Dermatovenerologist
Khasanova
Alina Rashidovna
8 years of experience
Make an appointment
Ring-shaped erythema is a multiform lesion of the skin, a characteristic feature of which is the appearance of ring-shaped spots and rashes on the skin. The skin color of the affected areas changes and becomes red, bright pink or bluish. Depending on the causes of the disease, swelling, local fever and other manifestations of the disease may be observed. Changes in skin color occur due to the expansion of the lumen of the blood capillaries penetrating the connective tissue and the associated stagnation of blood.
Types of pathology
Doctors distinguish several types of annular erythema, depending on the causes of the disease:
- centrifugal erythema Daria - most often affecting middle-aged men, less often - children and the elderly, related to infectious-allergic manifestations;
- migratory - a disease of an infectious nature that occurs as a result of a tick bite infected with Borrelia;
- rheumatic, or ring-shaped anular erythema is one of the symptoms accompanying rheumatism, characteristic of children and adolescents.
According to external signs, ring erythema can occur:
- in flaky form - with peeling of dead skin along the edges or the entire surface of the spots;
- in vesicular form - with the appearance of small liquid-filled bubbles along the edge or entire surface of the spots;
- in a garland-shaped form - with the easiest flow, which is characterized by pale pink spots, arranged in chains or garlands and disappearing after a few days;
- in a microgarland-shaped form - with small spots, up to 1 cm in diameter, sometimes accompanied by peeling or the formation of bubbles, with a long course.
The medical literature also mentions other, very rare types of annular erythema - telangiectatic, purpuric or indurated.
Erythema in children: types, causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention
Erythema in children is redness of the skin caused by physiological or pathological reasons.
If the appearance of even a small rash attracts the attention of parents, then a scattering of red spots is alarming.
The origin of erythematous rash varies, as there are several types of this disease. The pathology, among other things, can easily be confused with rubella, dermatitis or urticaria.
Causes
Erythema means “red” in Greek, fully reflecting the phenomenon occurring. Extensive areas of redness appear on the child’s skin associated with pathological expansion of the capillaries.
The disease is not independent; it is a symptom indicating the development of inflammation or the appearance of other changes in the child’s body. It develops after an external impact on the skin - a burn from fire, acid or alkali, or an internal process, such as an allergy. But redness of the skin is not always a sign of illness.
Physiological
Physiological erythema may appear after direct exposure to sunlight, visiting a bathhouse or sauna - the expansion of capillaries in these cases will be temporary. Severe stress or shame also causes redness, which is medically called reflex erythema.
Thus, the physiological type of erythema is caused by:
- Emotional outbursts (excitement, embarrassment, shame, anger);
- Temperature effects on the skin;
- Rubbing warming substances into the skin;
- Taking medications that affect blood vessels.
Typically, this form does not require specialized treatment and goes away after stopping exposure or taking medications. In case of exposure to high or low temperatures, it is enough to wait a while to cool down or warm up.
Pathological
Pathological causes can be infectious or non-infectious. Depending on this, the disease is classified into several varieties. The main causes and symptoms of each type need to be known to successfully determine the type of erythema. In the future, this will help prescribe successful treatment.
Types and symptoms
Erythema is divided into several types, differing in external manifestations and cause of occurrence. The clinical picture of each type of disease is also different.
Infectious
Erythema infectiosum in children is caused by the airborne paravirus B19. Children are at risk. The disease develops like a common acute respiratory infection. Viral erythema exhibits similar symptoms:
- Runny nose;
- Sneezing;
- Fever.
Rashes on a child’s skin appear 3–5 days after the first signs of ARVI. Outwardly, these are small red spots on the cheeks. As the disease progresses, the rash appears on the legs, arms, forearms, knees and neck.
The round patch of spots grows gradually, resembling lace woven on the skin. They are usually a deep red color, but turn pink over time. As the symptoms weaken, the spots also disappear, this happens within 7 days.
Erythema infectiosum in children practically does not appear after treatment. It may periodically remind itself after exposure to direct sunlight or when exposed to high temperatures. The spots appear for a while and go away on their own.
Erythema Chamera
A type of common infectious erythema in children, which has other manifestations. With it, there is no high temperature, the spots have an uneven shape and merge with each other. It appears suddenly, is practically asymptomatic - in rare cases, inflammation appears in the respiratory tract.
Erythema Chamera has a longer incubation period - from 9 to 14 days. The shape of the spots is characteristic - it resembles a butterfly. You can find out about it only through clinical blood tests - antibodies to parovirus B19 are detected. Immunity to the disease is lifelong.
Knotty
This form of the disease received its name because of the characteristic visual manifestations - nodules. Erythema nodosum in children forms deep in the skin.
There are no exact reasons for its development; researchers are inclined to believe that a rash of this kind causes an allergic reaction. This refers to an allergy to waste products of bacteria - for example, streptococcus.
This explains the location of nodule formation.
Nodular redness is a symptom of scarlet fever, streptococcal tonsillitis or bacterial otitis. Quite in rare cases - a sign of tuberculosis. It can also accompany inflammatory processes in the intestines and some cancers.
The nodules are dense, deep and vary in size - from 1 mm to 5 cm. They protrude above the skin and are accompanied by slight redness and swelling.
Five centimeters is the highest limit; after incubation is completed, the nodes stop growing and begin to shrink. At first they become brown, then yellowish - like bruises. The most common place of occurrence is the anterior surface of the legs.
With a complex course, nodules form on the child’s face, hips and butt.
Ring-shaped
Erythema annulare in children spreads in the form of rings. Otherwise it is called a stand. This type of disease spreads throughout the body, especially the cheeks and shoulders. Ring-shaped redness is one of the symptoms of rheumatism, any viral or bacterial disease.
Erythema Daria
A special variety of the usual ring-shaped spots are pink spots that protrude above the surface and have slight swelling. Constantly grow and spread throughout the body. They may peel off from time to time, but in fairly rare cases, they usually do not violate the integrity of the skin and go away after a couple of hours.
This form has several reasons for its appearance:
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- Oncological formations;
- Chronic diseases: sinusitis, cholecystitis;
- Tonsillitis.
Ring-shaped erythema is a chronic disease that occurs periodically. Such exacerbations are a sign of disease or environmental influences.
Toxic
Toxic erythema in children is allergic redness of the skin. Most often it affects newborns, since their immune system is not yet strong enough to deal with surrounding allergens. It can be caused by food products, medicines or allergenic substances: household chemicals, decorative and hygienic cosmetics.
A sign of the development of a toxic form of the disease is redness that is hot to the touch. The incubation period takes very little time, starting almost immediately after contact with the allergen.
A delayed allergic reaction may occur - the manifestation of the disease occurs 3 days after contact. The skin does not change, the spots are deep red and solid. The redness is large and located on the child’s face, abdomen, thighs and butt.
A characteristic feature is that this type of erythema never appears on the feet and palms. Over time, nodules and blisters filled with clear liquid appear on the lesions - this increases the chances of infection. A bacterial infection is associated with the disease.
Exudative
Exudative erythema in children is characterized by the appearance of redness not only on the skin, but also on the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and throat. Large lesions appear on the hands and feet, with rounded spots affecting the soles, shins, forearms and inner elbows. The rash is deep pink in color and has clearly defined edges.
The size of the papule starts from 2–3 mm, growing to 3 cm in diameter. A characteristic feature is a pit in the center, the skin of which is clean, but has a bluish tint. This rash is accompanied by the appearance of watery blisters and other redness of the skin. Because of this, erythema is called multiforme.
Polymorphic
Erythema multiforme is accompanied by symptoms:
- High temperature;
- Intoxication of the body;
- Weakness throughout the body.
The polymorphic form of the disease is a sign of a viral and bacterial disease, allergy. Most often, this type of erythema develops as a side effect of taking various medications.
How to treat?
A thorough diagnostic examination is necessary to exclude serious diseases that cause types of erythema. Treatment should be carried out by a dermatologist and pediatrician; they may prescribe additional examination by an allergist.
- Erythema infectiosum is treated with intravenous antiviral drugs. Since the main risk group is newborn children, hospitalization is required when the disease appears. Since the main causative agent is infection, treatment with antibiotics is not carried out. At home, drinking plenty of fluids and bed rest is recommended.
- The nodular type is treated simply - dry warm compresses are applied to the lesions. This is enough to relieve redness; with prolonged development of the disease, calcium supplements, vitamins and hormonal ointments are prescribed. The treatment regimen also includes antihistamines.
- Ring-shaped erythema is treated with drugs that affect the main cause of the appearance of rings - these are antihistamines and vitamins. If an infectious disease is present, antibiotics are prescribed. Quite rarely, to avoid allergic reactions, hormonal ointments are used. Treatment must be carried out to prevent the development of a chronic form.
- Erythema toxicum is treated only with antihistamines. Hormonal medications and vitamin complexes are not prescribed.
- When treating erythema multiforme, one is limited to antihistamines. Sorbents, medications with a high calcium content and diuretics are also prescribed to remove the allergen from the body. Hormones are prescribed only when a complex chronic form is established. The skin is treated with an antiseptic spray.
Forecast
The prognosis for cure is positive: the erythema goes away and rarely returns, since lifelong immunity is acquired.
The chronic form of the disease is characterized by relapses when exposed to a pathological or physiological nature, but will not cause serious harm to the child’s health. An examination is mandatory if reddened lesions appear on the skin. Erythema itself is not dangerous, but the diseases that cause it are - oncology or tuberculosis.
▼We RECOMMEND YOU TO STUDY▼
Source: https://LechenieDetej.ru/kozha-volosy-nogti/eritema.html
Symptoms
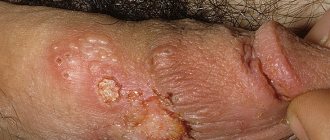
The main manifestation of the disease is the appearance on the skin of characteristic rashes in the form of irregular rings with a bright border raised above the surface of the skin. With Dardieu's centrifugal erythema, they appear, as a rule, on areas of the skin usually covered by clothing - on the back, abdomen and chest, and forearms. Ring-shaped erythema after a midge bite is a single spot spreading from the site of infection, and in its final form it can reach 20-25 cm in diameter. The spots may be accompanied by itching or burning. With the rheumatic form of the pathology, there are no unpleasant sensations.
What do rashes look like?
The name of the disease partially characterizes the appearance of the rash . The plaques are round in shape. The edges of the spots are more intense than the core, visually reminiscent of a ring.
Distinctive features are:
- whitish center of plaques,
- increase in spots along the periphery,
- the circumference of the rash is dotted with small bubbles with liquid,
- the core of the rash is smooth, flat,
- as they grow, the plaques merge with each other, forming a long “pattern” in the form of an arc,
- the rash goes away in 15-20 days, leaving pigmented light spots, where plaques will begin to appear again in the future.
The rashes are most often located on the legs and arms, and torso. Rarely, the buttocks, head and neck are affected.
Causes of the disease
There are many diseases and conditions that can cause erythema annulare, since it is not an independent disease and always occurs against the background of some pathological process. Skin manifestations most often develop against the background of:
- accumulation of toxins in the body;
- rheumatism;
- fungal, viral or bacterial infections;
- chronic inflammatory diseases;
- dysfunction of the endocrine gland;
- tuberculosis;
- borreliosis;
- reducing the protective function of the immune system;
- allergic reaction;
- cancer;
- helminthic infestation;
- taking certain medications.
In addition, in many cases, Darier's annular erythema occurs for no apparent reason in completely healthy people.
Therapy
The basis of therapy is getting rid of the root causes of erythema development . Treatment comes down to the sanitation of infectious foci, normalization of the endocrine system and gastrointestinal tract.
The therapeutic course includes:
- calcium gluconate together with sodium trisulfate,
- broad-spectrum antibiotics: Rifampicin, Streptomycin, Penicillin,
- antihistamines: Suprastin, Cetrin,
- vitamins (complex preparations are usually prescribed; vitamins A, B, E are used for monotherapy),
- corticosteroids: Hydrocortisone, Prednisolone, Dexamethasone,
- anabolic steroids: Winstrol, Sustanon,
- local antiseptics.
It is not recommended to self-medicate using unconventional methods. Some of the herbs used for compresses can aggravate the condition and cause new plaques to appear more quickly.
When treating children under 12 years of age, preference is given to homeopathy.
All patients with diagnosed erythema annulare are followed by a dermatologist. Delayed treatment or negligent attitude towards therapy leads to relapses, especially in the off-season.
People struggle with pathology throughout their lives; treatment is not always effective . Even in cases of complete destruction of the pathology, ulcerative formations with pronounced pigmentation remain on the skin in the places where the plaques were previously located.
Diagnostics
When annular erythema appears, diagnosis is based on data from a dermatological examination and anamnesis. The main task of the examination is to determine the cause that caused the pathological changes in the skin. For this, the patient is prescribed:
- analysis of skin scrapings for fungus;
- clinical blood test;
- testing for treponematosis;
- skin biopsy for histological analysis;
- serological blood test;
- allergy tests.
Based on the results obtained, specific studies can be prescribed to determine the condition of certain organs and identify the underlying disease.
Prevention
To prevent the development of pathology, you should adhere to the following rules:
- do not neglect personal hygiene,
- change underwear and remake the bed in time,
- monitor the health of the skin, use antiseptic and antibacterial drugs for wounds, moisturize the skin with special cosmetic oils and creams,
- undergo regular diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the digestive tract,
- Visit a dermatologist if strange rashes appear on your body.
Treatment
The basic principle of treating annular erythema is to stop the action of the factor that provokes the pathology. Depending on the diagnostic results, the patient may be prescribed oral medications:
- antibiotics, antivirals to treat infections;
- antiallergic and hyposensitizing agents;
- cytostatics;
- anthelminthic drugs;
- glucocorticoids.
In addition, external agents may be useful - antihistamines, steroids or zinc-containing ointments to reduce discomfort and reduce symptoms. For annular erythema, clinical recommendations may include limiting certain foods that cause an allergic reaction: confectionery, mushrooms, nuts, canned food, smoked meats, citrus fruits, etc. You should be prepared for the fact that the treatment process will last several months, as well as the possibility relapses.
Ring-shaped erythema in children: photos, symptoms, causes and treatment
Erythema annulare is a type of skin disease in which ring-shaped spots form on the body. In childhood, it most often manifests itself in the torso or limbs.
Another name used in medicine is Darier's annular centrifugal erythema. As a rule, the illness is short-term. However, with weakened immunity or emotional stress, it lasts a long time.
According to statistics, girls are more susceptible to pathology than boys.
Symptoms
Ring-shaped erythema in children is expressed by the appearance of a red ring on the skin, the center of which is a different color . The appearance of erythema occurs with swelling of the skin, which occurs due to the expansion of capillaries. The pathology is prone to progression. Therefore, the lesion may increase in size and the ring becomes larger.
At the initial stage of the disease, a small pink or red spot forms on the child’s skin. When pressed, it becomes paler or completely blends in with the rest of the skin. Then the middle of the spot begins to lighten, and it turns into a ring with a bright red edging. The element can be transformed into one ring or several.
The skin at the site of erythema may become dry and begin to peel. In some cases, the formation of bubble eruptions along the border is noted. In the photo you can see the nature of the rash.
In addition to the main symptom, there are other signs of the development of pathology:
- itching,
- burning,
- elevated temperature,
- muscle weakness,
- headache,
- loss of appetite.
There are the following types of disease:
- Paroxysmal - the appearance of spots occurs suddenly and quickly, the rash may disappear spontaneously.
- Acute - formations disappear within two months.
- Chronic - erythema persists for a long period.
- Recurrent - after disappearing after some time, the rings reappear.
Diagnostics
At the first symptoms, you should contact a medical facility. A dermatologist or venereologist can diagnose the disease.
As a rule, erythema in children is easily determined by its appearance. In addition to detecting the disease, the specialist finds out the reasons that could provoke its appearance.
To diagnose erythema, the doctor takes particles of the formation and sends them for histological examination..
The standard diagnostic procedure includes the following studies:
- serological,
- histopathological,
- mycological,
- examination for the presence of malignant neoplasms,
- hematological,
- biochemical analysis of blood and urine.
After making a reliable diagnosis, the doctor prescribes adequate treatment. In most cases, therapy takes place on an outpatient basis.
Treatment
Erythema annulare is a complex disease; removing symptoms alone is not enough. To effectively get rid of a disease, it is necessary to establish the cause of its occurrence and eliminate it.
The doctor prescribes a set of therapeutic methods.
- If erythema is accompanied by itching and swelling, treatment with antihistamines is necessary to cope with unpleasant symptoms (Fenistil, Trental). A budget-friendly way to get rid of flaking and itching, and relieve inflammatory processes is Zinc ointment.
- Glucocorticoid hormonal creams can stop pathological changes in the skin. They act by reducing the division of T-lymphocytes (Akriderm, Sinaflan). The use of these drugs is allowed only as prescribed by a doctor, as there are side effects.
- Treatment is supplemented with drugs that stimulate the child’s immune system (Amiksin). To increase the protective function, various vitamin complexes are prescribed.
- Means for improving blood circulation in tissues (Curantil). They can increase the rate of regeneration of epidermal cells and help the skin quickly restore its original appearance.
In addition, the following systemic drugs are often included in the complex of local therapy:
- Desensitizing agents. They are able to remove allergens and toxins from the patient’s body, reducing the permeability of vascular walls and normalizing immune cells, which helps reduce the release of histamine (Diphenhydramine, Suprastin).
- Antibiotics. Used in case of infection that provoked annular erythema (Azithromycin, Doxycycline).
- Antihelminthic drugs. Prescribed when tests detect worm eggs or immunoglobulins (Pirantel, Wormox).
- Cytostatics. Capable of inhibiting immune cells to reduce their activity. Prescribed for suspected autoimmune diseases (Rosevin).
Since annular erythema is most often not a separate disease, but appears against the background of the underlying disease, the treatment program is developed not only by a dermatologist, but also by other specialists. When the underlying cause is eliminated, the erythema can go away on its own .
Features of erythema in rheumatism
Sometimes erythema can occur during the rheumatic process, with polyarthritis, rheumatic carditis or other manifestations of rheumatism.
A harbinger of the disease is an exacerbation of rheumatism. This also indicates that the disease is in an active phase.
A feature of the course of the disease in rheumatism is the appearance of rheumatoid nodules, indicating an acute or chronic stage of the disease.
Other features of erythema in rheumatism:
- The appearance of joint and muscle pain.
- Restriction of mobility of joints and the patient himself.
- Changes in the quality of the skin towards dryness and thinning.
- Presence of vascular bleeding.
- The presence of elevated temperature, which is prolonged.
- Problems with the heart and blood vessels.
Often with rheumatism, the formed rings have a pinkish tint and unclear edges. The spots can be localized in any part of the body.
If the disease affects a child’s body, most laboratory tests show that the cause of the erythema was helminthic infestations or problems with the immune system.
With rheumatism, the disease depends on the causes that caused it.
- The paroxysmal nature is manifested by a sharp change in the skin, which passes quickly: within a few hours or one day.
- Acute - the resulting reddish spots evaporate within up to 2 months.
- Chronic – changes in the skin and its pigmentation in the form of ring-shaped spots are long-lasting.
- Recurrent - characterized by the appearance of spots on previously healed areas.
Signs and symptoms
In addition to distinguishing the above forms of annular erythema (rheumatic, migratory, Darier), in practical dermatology there is a classification compiled taking into account the characteristics of the clinical course, which, in general terms, differs in the nature of the rash, duration and other characteristics.
Currently, there are four clinical forms of erythema annulare. The first symptom of all forms is the formation of red spots on the surface of the skin, sometimes with itching.
Subsequently, the course of each form acquires its own characteristic features.