal waste products on the skin, others by a decrease in the number of beneficial bacteria (since fungi and bacteria constantly compete for the surface of the epithelium as a habitat).
Seborrheic dermatitis primarily affects the scalp - the scalp, the upper part of the forehead and the area behind the ears. In rare cases, inflammation spreads to the groin and armpits.
The affected areas of the skin behind the ears often crack and bleed. The situation is aggravated by the patient scratching the skin (this increases the risk of secondary infection). The fungus that causes seborrheic dermatitis can also affect the ear canals, in which case otitis externa occurs.
If left untreated, seborrheic dermatitis develops into seborrheic eczema.
Mechanism of development of allergic otitis
Otitis media occurs in dogs most often due to allergic reactions in the ear. External agents, allergens, enter the body and quickly spread; the body secretes lymphocytes to fight them.
Symptoms of otitis media appear when the body uses histamines to help, which in turn improves vascular permeability. As a result of these processes, plaques and nodes appear in the area of the outer ear. Inflammation with otitis media in dogs most often occurs on both ears at the same time.
Typically, allergic agents cause itching in the ear area of dogs. The pet scratches the area of irritation until there are open wounds, other pathogens get there and other infections are added to otitis media of allergic etiology.
Symptoms of the disease
An allergic reaction that affects only the ear area is a very rare occurrence. Usually this symptom appears together with other signs:
- allergic rhinitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- gastrointestinal disorders;
- difficulty breathing;
- cough;
- increased temperature;
- surges in blood pressure;
- febrile conditions;
- headache and dizziness.
If, in addition to dermatitis in the ear area, there are no other allergy symptoms, then these are most likely signs of other diseases: lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, oncology, seborrheic dermatitis or senile keratoma.
If this disease is of an allergic nature, then together with other signs it will manifest itself in the form of otitis media and be expressed in the form of the following symptoms:
- rash, peeling of the skin, wet eczema accompanied by itching;
- discharge of a large amount of fluid from the ear canal;
- swelling in the outer and middle area of the ear;
- pain;
- rhinorrhea (severe runny nose);
- hearing loss, autophony, feeling of congestion.
With otitis media, the patient's general condition worsens. Constantly present pain causes nervousness, irritability, sleep quality deteriorates, and headaches may occur. Due to ear itching, trauma to the deeper layers of the epidermis is possible, against which a secondary fungal or bacterial infection may develop, accompanied by purulent discharge and hearing loss.
Ear allergies in a child
In infants, breast milk can trigger an allergic reaction behind the ears. It's all about the allergens it contains.
The blame for this lies primarily with the mother, who, despite feeding, eats foods that contain allergens. The same applies to complementary foods.
The causes of allergic reactions in older children are not much different from the causes in adults.
Photo: Manifestation of diathesis
Other causes of itching and their elimination
There are a number of other reasons why a person’s skin behind the ears itches. These factors include:
- Stress – frayed nerves can cause itching and various skin diseases in adults.
- Allergies – to cosmetics, shampoo, hair dye, ingredients of a homemade cosmetic mask, jewelry, products and external irritants, including the material of the headdress. Allergies are treated with antihistamines and require limiting contact with the irritant.
- Climate change – a sudden change in environment weakens the body. In addition, unusual weather, for example, dryness and wind, can have an effect.
- Vitamin deficiency - a lack of vitamins is reflected primarily on the skin. Bad habits in adults increase this effect several times. You need to improve your diet and lifestyle.
- Dehydration – it is important to restore water balance. To do this, you need to drink more water and use humidifiers.
It is also important to maintain hygiene to avoid the accumulation of dirt and germs. If you notice itching behind the ears, you should definitely consult a doctor. to find out its origin and only then begin treatment.
Sources: , ,
Prevention
To prevent cracks behind the ears in a child and the possible consequences of this symptom, follow these rules:
- pay attention to any allergic manifestations after your child consumes a new product;
- walk in hot weather for no more than 1 hour in the shade;
- carry out timely wet cleaning of the room and ventilation;
- strengthen the child's immune system;
- carry out careful hygiene in the area behind the ears;
- select anti-allergenic detergents and hygiene products;
- moisturize the skin with special baby creams;
- carry out timely treatment of the parotid area in the presence of scratches, cuts and other microtraumas;
- During pregnancy and lactation, monitor your diet and do not overuse allergenic foods.
Allergic reactions and various skin dermatitis are not uncommon in childhood, so you need to carefully monitor your baby's skin. If you know that your child is predisposed to allergies, then try to take all preventive measures to avoid dangerous complications.
Rash on earlobe
The appearance of a rash on the earlobe may be associated with constant or periodic wearing of jewelry that causes inflammation. The phone may also be the cause of this phenomenon. In the latter case, it should be thoroughly treated with antibacterial agents. Another common cause of rashes on the lobe is insufficient hygiene. In addition, shampoos, masks and other hair products often cause a rash in this area.
If a rash does appear on the earlobes, you should not touch it, so as not to cause a secondary infection and prevent suppuration. Periodically, pimples should be treated with alcohol or aloe juice. Differin and tar soap can be used to treat rashes on the earlobe. Folk remedies are also suitable for these purposes: a decoction of celandine or plantain, an infusion of calendula or chamomile and others.
Diagnostics
In addition, it is much more difficult for an adult to identify the allergen to which such a reaction occurred. Most often, to determine the allergen, it is necessary to undergo a special provocative test using skin tests, smears, and a blood test. Recovery is possible only after contact with the allergen has been identified and excluded.
Otherwise, the patient is at risk of the allergy becoming chronic, which, in turn, is fraught with other, much more serious problems.
To identify hearing impairment, it is necessary to conduct a series of studies, based on the results of which doctors prescribe treatment for complications that arise.
Symptom manifestation
Initially, the symptom may be unobtrusive, and therefore many people simply do not notice it. Over time, with continued exposure to the irritating factor, the itching intensifies and other accompanying signs may appear, indicating a possible source of the problem.
Most often, the skin behind the ears itches in children and women. Children's bodies are more susceptible to irritants, and women come into contact with chemical allergens, including those contained in cosmetics. Hormonal fluctuations also have an effect.
Scratch marks remain on the affected area, which, in turn, can lead to the spread of irritation and infection. If it is an allergy, redness and characteristic rashes are added. The following symptoms may also occur:
- peeling of the skin;
- formation of blisters and crusts;
- plaque on the skin;
- malaise;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- swelling;
- increased lacrimation;
- gradual spread of itching to neighboring areas;
Over time, itching not only behind the ears, but also the ears themselves, the scalp, face and neck. If the symptom activates and intensifies, you should not hesitate to visit the hospital.
Treatment
After all the research, the doctor prescribes medication for ear allergies.
Swabs from the auricle make it possible to determine the flora located there, as well as to choose the most appropriate antibiotic for the patient to combat pathogenic bacteria.
Using this method, fungal infections of the skin inside the ear are also detected.
In no case should treatment of an allergic reaction inside the ear be delayed, as this will most likely lead to the spread of inflammation and infection to other areas, which is fraught with much more serious consequences.
Read how to prevent allergies to seeds. Can a child be allergic to cheese? How to identify it and how to treat it? Read here.
In addition to the antibiotic, the patient must be prescribed an antihistamine, this could be: diazolin, suprastin, fenkarol, lorano and others.
To boost immunity, immunomodulators are prescribed. In addition, you can take vitamin complexes. Rashes on the auricle and behind the ear are treated with special ointments and solutions.
The doctor may also decide to prescribe sedatives to normalize sleep, relieve stress, and make it easier to bear the itching that occurs.
At the same time, doctors may recommend a special diet, which not only excludes the consumption of allergy-causing foods, but also introduces a number of restrictions, for example, on:
- alcoholic drinks;
- tea and coffee;
- spices;
- smoked meats;
- dairy products.
In advanced stages of the disease, the patient may require surgical intervention. So, in particular, if the effusion in the middle ear does not go away within several months, the doctor may prescribe an operation to pump out the fluid.
Otherwise, the patient may:
- the eardrum atrophies;
- facial paralysis occurs;
- develop a tumor formation - cholesteatoma;
- retention cysts may form, which can also be called tumor formations.
Ear drops
For local treatment of otitis, ear drops are prescribed, which not only prevent the development of infection, but also relieve swelling.
Treatment options
Itching localized behind the ears is treated in accordance with the established diagnosis. That is why it is important to consult a doctor promptly to identify the underlying cause.
To reduce discomfort and at least temporarily eliminate itching, you can use sedatives and cooling sprays if there are no contraindications. Pain-relieving ointments are also used. For the treatment of adults, it is possible to use steroid drugs in accordance with the diagnosis. To get rid of the fungus, special antimycotic ointments are prescribed. To prevent allergies from complicating treatment, antihistamines are added to therapy. Only a doctor has the right to prescribe a specific list and course of medications after a thorough diagnosis.
For dermatitis and derivative diseases, it is advisable to limit contact of the affected area with water during an exacerbation. You cannot peel off the crusts that have formed, as this will only worsen the situation.
Description of the disease
Scrofula is a common popular name for a childhood disease similar to the manifestations of diathesis. It affects children of preschool and primary school age; it practically never occurs in adults.
The disease received this name due to the similarity of the crusts behind the ears (the main symptom of the skin disease) with gold. The crusts are pale yellow. It can be assumed that scrofula is the ancient name for allergic dermatitis.
Interesting fact: in the old days it was believed that a king could cure scrofula by touching his hand and chanting: “The King will touch you, the Lord will heal you.” The latest data on this method of treatment date back to 1825.
Important: Scrofula is a non-infectious skin disease. The disease affects children under 10 years of age and practically never occurs in adults.
Scrofula in children behind the ears
Signs of illness
- The very first sign of scrofula is the formation of diaper rash behind the ears, as well as on the scalp. Subsequently, the redness takes on a different form: yellowish crusts
- The affected areas are very itchy. The child may repeatedly scratch the sore areas with his hand or move his head on the pillow to relieve the itching.
- The location of scrofula is behind the ears and on the head. If the disease is not treated, the rash may spread to the face
In addition to yellowish crusts and itching, the following symptoms of scrofula may be observed:
- Bloating
- Indigestion
- Discharge from the nose and ears
- Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the neck
- Joint pain and swelling
- Redness of the eyes
These can be food products, pharmaceuticals, bacteria and other elements. In this case, characteristic lesions of the mucous and skin layers, lymph nodes are observed.
Scrofula can develop in children as a continuation of exudative diathesis; scrofula in adults in this case is the result of the spread of harmful agents from other foci - for example, from the lung area.
However, most often the pathology in the younger generation develops precisely because of diathesis, and scrofula behind the ears is accompanied by the appearance of golden crusts.
At the same time, doctors find it difficult to give an exact definition in terms of what specifically provokes the development of pathology in childhood, but presumably the impetus can be given by:
- The baby's stay in unsanitary conditions, prolonged refusal to take baths.
- Conceiving children under the influence of alcoholic beverages or drugs.
- The pathology is inherited when the parents of the affected children were previously diagnosed with scrofula disease.
- Children born to an older couple are also at risk, and the parents have a history of tuberculosis, malignant neoplasms, and syphilis.
- Lack of vitamins in the child’s diet and lack of a balanced diet.
- Sweets consumed by the baby unlimitedly.
- In cases where the causative agent of the disease enters the body of a woman carrying a child, the fetus may become infected.
- Artificial feeding - medical statistics state that a high percentage of children who were diagnosed with scrofula grew up on special formulas without receiving mother's milk.
Causes
A few small pimples on the neck do not cause big problems and, as a rule, go away quickly. It’s a different matter when the whole neck is covered with acne or they appear periodically. There must be a logical explanation for this, let's look at the most common ones.
Acne occurs when there are problems with the digestive or endocrine system. Their manifestation also provokes diabetes mellitus. Infections and colds also affect the skin.
Changes in hormonal levels occur during growing up; at this time, rashes can be located on any part of the body and the neck, face, and ear are no exception. Hormonal rashes can form in women with excess male hormones during menopause. They may also indicate that your period is approaching.
Heredity
Often acne is a “family” infection, and if parents constantly have it, then children usually suffer from this problem.
Environment
Humidity and hot weather promote excessive sweating, which leads to clogged and inflamed pores.
Pimples can form after using cream or perfume. Perfumes have pure oils, which are what causes the rash. Fatty creams clog the skin, preventing it from breathing, causing inflammation.
It is possible to accurately identify the cause only after examination by a dermatologist, especially for people with chronic diseases. Sometimes, to get rid of acne, you just need to cure the manifestation of the underlying disease; in other cases, only a properly developed treatment regimen will help.
Treatment of acne also depends on its location. As a rule, on the neck they are often located behind the ear, and in places of contact with tight clothing. That is, to get rid of them, you need to reconsider your wardrobe.
Considering that you were vacationing abroad, were in an environment that is unfamiliar to you and uncharacteristic for you, it is quite possible that the appearance of a rash behind the ears was the result of eating unfamiliar foods, swimming in salt water, an unusual climate, etc.
In acute allergic reactions, in most cases there is an increased body temperature (average 37.2 °C), loss of appetite, and mood becomes changeable. Sometimes rashes appear not only on the skin of certain parts of the body, but also on the mucous membranes, causing a lot of discomfort.
This is an equally common dermatological disorder associated with disruption of the sebaceous follicles. In most cases, rashes appear on the face, because... Most of the sebaceous glands are located in this area of the body. But there are cases when the disease also affects other areas - areas of skin behind the ears, scalp.
Even a cold can cause pimples to appear behind the ears. Moreover, in a hot, humid climate it is just as easy to catch a cold as in the cold, so this version cannot be ruled out either. In addition to a rash behind the ears, other characteristic symptoms of a cold also appear: itching, redness of the skin, pain in the ear.
A rash behind the ears can be a consequence of simple stress. Perhaps the excitement and anxiety associated with flying to another country caused these pimples to appear. By the way, during nervous shocks such a rash most often appears behind the ears.
Perhaps a change in diet led to such a reaction in the body. For some people, such sudden changes in diet cause the development of similar problems. First of all, it is necessary to exclude sweet foods and starchy foods.
Sincerely, Natalia.
There are many possible causes of skin rashes, including allergies, medications, cosmetics, and certain diseases such as chicken pox and measles.
Prickly heat
Heat rash
Heat rash is most common in children. It usually occurs due to excessive exposure to direct sunlight, as well as when the child spends a long time in warm clothes. Although it is not life-threatening, it may cause discomfort to the child.
The rash may be red, scaly, and sometimes the skin may begin to peel.
To avoid this, reducing sun exposure can help, baby powder and petroleum jelly can be helpful in soothing the skin. If this does not help, you need to visit your pediatrician.
Rubella
The rubella rash is reddish-pink in color and usually starts on the face, neck, and behind the ears and then spreads throughout the body.
Rubella, also called German measles, is caused by a virus. The causes and symptoms of the disease are more pronounced in children compared to adults. The virus is highly contagious and can be transmitted from one person to another through airborne droplets or contact (through objects). Symptoms associated with rubella:
- Lymph nodes behind the ears and neck become swollen and tender
- You may experience symptoms similar to those of a cold, such as a runny nose and red, watery eyes.
- Headache
- Eye inflammation
- Pain in joints and muscles.
The symptoms of rubella are not dangerous, but pregnant women should consult a doctor immediately, as if infected with the virus, it can be passed on to an unborn baby through the bloodstream (transplacental transmission). This is called congenital rubella syndrome and is a serious cause for concern as it can lead to miscarriages and stillbirths.
Once the virus is diagnosed, most cases can be treated at home with bed rest and acetaminophen, which helps reduce fever and itching. Reducing human contact is key to reducing the spread of the disease.
Measles rash (exanthema) appears on the face, especially behind the ears and along the hairline.
Measles is a viral infection of the respiratory system. It is highly contagious and can be spread from one person to another through contact with the mucus and saliva of an infected person. After contracting the virus, symptoms usually appear within 14 days and include: red eyes, muscle soreness, sore throat, runny nose, white coating in the mouth and rash behind the ears and other parts of the body.
Immunization can help prevent the likelihood of a viral attack in children. According to the Center for Disease Control, the number of measles cases has decreased over time, but has not been completely eliminated. There are no prescription medications for measles, and symptoms usually go away on their own in 2 to 3 weeks. The doctor may prescribe the following:
- Vitamin A supplements
- Large amount of liquid
- Getting enough rest to strengthen your immune system
- Acetaminophen may be used for fever.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with a mask with honey for the face. A mask of honey, lemon juice and green tea. How to melt honey in a water bath and how long to keep it
Seborrheic dermatitis
Crusting with seborrheic dermatitis, there may also be redness
Seborrheic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin condition that is usually associated with excessive activity of the sebaceous glands and a pathogenic fungus of the genus Malassezia, which begins to multiply very quickly, feeding on fat. The disease causes flaking skin (dandruff) in the form of white to yellowish scales that form on areas of oilier skin, such as the scalp, face (eyebrows, nose, beard) or inside the ear. This may occur with or without reddened skin.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis comes in different types.
In this photo, ordinary (left) and guttate (right) Another possible cause of a rash behind the ears and on the neck is psoriasis. This is a chronic skin condition caused by an overactive immune system. Its symptoms include skin inflammation and dense white or red patches.
Psoriasis is common in people with obesity, diabetes and heart disease. It can also be genetically inherited.
The condition is not considered completely curable, but steroid creams and gels, light therapy, and oral antibiotics can be used to treat some symptoms associated with psoriasis.
Contact dermatitis
Contact Dermatitis
According to the National Eczema Organization, contact dermatitis is the result of a skin reaction to the environment, or more specifically certain chemicals.
The skin may become swollen, inflamed, red and itchy. The condition is not life-threatening; antipruritic and anti-inflammatory creams or gels can be applied to relieve the itching. If symptoms do not disappear after a week, you should consult a doctor.
Eczema
Eczema (atopic dermatitis)
Eczema (atopic dermatitis) is characterized by a dry and itchy rash. The skin on any part of the body becomes red and swollen. The disease is recurrent in nature (usually the skin becomes inflamed in the winter, and everything goes away in the summer) and is caused by an abnormal reaction of the immune system due to genetic disorders.
Fungal infection
Fungus
Common symptoms associated with a fungal infection include:
- Rash behind the ear and/or on other parts of the body
- Red or white spots on the surface of the skin
- Peeling and flaking
- Sores may begin to appear.
Once a fungal infection is diagnosed, treatment is usually straightforward. Your doctor will prescribe antifungal medications depending on the type of infection.
- Antifungal ointments.
- Oral medications (tablets) and/or droppers in more severe cases.
Chicken pox
The first itchy pimples with chickenpox may appear behind the ear or in the neck area (in the left photo the first day of the disease).
Then the rash spreads throughout the body. Chickenpox is an infection caused by a virus. It is most common in children, but can also affect adults. After infection, the body develops immunity to the pathogen and the rash and other symptoms in most cases do not appear throughout life.
In children, the infection has the following symptoms: rashes, itching, red blisters on the body. Headache, loss of appetite and fever may also occur. The bumps are filled with fluid, very itchy and painful.
Treatment for chickenpox involves relieving symptoms. Antihistamines or topical ointments may be used. Anti-itch creams may be available over the counter. Infected children should avoid contact with other people to avoid spreading the virus. To prevent the disease, vaccination is carried out starting from 1 year.
Folk remedies
Along with traditional medicine, traditional methods can also be used to treat ear allergies.
Decoctions are used as an external remedy. The most effective of which is a decoction of lentil straw.
To do this, pour half a kilogram of straw with 3 liters of water and put it on the fire to boil. The broth should boil for 10 minutes. After which it is filtered and allowed to cool.
Then cotton pads soaked in the broth are applied to the affected areas of the skin on the ears and behind them. If the disease has entered deep into the ear canal, then you can make small tampons, which are also moistened in the broth, squeezed out and placed shallowly in the ear canal for half an hour.
If you are allergic to flower dust, it is recommended that after each return from the street, rinse your mouth and throat with water with the addition of a few drops of valerian or motherwort.
Allergies can be treated with calendula infusion.
To prepare it, pour 1 teaspoon of calendula flowers with 500 milliliters of boiling water, after which it is left to infuse for at least 3 hours. It is better to do this in the evening and let the infusion stand until the morning. After which the infusion is carefully filtered. You need to take 1 tablespoon 3 times a day.
It is worth noting that it is necessary to resort to traditional medicine only in combination with traditional methods of treating allergies, and not in any way replacing it.
In addition, beware of self-medication. All procedures must be prescribed by a qualified specialist based on test results and his or her experience.
Prevention
Despite the fact that the predisposition to allergies is genetic, this does not mean that fighting it is useless. Prevention of allergic reactions is as important as the treatment itself.
To prevent allergic reactions in children, the expectant mother must adhere to a diet.
The same applies to breastfeeding. The development of allergic reactions in the future is also influenced by the duration of breastfeeding.
The longer a young mother breastfeeds her baby, the less likely he is to have allergic reactions in the future.
Adults should reconsider the household chemicals in the house and switch to less dangerous substances, for example, phosphate-free powders, shampoos and other detergents.
In addition, it is necessary to get rid of cosmetics containing harmful substances: creams, shower gels, decorative cosmetics.
Lifestyle is no less important for prevention.
Find out what are the symptoms of atopic type allergies. Don’t know how to treat pimples if you are allergic to solariums? Find the answer here.
See photos of folic acid allergies here. Doctors recommend:
- adhere to a proper healthy diet;
- to refuse from bad habits;
- lead a healthy lifestyle;
- take care of your health;
- seek help from specialists in a timely manner.
Preventive measures not only reduce the likelihood of allergic reactions, but also help the body resist exacerbations that occur as a result of the onset of the disease.
When talking about ear allergies, you need to understand that this seemingly mild disease can lead to very serious and even irreparable consequences if you do not pay proper attention to it. At the first symptoms, be sure to contact a qualified specialist who will prescribe the necessary tests, and then treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Symptoms of an allergic reaction are most often accompanied by peeling and hyperemia of the skin, itching.
- The affected area itches and scratching may cause injury to the skin on the ears. As a result, inflammatory infectious processes may appear;
- at the first allergic symptoms, especially in a child, it is recommended to contact a medical facility;
- Often with allergic rashes, stuffy ears are noted. In this case, the symptoms of the disease mean the presence of purulent otitis media of the middle ear, which requires mandatory medical intervention;
- The typical symptoms of manifestations in the ear area do not always indicate the allergic nature of the disease. For example: signs of the development of the discoid form of lupus erythematosus or seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis may be similar to allergic ones, manifesting themselves as plaques in the ear area;
- The reasons for the development of nodular redness may lie in the presence of malignant neoplasms. If this disease is suspected, urgent treatment is required;
- A keratinized red area in the ear area in adult patients indicates the development of actinic keratoma or solar keratosis.
Thickening, induration and swelling in the ears indicate the presence of chronic forms of itchy dermatitis.
Preventive actions
You should also remember that you need to monitor the condition of your ears. This will make it easy for you to notice if your child has irritation or a red spot near his ear. The greatest attention should be paid to the condition of the ears of newborns, since babies are more susceptible to various diseases than others. If your young child's ears become red, try not to scratch them.
To protect the outer ear from redness, children should:
- arrange daily water treatments;
- Do not forget to give children hats to protect their ears from cold and sun rays.
If your child complains that his ears are itchy and you notice that the areas around his ears are red, contact a specialist right away.
Treatment tactics
Symptoms of ear allergies require a visit to a dermatologist, who can determine the causes of the allergy.
As a rule, the basis of any allergy treatment includes the use of antihistamines. The most common antihistamines are:
As a double action, it is recommended to combine antihistamines for internal use with local antiallergic agents (ointments, gels, creams). Independent use of antiallergic drugs, especially when treating a child, is prohibited. This can lead to various complications.
Treatment is prescribed according to the patient’s age category and the presence of chronic diseases. If there is a complication in the form of otitis media in the ear, a short course of antibiotic therapy may be prescribed.
If a child has increased sensitivity to sunlight, it is recommended to spend less time in the open sun and use protective hypoallergenic creams.
Treatment of ear allergies with folk remedies
Some patients claim that obvious symptoms of ear allergies can be neutralized with the help of traditional medicine recipes. However, it must be remembered that treating ear allergies with this technique cannot completely replace the main treatment, but is a method of auxiliary therapy.
- Symptoms of allergy development in the ear area can be relieved with a decoction of burdock. You need to take 50-60 grams of crushed powder from dry leaves, pour 1 liter of cold water. Boil the mixture for 3-5 minutes. After complete cooling, use 2 times a day after meals.
- Chamomile treatment has a good effect. This medicinal plant is one of the most powerful antioxidants. The medicinal decoction can be taken for purulent otitis caused by allergens. To prepare the decoction, you need to take 3 tablespoons of dry herb and pour 2 liters of water over it, boiling the solution for at least 10 minutes. Chamomile decoction is taken instead of tea. It should be noted that chamomile is absolutely safe for children.
- Actively relieve allergic symptoms on the ears with ointments for external use, which contain lanolin (15 g), petroleum jelly (15 g) and an alcohol solution of the series (2 tablespoons). The prepared mixture is applied to the allergy-affected areas of the skin until the irritation is completely relieved.
It must be remembered that such treatment with traditional medicine recipes is allowed to be performed after consultation with the attending physician, not forgetting that any medicines, including herbs, if used incorrectly and ineptly, can cause irreparable harm to health.
Allergy is a very common disease. According to some data, about 40% of the adult population of the planet is susceptible to it, which means that every fifth suffers from one or another type of it: food, medicinal, insect, infectious, respiratory, etc.
The reaction develops as follows: upon initial contact with a certain substance, sensitization of the body occurs, repeated interaction with the antigen causes an inadequate immune response, characterized by damage, first of all, to those cells and tissues of the body through which the allergen penetrated: bronchi, esophagus, skin, nasal cavity, mucous membrane of the eyes.
One of the unpleasant manifestations of allergies is damage to the skin on the ears and behind the ears, accompanied by severe itching, swelling and fever. These symptoms require special attention, since the development of infectious diseases and, as a result, hearing loss is possible.
How is the diagnosis carried out?
For effective treatment of hypersensitivity symptoms, it is necessary to identify the irritating agents that provoked the formation of pathology. In childhood, this is done mainly through blood sampling to determine the content of immunoglobulins.
In the first 12 months of life, a proven detection method is often used - complementary foods are introduced little by little in small dosages, checking the body's reaction. The same applies to the mother’s diet - you should not abuse highly allergenic foods while breastfeeding. To determine the allergen, the following is prescribed:
- General blood and urine analysis;
- Blood chemistry;
- Skin allergy tests;
- Identification of specific antibodies to irritants of various origins;
- Study of the functioning of the immune system;
- Blood cultures from infectious foci to establish susceptibility to antimicrobial agents (including the ear canal);
- Diagnosis of feces;
- Consultations with other highly specialized doctors.
After a comprehensive diagnosis, it is necessary to begin therapy without delay in order to prevent an increase in the area of pathology and the formation of other consequences.
If initial symptoms occur and an allergic reaction occurs in the ears, you should consult a specialist. Only specialized doctors are able to determine what triggered the allergy and prescribe appropriate therapy.
The body’s negative response to the ears should be treated as early as possible, which will make it possible to prevent the spread of pathology to other parts of the body. The question often arises whether ears can become clogged due to allergies. The answer will be yes. In such a situation, the symptoms of the pathological process mean the presence of purulent otitis, which requires mandatory drug treatment. At the moment, a large number of methods are known for the treatment of such a disease, but they must be used directly under the supervision of an allergist.
Antihistamines are mainly used to treat such conditions (in situations where the disease is caused by food). Independent use of medications for the treatment of children is prohibited - this can cause aggravation of well-being. Taking into account age indicators, the general condition of the patient, and the presence of other diseases, medications are prescribed.
Some of the most popular therapeutic remedies for allergic reactions in the ears are:
The main goal in countering a negative reaction is to exclude from the menu or everyday life the product, cosmetic preparation or substance that provoked the pathological process.
External means
For an enhanced effect, experts advise using special ointments locally. Ear allergies in adults and children can be effectively treated with ointments.
The skin near the ears is extremely thin and sensitive, so it is optimal to use non-hormonal ointments (Fenistil, Psilo-balm). When a specialist prescribes a hormonal drug, it must be used very carefully on susceptible areas.
Often, allergies manifest themselves in the shortest possible time. For example, after an insect bite or contact with certain plants. In such a situation, special allergy ointments help, which can quickly eliminate the symptoms of an allergic reaction:
Hormonal ointments include the following:
- Sinaflan;
- Advantan (used infrequently and quite carefully).
In addition, in order to eliminate itching, it is possible to use local anesthetics containing lidocaine or novocaine. Such drugs can be used only when the patient is not allergic to lidocaine or novocaine.
In addition, ointment made from birch buds effectively relieves inflammatory changes, redness, ear itching during an allergic reaction. The saturated decoction is mixed with Vaseline in the same amount and applied 5-6 times throughout the day to the affected area where there is redness.
ethnoscience
Some patients believe that the severe symptoms of an allergic reaction in the ears can be neutralized through traditional recipes. But it must be borne in mind that therapy for such a disease with this method cannot fully replace the main therapy. The most common means:
- Burdock decoction. You need to take 50 g of crushed powder from dried leaves, pour 1 liter of cold water. The mass is boiled for several minutes. Then, when the mixture has completely cooled, take it twice during the day after meals.
- Chamomile therapy. This medicinal plant is considered one of the most powerful antioxidants. The medicinal tincture is taken for purulent otitis media, which is caused by irritating agents. To prepare the decoction, take 3 tbsp. l. dried herb and fill it with 2 liters of liquid. The mass is boiled for at least 10 minutes and consumed instead of tea. It should be noted that the product is completely harmless to children.
- Ointments for external use containing lanolin (15 g), petroleum jelly (15 g) and a solution of string in alcohol (2 tbsp. L.). The finished mixture is applied to parts of the skin damaged by an allergic reaction until the irritation is completely eliminated.
It must be remembered that such therapy can only be carried out in consultation with a specialist. It is worth considering that any medications, including herbs, can cause harm if used improperly.