The danger of infection with HPV type 16 in women is the high likelihood of subsequently developing a malignant tumor. The virus greatly reduces the body's protective functions. Whether HPV type 16 can be completely cured depends on the intensity of the lesion, the general health of the patient and human factors.
The papilloma virus is especially dangerous for women
What is HPV type 16 and symptoms?
Hpv 16 (papillomavirus) poses a threat to women; it develops against the background of cervical erosion and epithelial dysplasia - background conditions of malignant transformation of cells located in the epidermis. Men can also become infected, but they have a lower incidence of cancer complications.
HPV infection is characterized by clinical signs, which include the appearance of genital warts, flat condylomas in the area of the external and internal genital organs, in the vagina, near the anus or in the perineum.
Human papillomavirus type 16 rarely manifests itself as papillomatosis. It is characterized by epithelial dysplasia, pseudo-erosion and associated complications (colpitis, cervicitis), often found in gynecology.
Manifestations of pathology
The symptomatic picture manifests itself under the influence of external and internal factors: decreased immunity, the presence of chronic diseases, deterioration in the performance of the central nervous system, overheating, hypothermia.
Main symptoms:
- the appearance of papillomas in the intimate area: localized inside the vagina, uterine walls, labia,
- pain during sexual intercourse,
- bleeding after sexual intercourse,
- unpleasant-smelling vaginal discharge.
Papillomavirus is incurable. Once settled in the body, pathological cells remain there forever. Men are carriers of the disease and practically do not suffer from the manifestations of the disease. In women, the disease progresses and can cause the appearance of carcinogenic cells. On average, it takes 10 years for a condyloma to transform into a tumor.
Why is papillomavirus 16 dangerous?
Papillovarius type 16 is dangerous due to the presence in the DNA structure of special genes responsible for the synthesis of oncoproteins E6 and E7, which contribute to the malignant degeneration of growths. At the same time, the risk of malignancy is high.
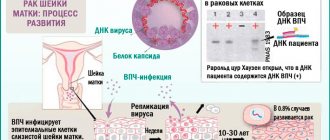
The danger is posed by the integrated form of the virus, when there are no clinical signs and the person is unaware of the infection. HPV type 16 DNA is integrated into the genetic apparatus of the host cell and the synthesis of viral proteins necessary to complete the assembly of new viral particles begins. Certain HPV genes control the process of cell malignancy. These include DNA fragments involved in the synthesis of early proteins E1-E7, necessary for regulating genome reproduction. E6 and E7 belong to a group of oncoproteins that can interact with important regulatory proteins of the host cell (pRb, p53). The pRb protein is an antioncogene that prevents frequent cell division and is responsible for the normal functioning of the hereditary apparatus. The p53 protein regulates cell cycle duration. Binding and disruption of their work by oncoproteins leads to cell degeneration, which is a key point in the development of endocervical neoplasia.
In addition to cancer and ectopia (erosion) of the cervix, HPV 16 can provoke the appearance of Bowen's disease.
Treatment and removal methods
All HPV treatment comes down to conservative and radical methods. The former are designed to help strengthen the immune system and restore the normal state of immune defense. The second relate directly to the removal of manifestations of the virus, that is, genital warts.
Possible drugs for treatment include:
- antiviral agents (Allokin-alpha, Panovir, etc.);
- immunomodulators (Interferon, Viferon, etc.).
Both of these groups of drugs help not only boost natural immunity, but also inhibit the virus, so that the growths stop reproducing.
Surgical methods for removing tumors are as follows:
- radio wave destruction;
- laser removal;
- cryotherapy;
- electrocoagulation.
[Show slideshow]
Both methods must be used together to achieve the best therapeutic effect.
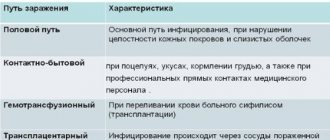
Routes of transmission of the virus
HPV type 16 can be transmitted through contact and household contact. The first route of transmission is through direct contact with the skin or mucous membranes of an infected person. This is facilitated by the presence of small cracks and injuries on the surface. The causes of infection are the following:
- sexual intercourse;
- constant change of partners.
During childbirth, there is a high chance that the baby will become infected. Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis and skin lesions develop. If a pregnant woman is infected, delivery via cesarean section is recommended.
The household contact route involves using the same hygiene products with an infectious person.
The infectivity of HPV 16 carriers increases with the appearance of condylomas. Viral particles mature in parallel with the process of differentiation of young epidermal cells. Upon reaching the stratum corneum, their final assembly and release from the cells by budding is observed. As a result, viral particles are located directly on the surface of the skin. Such areas are dangerous.
There is a possibility that the exfoliated cells of the keratinized epithelium will remain infectious.
Need advice from an experienced doctor?
Get a doctor's consultation online. Ask your question right now.
Ask a free question
Carrying out prevention
Prevention of HPV type 68 infection is based on preventing the virus from entering the body. Considering that the main route of spread is sexual, you should refrain from casual relationships. The virus is transmitted even through the use of a condom, oral intercourse, or kissing. Avoidance of early sexual contact by adolescents and strong family relationships greatly reduce the likelihood of infection.
It is necessary to adhere to the rules of personal hygiene. Be sure to wash your hands after using the toilet, especially public ones. You can sit down at the table only after thoroughly cleaning your palms. Do not bring contaminated fingers to your face or mouth. The family should have separate towels, washcloths, and toothbrushes for all members.
You need to behave with caution when visiting saunas, swimming pools, and beaches. One of the main methods of protection is a strong immune system. It responds to the penetration of the virus with antibodies that suppress it.
You should get enough sleep and try to avoid stress that depletes the body. Nutrition must be correct and balanced, with the amount of vitamins, microelements, and amino acids necessary for normal life. It is important to prevent the development of acute respiratory diseases and influenza. Chronic diseases require timely measures to prevent exacerbations. Alcohol abuse and smoking are unacceptable.
Incubation period
Symptoms of HPV type 16 disease appear after a long incubation period. The papillomavirus is capable of remaining latent in the layers of the epidermis for a long time. The incubation period ranges from several months to 2-10 years. In some cases, spontaneous elimination of the virus from the body occurs after several months (up to 2 years). The incubation period depends on the body’s resistance, that is, resistance to the influence of internal and external factors. There are a number of conditions that contribute to the transition of the infection to the active phase:
- violation of the barrier function of the integument (abrasions and other injuries);
- primary or secondary immunodeficiency;
- hypo- or avitaminosis, especially vitamins such as C, A, folic acid;
- bad habits;
- hormonal imbalances (pregnancy, menopause, endocrine diseases);
- concomitant sexually transmitted infections.
The disease may transition to a recurrent course, in which there is a possibility of intraepithelial neoplasia and the development of cancer.
Features of DNA virus symptoms
Features of the symptoms of the 68th strain of HPV depend on the stage of development of the disease:
- Stage I (initial) . Symptoms practically do not appear. In rare cases, papilloma may begin to form in the genital area.
- Stage II . The first characteristic signs appear - spiky growths of a whitish, flesh-colored or pink hue. Typical localization is the genital organ, urethra, anus.
- Stage III (dysplastic) . At this stage, the DNA of the pathogen actively changes the structure of cells. Koilocytosis develops. Many papillomas of different types appear - flat, raised, loose.
- Stage IV . As a result of the rapid progression of papillomas, carcinoma arises. A benign tumor transforms into a malignant neoplasm.
If in the first 2 stages the symptoms are limited to a visible manifestation, i.e. the appearance of warty growths, then at the next stages a pathological picture with the following signs is added:
- gastrointestinal dysfunctions with stool disorders (constipation or diarrhea);
- pain and discomfort during bowel movements;
- increased gas formation, flatulence;
- bloody vaginal discharge not associated with menstruation;
- noticeable weight loss;
- general weakness, fatigue;
- unpleasant odor from the vagina;
- pain during sexual intercourse.
These symptoms indicate the presence of a serious danger of malignancy of the formations. When the first such signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Diagnostic methods and interpretation of test results
To be diagnosed with HPV type 16, you need to seek help from a doctor (dermatologist, urologist or oncologist).
Diagnostic methods:
- visual;
- colposcopy;
- cytological examination;
- histology;
- immunocytochemical;
- DNA methods.
During the examination, the doctor examines the suspected areas of damage (internal and external genitalia, perineum, anus) for the presence of growths, and assesses the area of the lesion. Then he prescribes the appropriate tests. The disadvantage of the method is the inability to judge the nature of the course of the disease.
Colposcopy is a method that allows you to assess the condition of the mucous membrane of the cervix and vagina. Allows you to identify different types of epithelium, the presence of foci of keratinization, vascular patterns and perform an accurate tissue biopsy. However, it is impossible to determine areas of benign HPV infection type 16 or cervical dysplasia.
Dangers during pregnancy
Types 16 and 18 of papillomavirus are more threatening to the life and health of the mother, not her fetus. The unborn child develops in the same way as other children; there are no obstacles to the formation of internal organs. Intrauterine development of the fetus proceeds in accordance with the norm.
However, the presence of genital warts on the genitals of a pregnant woman can affect the health of the child after birth. While passing through the natural birth canal, the baby comes into contact with a viral growth, which causes it to become infected. And from birth, the child will become a carrier of a highly oncogenic type of virus, which can contribute to the development of a cancerous tumor.
Therefore, a pregnant woman must be diagnosed for the presence of papillomavirus and take timely treatment to avoid risks. If the problem is detected late, a cesarean section is usually recommended. This operation will help avoid unwanted consequences for the child and reduce the risk of infection.
How to live with HPV 16 to avoid cancer
If you have been diagnosed as a carrier of HPV 16, this does not mean that the disease will lead to oncology. It all depends on the body’s resistance. In some cases, spontaneous recovery occurs thanks to the immune system. Cancer develops only from a precancerous condition, which is severe dysplasia.
The primary task for cancer prevention is preventive examinations by specialists. Only constant monitoring of your health will allow timely treatment and avoid serious consequences.
Any form of dysplasia is reversible.
Monitor your immune system. It is necessary to lead a healthy lifestyle, eat rationally, and give up bad habits. Only immunity provides effective suppression of the reproduction of HPV 16 in the body and voluntary cure. It is important to understand that there is no specific therapy that can specifically target viral particles. Most antiviral drugs (isoprinosine, for example) are aimed at enhancing natural immune processes.
As for your personal life, your partner should also be examined. It is necessary to avoid sexual intercourse with a carrier of HPV 16.
Treatment methods
How to cure HPV type 16:
- remove all neoplasms,
- take a course of immunomodulation,
- use folk remedies to maintain immunity.
Removal of papillomas is a mandatory procedure at any stage due to the high risk of transformation of neoplasms into malignant tumors. The method of removal is determined in accordance with the location.
Removal of condylomas
Electrocoagulation, cryodestruction, laser treatment are carried out in the presence of papillomas on the skin of the labia, around the anus, and inner thighs. These methods ensure rapid healing of damaged tissues and do not leave scars.
During the procedures, deformed capillaries are fused, which reduces the risk of bleeding.
Neoplasms located on the mucous membranes and cervix are removed by radio waves. After the procedure, there are no scars or adhesions left on the reproductive organs, which makes it possible to use the method in the treatment of patients planning a pregnancy in the future.
Immunomodulatory therapy
How to treat HPV 16: you can carry out high-quality immunomodulation, including taking special medications and vitamin complexes. Infection in the body is suppressed by antiviral and immunomodulatory agents. They increase the body’s protective functions and prevent the disease from progressing.
Let's take a closer look at effective antiviral drugs for HPV 16.
- "Groprinosine", "Isoprinosine" - tablets designed to suppress the synthesis of the virus by damaging the genetic material. It binds to the ribosomes of body cells, changing their spatial orientation, which prevents the accumulation of pathological bodies. Increases the activity of monocytes, monophages that destroy foreign cells.
- "Allokin-alpha" - injections against HPV. Strengthen the immune system at the humoral and cellular level, increasing the performance of T-lymphocytes. Promotes the production of interferon in the body, regulates the performance of smooth muscle nerves. They can enhance the effects of histamine, oxytocin, and serotonin on the body.
- "Gepon" is a prophylactic drug for stopping relapses. Prescribed in courses for 1-2 months after the main treatment.
- "Epigen intimate" is a spray for treating the genitals. It is used in combination with injections, tablets, and for preventive purposes.
- Pure immunomodulators are used in conjunction with antiviral agents. Interferon is produced by body cells during illness and destroys pathogens. If it is deficient, the immune system is unable to function normally.
- The main drug for the treatment of HPV 16 is Viferon. Produced in the form of suppositories, ointments, and gels. The drug inhibits the replication of viruses containing RNA and DNA. Enhances the phagocytic activity of macrophages, increases the cytotoxicity of lymphocytes towards target cells, causing indirect antiviral activity.
- "Immunomax" is used more often after surgical interventions or as a prophylactic agent. Has a systemic effect. Already 4 hours after the substance is ingested, active production of cytokines by monocytes begins. Activates tissue macrophages, which accelerate the production of antibacterial secretions and the synthesis of antibodies to suppress foreign agents.
- "Licopid" is used in the treatment of the disease and its relapses. The drug enhances the production of interleukins and colony-stimulating factors.
For a detailed treatment regimen, contact your doctor. Antiviral and immunomodulatory drugs can cause significant harm to the body if combined in the wrong order. They must be taken strictly at the same time.
Allokin-alpha stimulates the immune system
Can HPV 16 go away on its own?
Virus 16 can go away spontaneously. After infection, the body is able to cope with the infectious agent. This happens in 30% of cases and can take up to one year. If this does not happen, then there are two possible ways:
- manifestation of clinical symptoms;
- transition to an integrated form (which is more typical for HPV 16).
It turns out that every 3 is able to recover on their own, but you should not neglect the help of doctors. You definitely need to see a specialist and go through the entire course of examination to protect yourself.
It is more difficult for those who are infected with several genotypes at once. Thus, HPV 6 or 11, which have a low oncogenic risk, can be combined with representatives of a high oncogenic risk (strains 16, 18).
The article has been reviewed by the site editors
Symptoms of infection
Until the virus begins to actively spread, it is almost impossible to track its presence. Therefore, symptoms of infection become visible only some time after infection. The main sign of the presence of HPV is the appearance of various growths that arise due to changes in the structure of tissue cells.
Possible neoplasms include:
- warts;
- papillomas;
- genital warts.
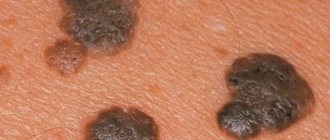
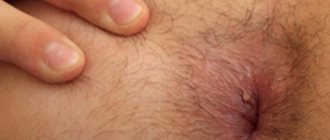
Strains 16 and 18 are characterized by the development of condylomas that appear exclusively in the genital area. They are considered the most dangerous type of neoplasm, since it is precisely such growths that subsequently change into cancerous tumors. Due to their elongated shape ending in a rounded end, condylomas are called genital warts.
Genital warts are flesh-colored
Subsequently, symptoms such as:
- burning;
- constant itching;
- pain;
- weight loss.
All this manifests itself at the location of the condyloma and is caused by its presence. When tumors begin to grow and multiply, this indicates an exacerbation of the virus and a low level of immune defense.
Diagnostics
Yes, the symptoms of this strain of the papilloma virus are indeed more abundant than in the case of other types of the disease, but this does not help much in diagnosis. The fact is that similar signs often occur with other sexually transmitted diseases, so a simple history taking will simply establish the fact of a certain disease, but nothing more. For a high-quality diagnosis of HPV, you need to undergo special analyzes and tests that not only detect the virus, but also accurately characterize it, which allows you to immediately determine the optimal therapeutic strategy.
Modern medicine uses several highly accurate methods for detecting HPV of any type:
- PCR. The method is accurate, but gives a number of false results. In addition, this diagnostic is not able to determine the concentration of the microorganism in the cells.
- Digen test. The most modern, the most accurate, but also one of the most expensive. Using this technique, you can find out everything about the virus: its type, DNA features and their quantity.
- Bacterial culture . The method is accurate, but takes a lot of time. In an artificial environment, a sample of the papilloma virus strain is grown from the patient’s biomaterial, which is then subjected to detailed study.
As for a biopsy, when examining for the papilloma virus, doctors try to avoid prescribing it - it poses too much stress for the body. But if there is a suspicion of the beginning of the degeneration of neoplasms, then it will have to be done - it is a matter of life and death.
Don't forget about an examination by a gynecologist. He will be able to visually detect those symptoms of the disease that are hidden to the average person.
Diagnostic features
Most often, identifying papillomas is not very difficult; a simple examination is sufficient. It is important to determine the strain of the virus and its oncogenicity. For this purpose, a whole range of diagnostic studies is carried out:
- Colonoscopy. Using a special magnifying device (tenfold magnification), the surface of the mucous membrane is examined.
- General blood and urine analysis, venous blood test for HIV and syphilis, genital smear examination.
- PCR analysis. These studies make it possible to determine the type of virus, but the probability of error is also quite high in case of any violations during PCR.
- Digene testing or hybrid capture method. This is a fairly new technique that allows you to analyze the virus on DNA. This way you can give not only a qualitative, but also a quantitative assessment of HPV 68.
- Cytology. Examination of smears makes it possible to assess the degree of cellular destruction.
- Histology. Studying a biopsy taken from the affected area makes it possible to establish with a high probability the risk or onset of cell malignancy. This is the only way to establish oncology.
Comprehensive diagnostics allows you to accurately identify HPV and its type, as well as the stage of the pathology and the risk of complications. When conducting research, the participation of specialists such as a gynecologist, urologist, oncologist, and surgeon will be required. Also find out what indirect signs will help you identify HPV.
Features of type 68 and danger for women
If the tests reveal HPV DNA of strain or type 68, this indicates a risk of developing oncology, cervical cancer. This type of virus indicates a possible precancerous lesion of the cervix - dysplasia. Many patients in whom type 68 DNA is detected in tests are diagnosed with cancer. Papillomavirus type 68 in women is detected with a malignant tumor of the cervix.
Upon examination, a diagnosis of cervical dysplasia or erosion may be made. To ensure the safety of the health condition, women undergo a biopsy. Based on the results of the study, the presence of cancer cells is determined.
From the moment of infection to the first symptom it can take from 3 to 8 months. With strong immunity, the body itself tries to cope with the foreign agent, and it often succeeds. HPV attaches only to the damaged surface of the epithelium (during erosion). If the pathogen does not detect damage, dysplasia does not develop, the virus leaves the mucous membrane within 2-3 menstrual cycles.
All medications against infection are aimed at strengthening the immune system. Taking pills cannot remove the virus.