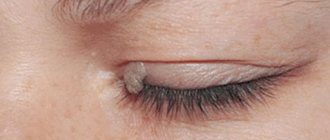
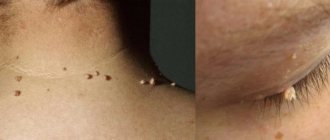
The term “papilloma” is applicable to define a benign growth that is the result of HPV activity and can be located on the skin and mucous tissues.
Infection with papillomavirus can occur as a result of bodily contact, when visiting public places, as well as when using other people's things, personal hygiene and household items.
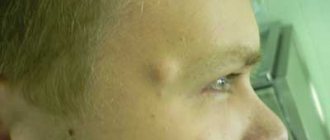
Separately, we should talk about hanging papillomas, which are relatively small growths located on a long thin stalk and appear mainly in the décolleté area, on the neck, in the armpits, and rarely on other parts of the body. Growths of this type are not dangerous, however, against the background of exposure to harmful factors, there is a risk of their transformation into malignant and benign tumors.
What do hanging papillomas look like?
Hanging papillomas are formations on the human skin. Outwardly, they resemble elongated warts, as if attached to the human body with a thin stalk.
When papilloma develops, a small papillary growth first forms on the skin. Then it gradually increases and stretches. Its color can vary from light flesh to dark brown. An important sign of hanging papilloma is its lumpy surface.
Types of hanging papillomas:
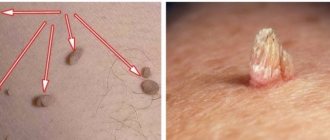
- Thread-like. The color can blend in with the skin or have pink, brown, yellowish shades. They vary in size from barely noticeable to large formations up to 1 centimeter in size. They can be not only single, but also merging into groups.
- Finger-shaped. They are observed less frequently than filamentous ones and can occur on the scalp. They grow on a thick stalk and reach 2 centimeters in size. Never group. The color is flesh-colored or pinkish.
Types and localization
Hanging warts are one of many papillomas, the occurrence of which is provoked by the virus of the same name. They, in turn, are also divided into several types, which have their own characteristics regarding appearance and localization.
| Signs | Finger type | Threaded type |
| Size | From half to two centimeters. | Up to one centimeter |
| Localization | Scalp, along the hairline | Under the arms, in the groin, on the face, neck, in women under the mammary glands. |
| Hue | Skin color, pink | Light and dark brown, yellow, flesh |
| Manifestations | Singles | Multiple, sometimes single |
| general description | A hanging finger-shaped wart is similar in shape to a pea, the base is elongated, and the skin of the papilloma is rough. | Filiform papilloma appears in the form of a small bump; as they develop, they stretch out and take the form of “strings.” Multiple clusters of hanging warts of this type resemble cauliflower, cockscomb. |
A hanging wart causes inconvenience not only in aesthetic terms; being in places exposed to external influences, papilloma can bring unpleasant, painful sensations, transform into a low-quality tumor and require immediate treatment.
- Hanging papilloma under the armpit is often injured by a razor during a hygienic procedure, and the presence of many sweat and sebaceous glands in the armpit becomes a favorable environment for infections of various kinds, including papillomavirus.
- Hanging warts located on the neck are often damaged. Treatment of such growths should begin as soon as possible. By injuring the papilloma with jewelry, clothing, careless movements of a comb, or while cutting with scissors, you can contribute to the development of the papilloma into a malignant type, especially under the influence of UV rays.
- Hanging warts in an intimate area can also be wounded, cut off by a razor during shaving, or rubbed by tight underwear. Damaged areas become inflamed, red and painful.
Why do papillomas form?
Papillomas appear due to infection with the human papillomavirus or papillomavirus. There are a large number of its strains, which have different effects on the body. According to statistics, this virus is present in 80% of the world's inhabitants. However, not all of them have benign formations in the form of papillomas on the skin.
The incubation period of the virus ranges from several days to several decades. Therefore, the formation of hanging papillomas often worries adults over 40 years of age. When the virus enters the body of a person with a strong immune system, it lives in it in a latent state. If the immune system weakens, sooner or later papillomas appear on the skin.
Causes of papillomavirus infection:
- during childbirth, during passage through the mother's birth canal,
- when touching a carrier of the virus,
- during sexual intercourse,
- through personal hygiene items, in the pool, transport, etc.
The virus penetrates through cuts, scratches, wounds and other lesions on the skin and invades cells. The duration of the incubation period depends on the state of immune defense. Sometimes people find out about infection decades after the virus enters the body.
Reasons for appearance
The cause of filamentous warts is papillomavirus types 3, 5, 8 and 9, which are activated in the body against the background of decreased immunity or impaired protective function of the skin. According to statistics, about 50% of people over 40 years of age are infected with HPV of these serotypes.
Hanging papillomas can occur in the presence of risk factors such as:
- damage or irritation of the skin by clothing;
- sweating;
- irregular hygiene procedures;
- allergic skin reaction to a cosmetic product (perfume, cream).
In addition to local factors, the external manifestation of HPV indicates that the immune system is not able to cope with the pathogen. The weakening of the body's defenses is caused by:
- poor nutrition;
- bad habits;
- frequent stress;
- the presence of foci of chronic infections in the patient’s body;
- immunosuppressive therapy, hormonal causes of decreased immunity (for example, pregnancy);
- poor environmental conditions;
- heavy physical activity.
Another cause of warts on the neck is the use of cosmetics in combination with active sweating. This creates a favorable environment for the introduction of human papillomavirus.
Infection with the virus occurs through sexual or household contact with a carrier of virions, as well as during the process of delivery from a sick mother to a child.
Risk factors
Various factors can trigger the activation of papillomavirus and the appearance of growths on the body:
- smoking,
- alcohol consumption,
- narcotic substances,
- non-compliance with hygiene standards,
- infection with viral infections,
- hypothermia,
- avitaminosis,
- pregnancy,
- endocrine system disorders,
- surgical interventions,
- stress and overwork.
In what areas of the body do papillomas occur?
The appearance of hanging papillomas can be confused with other formations on the skin. Their peculiarity is their appearance on delicate areas of the skin: on the face, in the neck, armpits, in the groin folds and under the breasts.
In these areas, the integrity of the skin is often compromised due to rubbing with clothing, scratching, and the use of scrubs and peels. A warm and moist environment is constantly maintained in the armpits and groin area, under the breasts. All this provokes the penetration of the virus and the development of formations on the skin. Their growth does not have any symptoms and does not cause pain to a person. In rare cases, he may experience mild itching.
Removal of warts in the clinic
In most cases, people asking the question: “How to remove a hanging formation?” are advised to remove it surgically. There are several different techniques.
Methods:
- Cryodestruction. Removal is carried out using low temperature liquid nitrogen. Sometimes small marks may remain after healing.
- The radio wave technique involves the use of a radio wave knife, with which the operation is performed. The method is good because there are no traces after removal and no risk of infection.
- Removal by high-frequency electric current - electrocoagulation. The procedure is somewhat painful. After removal, small stains remain that disappear over time.
- Using a laser to get rid of hanging lesions is the most popular method. The procedure does not take much time, and after removal there are no traces left. The wound is immediately cauterized, the infection cannot penetrate inside.
- Removal with a scalpel is used when the wart becomes malignant. In this case, the growth and nearby healthy tissue are cut out.
The choice of technique remains with the treating specialist and depends on the patient’s condition.
Are hanging papillomas dangerous?
The appearance of growths in itself is not dangerous to health. But papillomas differ from other formations on human skin in that they are more prone to injury than others. Even with a slight impact during shaving, when using combs, washcloths, due to friction of clothing and jewelry, they can be damaged or torn off. The root continues to live.
The growths can cause discomfort and itching. And if they are damaged, bleeding occurs, which is dangerous due to the addition of a bacterial or fungal infection. In case of injury, it is necessary to treat the wound with an antiseptic, seal it with a fabric plaster, and then show it to a doctor. The specialist will diagnose, prescribe treatment and advise how to remove the tumor.
If hanging papillomas are frequently damaged, the surrounding tissues also become infected, which leads to multiplication and fusion into a large growth.
Should I worry?
By themselves, any benign neoplasms (hanging papillomas, warts, nevi) do not pose a health hazard. Nevertheless, external manifestations of HPV require more attention than moles, since they indicate a decrease in immunity and are associated with a higher risk of malignancy (malignancy). The latter is due to the fact that thread-like formations are localized in places that are often in contact with clothing and exposed to harmful environmental factors (UV radiation).
Damage to the surface of papillomas not only increases the risk of developing cancer, but also contributes to the rapid growth of tumors and the spread of the virus to other areas of the skin.
Large growths are prone to bleeding, which can lead to chronic anemia. As a result, in a short period of time, a minor formation can become large and unsafe.
The following symptoms indicate the danger of malignant papilloma:
- frequent bleeding;
- suppuration;
- discoloration and rapid growth;
- soreness, burning sensation and itching in the area of the growth;
- the appearance of an inflammatory zone around the papilloma;
- cracks, ulcers on the surface of the neoplasm;
- change in the vascular and skin pattern around the growth.
At a later stage of transition to a cancerous tumor, not only local but also systemic symptoms appear: chronic weakness, fatigue. It is possible that the temperature may rise to subfebrile and the lymph nodes next to the papilloma will become enlarged.
But not only dangerous signs are a reason to consult a doctor. Dermatologists recommend diagnosing any neoplasms and removing papillomas if they are located on an open area of skin or are frequently injured. With the help of an examination and a PCR test, a specialist will determine the degree of risk of malignancy of the growth, the level of danger of the virus (oncogenicity of HPV).
Modern methods of treatment
In order to get rid of papilloma, you need to consult a doctor. He will conduct a diagnosis to ensure that the skin lesion is benign and recommend the best removal method.
Drug therapy
Growing small hanging formations on the neck, face and other parts of the body can be removed without surgery, with the help of medications. Pharmacologists have developed products that can effectively combat skin growths. For conservative removal of papillomas, dermatologists prescribe special ointments and creams.
Antiviral ointments are also used as therapy. But they can only cope with recently appeared growths that have not had time to get stronger and grow. To remove HPV, it must be treated from the inside, using antiviral drugs, and care must be taken to strengthen the immune system.
Surgical methods
To combat hanging papillomas, as well as many other types of skin tumors, hardware methods of disposal are used.
- Freezing with liquid nitrogen. Eliminates growths quickly, but requires careful care of the wound formed after the operation. The procedure is expensive.
- Laser removal. This method is often used. It allows you to get rid of large tumors in one session.
- Current therapy or electrocoagulation. Uses a current of a certain strength. Does not always provide effective results. There is a possibility that the procedure will have to be repeated several times.
- Radio wave method. Quickly removes formations on any part of the body. After its use, wounds remain on the skin. Over time, they tighten and leave almost no traces.
- Surgical intervention. The main disadvantage of this method is that after removing the growths, scars remain. And patients are forced to undergo rehabilitation.
Diagnostics
Often, filamentous papillomas are similar to more harmless moles: if the dermatologist is insufficiently qualified and there is no equipment for research, these neoplasms can be confused. Most nevi have a denser structure, are distinguished by the absence of blood vessels and a wide variety of locations and shades. However, it is possible to accurately determine the nature of the growth only with the help of comprehensive diagnostics, which includes:
- External examination of education. The doctor examines the growth using a microscope to study its structure and boundaries, see the vascular network and make sure there are no inclusions of a different color.
- Anamnesis collection. Information about the patient’s age, chronic infectious processes, health status, medications taken, and the presence of papillomas in family members is important.
- PCR or Digene test. The test determines the HPV serotype and viral load. Based on these signs, the doctor concludes that there is a risk of malignant degeneration of papilloma.
In addition to standard tests, experts often recommend a biopsy of the thread-like growth and examination of its tissue for signs of cancer. Histological analysis can be performed after the growth is removed.
Traditional medicine to combat papillomas
An alternative to professional methods are folk methods that can be used at home.
If papilloma appears on the skin, you can try:
- treat the growth every day with fresh celandine juice,
- rub with a clove of garlic,
- At night, apply onion soaked in vinegar to the skin area,
- make compresses from castor oil.
These folk recipes are not recommended for removing growths on the face to avoid the appearance of scars or pigmentation.
When dealing with hanging papillomas, you should stick to traditional removal methods and consult a doctor. Incorrectly selected drugs and methods can cause the growths to increase in size and begin to cause serious inconvenience. And for prevention, you need to be careful about your health, eat more vegetables and fruits rich in vitamins C and B.
Prevention of growths
To avoid the appearance of warts and hanging papillomas, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system, eat right, observe good hygiene and promptly eliminate foci of infection in the body. Using personal hygiene products, using barrier protection during sexual intercourse, and treating skin lesions and dermatitis can help reduce the likelihood of HPV transmission.
To prevent bacterial complications and the reappearance of hanging papilloma after the procedure for removing the growth, it is necessary to treat the skin with antiseptic solutions (Furacilin, Chlorhexidine) and antibiotic ointment.