What is atheroma, a dermatologist most often tells people prone to acne, those suffering from obesity or diabetes, as well as patients during periods of hormonal imbalance. Contrary to popular belief, this type of subcutaneous neoplasm is not a tumor, but a cyst. The difference between these two concepts is that a tumor is an accumulation of new uncontrollably growing cells limited by a capsule (it can be malignant or benign), and a cyst is formed in the cavity of the epidermis and consists of a capsule with liquid.
What is an epidermal cyst
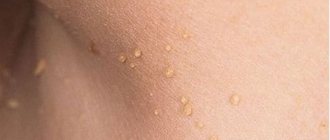
An epidermal cyst is a benign pathological neoplasm that resembles a small ball. The pathology can be localized in any part of the body, most often growing on the head and in the back. Neck cysts are much less common. One patient may have from one to two or three cysts. The causes of the disease are varied - from neglect of personal hygiene to hormonal disorders.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
Timely detection and treatment of a tumor will prevent the complication of the disease - degeneration into a malignant neoplasm. The disease occurs equally often in both men and women, and is less common in children.
Atheroma is diagnosed by appearance, histological examination, and ultrasound and MRI are prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
Therapeutic measures depend on the size of the tumor: for larger sizes, the lesion is removed surgically (radio wave method, laser destruction and electrocoagulation are used). The prognosis is positive.
Causes of epidermal cyst
An epidermal cyst is formed in the process of blocking pores when the outflow of secretions from the sebaceous glands is disrupted. Most often diagnosed in patients prone to acne.
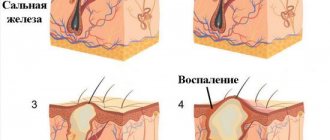
To better understand the mechanism of tumor formation, it is worth considering the functioning of the sebaceous glands, which produce a secretion that protects the skin from pathogenic bacteria. When the duct is blocked, the secretion accumulates inside and causes expansion of the walls of the gland, followed by inflammation.
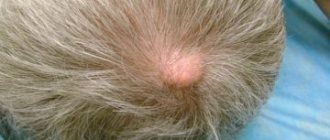
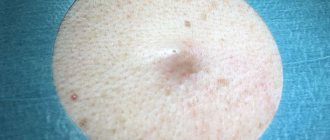
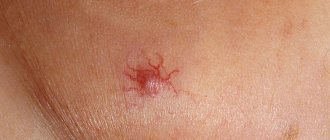
An epidermal cyst externally looks like a round-shaped node with an unchanged or reddish skin color. The pores are enlarged and visually visible. The size of the formation is from 0.5–5 cm to a full apple.
The main causes of clogged pores:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- low-quality cosmetics that cause clogged pores;
- hormonal imbalances;
- metabolic disease.
The appearance of a cyst on the ovary is associated with embryonic malfunctions in the intrauterine development of the fetus. It can occur in women and is associated with physical and emotional stress, ovarian dysfunction and constant abortions, triggered by inflammatory processes.
Causes of sebaceous cysts
The cause of a skin cyst is a blockage of the lumen of the gland duct. As a result, the patency of the canal is disrupted, and a capsule filled with secretion is formed.
The sebaceous glands are located over the entire surface of the body and secrete a secretion, a substance whose task is to protect and moisturize the skin and hair. The glands are connected by their excretory part to the areas where formations arise. These areas include:
- Eyelids, lips, external auditory canal, anus, nipples, penis, foreskin. The duct is open on the surface of the zone of these areas, therefore, when the duct is blocked, subcutaneous cysts often appear here;
- Hair follicles. The duct opens into hair follicles throughout the body.
The largest localization of the sebaceous glands is the facial area. In descending order follows the neck area, back, scalp, chest, pubis, and abdomen. The fewest glands are located in the area of the shoulders, forearms and legs.
The main factor in the occurrence of atheroma - sebaceous gland cysts is blockage of the excretory duct. As a result, secretion begins to accumulate here, an increase in the volume of which pushes the walls of the duct apart. A cavity is formed, limited by the walls of the connective tissue.
Factors that create favorable conditions for the formation of cysts under the skin include:
- Disorders of the metabolic process, as a result of which the consistency of the secretory fluid changes;
- Congenital structural pathologies. Occasionally, babies develop a congenital cyst near the ear, due to an abnormal development of the skin. This phenomenon does not affect the child’s development level and does not pose a danger;
- Inflammatory processes affecting the upper layer of the skin, damage to the glands;
- Excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis). As a result of excessive sweating, excess sweat accumulates and dries on the skin. This can lead to blockage of the duct, the formation of both a sebaceous neoplasm and a sweat gland cyst;
- Damage, inflammation of the follicle. This condition provokes disturbances in the outflow of fluid, blockage of the hair follicle, and the formation of a trichodermal cyst;
- Hormonal imbalances. Often, an increase in male sex hormones (testosterone, dehydroepiandrosterone) contributes to changes in the composition of the secretion. A thicker concentration is less clearable and leads to blockage. Atheromas can form due to a decrease in female sex hormones (estrogens), which also affects the consistency of secretory secretions;
- Blackheads, acne, skin trauma. Trauma can occur during independent cosmetic procedures (scrubbing, shaving). During such manipulations, cells from the injured skin can enter the gland duct, which often leads to blockage. Thus, improper shaving or epilation of the lower part of the face can provoke a cyst on the chin;
- Poor quality cosmetics, use of cosmetics that are not suitable for a specific skin type. Illiterate selection and use of cosmetic products often provokes clogged pores and the appearance of sebaceous gland cysts on the face (including multiple ones);
- Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules. The smallest particles of dust, earth, dirt can accumulate on the surface of the skin, leading to disruption of secretion and the formation of subcutaneous cysts on the face and body. Therefore, it is important to regularly cleanse the skin and carry out water procedures;
- Genetic factor. One of these pathologies is cystic fibrosis. The disease contributes to the thickening of body secretions and the formation of various formations.
Classification
Epidermal skin cyst has a classification:
- True tumor. It is formed from appendages of the epidermis, has a congenital nature of origin and is diagnosed in women on the head. The growth of the tumor is slow, the risk of degeneration into malignant atheroma is very low.
- False tumor. Appears due to excessive secretion of sebaceous glands, which accumulates in the pores, forming a plug. The usual location is on the back, but it occurs on the face and scalp.
There are cases where an epidermal cyst has formed on the labia. The patient should be observed by a specialist. If the tumor grows quickly, the lesion is removed surgically.
An epidermal cyst can be localized in the perianal zone, which affects the area around the anus. Occurs infrequently.
False forms of cysts quickly increase in size, and the percentage of degeneration into a malignant neoplasm is high.
Symptoms of an epidermal cyst
Epidermal cyst photo.
Epidermal cyst is the most common neoplasm. True atheroma visually resembles a subcutaneous node; the surface of the skin is clogged with pores. It can be located on the cheeks, ears, back and other parts of the body.
The node quickly grows and opens into the dermis, which causes severe pain and inflammation. The growth of the pathology is slow, the lesion has a tendency to thicken. A false epidermal cyst grows quickly.
You should consult a doctor if the following signs appear on your skin:
- inflamed nodules;
- pain in the tumor;
- rapid cyst growth.
A quick response and medical assistance will protect the patient from possible complications.
Why is atheroma dangerous?
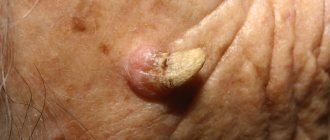
Multiple atheromas (atheromatosis) are not as dangerous as inflammation and suppuration of a single epidermal cyst. Suppuration is the only complication that can arise as a result of its infection with bacteria. This happens when a person tries to squeeze out the contents of the atheroma or accidentally injures it.
Inflammation can develop in one of two ways:
- Septic. After infection attaches, the cyst grows faster (in a day or two it increases to the size of a plum). The skin over it becomes tight and red. A few hours after infection, the festering atheroma becomes swollen and painful when pressed. The pus makes it soft to the touch and hot.
- Aseptic. After mechanical impact, the atheroma becomes swollen and painful. Pus does not form in it. After 2-3 days, the swelling subsides and the tumor stops hurting. But due to the inflammation that has occurred, the body encloses the contents of the cyst in a durable shell of connective fibrous tissue. Sometimes such a capsule does not have access to the surface of the epidermis.
Infectious atheroma can break through on its own, but it is better to prevent this.
Squeezing out an epidermal formation at home, even if we are talking about a painless small atheroma, in 100% of cases leads to the resumption of the pathology. This is due to the fact that the cyst capsule remains under the skin and does not stop producing sebum, gradually filling with it.
If the cyst bursts and its contents spill into the subcutaneous tissue, the purulent-inflammatory process will spread to adjacent areas of the skin and provoke an abscess. Treatment of this condition will be long-term and will require the use of hormonal and antibacterial drugs.
Diagnostics
An epidermal cyst is diagnosed after an external examination. For unclear etiology, the following is prescribed:
- ultrasound examination of the tumor - the presence of a cavity and its size are determined;
- Magnetic resonance imaging - required in rare cases of cyst localization.
After examination and detection of rapid growth or large size of the tumor, the lesion is eliminated through surgery. After removal, a mandatory histological examination is carried out.
When making a diagnosis, differentiation is made from lipomas, hydromas, paronychias, adenophlegmons and dermatofibromas.
Treatment of epidermal cyst
An epidermal cyst cannot be eliminated mechanically. If the lesion is squeezed out, after a while it forms again in the same place. To prevent relapse, the tumor should be surgically removed along with the capsule.
If the cyst is severely inflamed, treatment will be as follows:
- eliminate the inflammatory process;
- conservative therapy.
The purulent inflammation is opened with drainage; only after the wound is cleansed and healed is it possible to remove the capsule to prevent the risk of blood poisoning.
The operation is performed with local anesthesia and can have the following types:
- traditional surgical removal;
- use of laser;
- radio wave technique.
Classic surgical removal involves cutting the skin over the cyst. The surgeon, using a special clamp with a gauze swab, carefully peels off the surrounding tissue from the cyst and removes the lesion along with the capsule. Stitches are then applied.
The following techniques are used to eliminate pathology with laser:
- Photocoagulation. Applicable for cyst diameters of no more than 5 mm. It is removed along with the capsule without suturing. During healing, a crust forms, which disappears at the final stage.
- Excision with capsule. Prescribed when the tumor is from 0.5 to 2 mm. Removal is similar to surgery, but a laser is used instead of a surgical instrument. The wound heals quickly.
- Vaporization of the capsule. The procedure is performed with a tumor larger than 2 cm.
It is worth undergoing treatment in a high-quality clinic with modern equipment and experienced staff.
Treatment of sebaceous cysts
A reliable method of treatment to get rid of cavity formation is removal of a cyst on the face or body. None of the other methods of treatment - medication, non-traditional method - will eliminate the pathology forever and cannot guarantee relapse. Even if improvements occur, the formation may form again after a certain amount of time.
Emergency surgery is performed when an inflammatory process or suppuration occurs. At the first signs of inflammation, it is necessary to go to surgery to immediately excise the cystic formation and prevent complications.
In the absence of inflammatory processes and pus, the cyst is operated on as planned.
The main task of surgical intervention is to remove the formation, cleanse its cavity, and destroy its tissues.
Basic surgical methods for treating uncomplicated atheromas
| Method of removing cystic formation | The essence of the method | Advantages of this method |
| Conservative surgical excision | This operation is performed using a scalpel, which makes a skin incision at the site where the sebaceous gland tumor forms. The size of the formation determines the length of the incision. Then it is removed and completely removed. The wound bed is sutured with non-absorbable sutures, which are subsequently removed by the doctor. |
|
| Laser exposure | The laser evaporates the affected tissues and the contents of the cavity layer by layer. The targeted effect ensures that there is no trauma to nearby tissues. The most common way to destroy epidermal cysts in children. The operation time is minimal. |
|
| Exposure to radio waves | Radio wave exposure affects only the affected tissues of the formation. Healthy tissue areas located nearby are not damaged. After radio wave surgery, the risk of inflammation is minimal. Tissues heal and are restored quickly due to the sterilizing effect of radio wave exposure. | |
| Electrocoagulation | The cystic formation is destroyed by exposure to alternating current. The neoplasm is burned off, leaving a small crust in its place that cannot be torn off to avoid infection. The healing process takes about 7-10 days, after which it will fall off on its own. | |
| Argon plasma coagulation | Destruction is carried out using a special tool - a scalpel with a directed plasma beam. It has a targeted effect on the formation of the sebaceous gland without damaging nearby healthy tissue. Simultaneously with the destruction, the vessels are cauterized, which qualitatively sterilizes the damaged area and reduces the risk of inflammation to zero. |
|
Regardless of the method used to destroy the formation of the sebaceous gland, its elimination is performed under local anesthesia.
Elimination of an inflamed sebaceous cyst
The operation process is similar to the removal of uncomplicated atheroma. An important difference is the final stage of surgery. When removing an uncomplicated sebaceous gland cyst, the surgeon tightly sutures the edges of the wound bed so that there are no cavities left, the process of fusion of the edges of the incision and tissue healing occurs faster.
The final stage of excision of the inflamed cystic formation requires a different approach. Regardless of the method of destroying the atheroma (laser, scalpel, argon), the wound bed should remain open. The wound is treated with an antiseptic solution, a special graduate is placed inside, and an aseptic bandage is applied.
Possible complications
An atheroma or epidermal cyst can transform from a benign tumor to malignancy. There is a high risk of wound infection if you try to get rid of the pathology yourself.
Suppuration of the tumor is dangerous - without disinfection, the inflammatory process can worsen. Large cysts on the head often cause vision problems and regular headaches.
For prevention purposes, you should carefully monitor your personal hygiene, use high-quality cosmetics, visit beauty salons and clean your pores, and consult a specialist in a timely manner.
What to do
If you think you have an Epidermal cyst
and the symptoms characteristic of this disease, then doctors can help you: therapist, surgeon, dermatologist.
We wish everyone good health!
Diseases with similar symptoms
Median neck cyst (overlapping symptoms: 2 out of 5)
Median neck cyst is a rarely diagnosed congenital malformation. It is characterized by the appearance of a neoplasm with liquid content in the neck area. There are lateral and medial pathologies of the neck. The lateral forms are recognized immediately after the birth of the child, while the middle ones can appear as the child grows. Most often, the formation can be eliminated through surgery, which is performed in adults and children.
Did you like the article? Share with friends on social networks:
What is atheroma
Externally, atheroma is a moving ball in the upper layer of the skin. Inside is a capsule filled with sebum. Subcutaneous cysts appear most often in areas of the skin with a large number of sebaceous glands. The only condition for the formation of atheromas is the blockage of the ducts of the sebaceous glands, through which sebum exits to the surface of the epidermis. As soon as a blockage occurs, the secretion begins to accumulate inside the duct and stretches it. In response to this, the skin's immunity, in order to stop the pathological process, encloses the accumulated secretion along with the walls of the duct in a capsule of connective tissue.
To remember what an epidermal cyst looks like and not mistake it for a malignant tumor, it is enough to pay attention to the shape of the subcutaneous formation (it is round) and such a feature as the presence of an excretory duct.
If an epidermal neoplasm appears as a result of trauma (scratches, abrasions), then it is characterized by a higher density. This is due to the fact that epidermal cells enter the sebaceous gland duct. They mix with sebum, but do not stop producing keratin. The resulting mixture, due to its thickness and viscosity, cannot reach the surface of the skin, resulting in a blockage of the sebaceous gland duct. Such atheromas can grow to the size of a chicken egg, since inside their capsules they continue to produce substances necessary for the functioning of the skin, but in this case useless.