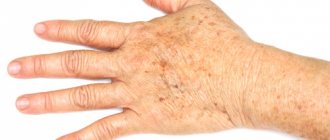
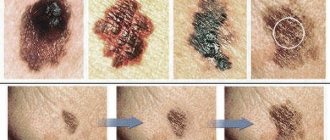
Among visitors to cosmetology clinics and dermatology offices, the number of patients with various skin pigmentation disorders, especially hyperpigmentation, has increased significantly.
…
Skin hyperpigmentation is a disorder of melanin formation in the form of excessive synthesis of melanin pigment. As a result of its deposits, spots of different colors, shapes and quantities are formed on different parts of the body. Is it possible to remove pigment spots with laser?
Why do age spots appear on the face?
Special skin cells – melanocytes – are responsible for the color of each person’s skin. If they do not function correctly, age spots appear on the epidermis, which have several forms:
- ephelides (freckles);
- chloasma (hormonal);
- lentigo (senile);
- melasma (common);
- nevi (moles);
- wine (vascular).
There are many factors that provoke age spots - the reasons for their appearance on the face:
- genetic predisposition;
- ultraviolet irradiation;
- age-related changes in the body;
- hormonal disbalance;
- diseases of the digestive tract;
- taking certain medications;
- use of photosensitizing cosmetics;
- deficiency of vitamins C and PP;
- excessive or aggressive skin care;
- pathologies of the kidneys and urinary system;
- liver diseases;
- endocrine disorders;
- cardiovascular lesions and others.
General information about pigmentation
Age spots are nothing more than a change in the normal color of the skin of certain areas of the face and body. The occurrence of formations of this kind is due to the presence in the human body of a unique pigment - melanin. It is on its quantity that the local change in the color of our skin depends. The catalyst for such a process can be:
- excessive exposure to ultraviolet radiation (frequent visits to the solarium or regular sunbathing);
- natural age-related changes;
- hormonal changes in the body;
- use of low-quality cosmetic products.
Is it possible to remove pigment spots with a laser?
Using the technology in question, any type of excessive coloration of skin areas is eliminated. Whether the laser completely removes pigment spots depends on the depth of melanin. Surface defects disappear after 1-2 sessions. For more serious cases, 1-3 courses of 8-10 manipulations are required at intervals of at least 20 days. This is a long and expensive treatment, but so far no other therapy produces such an effect as laser pigmentation removal; before and after photos confirm its effectiveness. The final results are shown on already healed skin.
Why choose laser to treat hyperpigmentation?
Today, the laser method of treating hyperpigmentation is the most common and effective. The following advantages of using a laser are highlighted:
- Possibility to vary the intensity and duration of the pulses.
- Complete absence of scars or serious injuries after the procedure.
- No recovery period. After the procedure, the patient can live a normal life, only by following some post-procedure recommendations.
- Possibility of treating absolutely any area of the skin.
What laser is used to remove pigment spots?
There are several types of devices used to correct this facial problem. A specialist can suggest the following laser against age spots:
- fractional;
- alexandrite;
- neodymium;
- ruby.
Fractional laser pigmentation removal
The essence of the operation of this type of device is a selective effect on the skin of the face. This anti-pigmentation laser destroys only cells that excessively produce melanin. Healthy tissue remains intact, which ensures rapid recovery of damaged areas. To remove a pigment spot on the face with a fractional laser, you do not need to burn the upper layers of the epidermis around the defect. The beam forms from 100 to 1100 microzones on every square centimeter of skin, penetrating to a depth of up to 1.5 mm.
Removal of age spots with alexandrite laser
The described device is an optical long-wave quantum generator. Removal of pigment spots using a laser with an alexandrite emitter occurs by heating the melanin. Under the influence of high temperature it is completely destroyed (evaporates). Removal of age spots on the face with a laser of this type occurs as quickly as possible. The Alexandrite emitter acts only on melanocytes, without affecting healthy skin with normal coloring.
Removal of age spots with neodymium laser
The main feature of this device is its ability to heat not only melanin, but also oxyhemoglobin. Thanks to this, neodymium laser pigmentation removal allows you to get rid of all types of spots on the face, including vascular formations. The beam of the device is not scattered, it affects only the desired areas without damaging healthy tissue. The neodymium device belongs to the group of the most powerful devices. Its radiation penetrates to a depth of 8 mm.
Ruby laser pigmentation removal
This type of equipment is rarely used in the treatment of the described defects. Removing pigmentation with a laser based on a ruby crystal is fraught with discoloration of healthy areas of the skin. Such a device “does not see” the difference between the pathological and normal content of melanin in cells, so it evaporates it regardless of the concentration. Removing age spots on the face with a laser of this type is almost never practiced. Sometimes one of its forms (Q-switched) is used for very fair-skinned patients.
Pigment disorders are one of the most common types of dermatoses - in some populations, the percentage of people with such defects reaches 60%. This can be either hereditary or acquired darkening or lightening of skin areas, and even dyschromia of unusual color. Most pigment defects are associated with qualitative or quantitative disorders in the production or deposition of melanin, however, abnormal variations of other endogenous pigments are also found, and in some cases, even the deposition of exogenous pigments can lead to dyschromia (read our material about argyria). However, it is certainly defects associated with excess melanin deposition that make up the bulk of pigmentary disorders.
Today, lasers and intense pulsed light (IPL) sources are becoming increasingly popular in their correction. Sometimes they are considered almost a magical tool that can remove any type of damage. However, effective and safe removal of pigmentation is not possible with any device, and in order to choose them, you need to understand the peculiarities of the interaction of laser radiation with the skin and its chromophores. It is also necessary to take into account the main pathophysiological processes leading to this particular pigment disorder, as well as the types and location of pigments in the skin. Experts from the European Society of Laser Dermatology analyzed nearly 1,000 studies and articles published from 1983 to April 2021 and formulated a Position Statement regarding the correction of various types of dyschromia using lasers and IPL devices.
Types of lasers for correcting pigment defects
The principle of light therapy for pigment defects is based on the concept of selective photothermolysis. It lies in the fact that melanin, like other skin chromophores, is able to absorb certain wavelengths more intensely than the structures surrounding it. Ideally, "pigment" lasers should generate radiation that is absorbed only by melanin, with minimal absorption by hemoglobin or water. However, the absorption spectrum of melanin overlaps with the absorption spectrum of these chromophores. The range between 630 and 1100 nm is considered relatively selective for affecting melanin, where there is good penetration of radiation into the skin and preferential absorption of melanin compared to oxyhemoglobin.
The intensity of melanin's absorption of light energy decreases with increasing wavelength of radiation, but a longer wavelength allows it to penetrate deeper into the skin. At the same time, shorter waves (<600 nm) can damage pigment cells with relatively low energy, while longer waves (>600 nm) penetrate deeper, but require more energy to cause damage to melanosomes. Thus, it is not possible to achieve an isolated effect on melanin only by selecting the wavelength (optical selectivity).
Therefore, another task arises - it is necessary to deliver the maximum number of photons to the target chromophore before they are “captured” by competing chromophores that are located near the target. This is possible thanks to the optimal selection of pulse duration and radiation energy density.
Since melanin and the melanosomes containing it are very small, their destruction requires less prolonged heating than, for example, coagulation of blood vessels. It is believed that in order to achieve selective laser action, the pulse duration must be at least equal to, and ideally several times less than, the thermal relaxation time (TTR) of the target structure - the period during which the heated target dissipates about 50% of its heat, i.e. cools (thermal selectivity). Otherwise, it does not have time to cool down and significant heating spreads to adjacent non-target tissues, causing them thermal damage.
The TTR of melanosomes is 0.25 μs, and that of melanocytes is 0.1 μs; accordingly, for their effective and safe destruction, the duration of the laser pulse must be in the nanosecond and even picosecond range. In this case, the pulse energy must be high enough to destroy the target.
Taking this into account, the main lasers used to correct pigment defects are devices with Q-switched (QS) technology. This technology allows you to get very short and very powerful pulses. When they are absorbed, the target is instantly heated with rapid thermal expansion, leading to their explosion - a photoacoustic effect. Moreover, the shorter the pulse duration, the greater its severity, with a corresponding decrease in the thermal component. Currently, there are both nanosecond and picosecond Q-switched lasers, although the Q-switched prefix is usually used only next to nanosecond ones.
Intense pulsed light (IPL) sources can also be used with filters to target pigmentary pathology. In addition, for some purposes (for example, to enhance the penetration of depigmenting agents), conditionally non-selective, water-targeting lasers can be used, such as non-ablative Er laser with a wavelength of 1550 nm, ablative 2940 nm Er:YAG, ablative 10,600 nm CO2 laser and the later 1927 nm thulium laser.
Position of the European Society of Laser Dermatology 2019
As mentioned, experts analyzed nearly 1,000 studies and articles published from 1983 to April 2021. For many types of pigmented lesions, the level of evidence was low and was primarily based on anecdotal case reports with no further substantiation. Moreover, in most cases, post-treatment follow-up was very limited, making it difficult to draw conclusions about the long-term effectiveness of the procedures. Thus, some recommendations are based more on expert opinion. These limitations clearly highlight the need for controlled studies when evaluating laser therapy (when possible and compared with first-line treatments).
However, the analyzed information allowed the authors to create a whole list of recommendations on devices and parameters of their effects for the correction of various pigment defects - both epidermal, dermal and mixed. You can read more about them in the next issue of the journal “Hardware Cosmetology”, and now we present short conclusions on the optimal correction options for various types of pigmentary pathology.
- Actinic lentigo with a relatively small number of lesions - ultrashort nano- or picosecond QS lasers. It usually takes one to two sessions for the lesions to completely disappear.
- QS lasers are excellent for lentigo In the case of multiple lentigines, it is imperative to exclude a connection with systemic diseases before starting treatment.
- Freckles - due to the high content of pheomelanins, correction of ephelids is best done using QS 532 nm lasers. In this way, improvements can be achieved, but they are usually temporary and relapses are possible. Regular use of sunscreen is recommended to maintain results.
- Café au lait pigment spots are difficult to treat with lasers and have a high recurrence rate. Patients should be warned about the possibility of such outcomes. It is also possible to conduct a test session to predict the effectiveness of treatment.
- Linear nevoid hypermelanosis - QS lasers are effective with a small number of sessions, but it is unknown how long the effect will be.
- Spotted nevus (Naevus spilus) - can be effectively treated with QS lasers, but, unfortunately, relapses are not uncommon. The macular type responds better to treatment than the papular type.
- Becker's nevus (Naevus Becker) - excess hair growth on a nevus can be easily eliminated using long-pulse lasers, but the treatment of the hyperpigmented defect itself is much more difficult. Despite some successes, failures and relapses are common.
- Cutaneous hypermelanocytosis: Nevus of Ota, Nevus of Ito - the gold standard for the treatment of these pathologies are QS lasers with a wavelength of 1064 nm.
- Acquired dermal melanocytosis : including acquired bilateral nevus of Ota (ABNOM) - the diagnosis should be recognized by clinicians. QS lasers with a wavelength of 1064 nm are highly efficient.
- Congenital nevomelanocytic nevi - the use of pigment-specific QS, long-pulse and fractional lasers can improve the cosmetic appearance of this pathology. They can also be used as complex therapy.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) - Laser treatment can improve the appearance of PIH, but can also worsen or cause it to appear. Before using the laser on the entire affected area, it is recommended to conduct a test on a small area.
- Melasma - Experts believe that the gold standard treatment for melasma is still Kligman's triad. Laser treatment should only be considered after topical depigmentation agents and peels have failed. The most effective laser approach appears to be using wavelengths that target vascular components.
For non-melanogenic pigment defects:
- Drug-induced non-melanin hyperpigmentation - QS lasers are the best treatment option. They eliminate hyperpigmentation caused by drugs and metal salts. Cessation of exposure to the etiological factor is mandatory, if possible.
- Exogenous ochronosis - multiple sessions of QS lasers and/or fractional ablative lasers.
- Siderosis and hemosiderosis are effectively treated with several sessions of QS lasers.
- Seborrheic keratosis pigmentosa and papular nigra dermatosis - LP Nd-YAG laser (1064 nm) and ablative erbium laser.
Read more about the recommendations, as well as other interesting news regarding the use of lasers and other high-energy devices, in the upcoming issue of the Hardware Cosmetology magazine.
Sources:
- Halder RM, Nootheti PK Ethnic skin disorders overview. J Am Acad Dermatol 2003; 48: 143-148.
- Anderson RR, Parrish JA Selective photothermolysis: precise microsurgery by selective absorption of pulsed radiation. Science (New York, NY) 1983; 220:524-527.
- Calderhead RG, Vasily DB Low Level Light Therapy with Light-Emitting Diodes for the Aging Face. Clin Plast Surg 2016; 43(3): 541-550.
- Patil UA, Dhami LD Overview of lasers. Indian J Plast Surg 2008; 41(Suppl): S101–S113.
- Garden JM, Bakus AD, Domankevitz Y. Cutaneous compression for the laser treatment of epidermal pigmented lesions with the 595-nm pulsed dye laser. Dermatol Surg 2008; 34: 179-183.
- Passeron T., Genedy R., Salah L., Fusade T., Kositratna G., Laubach HJ, Marini L., Badawi A. Laser treatment of hyperpigmented lesions: position statement of the European Society of Laser in Dermatology. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2019; 33:987-1005.
Laser removal of age spots - contraindications
The cosmetic procedure is almost a surgical procedure, so in some situations it cannot be performed. Laser treatment of pigmentation on the face has relative contraindications, in which manipulation is not prohibited, but should be postponed:
- acute infections;
- pregnancy;
- breastfeeding period;
- relapses of chronic diseases;
- taking antibiotics;
- inflammatory processes and skin damage in the treated area;
- fresh tan;
- recent peeling.
Laser removal of age spots on the face is absolutely contraindicated in the following situations:
- oncological diseases;
- diabetes;
- immunodeficiencies;
- connective tissue pathologies;
- the presence of keloid scars in the laser impact area;
- rheumatoid arthritis;
- bronchial asthma;
- hypertension 3 degrees;
- epilepsy;
- severe mental illness.
Indications and contraindications for the procedure
The laser procedure is indicated in the following cases:
- the presence of age-related lentigines (pigment spots that appear in older people);
- photoaging;
- acquired pigmentation as a result of various factors;
- the presence of chloasma in pregnant women.
Contraindications:
- damage and injury to the skin;
- fresh tan;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- diabetes;
- presence of a cardiac simulator;
- infectious diseases;
- dermatological diseases;
- poor blood clotting;
- blood diseases;
- tuberculosis;
- age under 18 years;
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- oncology;
- taking certain medications that increase skin sensitivity.
Unfortunately, there are cases when it is almost impossible to eliminate brown spots on the face. Most often this occurs in diseases of the internal organs.
Consequences of laser pigment spot removal
Ignoring contraindications or performing the procedure incorrectly leads to dangerous complications. Removing age spots on the face with any laser carries the risk of thermal burns to the skin. If the specialist performing the manipulation incorrectly configures the device and selects too intense a force, the treated areas may be irreversibly damaged. Removing facial pigmentation with a laser in rare cases has the following consequences:
- tissue scarring;
- suppuration;
- acute inflammation of the epidermis;
- addition of a secondary infection;
- skin necrosis;
- damage to healthy tissue;
- hypopigmentation (excessive lightening of the epidermis);
- erythema.
To avoid complications after laser pigmentation removal on the face, it is important to adhere to the following skin care rules:
- Do not use decorative cosmetics for 3-4 days.
- Protect your face from sun rays for 2 weeks.
- Avoid thermal treatments, saunas or steam baths for the next 2 months.
- Moisturize the skin with a hypoallergenic cream.
- Avoid aggressive cosmetic manipulations on the face (peeling, scrubbing).
- Apply anti-inflammatory agents prescribed by a dermatologist.
Laser device FRAXEL (Fraxel)
The Fraxel installation was developed in the USA; the method is remodeling the surface of the skin. Under the influence of a laser, damaged micro-areas self-heal, regeneration and the production of natural substances are activated. The result will be clean, smooth skin without deep age-related changes and unaesthetic hyperpigmentation.
The impact is carried out by two fiber optic lasers - erbium and thulium, each of which generates waves of different lengths. Their synergy allows you to affect the deep layers, destroying old tissues, but without damaging the epidermis.
The beam directed at the area is fractionated, dividing into many ultra-fine beams. Depending on the indications, the doctor calculates the treatment area and the depth of impact.
The indications are:
- Elimination of stretch marks, scars, scars.
- Age-related changes, skin lifting.
- Pigment spots, post-acne marks, melasma.
- Unhealthy complexion.
- Warts, flat moles, papillomas.
There are a number of contraindications:
- malignant, benign neoplasms;
- dermatological diseases;
- herpetic infection in the active stage;
- epilepsy;
- diseases of the endocrine system, hormonal imbalance;
- pregnancy and lactation period;
- acute infections.
After the procedure, redness, slight swelling, and peeling may be observed. Complications disappear within 1-3 days after the session. The resulting effect after the course lasts up to 10-15 years.