H1 CC
Skip to content
- cosmetologist
- Contacts
Home »Health
When spots appear on your hands, they may not bother you, they may not itch or hurt. Still, some people feel discomfort from having such a cosmetic problem, so they want to get rid of it. Before starting therapy, you need to figure out why the spots appeared on your hands.
Skin diseases
Skin diseases not only create discomfort, but are also often signs of serious diseases that are beginning to develop in the body. Skin diseases include:
- psoriasis;
- acne;
- fungal skin diseases;
- vitiligo;
- eczema;
- seborrhea;
- dermatitis;
- lichen;
- papillomas, condylomas.
You can determine individually which skin disease manifests itself as red spots on your hands only by contacting a dermatologist.
Why do red spots with blisters appear on the body?
The human skin is a unique organ that is quite susceptible to environmental changes, as well as to changes in the internal environment of the human body. A characteristic reaction to irritating factors can be red spots, which are accompanied by a rash in the form of blisters. Such formations can cause discomfort to a person, which is manifested by severe itching, pain, peeling and irritation of the skin.
A person needs to know some of the reasons that cause the appearance of red spots with various rashes, which may take the form of blisters. Experts consider the following diseases to be the main causes, which can affect the body of any person, regardless of age or gender:
1 Ringworm. The disease is a fungal pathogen that occurs most often in children under ten years of age. The characteristic signs of the disease will be the following: round or oval spots, the edges are clearly visible, the affected area may be covered with vesicles and papules. You can become infected from direct contact with a sick person.
2 Trichophytosis. Also refers to fungal diseases, a characteristic feature is the appearance of one affected area first, and then spreading to others. Red spots have unclear boundaries that are covered with scales. As the disease progresses, the affected areas become covered with blisters or crusts. The disease occurs after contact with a sick person.
3 Some types of dermatitis. The skin in the affected areas will have a pale red tint, the skin will be swollen, and may become covered with cracks. As the disease progresses, the affected areas of the skin may develop blisters that will dry out and a crust may form. Exacerbations are observed in the spring and summer periods of the year.
Diseases of internal organs
The skin reflects all processes that occur in the body, including negative ones. There are many causes of skin diseases, the main ones are hidden in the internal organs:
- liver;
- kidneys;
- stomach;
- lungs;
- thyroid gland;
- heart.
Redness often occurs due to hormonal imbalance or after severe stress.
A rash or small red spots may appear due to diseases of the digestive tract , in particular, become a manifestation of:
- pancreatitis,
- gastritis,
- ulcers.
Inflamed internal organs can declare their pathology this way when there is any infection in the human body:
- In the genitourinary system;
- Respiratory system;
- Biliary system (biliary tract, liver);
- Gastrointestinal tract.
To identify the onset of the disease, it is necessary to urgently consult a doctor to diagnose and determine the etiology of the disease, that is, the main causes of its occurrence.
Red spot on the back with blisters
A rash in the form of blisters on the back is a separate symptom that is a consequence of the disease. Before starting treatment, it is necessary to accurately identify the cause that caused the appearance of the skin defect. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon. The main causes of spots with bubbles are considered to be the following: an allergic disease, a disease of the blood or circulatory system, an infectious disease or intoxication.
Primary skin defects manifest themselves in the appearance of blisters on the affected areas of the skin. In a child, such defects appear due to infections, most often chickenpox. Such diseases resolve with the formation of blisters on the skin, which then burst or dry out. The blistering rash should not be scratched - ulcers will form, which will be much more difficult to eliminate.
Allergy
Allergic spots are a symptom of some disease. And it is necessary to treat rashes only after the true cause of the skin rash has been established. And there are many such reasons: consumption of certain foods , contact with animals or plants, exposure to heat, cold, water or sun, the presence of fungi, viruses, bacteria, and inflammatory processes in the body.
Also, rashes can simply be a consequence of stress, hormonal imbalances, metabolic deterioration, or the result of a malfunction of the gastrointestinal tract.
All types of rashes have a certain shade, their location, shape, location. They may be accompanied by peeling of the skin, swelling, purulent discharge, and so on. Determining the cause of red spots and effectively ridding patients of allergic rashes is the task of any dermatologist.
Sun spots
Such spots can occur both when the skin burns - from excessive exposure to direct rays, and from allergic reactions to ultraviolet radiation. Spots can occur when the body has:
- hormonal imbalances – in adolescents, older people, pregnant women;
- disruption of the endocrine system;
- problems with the genitourinary system;
- vascular diseases.
Unbalanced diet
Small red spots can appear due to poor nutrition, when a person abuses:
- fried;
- sharp;
- sour;
- salty;
- smoked;
- canned;
- carbonated drinks;
- sweet.
Then inflammatory processes of the digestive organs begin in the human body: stomach, pancreas, intestines. The acid-base balance is destabilized, which causes increased secretion of hydrochloric acid, which can provoke such a reaction on the skin.
In this case, after diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a diet for the patient that will reduce irritation of the inflamed organs and stabilize the acid-base balance and metabolic processes in the body. Treatment can also be medicinal or, in severe cases, surgical.
Temperature changes
Burns or hypothermia of the skin tissue can also cause redness. This is due to the ambient temperature and the length of time the skin is exposed to hot or cold conditions. It is simple to prevent such redness - you need to insulate your hands in cold weather and protect them when cooking, boiling or possible contact with red-hot, hot substances and objects.
For these types of pathologies, in the initial stage, it is enough to use external preparations for treatment. For stages 3 and 4, frostbite or burns require skin grafting.
Nervous disorders
Skin diseases that are provoked by stress, nervous diseases, overwork, constant irritation and anxiety are also characterized by the appearance of red spots on the skin. The location can be anywhere: on the face, neck, abdomen, limbs, back. Such diseases include neurodermatitis or atopic dermatitis and psoriasis.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is a serious dermatological disease that occupies a leading place among skin pathologies. Both women and men of different ages are affected. The affected area may be:
- face;
- legs;
- hands;
- palms;
- Feet;
- forearms;
- nails.
Diagnosticians identify a number of main causes: hereditary predisposition, overwork and stress, decreased immunity. Based on the severity of the disease, psoriasis is divided into three stages, each of which has its own treatment methods.
Unfortunately, today it is impossible to completely recover from psoriasis; the main thing is to get remission of the disease for as long as possible.
Pyoderma
Pyoderma is a skin disease caused by pathogens. The disease has various forms and types, which include: vesiculopustulosis, furunculosis, streptoderma, staphylococcal sycosis . These microelements are present in the skin of any person, but their activation occurs when immunity decreases and the body malfunctions.
The causes of the disease can also be: hypothermia or overheating, stress and overwork, diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, climatic conditions, in particular, high humidity, other skin diseases, etc. Self-medication of pyoderma is excluded.
Symptoms:
- the presence of multiple inflammations in the form of yellow dots with purulent contents, pain and itching are felt,
- pustular formations can vary in depth and size,
- in severe cases of pyoderma, carbuncles and abscesses appear,
- pustules of hair follicles form,
- sharp pain,
- absence of purulent core,
- a large number of pustules appear on the back, face, and chest.
At your first visit to the doctor, you will talk with the doctor, based on the results of the diagnostic procedures, recommendations will be given and prescriptions will be made for effective treatment.
One of the methods of treating pyoderma is diet therapy prescribed by a doctor.
Scleroderma
This disease is characterized by inflammation of overgrown connective tissue not only of the skin, but also of internal organs. The main reasons for the appearance of this disease and red spots on the skin are:
- Genetic predisposition;
- Infection in the body;
- Reduced immunity;
- Chemical intoxication, which may occur due to excessive or chaotic use of medications;
- Poor environment and dirty water.
Lichen
Ringworm is a contagious skin disease characterized by a wide variety of types and forms:
- shingles;
- psoriasis or scaly lichen.
The occurrence is based on viral and fungal microflora, which affects people with reduced immunity and other diseases, including neurological ones.
The longer the disease lasts, the greater the likelihood of complications developing. Do not delay treatment, contact clinics where professional dermatologists do this.
Any type of skin disease requires a special approach to diagnosis and selection of a treatment regimen.
Scabies
This is a parasitic disease caused by scabies mites. The appearance of small red spots on the skin may indicate infection with this disease. Severe itching during the disease intensifies in the evening. This disease can be easily cured with medications and external preparations.
Impetigo
An infectious skin disease, which in most cases is caused by Staphylococcus aureus. First, red spots appear on the skin of the hands, then they turn into golden crusts. The disease is contagious and transmitted through household contacts. Chronic diseases, for example, diabetes, can provoke the disease.
Shingles
The same lichen, only outwardly its shape is similar to the outline of a circle. It also starts with general redness. Then there are red rims that itch, hurt, flake and bring great discomfort to its owner. Treatment is necessary.
Rosacea
This is a chronic disease, one of the symptoms of which is redness of the skin. The main causes of the disease are not only genetics or poor hygiene, but also malfunctions of the thyroid gland and endocrine problems. Often the cause of the disease is improper cosmetic skin care . The disease develops with the appearance of red pimples, then:
- pustules form
- skin sensitivity increases,
- burning and itching appears,
- vascular networks.
Bather's Itch
This skin disease is extremely rare and is caused by the schistosomatid parasite, which primarily lives on the skin of waterfowl, but can be transmitted through water and settle in human epidermal cells. Treatment for this disease is also necessary.
Syphilis
Syphilis is a bacterial type of sexually transmitted infection. The disease is classified as a latent infection, since it develops without symptoms for a long time. All hidden infections are transmitted sexually.
It is impossible to start sexually transmitted infections; this is fraught with complications such as infertility.
Infections of various types
Infections can occur in any system of the body and can be caused by:
- Viruses;
- Bacteria;
- Herpes;
- Fungi;
- Parasites;
- Reduced immunity.
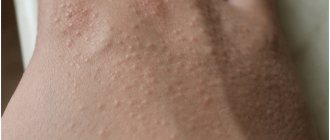
Types of stains on hands
Spots on the hands can be of different colors and cover different parts of the hands - elbows, forearms or hands. The spots also vary in size (small or huge). Their edges are usually smooth, but they can be located both on the upper layer of the skin (epidermis) and touch the dermis. Some people may have mixed types of pigmentation.
Important. Particular attention should be paid to the color of the spots.
The spots on the skin of the hands are often white, brown or have a pink tint.
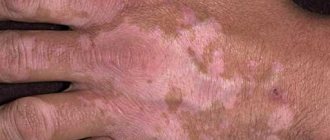
White spots
White pigmentation on the hands (congenital or temporary) is explained by the following factors:
KK Adapt. 5 paragraph
- Vitiligo. In the presence of this disease, the human immune system does not work correctly, destruction of melanocytes occurs and the rapid development of the process (appearance of spots).
- Idiopathic guttate hypomelanosis. The causes of this skin pathology remain unknown, and the spots themselves are small in size and lighter in color than human skin. They appear either at a young age due to hereditary predisposition, or in adulthood.
- Pityriasis versicolor. It is provoked by a yeast-like fungus present on the epidermis. Under the influence of certain conditions, the fungus begins to actively multiply, resulting in the skin of the hands being affected.
- Pigmentless nevus. A white spot that has been on a person’s skin since birth. As a rule, it has a semicircular shape, and the hair growing in this area is colorless. Since nevus cells have the ability to degenerate, this can lead to the development of a tumor.
- Pityriasis alba. The affected area becomes white with unclear contours. Sometimes the skin on the hands peels off, the affected areas do not tan in the sun, but pityriasis alba is not dangerous. It often occurs in children and goes away on its own.
Some of the listed diseases can be distinguished on your own, but it is better to consult a doctor if you notice the appearance of such pigmentation.
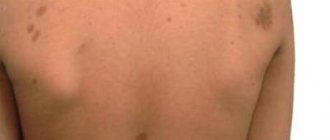
Brown spots and pigmentation on hands
Brown pigmentation occurs due to the fact that skin cells, under the influence of external or internal factors, more actively produce pigment (melanin). Its excess in certain areas changes the color of the epidermis from light brown to dark.
The color of the spots is influenced by the reasons for their appearance. Since it is quite difficult to determine exactly what caused the problem, it is recommended to visit a dermatologist - he will prescribe an examination and draw up a clinical picture based on the results obtained. If there are no health problems, getting rid of pigmentation is easier. Otherwise (if some disease is discovered), you will need to undergo a full course of treatment.
So, what can affect the formation of brown spots on the hands:
- Sun. This factor is considered the most common. Ultraviolet radiation can damage epidermal cells, and prolonged exposure to direct sunlight triggers the body's defense mechanisms. A failure in the process of melanin production is its reaction.
- Age. As a rule, pigmentation in old age is a consequence of cells losing the ability to control the production of melanin. The problem occurs in people over 40-50 years of age, since at this age health begins to deteriorate.
- Genetic predisposition. With a genetic predisposition, any unfavorable factor can provoke the appearance of brown spots on a person’s hands.
- Cosmetical tools. Low-quality cosmetics or products containing harmful components and substances used for a long time also affect the appearance of pigmentation.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals. For example, this is how the body signals a vitamin C deficiency.
- Chemical substances. When contacting the skin of the hands with strong chemicals, an allergic reaction sometimes occurs, which is accompanied by the appearance of spots.
- Health problems. Skin diseases, neurofibromatosis, liver or thyroid diseases, gastrointestinal problems and chronic inflammation - these and other diseases are also accompanied by the appearance of small brown spots.
- Changes in hormonal levels. Many people face a similar glitch. Spots on the hands appear especially often in pregnant women and those who use certain medications. The occurrence of such a cosmetic defect is also influenced by the production of hormones - it changes over the years.
Taking into account the number of different factors, therapy for each patient is selected individually.
Treatment methods
If you have red spots on your arm, whether they itch or not, you should contact a dermatologist who, after diagnosis, will determine your individual course of treatment. The main treatment methods include:
- Medication;
- Hormonal therapy.
- Drug-free methods:
- diets;
- natural preparations;
- ethnoscience;
- phytotherapy.
Physiotherapy : narrow-wave, laser therapy.
Medication , in turn, is divided into:
- Antibiotic therapy;
- Immunostimulating therapy – treatment with drugs to enhance immunity;
- Enzyme therapy – natural preparations with enzymes needed by the body;
- Local treatment with external preparations.
Treatment
In a therapeutic way
Local remedies that relieve skin manifestations - itching, erythema, swelling: Radevit, Elidel, Psilo-balm, Protopic, Eplan, La-Cri, Skin Cap. Glucocorticoid external agents help in severe cases.
They are divided according to their effects:
- Weak glucocorticoid ointments: Sinaflan, Flucinar, Laticort, Hydrocortisone.
- Medium: Afloderm, Fluorocort, Triamcinolone;
- Strong: Advantan, Celestoderm B, Lokoid, Elokom, Cloveit, Dermovate
By medication
Dermographic urticaria is treated with the same groups of medications as other types of urticaria. First of all, antiallergic drugs of different generations are used, which are selected depending on the patient’s individual reaction to a particular drug.
- Some doctors recommend vasoconstrictors for the red form of dermographism and vasodilators for the white form.
- Others have a negative attitude towards this treatment option, since the effect of such drugs on the body is general, which means their influence extends to the vessels of all organs, including the brain and heart. Therefore, the use of vasodilators (vasodilators) or drugs with opposite effects can lead to problems in the blood supply to the cerebral and coronary vessels or their sudden expansion, which threatens hemorrhagic stroke and thromboembolism.
The treatment regimen for urticarial dermographism is discussed below point by point.
Antihistamines II – III generation
Typically, therapy begins with the use of standard doses of antihistamines of the 2nd - 3rd generation. Daily dosage for adults:
- Claritin, Lomilan (loratadine) – 10 mg;
- Telfast, Fexadine (fexofenadine) – 150 mg. Strictly prohibited for pregnant women, nursing mothers, and children under 6 years of age;
- Xizal, Suprastinex, Zodak, Glencet, Cesera (levocetirizine) – 5 mg, contraindications are the same as for drugs with fexofenadine;
- Ebastine (piperedine) – 10 mg;
- Erius, Allergostop (desloratadine) – 5 mg;
- Zyrtec, Zodac (cetirizine) – 10 mg.
A new drug that helps well with dermographic urticaria, but does not cause sedation (drowsiness) is Trexyl with the active component terfenadine. Used in tablets and suspensions. The recommended dose for adult patients, starting from 12 years of age, is 60 mg (or 10 ml of suspension) 2 times. Children's doses: 3 - 7 years old - 15 mg, 7 - 12 years old - 30 mg, morning and evening.
If the latest generations of antistamins do not help, the dosage, as a rule, is not increased, but a second medicine with a different active substance is added to the treatment regimen.
Or they use 1st generation remedies, which are often more effective for urticaria: Diphenhydramine, Suprastin, Tavegil, Pipolfen. For severe skin manifestations with severe itching, Tavegil and Suprastin are administered intramuscularly.
For frequent exacerbations of long-term dermographism, use:
- Ketotifen. Adult dose 0.001 - 0.002 g twice a day. Children are given syrup: up to six months - in a daily dose of 0.05 mg per kilogram of the baby's weight, from six months to 3 years - 0.5 mg twice a day, from 3 years - 1 mg.
- Cyproheptadine: 4 – 8 mg (3 or 4 times); The pediatric dose, based on the norm of 0.25 - 0.5 mg/kg, is also divided into 3 - 4 doses.
Histamine H2 receptor suppressors
If the patient does not respond to therapy with antiallergic medications, they try the introduction of drugs that suppress histamine H2 receptors:
- Cimetidine: 0.3 grams up to 4 times a day. Children's daily doses from one year of age are calculated: 25 - 30 mg per 1 kilogram of weight, for infants up to one year - at the rate of 20 mg / kg of weight;
- Ranitidine for patients over 12 years of age: 0.150 - 0.300 g (2 or 1 time per day);
- Famotidine (from 12 years old) - twice 0.020 g.
Hormonal agents
In those rare cases when the severity of symptoms does not decrease, it is necessary to use hormonal agents in short courses (2–4 days) that quickly relieve swelling and itching.
Prednisolone is usually prescribed in a daily adult dose of 0.04 - 0.06 grams, Dexamethasone - 0.004 - 0.020 g (or 1 injection per day) in the acute period.
Elimination of common symptoms
General symptoms are eliminated by taking:
- Paracetamol, Ibuprofen, Ketonal for painful blisters, headaches, fever;
- Cerucal - for nausea;
- Decitel, No-Shpu - for abdominal cramps.
Since experts associate the development of dermographic urticaria with instability of the nervous system, they prescribe courses of:
- B vitamins, including Neuromultivit, Milgamma, vitamins B1, B6, B12 in injections;
- sedatives: decoctions, tinctures, tablets with valerian root, motherwort, Novopassit;
- during exacerbations - Bellantaminal, Belloid (tablet 3 times a day).
Since skin manifestations of dermographic urticaria are associated with abnormally high permeability of the vascular wall, the following is used:
- ascorbic acid;
- flavonoids (Rutin, Ascorutin, Quercetin, Vitamin P) under the control of blood clotting to avoid increased viscosity;
- vitamers (semi-synthetic derivatives) – Venoruton, Phlebodia, Detrolex, Troxevasin in various forms (capsules, gel, solutions).
For severely tolerated symptoms - particularly severe itching, insomnia, neurological disorders, it is advisable to prescribe tranquilizers from the group of benzodiazepines (Phenazepam, Xanax, Diazepam) and antidepressants - Paxil, Doxepin.
Ointments
Ointments belong to external use preparations and are divided into two main groups:
- hormonal;
- non-hormonal.
If the doctor has the opportunity to save the patient from the disease with non-hormonal means. then he will definitely do this, since hormonal ointments with long-term use are more harmful than beneficial and are a complex, strong medical preparation. The ointment is selected individually, taking into account:
- severity of the disease;
- clinical picture;
- localization of the lesion,
- etiology of the disease;
- individual intolerance to components.
Ointments are part of complex therapy, sometimes for simple skin diseases they are the only therapy. Naturally based ointments are widely used - “Nanovit Derma” and “Derma Cream”, “Nanovit Immuno” (to increase immunity). Preparations based on Dead Sea mud are used.
Symptoms
The symptoms of autographism depend on the type of disease, but in any case, with mechanical irritation of the skin, the basic signs remain as follows:
- the appearance of red, pink, whitish stripes directed in the direction of the stimulus or repeating its shape;
- itching, swelling, burning and feeling of skin tension;
- swelling of the skin in the form of blisters.
A feature of dermographism, unlike many other allergic skin reactions, is the frequent absence of itching or its very weak intensity.
Types of dermographism and symptoms Table No. 1
| Reaction | Type of dermographism | Basic symptoms | May appear | Onset of manifestation and duration |
| immediate | white (weak fast pressure); red (strong, longer pressure) | red or white streaks, blisters, erythema (redness) | Itching, burning, soreness, general weakness, chills, headache, nausea | appear in the range from 3 seconds to 10 minutes after pressure on the skin; |
lasts 0.5 – 2 hours
Stage 2: Linear whitish blisters rising above the skin (similar to burn blisters) surrounded by a pinkish-red area
Diagnostics
Before treating skin redness, differential diagnosis is necessary, which will identify not only the cause of skin pathology, but also concomitant diseases. Therefore, a whole range of laboratory and clinical studies and consultations with doctors of various specializations are carried out.
The admission process itself can be divided into stages:
- Consultation with a dermatologist and other specialists as prescribed;
- Biopsy;
- Physical examination;
- Sensitivity test or dermatoscopy;
- Digital photography;
- Laboratory research:
- dermatoscopy of lesions;
- seeding from the surface of the skin;
- examination of skin scales;
- clinical blood test.
Treatment for itchy red spots on the arm
Redness that appears on the arm, leg, face and foot, palm and other places is treated after a thorough diagnosis. Various types of treatment are used:
- antibiotics;
- antifungal agents;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- immunomodulatory therapy;
- physiotherapy (ozone therapy);
- desensitizing therapy;
- electrocoagulation.
- Ozone therapy has antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, immunostimulating, antiviral effects, and helps accelerate metabolic processes.
- Plasmolifting is an injection of the patient’s own blood plasma under the skin, as a result of which the natural processes of skin regeneration are activated, collagen synthesis occurs and inflammation is relieved.
- Medication methods:
- tablet form: desensitizing drugs;
- corticosteroid ointments (aerosols);
- antiallergic drugs.
Drug-free methods:
- diets
- natural preparations based on the Dead Sea
- phytotherapy
Physiotherapy : radio wave, narrow wave, magnetic therapy, laser therapy, etc.
The treatment regimen for an allergic rash is developed individually for a specific patient. In addition to medications, biological products and diet therapy are successfully used. It is important to limit contact with the allergen.
Possible allergy treatments:
- antihistamines;
- local treatment;
- immunotherapy;
- vitamin therapy;
- biological products;
- diet therapy.
If possible, you should try to minimize treatment with hormonal drugs, using natural ones.
Classifications of demographic urticaria
By shape
- primary form , which develops directly under the influence of a provoking factor;
- secondary , when the disease is provoked by an existing internal pathology (mastocytosis, neurological diseases, systemic lupus, serum sickness).
This video will tell you what autographism is:
By reaction speed
Based on the speed of reaction, there are three types of autographism:
- immediate type (more frequent), in which the skin reaction is visible 2 to 5 minutes after pressure, lasting about half an hour;
- medium , when swelling and irritation develops in the interval from half an hour to 2 hours and lasts up to 3 – 9 hours;
- late (rare type), giving a skin reaction after 4–6 hours, which lasts up to 2–3 days.
With a medium and late reaction, itching, soreness, swelling and hyperemia appear in places where prolonged and strong pressure was applied to the body:
- on the shoulders after the straps of a backpack or shoulder bag;
- on the ankles after squeezing them with a tight elastic band of socks;
- on the wrists after the belt of a bag or bracelet;
- in any places squeezed by tight underwear or belts;
- on the feet after prolonged walking;
- on the buttocks when sitting for a long time, on the skin from the inside of the thighs after horseback riding and cycling.
With all types, a clear sequence of skin changes is observed: the action of a physical irritant causes redness of the skin, then the reddened area swells, swelling forms, which increases, becoming wider.
By type of reaction
They differentiate according to the type of reaction:
- Local dermographism , in which skin reactions are limited to the area of irritation.
- Reflex , when changes in the skin after pressing and running a hard, sharp object over the body appear after 5–20 seconds in the form of a bright red stripe up to 6–7 mm wide. This phenomenon is explained by the expansion of small arterioles and is a typical vasomotor reflex.
By manifestation
There are several types of dermographism:
- Red , in which red or bright pink streaks appear on the skin, caused by strong pressure from a blunt, hard object. Better expressed on the upper body.
- White dermographism. With slight short pressure, it is characterized by the appearance of white stripes, which is caused by a spasm of the capillaries. It is more pronounced on the legs and lasts longer than “red” dermographism. Unlike “red,” this vascular reaction is explained not by expansion, but by narrowing of the capillaries.
- Dermographism sublime , in which red stripes up to 60 mm wide with uneven contours are initially formed, which after 2 - 3 minutes are replaced by white blisters that swell above the skin and persist for a long time. Such skin changes are due to the high permeability of the vascular wall.
The following are the causes of urticarial dermographism.
Prevention
So that you are not bothered by any red spot on your arm, palm, leg , and you do not ask in horror: “What is this?!”, and then do not run to the doctor, you need to remember a few rules:
- don't overwork yourself;
- do not be nervous;
- move more;
- walk in the fresh air;
- eat properly according to the regime;
- keep a daily routine;
- do not get too cold or overheat;
- observe moderation in everything.
Then many diseases, in which redness on the hands and face creates discomfort and signals illness, will simply never arise.
What do red disappearing spots on the body look like?
Disappearing spots on the body always look different. Their shape, color and texture depend on the root cause of their occurrence. If this is associated with an allergic reaction, then the spots appear in the form of a rash that itches and bothers the person. With a bacterial infection, the spots may not bother a person at all, have a flat shape and a pale color.
If the spots are associated with nervous disorders, then they cause discomfort to the person, causing itching.
Disease prevention
In order for exacerbations of dermographism to occur less frequently, it is necessary:
- Avoid situations involving pressure on the skin, especially long-term pressure accompanied by friction.
- Do not wear clothes made of synthetic or woolen fabrics.
- Do not use hard washcloths or rub your body with a towel.
- Avoid power massage (only the stroking type).
- Avoid overwork, stress, overheating and cooling, which can provoke illness.
- Conduct consultations and examinations with a gastroenterologist to exclude infection of the gastric mucosa with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, an endocrinologist (diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease), a parasitologist (to identify possible giardiasis, helminthiases), and an immunologist.
Complications
With the development of urticarial dermographism, the consequences may be as follows:
- Frequent exacerbations of urticaria deplete the nervous system of patients, leading to depression.
- Prolonged pressure, often repeated in the same places, contributes to thinning and damage to the dermis. At the same time, pyogenic bacteria easily penetrate deeper, leading to pustular skin infections, furunculosis, local suppuration with the development of an abscess.
- General symptoms of malaise that often accompany skin reactions - fever, nausea, headaches - contribute to a decline in the body's immune defense.
- Since any allergic diseases are “reinforced” by other types of allergies, dermographic urticaria in rare cases is complicated by Quincke’s edema, dangerous laryngeal edema, and anaphylactic shock.