Psoriasis occurs on the skin for many reasons. If you do not consult a dermatologist in time, the disease can have serious consequences for the patient, and then hospital therapy will be required.
Reasons why a person should receive treatment while in hospital:
- If treatment of psoriasis on an outpatient basis for a month does not bring positive results;
- Active development of symptoms;
- Infectious infection with the spread of inflammation and other rashes on the surface of the skin;
- Development of psoriasis of the erythroderma type or generalized Tsumbusha stage;
- The indispensability of medications that can only be used in a hospital;
- Damage to the dermis by psoriatic rashes by more than 25%;
- Manifestation of pathological diseases: oncology, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases and disorders of the urinary system;
- 24-hour monitoring of patient tests is required;
- Disability as a result of the development of psoriasis;
- Progressive spread of psoriatic plaques throughout the body.
How to determine the severity and stage of psoriasis?
Many patients are interested in what psoriasis looks like at the initial stage. The fact is that the early stage of psoriasis can be similar to other diseases, so it is important to consult a specialist to establish a diagnosis. During a diagnostic examination, doctors assess the severity of psoriasis. The following severity levels of psoriasis are distinguished:
- light,
- medium-heavy,
- heavy.
The severity is set depending on the following parameters:
- BSA (Body Surface Area) is the area of skin affected by psoriasis. BSA is measured in %. Moderate degree is established when the area of affected skin exceeds 10%, severe - when 30% or more of the body surface area is affected. It is not difficult to determine this indicator. For example, the area of an open palm is approximately equal to 1% of the total skin area of the body.
- DLQI (Dermatology Life Quality Index) is a dermatological quality of life index. This index measures the extent to which psoriasis affects your life. To determine DLQI, you need to fill out a questionnaire that includes questions about the state of your health, skin, emotional background, etc. Like other indices, it is measured in %. With moderate and severe degrees, DLQI becomes more than 10%. It is a very important index, since the DLQI indicator helps the doctor choose the appropriate treatment tactics.
- PASI (Psoriasis Area and Severity Index) is an index of the area of skin affected by psoriasis and the severity. PASI is also measured in %. If PASI is more than 10%, then the patient is diagnosed with a moderate or severe stage. An index of more than 40% is extremely rare.
In addition to the area of the affected skin surface, the PASI index evaluates:
- severity of erythema (redness of the skin);
- severity of infiltration (compaction) of rash elements;
- severity of peeling on the surface of plaques;
All parameters are measured on a scale from 0 to 6
Doctors use the PASI index not only to determine the severity of the disease, but also to evaluate the effectiveness of treatment. For example, if at your follow-up appointment the doctor says that you have reached PASI 75, this will mean that the area of affected skin and the severity of psoriasis have decreased by 75%, but if you reach PASI 100, then your skin has completely cleared of psoriatic plaques.
dermatological quality of life index
CALCULATE
Diagnostics
In most cases, in order to diagnose the vulgar type, it is enough for the doctor to conduct an external examination of the patient. There are no special diagnostic procedures other than a standard blood test.
Photo of the disease. May be unpleasant to watch
However, at a progressive stage, abnormalities can be found in the blood, due to which specialists pay attention to the presence of a pathological process: systemic autoimmune, inflammatory, or rheumatic (increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate, leukocytosis, etc.), as well as disorders of endocrine function.
In exceptional cases, a skin biopsy is performed to confirm the diagnosis and exclude other possible diseases. Also in some cases, dermatoscopy is performed.
Why determine the stage and severity of psoriasis?
Depending on the severity and stage of psoriasis, the doctor prescribes treatment. For example, for a patient with moderate to severe psoriasis, local therapy alone may not be enough. Therefore, the doctor can prescribe systemic treatment: non-biological or genetically engineered biological drugs (GEBP).
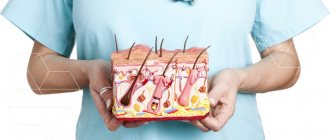
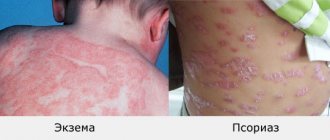
Psoriasis is a chronic inflammatory non-infectious skin disease associated with excessively rapid division of cells in the outer layer of the skin - the epidermis. Psoriasis is accompanied by the development of inflammation in the skin, which is caused by immune disorders. As a result, accelerated growth and division of epidermal cells, multiple biochemical, immunological and vascular changes are observed. All these processes occur against the background of carriage of certain genes predisposing to psoriasis. Therefore, this skin disease is a genetically determined disease.
The development of debut and/or exacerbation of psoriasis occurs under the influence of provoking factors, including:
- errors in diet;
- alcohol abuse;
- taking certain medications;
- damage to the integrity of the skin (the so-called Koebner phenomenon);
- psycho-emotional stress;
- suffering from acute or exacerbation of chronic diseases;
- injuries, surgeries, etc.
Psoriasis has a rather complex nature, and the clinical manifestations of the disease develop under the influence of a number of external factors in people with a genetic predisposition.
Reasons for the development of the disease
To date, the nature of psoriasis is not fully understood. However, medical research shows that plaque psoriasis can develop in the body under the influence of the following factors:
- Hereditary pathology transmitted cyclically through two generations.
- Disturbance of metabolic processes: disturbance of cholesterol metabolism, fermentation.
- Severe psychological shocks can contribute to the development of pathology.
- Laboratory studies indicate that psoriasis is viral in nature.
- Dysfunction of the endocrine system, including dysfunction of the gonads and adrenal glands.
- Lack of essential microelements in the body: calcium and potassium.
In addition, there are concomitant diseases that can accelerate the development of psoriasis and immediately lead to the progression stage:
- diabetes;
- atherosclerosis;
- obesity;
- gastrointestinal dysfunction
In addition, a sharp outbreak of psoriasis can occur under the influence of chemicals, long-term use of medications, severe damage to the skin, or intoxication. This disease also affects people who abuse fast food, as well as drink alcohol in excess.
In each specific case, medical diagnostics can reveal the true causes of the disease. The causes of the appearance and development of psoriasis are shown in photographs in medical reference books and on Internet sites, and methods of combating the disease are also described in the medical literature.
Characteristic signs of different stages of psoriasis
Doctors stage psoriasis based on severity. There are three stages of psoriasis:
- progressive stage of psoriasis - psoriasis during the period of exacerbation, with worsening symptoms and an increase in the affected area ;
- stationary stage of psoriasis - a stable state of the process on the skin without the appearance of new rashes ;
- regressive stage of psoriasis - remission phase with weakening of symptoms .
Medicines
In the treatment of vulgar psoriasis, non-steroidal drugs, as well as glucocorticosteroids, are used. Moreover, each patient uses his own approach to selecting medications. Most of the medications against vulgar psoriasis consist of medications for external use - creams and ointments. Such products soften the skin, relieve redness, itching, and prevent the development of fungal and bacterial infections.
Groups of medications have these properties:
- Non-hormonal. A feature of this group of drugs is their relative safety. However, they have little effectiveness and are most often used for maintenance therapy or as an adjunct to other medications.
- Corticosteroids. They are characterized by increased efficiency and are included in the treatment of vulgar psoriasis with extensive complications on the skin. May cause a number of side effects.
- Ointments and creams with vitamin D. Have an additional therapeutic effect on the skin, help restore the upper layer of the dermis and delay the period of regression of psoriasis.
Medicines for oral administration (included in therapy at the discretion of the attending physician):
- Immunomodulators to regulate the functioning of the body's defense systems (Methotrexate, Cyclosporine);
- Natural and chemical-based sedatives for relieving stress and treating depression (valerian extract, Afobazol, Persen, motherwort tincture, etc.);
- Antihistamines (Loratadine, Suprastit, Cetrin, etc.).
Methotrexate
Cyclosporine
Afobazole
Persen
Loratadine
Suprastit
The selection of medicines of any group can only be carried out by the attending physician based on the received conclusion about the patient’s health condition. Self-medication is strictly prohibited.
Progressive stage of psoriasis
It is characterized by both the appearance of new psoriatic papules and plaques on the skin and an increase in the size of existing ones. This is usually facilitated by one of the provoking factors.
This stage of psoriasis is characterized by the appearance of a red rim along the edge of psoriatic papules and plaques, not covered with scales, which appears as a result of the peripheral growth of the element. Also at this stage of psoriasis, the Koebner phenomenon (symptom) may occur, when, when an area of the skin is damaged or irritated, fresh rashes appear at the site of injury.
Traditional methods of treatment
Patients suffering from acute psoriasis should consult a specialist before using any traditional method.
Night ointment
An effective recipe, for the preparation of which you will need: 150 g of butter and 15 g of propolis. The butter must be melted in a water bath, then add the second ingredient to it. Propolis can be in 2 forms: solid and powder. It is best to use powder, as it is much more convenient.
Propolis has healing properties
The mixture of propolis and melted butter should be placed in a glass container. The mixture should be stored in a dry place, away from direct sunlight. The ointment is applied pointwise (to the areas of the disease) and left overnight.
Also on the topic: Psoriasis - ICD 10 code
Regressive stage of psoriasis
It is characterized by the appearance along the periphery of papules and plaques of a shiny, light ring of slightly wrinkled skin, the gradual disappearance of clinical symptoms, and the resorption of papules, starting from the center of the elements towards their periphery. At the same time, peeling stops, the color of the papules turns pale, and then they disappear, leaving behind areas of hyperemia (redness), pale or, conversely, dark spots (depending on the pigmentation characteristics of the patient’s skin), which gradually disappear within 2-3 months.
Initial stage: how to recognize psoriasis at an early stage?
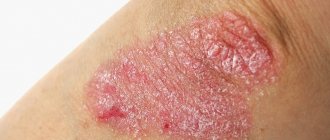
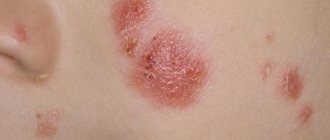
Ordinary, vulgar or plaque psoriasis is the most common type of disease. At the initial stage, plaque psoriasis looks like inflamed red patches of skin on the bends of the limbs, head, and skin folds. Such lesions are covered with silvery scales. The stages of vulgar psoriasis include an exacerbation period, a stationary stage and a remission stage.
Early stage pustular psoriasis With pustular psoriasis, pustules filled with pus form on the skin. This form of psoriasis is very dangerous and often requires hospitalization.
Guttate psoriasis in its early stages appears as a large number of small nodules or plaques on the abdomen, limbs or head. Most often, this form of psoriasis occurs in children and adolescents.
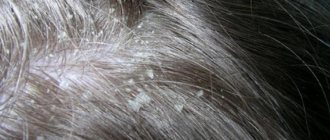
Psoriasis of the scalp may not be recognized at an early stage, since the hair hides the lesions. The scalp begins to peel off severely and itching appears.
Psoriasis on the arms and legs in the initial stage most often occurs in middle-aged people. The stages of psoriasis on the arms and legs may coincide with those of vulgar psoriasis, or may look like continuous keratinization of the skin.
Prevention
To prevent the disease it is necessary:
- distance yourself from any stressful situations and put your emotional state in order;
- restore proper metabolism in the body;
- monitor for any diseases that may be associated with psoriasis;
- avoid infections.
The most common form of psoriasis is vulgar. The disease has an extensive list of causes and consequences. Quite simple to diagnose, this disease requires strict adherence to the instructions for its treatment.
Signs of exacerbation of psoriasis
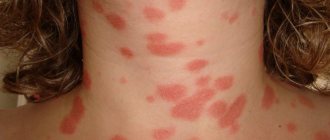
As with any skin disease, the clinical manifestations of psoriasis are visible to the naked eye. At the initial stage of psoriasis, the disease is characterized by the appearance of a rash in the form of bright pink, pink-red papules, which, when fused, can form quite large plaques. They are often covered with loosely arranged silvery-white scales.
Symptoms characteristic of psoriasis are observed, which are diagnostically significant and form the so-called psoriatic triad:
- Symptom of a stearin stain - manifests itself in increased peeling when even smooth papules are scraped, from which they acquire a whitish color, giving a resemblance to a stearin stain.
- A symptom of psoriatic film is that after continuing to scrape the psoriatic papule or plaque and after complete removal of the scales, a shiny red surface is exposed.
- Symptom of blood dew - with further scraping and removal of the terminal film, small droplets of blood appear on the exposed wet surface.
Psoriasis has a chronic, relapsing course, that is, it occurs in the form of periodic exacerbations, accompanied by the appearance of skin rashes, and improvements - remission, when the skin can clear almost completely. Moreover, the duration of both relapses and remissions can vary, from several weeks to several months. Psoriatic rashes, if left untreated, can persist for a long time in the same areas of the skin, gradually progressing. Typical places of localization of psoriatic elements are the scalp and the extensor surfaces of large joints. However, psoriatic plaques can be found on almost any part of the body, with the exception of mucous membranes.