Pemphigoid is a chronic dermatological disease that is presumably autoimmune in nature (the exact causes of development have not yet been established). It is characterized by the appearance of subepidermal tense blisters on the surface of the skin and mucous membranes. The rashes are localized mainly on the chest, abdomen, and limbs. Their sizes can be different (depending on the form of the disease). Diagnosis of pemphigoid includes an external examination, assessment of clinical manifestations, biopsy and histology of the affected tissue. In addition, the doctor may prescribe immunological tests. Treatment of the disease is complex. Corticosteroids and immunosuppressive drugs are prescribed. In addition, local treatment is also indicated to prevent secondary infection. The disease responds well to therapy, but the drugs will have to be used for a long time to avoid relapse.
…
Treatment
Treatment for pyoderma usually depends on the direction and depth of the disease. It could be:
- local therapy;
- antibacterial agents;
- increasing immunity.
In some cases, the patient may undergo surgery. In others, it is recommended to turn to folk remedies.
You can’t start with folk remedies - only a doctor can determine how serious the disease is.
Medication methods
Local therapy is carried out if pyoderma has affected only the epidermis. Before resorting to it, the pustules are opened, the purulent contents and dead tissue are removed. Afterwards are used:
- Salicylic acid in the form of an ointment. Prevents inflammation, inhibits bacterial growth, softens the skin. It is used twice a day - the affected area is lubricated and covered with a sterile swab, also soaked in ointment.
- Zelenka. Prevents the proliferation of streptococci and staphylococci. Apply to the affected areas pointwise.
- Fukortsin in the form of a solution. Prevents the proliferation of pathogens, fights fungal infections, which is useful if they accompany pyoderma. Apply three times a day to affected areas.
- Triamcinolone cream. Prevents inflammation and allergies. Apply to affected areas three times a day.
- Hyoxysone in the form of an ointment. Suppresses inflammation and allergies, prevents pathogen proliferation, and relieves itching. Apply twice daily to affected areas.
Antibiotics are used if ointments and creams have no effect. In mild cases, tablets are used, in more serious cases, intravenous injections are used.
- Cephalexin. 500 mg every 6 hours, half an hour before meals.
- Cefazalin. Intravenously 3-4 times a day.
- Cefotaxime. Intravenously 2 times a day.
- Doxycycline. 200 mg per day, take with plenty of liquid.
Only a doctor can prescribe antibiotics after a microbiological examination, when it becomes clear which of them the pathogen is sensitive to.
If the course of the disease is chronic, with frequent relapses (at least once every 3 months), the doctor may prescribe immunotherapy, which will result in the production of specific immune cells that can fight back against a specific bacterium. Staphylococcal toxoid, dry staphylococcal vaccine, streptococcal bacteriophage and other drugs can be used.
In rare cases, surgery may be used in cases where other treatments do not help. It is most often used when working with boils and carbuncles, and proceeds sequentially:
- local anesthesia is used;
- the wall of the abscess is pierced with a sharp scalpel, the cavity is opened;
- dead tissue is removed;
- Anti-inflammatory drugs are placed into the cavity, and a bandage is applied on top.
It is categorically not recommended to carry out a similar surgical intervention at home - there is a high probability of serious complications.
Traditional methods
Folk remedies are used only if recommended by a specialist and only if the patient has one of the mildest forms of pyoderma. Apply:
- Dandelion infusion. Add 2 teaspoons of dried flowers and roots to a glass of warm water, leave for 8 hours and drink half a glass before meals.
- Celandine ointment. Mix dry celandine and sunflower oil and lubricate the affected areas of the skin.
- Poplar bud ointment. Grind the buds, mix with oil, leave for a day. After boiling, cool and apply to the affected areas three times a day.
The skin on which the products are applied must be clean and dry.
Affected Populations
PD is a rare disease that affects men and women in equal numbers. The disease mainly affects older people, with an average age of about 80 years. However, cases in infants and adolescents have also been reported.
Recently, scientists have learned about the connection between PD and neurological disorders. It is reported that between a third and half of all patients with the disease have neurological diseases such as dementia, Parkinson's disease, stroke, epilepsy and multiple sclerosis. These diseases usually occur before the onset of bullous pemphigoid.
Pyoderma - photos, treatment and symptoms
All pyoderma differ significantly in symptoms, prognosis and treatment. The clinical picture depends on the pathogen, localization and severity of inflammation, etc.
Ostiofolliculitis
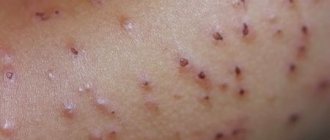
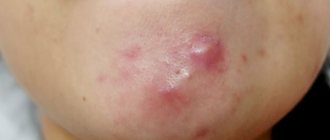
With the development of ostiofolliculitis (Bockhard's impetigo), the appearance of pointed, small, yellowish-white pustules with a hair in the center is noted. In this case, the inflammatory process develops at the mouth of the hair follicles.
A characteristic halo of hyperemia (redness) forms around the purulent pustule. This type of pyoderma most often develops in men in the area of the beard or mustache (pyoderma on the face is quite common). This pyoderma is rare on the skin of the body and around vellus hair.
This pyoderma practically does not occur in children before puberty.
Spontaneous opening of the pustule is usually observed by the third or fourth day. There are no scars left.
Folliculitis
Folliculitis is characterized by the development of acute inflammatory damage to the hair follicles. In this case, a red, dense, painful infiltrate appears around the inflamed follicle. Over the course of several days, a pustule forms in the center.
After five to seven days, the pustule gradually dries out with the formation of yellowish crusts.
In some cases, purulent melting of the inflammatory infiltrate with the appearance of a scar is possible.
Staphylococcal pyoderma: photo of facial skin lesions
Vesiculopustulosis
With this type of pyoderma, a purulent-inflammatory process affects the mouths of the merocrine sweat glands. This pyoderma is registered more often in children than in adults. In most cases, the development of this pyoderma in children is preceded by prickly heat.
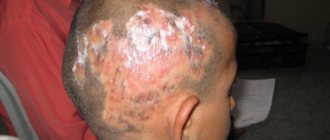
The rashes are initially single, small, bright red. Subsequently, the formation of a pustule is observed in the center of inflammation. Most often, the rash is localized on the torso, scalp and skin folds.
In children with immunodeficiency conditions, without timely medical care, the inflammatory process can quickly spread, leading to the occurrence of abscesses and phlegmon. In severe cases, the disease may be complicated by sepsis.
Photos of pyoderma in children
Epidemic pemphigus (pyococcal pemphigoid) of newborns
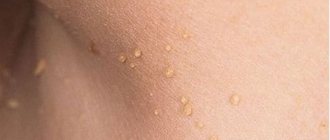
Symptoms of this pyoderma in children develop within 3-10 days after birth. The appearance of flaccid blisters (phlyctena) of various sizes on the skin is noted. The contents of the conflict are cloudy, the formations themselves are surrounded by a halo of inflammatory redness.
Subsequently, the contents of the conflict quickly fester. The flicten tire is very thin and breaks easily, leading to the appearance of erosive surfaces. Crust formation is not typical.
The period of rash can last from several days to several weeks.
An increase in temperature, lethargy, tearfulness of the child, refusal to eat, etc. are also noted.
Pyoderma in newborns - photo of the skin
Types of disease
This group of diseases includes blistering dermatoses that are not accompanied by acantholysis, a pathological process in the spinous and granular layers of the epidermis.
Types of pemphigoid:
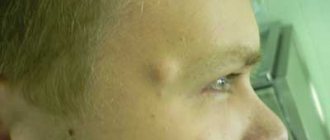
- scarring. This type of pemphigoid primarily affects the mucous membranes (conjunctival membrane, tonsils, uvula, soft palate). Women are more susceptible to pathology than men. People over 50 years of age are at risk. Bubbles appear in the same places, which leads to atrophic scar changes on the mucous membrane;
With cicatricial pemphigoid, the vesicles are localized on the conjunctiva of the eyes, in the oral cavity
- bullous (Lever's pemphigoid). The main place of dislocation of vesical elements is the limbs and torso. The oral mucosa (cheeks, border of the hard and soft palate) is affected in 30% of patients. The disease affects only the top layer of skin. The rash is painful and accompanied by itching. Inside the blisters there is a clear liquid (sometimes mixed with blood);
- benign non-acantholytic pemphigus. It affects only the oral mucosa and is characterized by a chronic course;
- juvenile This is pemphigoid, which occurs in childhood;
- gestational. This is a fairly rare autoimmune pathology observed during pregnancy and in the early postpartum period. In 90% of women, the first elements of the rash appear in the navel area. Subsequently, the rash spreads to other areas of the abdomen, thighs, and hands;
Gestational pemphigoid is a rare autoimmune disease in pregnant women.
- staphylococcal (pyococcal). Characterized by rapid and significant spread of bubbles. The causative agent of the disease is Staphylococcus aureus. The disease affects newborns in the first days of their life. The carrier of the infection is medical personnel and mothers of babies.
Video: all about bullous pemphigoid
Symptoms of pyoderma
Strepto- and staphylococcal pyoderma develops according to the same pattern:
- The bacterium penetrates the layers of the epidermis and begins to secrete exotoxins.
- To neutralize the microorganism, leukocytes and macrophages are sent to the pathological area - cells that neutralize foreign bodies.
- Due to massive infestation or weakened immunity, bacteria are not destroyed. Small blisters (phlyctenas, pustules) with purulent contents form.
- Nonspecific symptoms of intoxication progress.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the location of the skin lesion.
General symptoms of pyoderma:
- The appearance of pustular elements on the corresponding area of the skin.
- Itching or pain in the affected area.
- Redness.
- Local increase in temperature. Sometimes, with massive skin lesions, fever progresses.
- Weakness, fatigue.
- Formation of erosions, ulcerations.
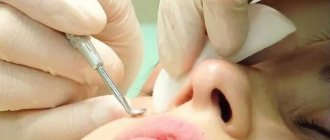
The streptococcal or staphylococcal form of bacterial infection of the facial skin is additionally accompanied by a visual defect, which causes moral discomfort for the patient.
The combination of coccal flora with fungi or bacteria is accompanied by the appearance of additional symptoms. A film may appear over the affected areas, and allergy symptoms develop in parallel.
Regression of the disease is accompanied by a gradual decrease in the number of pathological skin elements. At the sites of pustules, zones of increased pigmentation and peeling are formed, which disappear without a trace within 1-3 weeks.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of Bullous Pemphigoid or Cicatricial Pemphigoid is made on the following grounds.
1. Inspection: pemphigoid has a characteristic localization and a typical high density of blisters.
2. Skin biopsy, according to which the following is carried out:
- conventional microscopy: acantholysis is excluded (loss of communications between the spines of cells of the spinous layer);
- immunofluorescence microscopy, which allows the dermatologist to see the glow of the skin in the area not of the spinous layer, but of the basement membrane;
- immunoelectron microscopy: gold labeling of immunoglobulins is used, after which its location is studied;
- method of immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation.
Combined medications for the treatment of pyodermatitis in adults
The following combination medications can be used to treat pustular skin rashes:
- Fucicort is a cream that reduces the severity of inflammatory manifestations (redness, pain, swelling). The antibiotic contained in the drug, interacting with the skin, helps suppress the growth of pathogenic microorganisms;
- Hyoxysone is an ointment whose mechanism of action is aimed at weakening allergic and inflammatory reactions, which can occur as a complication of pyodermatitis. The drug has an antipruritic effect. The duration of the course is selected individually;
- Lorinden S is a cream for external use that has an anti-inflammatory effect, reduces the severity of allergies, and also suppresses the growth of staphylococcal and streptococcal infections. After applying the cream, a special bandage is applied to the skin, which must be changed once a day.
Causes of pemphigoid
Why this disease develops is not known exactly. It is believed that pathology can occur due to:
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- taking certain medications: Penicillin, Furosemide, 5-fluorouracil, Salazopyridazine, Phenacetin, Potassium iodide, Ciprofloxacin, Amoxicillin or even Captopril;
- tumor process of any localization (therefore, when making a diagnosis of “Bullous pemphigoid”, doctors search for cancer in all possible localizations).
How to treat pyoderma?
Complex treatment is prescribed only by a dermatologist. Therapy can be etiological, pathogenetic and symptomatic. For mixed forms of pyoderma, treatment can be outpatient or inpatient, which is determined individually, based on the severity of the clinical manifestations characteristic of each specific case.
- In the affected area, the hair is carefully trimmed, but not shaved, to prevent the spread of pathogenic microflora to healthy areas of the skin. In case of extensive damage to the skin, the patient is prohibited from performing water procedures: contact with water, if the disease is acute, is extremely undesirable. The epidermis around the affected area is treated with alcohol solutions of aniline dyes and disinfectants. Solutions of salicylic acid and potassium permanganate have a good effect.
- Although contact with water should be minimized, washing your hands daily is essential. After this, the nail plates should be treated with a 2% iodine solution to prevent the spread of infection. Several times a day, it is necessary to thoroughly wipe healthy areas of the skin with a damp sponge.
- Nutrition is of great importance. Throughout the entire course of treatment, it is necessary to follow a dairy-vegetable diet, giving up simple carbohydrates, alcohol and extractives.
- In the presence of concomitant diseases, symptoms of intoxication or exhaustion, or in case of a protracted course that threatens to become chronic, antibiotic therapy is carried out. Before prescribing specific drugs, a bacterial culture and antibiogram is performed. In this case, antimicrobial agents of the penicillin series are practically not used. Instead, patients are prescribed macrolides or tetracyclines. But Erythromycin and Tetracycline are not used in the treatment of children and pregnant women.
- If several pathogens are detected at once, combined antimicrobial drugs, as well as cephalosporins, are prescribed. They have a wide spectrum of action and are resistant to any changes in the bacterial microflora in the patient’s body. The course of therapy is usually 7 days. The dosage is prescribed by the doctor for each patient individually. Sulfonamide drugs are considered ineffective for pyoderma, but if the patient is intolerant to other antibiotic drugs, Sulfamethoxazole can be used in combination with Trimethoprim, or Sulfonomethoxime in the required dosage.
- Specific immunotherapy in combination with antibiotic treatment gives positive results in sluggish or chronic cases.
- During inpatient treatment, the patient is administered toxoids, specific antigens or staphyloprotectins. Manipulations are carried out twice a week. Method of administration: subcutaneous.
- To stimulate the nonspecific human immune system, autohemotransfusion, transfusion of individual blood components, and ultraviolet irradiation of blood are performed. It is also advisable to use methyluracil and alcoholic extracts of Schisandra or Eleutherococcus. They also improve the functioning of the immune system.
- In the presence of immune failures, immunostimulating drugs from the thymus group, gamma globulins, and stimulators of interferon production are prescribed. Vitamin therapy is carried out for all types of pyoderma.
Prevention recommendations
Prevention of pyoderma has recommendations that are common to any age category; it’s just that special attention should be paid to it in relation to young children.
- It is necessary to prepare in advance for the fact that a newborn baby will have to deal with evil microbes at birth. To do this, you should follow the recommendations of the doctor managing your pregnancy, undergo examination for IUI and their treatment according to the timing. It seems strange to many women that it is mandatory to sanitize the oral cavity before giving birth, however, even a single carious tooth in the mouth can serve as a source of microbial infection for the baby (especially if delivery is carried out using a cesarean section). Chronic microbial lesions in the throat with frequent sore throat and in the nose are also dangerous.
- The umbilical wound of a newborn is an entry point for infection, so it is necessary to carefully follow the instructions for caring for it until complete healing: carry out antiseptic treatments, make sure that the diaper does not cover this area. In modern pediatric practice, it is not recommended to treat the navel with dyes: although brilliant green has good antiseptic properties, you may not notice the first signs of inflammation under the painted surface.
- At the height of the disease, you should not bathe the baby; water can cause autoinoculation, that is, the transfer of the pathogen to healthy areas with subsequent infection. It is necessary to carry out local hygiene of contaminated areas, the area under the diaper, while avoiding contact with water on the source. If the affected area is located on the child’s genitals, then after washing this area, an antiseptic should be immediately applied.
- Bedding should always be clean, cloth diapers and clothes must be ironed on both sides at least until the first month of life.
- Avoid overheating. In hot weather, under warm clothing, harmful microbes multiply especially readily.
- The child must have individual towels and personal hygiene items.
- Germs can be transmitted through toys, so you should wash and wash them as often as possible. If for some reason you are hospitalized with your child, then you should not take soft toys with you, as hospital-acquired infections can persist for a long time on them.
- The baby's nutrition should be complete, breastfeeding is optimal to strengthen the immune system, but if this is not possible, then you should carefully choose a substitute for human breast milk.
- Treat any skin damage with an antiseptic. A mosquito bite or a small scratch is enough for an infection to develop.
- It is not necessary to strive to create sterile conditions around the child; one way or another, he needs to become familiar with the dangers of the outside world, but in doses and not all at once. Maximum cleanliness is needed during the active phase of the disease, and if the baby is healthy, it is enough to carry out proper cleaning and hygienic care.
Types and symptoms of pyoderma
Depending on the causative agent of the disease, two types of pyoderma are distinguished - staphyloderma and streptoderma.
The causative agents of staphyloderma are staphylococci. This type of pyoderma is characterized by rashes in the area of hair follicles, sweat glands and sebaceous glands. Symptoms of this type of pyoderma are the formation of hemispherical or conical abscesses with thick walls, the center of which is often penetrated by hair. Green-yellow thick pus is released from the abscesses. There are the following types of staphyloderma.
1.Ostiofolliculitis. Small follicular rashes of pustules (vesicles with pus) with purulent heads are localized on the face, arms, torso, and legs. After 4-5 days, the pustules turn into crusts, which, falling off, do not leave scars.
2.Folliculitis. With this type of pyoderma, the hair follicle itself becomes inflamed. Pustules with greenish-yellow contents form on the forearms, thighs, and back of the hands. The pustule dries out after a week, forming a yellowish crust.
3.Folliculitis is deep. A symptom of this type of pyoderma is painful rashes. The rashes look like pustules with a diameter of about 1.5 cm. If the rashes spread widely, the patient’s general condition worsens.
4. Superficial folliculitis. Characterized by pustules containing greenish-yellow pus. In the areas of the rash, mild pain occurs, which disappears after the ulcers are opened. But the general condition of the person remains satisfactory.
5. Epidemic pemphigus of newborns. Pyoderma, which affects newborns in the first week of life. The entire surface of the skin, except the palms and soles of the feet, is affected by multiple blisters of different sizes. Over time, the bubbles dry out, forming a thin crust. There are known cases of severe disease leading to death.
6. Sycosis vulgar. Pyoderma, which most often affects men. Damage occurs to hair follicles in the mustache, beard, and sometimes pubic area.
7. Furuncle. This type of deep pyoderma is characterized by purulent and necrotic inflammation of the hair follicle and the tissues surrounding it. Common locations for boils are the cheeks, nose, shoulders, neck, buttocks and thighs. With multiple boils, the general condition of the patient worsens significantly.
8. Hidradenitis. A type of pyoderma that is a severe purulent inflammation of the sweat glands under the armpits or in the groin. It is caused by staphylococci, which enter the sweat gland through microtraumas of the skin. The disease is accompanied by malaise, pain, and fever.
9.Carbuncle. Pyoderma is formed by purulent, necrotic inflammation of several hair follicles at the same time. At the same time, cellular elements mixed with lymph and blood accumulate in the tissues. The patient has a serious condition caused by severe intoxication of the body.
The causative agents of streptoderma are streptococci. Most often the disease occurs in children and women. The following types of pyoderma of this type are distinguished.
1.Streptococcal impetigo. It is a superficial non-follicular cystic formation, which is filled with purulent-serous contents. Most often it affects a person's face.
2. Ecthyma vulgar. A deep ulcerative form of pyoderma that heals over quite a long time.
3. Ringworm of the face. The disease is an atypical form of pyoderma. Often occurs in children's groups.
4. Erysipelas. The main symptom of this type of pyoderma is the superficial nature of the process and a clear demarcation of the marginal zone.
5. Dry streptoderma. This disease is typical for children and adolescents. Symptoms of pyoderma include the formation of one or more red-pink spots covered with flour-like small scales. The rash is usually localized on the skin of the extensor surfaces of the extremities.
Clinical signs
In the initial stage of the disease, symptoms are often nonspecific . Patients experience itching of varying intensity, sometimes there is redness on the skin, swelling and minor rashes, which can persist for a long time (up to several months). The bullous stage is characterized by the development of blisters on reddened or visually healthy skin. The blisters contain clear, sometimes blood-laced, fluid. The lesions are symmetrical in nature and are located on the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, esophagus, and flexor surfaces of the limbs.
With bullous pemphigoid, the blisters can coalesce and affect large areas of the skin.
In the acute stage, the patient feels general malaise and loses appetite. With Lever's pemphigoid, the blisters last for several days and then spontaneously burst. In this case, erosive and ulcerative defects remain on the dermis, which heal after a few weeks.