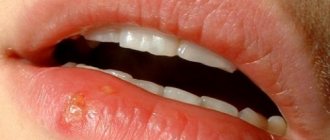
This virus can be easily picked up everywhere and through contact with a sick person. The ease of infection explains the fact that about 95% of the population are carriers of this infection. However, not everyone suspects that they have herpes.
It can remain latent for many years. This type may never appear or may make itself felt after severe stress or with a significant decrease in immunity. Therefore, it often happens that herpes appears in the intimate area during pregnancy, although the woman had not noticed such signs before. Herpes in the intimate area can occur in pregnant women due to a sharply weakened protective ability of the body. Thus, nature dictates that all forces during this period are aimed at maintaining and developing the fetus.
A woman will have to take care of her body on her own, supporting it as much as possible and protecting it from various viral and bacterial infections. However, when the disease manifests itself, you should not immediately panic. An experienced doctor will be able to select a treatment for herpes in the intimate area that does not harm the course of pregnancy.
You should consult a specialist as soon as the first rash appears on the labia during pregnancy. Other symptoms of herpes in the intimate area may also accompany the rash. These include deterioration in well-being, increased temperature, the appearance of itching or burning sensation in the intimate area, etc. These symptoms are also a reason to visit a gynecologist. An experienced doctor can conduct an examination, take swabs and prescribe other tests. Based on the results of the study, the primary diagnosis will be confirmed or refuted and adequate treatment will be prescribed.
Genital herpes during pregnancy: causes, symptoms, methods of diagnosis and treatment
It is not customary to speak out loud about pathologies affecting the genital organs. In some cases, a moment of embarrassment is present even when contacting a specialist.
This is primarily due to the fact that many people think that the manifestation of diseases of the genital organs directly depends on promiscuity.
No one is immune from the manifestation of herpes in the intimate area. Anyone can become infected with the virus, regardless of gender and age.
There are known cases of genital herpes in pregnant women, and they are rare. During such an important period, the first thing that worries the expectant mother is the health of her baby.
There is no need to worry about this; provided timely treatment is taken, herpes does not pose a danger to the baby. Statistics are reassuring: the disease is not transmitted to the fetus in 95% of cases.
Advice ! Only timely contact with a specialist will help to avoid irreparable consequences in the form of a threat to the health of the mother and child.
Herpes in the intimate area is classified as a sexually transmitted disease, but women and men who have a single, permanent sexual partner can become infected with it.
This is due to the fact that the herpes simplex virus can be present in the body of any person, but without manifesting itself.
That is, a person can infect his partner without knowing that he is sick.
Pathology therapy is aimed at suppressing the replication of the virus and eliminating the symptoms of the disease.
To prevent recurrence of the pathology, it is extremely important to pay special attention to strengthening the immune system.
Nevertheless, genital herpes is an extremely undesirable disease for a pregnant woman, therefore it is necessary to pay special attention to the prevention of its manifestations.
Herpes in the intimate area during pregnancy
Clinical picture
The main symptoms that occur with genital herpes during pregnancy depend on the form of its course. It happens:
- Primary . When a woman is infected for the first time.
- Recurrent . In which repeated exacerbations are observed due to weakened immunity.
Primary infection is accompanied by:
- The presence of rashes on the labia, vaginal mucosa, anus, and pubis.
- Severe itching, pain in the urethra.
- Redness and swelling of the genitals.
- Acute pain in the perineum.
- Copious vaginal discharge that does not have an unpleasant odor.
During an acute period, the virus can cause:
- Headache.
- Lethargy, fatigue.
- Increased body temperature.
- Chills, aches in muscles and joints.
- Enlarged lymph nodes.
- Irritability, nervousness, apathy.
- Painful urination and defecation.
- Insomnia.
First, the woman feels painful itching and burning in the intimate area. The labia become red and swollen. Then bubbles filled with exudate appear. After a few days they burst, leaving behind ulcers that gradually heal.
Exacerbation of recurrent herpes during pregnancy is not so pronounced: the temperature does not rise, the size of the lymph nodes remains normal. Bubbles form in the places where they were noticed when they first appeared.
Recurrence of herpes infection can occur quite often. In some cases, new rashes may appear in place of blisters that have not yet healed.
How is pathology transmitted?
Genital herpes is a common disease. In general, the virus can lead to damage to any skin and mucous membranes.
In the absence of timely treatment, genital herpes can spread to other organs, in advanced cases, disrupting their functionality.
The provocateur of the pathology can be a virus of the second and first types. Both infections belong to a large group of herpes viruses.
The pathogens are extremely viable and this allows them to remain active on open surfaces for a long time.
In medicine, there are two types of herpes - recurrent and primary. In case of relapse, the clinical picture may be blurred or completely absent.
At this moment, a person is often unaware of the presence of the disease and unintentionally infects his sexual partner.
Primary infection is characterized by a pronounced clinical picture; the rash appears several days after infection.
Genital herpes occurs in 85% of cases as a result of sexual contact with an infected individual. But we cannot exclude the possibility of the disease manifesting itself in people who are not sexually active.
Among the main methods of infection are the following:
- Household . Using a towel or soap that has been used by an infected person.
- Sexual intercourse . You can get the herpes simplex virus from any type of sex, including oral sex.
- Perinatal . The disease can be transmitted from mother to child during childbirth or in utero.
- Inoculation . The patient, due to personal inattention, transfers the manifestations of the disease from one part of the body to another.
The incubation period can last from several days to several months.
This moment has the opportunity to play a cruel joke, because herpes can appear in an intimate place in a pregnant woman immediately before childbirth. Then the only option is a caesarean section.
Attention ! As immunity decreases, the risk of relapse of the disease increases. This is why it is important to pay special attention to strengthening the immune system.
If herpes occurs during pregnancy, you should immediately consult a specialist. Only correct and timely treatment can be the key to successful recovery and reducing the risk of infection in the baby.
Consequences for the newborn
The lowest percentage of transmission of infection to a child from a sick mother is recorded during relapse of the disease - in 3% of cases.
Infection of a pregnant woman with genital herpes after 32 weeks leads to intrauterine infection of the fetus with the development of herpetic rashes after birth.
Infection during passage through the birth canal manifests itself in the first two weeks of a child’s life. Typical small blisters filled with serous contents appear on the skin of the body, on the face, in the area of the nose, lips, and chin.
If treatment is started at the wrong time, damage to the nervous system is observed in the form of respiratory failure, convulsions, muscle hypotension, and drowsiness. With inadequate treatment, the mortality rate of newborns from herpetic infection reaches 85%.
The disease occurs in three forms:
- local. When there are symptoms of skin lesions in the form of vesicles on the face, near the nose, on the lip,
- neurological Occurs due to intrauterine infection,
- generalized form with multiple organ pathology. With it, there are no skin rashes, and neurological symptoms come first: drowsiness, refusal to eat, monotonous screaming, convulsions.
With genital herpes, damage to the central nervous system is observed in a third of newborns: serous meningitis, encephalitis, meningoencephalitis. After treatment of such severe forms, consequences remain in the form of cerebral palsy, blindness, deafness, and delayed psychomotor development.
Diagnostic measures
The following diagnostic methods will help diagnose the presence of the herpes virus:
- Gynecological examination.
- General blood and urine analysis.
- Culture method.
- Linked immunosorbent assay.
Other diagnostic methods are also used to identify the causative agent of the disease.
Important ! If a herpes virus is detected in a pregnant woman, it is advisable to examine her sexual partner.
Therapy
Despite the fact that pharmacology and medicine have made a confident step forward, it is completely impossible to cure herpes.
The action of drugs is aimed at suppressing the activity of viruses. Complex therapy must necessarily include restorative drugs.
This is necessary because stable immunity is the key to reducing the risk of relapse of the disease.
Among the list of popular antiviral drugs prescribed for herpes are:
- Panavir;
- Famvir;
- Acyclovir.
The products are available in the form of tablets for oral administration and ointments for external use.
Self-medication during pregnancy is unacceptable; only a doctor who has studied the general picture of the course of the pathology and is aware of the patient’s stage of pregnancy will be able to select an effective and safe treatment.
Important ! Antiviral pills are prohibited in early pregnancy. Intensive treatment of herpes in an intimate place during pregnancy begins several weeks before birth.
Prevention of recurrence of infection
An important aspect of pregnancy management is the prevention of relapses of not only genital herpes, but also labial herpes on the lips. Important preventive aspects are:
- proper balanced nutrition throughout the entire period of bearing a child;
- prevention of overheating and hypothermia of the body;
- adherence to daily routine;
- daily walks in the fresh air;
- avoiding stressful situations and nervous tension;
- complex fortification.
Regular monitoring by a gynecologist should be considered as an important preventive component.
Useful tips
In order to speed up the recovery process, you must follow the following recommendations:
- Pay special attention to hygiene procedures.
- Both sexual partners must undergo treatment at the same time.
- Avoid wearing synthetic underwear.
- Limit visits to the beach and solarium.
- Do not scratch the rash.
- Use personal hygiene items.
The simple points listed will help to significantly shorten the clinical recovery period.
Cervical herpes during pregnancy
The causative agent of the disease is herpes simplex virus type 2.
The danger is that cervical herpes can often only be detected by visual examination. The reason for this is the asymptomatic course of the pathology after infection.
Important ! Cervical herpes during pregnancy can be dangerous for the baby.
Only timely detection of pathology and treatment with medications will help reduce the risk of severe consequences for the mother and baby.
There are primary and recurrent herpes. During primary infection, the disease is asymptomatic.
In the case of immunodeficiency, the disease manifests itself more intensely. During colposcopy, lesions of the cervix with characteristic manifestations of small bubbles with clear outlines are detected.
Cervical herpes is rarely an independent pathology; the following organs may be affected:
- vulva;
- labia minora and labia majora;
- inner thigh.
Such lesions are disturbing and quite painful on palpation.
Important ! If genital herpes is detected in a pregnant woman, treatment begins in the last weeks of pregnancy.
If therapy does not produce results, the only correct solution to prevent transmission of the virus to the baby is a cesarean section.
Causes
Genital herpes during gestation occurs due to the herpes simplex virus, which belongs to the second type. From infection to the moment of primary manifestations of infection, as a rule, 2-12 days pass. The conductor for the pathogen is the skin of the genitals, mucous tissues of the urinary system, and genitals. Once the goal is achieved, the infectious agent is sent to the blood, lymph nodes, and nerve cells.
Primary infection
Many people are mistaken in believing that primary infection and relapse of genital herpes are the same thing. These are completely different concepts. The first infection means that the pregnant woman’s body has not yet developed antibodies to the virus, that is, this is the first time she has encountered it.
What are the dangers during pregnancy?
Herpes in the intimate area is an unpleasant pathology, but during pregnancy its danger increases even more.
This is due to the fact that when a baby is infected intrauterinely, the risk of developing all kinds of abnormalities, including physical deformities, increases.
The herpes virus detected during pregnancy can be dangerous:
- Infection in the first trimester of pregnancy can cause fetal death and miscarriage.
- With intrauterine infection, the development of heart, lung, brain and liver defects in the baby is possible.
- The presence of recurrent herpes in the mother rarely causes the development of herpes in the baby. Infection for this reason occurs in 0.02% of cases.
- With primary infection of the mother with the virus in the later stages, the risk of congenital infection of the fetus increases by 50%.
To reduce the risk of infection of the baby at the time of birth, antiseptic treatment of the birth canal is performed.
It should be noted that herpes in an intimate place during pregnancy is a rather unpleasant disease, the manifestation of which during pregnancy should be a good reason to consult a specialist.
Treatment
During pregnancy, the treatment regimen for genital herpes includes drug therapy and external application of antiviral drugs in the intimate area. Treatment during gestation is difficult due to the threat of provoking adverse reactions to drugs and the risk of harming the fetus.
The scheme includes:
- antiviral agents;
- immunomodulators;
- symptomatic topical medications.
The scheme includes anti-virus agents.
The list of drugs used depends on the gestational period.
Diagnostics
Genital herpes is detected using PCR - polymerase chain reaction. When examining venous blood and other biological fluids, women detect DNA and RNA of the virus. The analysis allows you to determine the type and type of virus based on fragments of genetic material. The test detects the presence of HPV, even if there are no clinical manifestations.
In case of primary herpes, the activity of antibodies to the herpes virus and the stage of the disease are determined using ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) in blood serum and urine, and the material at the active stage of the disease is examined using the RIF method (immunofluorescence reaction).
In addition to the main laboratory research methods, hardware methods are used - ultrasound. It is prescribed in the following gestational periods:
- 1 - to identify chromosomal abnormalities;
- 2 - for studying the fetal cardiovascular system;
- 3 - to detect gross pathologies of fetal development.
In addition to the main laboratory research methods, hardware methods are used - ultrasound.
Before birth, the birth canal is examined, and if signs of pathology are detected, a study of material from the cervix is prescribed.
How to treat?
Drug treatment begins with a course of Acyclovir and other antiviral drugs (Valacyclovir, Gerpevir, Famciclovir). The dosage and duration of therapy depend on the severity of the disease.
Oral remedies for herpes are complemented by local preparations - cream, rectal and vaginal suppositories (for the vagina), gel, spray and ointment. For rashes on the pubis and skin of the urogenital area, Zovirax ointment is used, since its penetration into the circulatory system is minimal.
To boost immunity, immunomodulators Cytotect or Pentaglobin are prescribed. To prevent the penetration of secondary infection through ulcers, it is recommended to smear the genitals with antibacterial agents for external application - Neosporin, Riodoxol, Vidarabine.
Preventive measures
To prevent the manifestation of secondary herpes, you must:
- eliminate the causes of virus activation;
- take medications to boost immunity.
To prevent primary infection, it is necessary to avoid contact with virus carriers, practice protected sex with one partner, and eliminate other factors that contribute to the spread of HPV.
To prevent primary infection, it is necessary to eliminate factors that contribute to the penetration of HPV into the body.