An impeccable personal appearance is extremely important for many modern people. Therefore, any defects on the skin, and especially on the skin of the face, are perceived by many members of society as a real tragedy.
When papilloma appears on the face, owners of such a diagnosis may become despondent, depressed, and may develop a very serious inferiority complex.
In the meantime, the disease that results in growths appearing on the face is, of course, not fatal. And with the right approach, timely diagnosis and sane therapy, you can get rid of these defects and even forget that such a nuisance ever happened.
HPV - what is it?
Papilloma is considered a benign formation, localized on the mucous membranes and superficial layers of the skin. Externally, a wart is a growth with a thin stalk.
The tumor does not cause painful discomfort. Its size is 2-20 mm.
According to statistics, up to 90% of people are infected with the HPV virus, which can manifest as papillomas localized in the face. Human Papillomavirus has about 170 strains, 43 varieties and 5 genera.
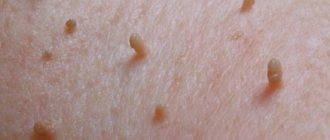
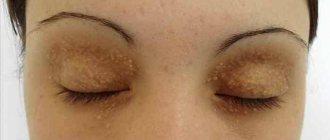
When an infection enters the body, it manifests itself by the formation of skin growths that appear in different parts of the body, including the face. The bumps are gray, pink or dark brown in color. They are shaped like a small round flower with sharp petals.
Common locations for warts on the face are the upper eyelid, nasolabial triangle area, and cheeks. The formations are painless, but from an aesthetic point of view they cause psychological discomfort to their owner.
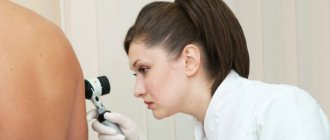
Diagnostics
At first glance, it seems that distinguishing papilloma from other neoplasms will not be difficult. However, the growths are often confused with various types of skin diseases. Therefore, the patient needs to go to a medical facility.
Even a doctor after the first examination cannot always make the correct diagnosis and prescribe treatment. HPV has the ability to change its course depending on the stage and type of virus that has entered the body.
After examination, the doctor prescribes the necessary examinations
Among the laboratory methods for making a diagnosis are:
- cytological analysis, which allows to identify the presence of changes in the cells of the material being studied;
- polymerase chain reaction, carried out to detect viral DNA in a sample;
- a biopsy, during which a sample is taken to be examined under a microscope;
- histological analysis to confirm the benignity of the removed papilloma;
- The Digene test is the most accurate analysis for HPV, determining the presence of the virus, its type, the level of concentration in the tissue and the nature of oncogenicity.
It is not difficult for a modern dermatologist to diagnose papilloma.
The diagnosis is made based on:
- A clear clinical picture of the appearance of a particular growth on the skin - the symptoms usually speak for themselves.
- When questioning, they find out: sexual contact, the presence of infection in someone in the family, age, etc.
- To definitively confirm the diagnosis of genital warts, the material is analyzed for PCR or Digene test for the HPV virus.
- A control analysis is carried out 2 months after the end of treatment.
Peculiarities
Papillomas on the face are formed due to the rapid division of pathological epithelial cells. Moreover, warts that appear on the eyelid, near the nose, cheeks or lips can grow quickly. When palpated, the growths are soft and do not hurt.
Papillomavirus sometimes leads to the transformation of benign tumors into cancerous ones. The risk of developing malignant papillomas increases with stress, regular sunbathing, and poor personal hygiene.
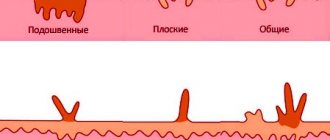
Popular types of tumors caused by HPV:
- thread-like formations. The eyelids are most often affected. Outwardly they resemble a flesh-colored papilla with a thin stalk.
- Vulgar warts. These are convex oval or round growths of light brown color.
- Flat formations. Often formed in adolescents and children. They do not rise above the skin and are flesh-colored.
Virus shape
The types of papillomas affecting the skin of the face are determined by their shape. Often warts are benign. This is the episomal type, in which the viral infection does not change the genome of the cell.
Less commonly, education may be of poor quality. The intrasromal form is a malignant, integrated form. This is an aggressive type of HPV in which the virus invades the DNA of the cell.
The first form does not cause any particular harm to the body. Benign growths respond well to treatment, so when they are episomal, they resort to surgical therapy. With proper treatment, complications do not arise.
The second form is a malignant formation that degenerates into a cancerous tumor. This type of HPV is not always treatable and can lead to death.
Strains
Papillomas located on the surface of the facial skin are conventionally divided into 3 types:
- oncogenic minimal risk (HPV 73, 3, 72, 6, 61, 11, 51,13, 44, 32,43, 34, 42, 41, 40).
- Oncogenic medium risk (HPV 58, 30, 56, 35, 35, 52, 45).
- High-risk oncogenic (HPV 70, 16, 68, 18, 64, 31, 59, 33, 50, 39).
Oncology in 90% of cases is diagnosed with the latter type of virus.
Papilloma on the forehead can become malignant in the presence of subtypes 33, 16, 31, 18. However, flat papules degenerate into cancer for a long time - from 10 to 20 years.
Color
The formations on the face can have different shades, which is determined by the characteristics of the skin, the type and age of the virus.
Possible colors of warts:
- brown - old growths that have acquired a dark shade due to genetic mutation of cells or under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
- Pink - can have a pale or bright color, often blending into the skin.
- Gray warts resemble ordinary warts, which makes diagnosis difficult.
White papillomas may also appear on the face. This color of growths is characteristic of a pigmentation disorder in infected cells.
Appearance
The difficulty of removing them depends on how papillomas look on the face.
The following types of formations are distinguished:
- spherical. They have a thin stalk that can be easily removed using laser techniques. Vulgar warts are round, up to 5 mm high, and have a brown or gray color.
- Acrochords. They are distinguished by a narrow stem and a rounded shape. The formations are easily removed surgically.
- Pointed. Externally similar to cockscomb or cauliflower. Brown condylomas very often become malignant.
- Flat. The height of the stem is up to 2 mm, the growths are light brown. After surgical removal of juvenile growths, red spots and scarring often occur because this type of HPV spreads to large areas of the skin.
Dimensions
Papillomas on the face vary in size. Thus, the diameter of vulgar warts is 2 mm. Hanging formations have a protrusion up to 1 cm in length.
With human papillomavirus, flat papillomas on the face appear as protrusions up to 2 mm high. The size of the acrochord is up to 6 mm.
Age-related warts are small, ranging from 1 mm in area. The diameter of genital warts is 0.1-20 cm.
Localization of filamentous papillomas
I have already spoken about my favorite localization places.
The neck area is the most popular.
The areas of the neck and face are most often exposed to hand touch.
In women, for example, in this area there are elements of makeup and accessories located on the neck.
Therefore, HPV migrates and self-infection occurs.
Science has proven that this area is at increased risk of infection.
Particularly prone to sweating in the neck, this area is favored for possible HPV infection.
The primary infection is HPV, and then new growths appear - warts, papillomas or genital warts.
Therefore, the most important protection is not against papillomas, but against HPV infection.
Preventive measures against the appearance of papillomas:
- maintaining hygiene;
- barrier methods of contraception;
- do not contact people infected with HPV.
The best protection against papillomatosis is strict adherence to preventive measures and timely treatment for HPV in the active phase.
It is also very important to vaccinate with Gardarsil and Cervarix prophylactically.
Papillomas and condylomas of any kind are formed in the body as a result of viral infection. The analysis reveals that the invading microorganism is the human papillomavirus. There are several ways to transmit it:
- sexual;
- as a result of childbirth;
- domestic;
- contact, through wounds and cracks in the skin.
An increased risk of pedunculated papillomas is observed in women of reproductive age. Neoplasms are especially common in patients who have skin problems:
- increased sweating;
- active work of the sebaceous glands;
- skin moisture.
Formations on a thin or wide stalk are caused by a special type of HPV. Their occurrence is influenced by 3, 5, 8 and 9 strains of the virus. After penetration into the body, the disease may not manifest itself. When the body’s immune defense decreases, infection activates.
After penetration into the epithelial tissue, the stage of active reproduction of the virus begins. At this moment, papillomas can appear.
Neoplasms appear as a result of HPV infection
Neoplasms can appear in various areas. But the most characteristic zones are:
- neck;
- faces;
- armpits;
- fingers.
Most often, pedunculated papillomas appear in the neck area. Women who are most susceptible to neoplasms are very complex and worry about their unaesthetic appearance.
Localization of pedunculated papillomas – cervical region
The neck and face are the parts of the body that are most often touched by hands. Women can adjust their makeup and accessories on their necks, carrying viruses on their hands.
Scientific research has also confirmed the susceptibility of this zone to infection. The process is due to the tenderness of the skin in the areas. In addition, the neck often sweats, which increases the risk of pedunculated papillomas.
Causes
The basic reasons for the appearance of papilloma on the face are household contact, infection during labor, unprotected sexual intercourse with different sexual partners.
Common factors for human papillomavirus infection:
- stress;
- hyperhidrosis;
- age-related changes;
- acrocyanosis;
- neuroses.
A common reason for the appearance of papillomas on the face is increased oiliness, dryness or sweating of the skin, and insufficient hygiene. The appearance of warts is promoted by the habit of biting nails and constantly touching the face.
Why do tumors grow?
The virus enters the body in various ways and its active development or latent carriage occurs:
- through microtraumas on the skin;
- during sexual intercourse;
- through handshakes;
- in direct contact with the belongings of the carrier or a sick person;
- while passing through the birth canal.
A person’s health condition may change for the worse and this is a trigger for the spread of the virus:
- frequent stressful conditions;
- persistent viral colds;
- difficult working conditions with high humidity or hypothermia;
- weakening of the immune system for various reasons;
- dysfunction of the hormonal system;
- increased sebum production and increased sweating;
- state of apathy or depression.
The protective properties of the body are significantly reduced, and there is an active growth of papillomas, varieties of which can be seen in sufficient quantities in photos on the Internet or in informative printed publications.
Treatment methods
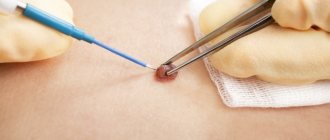
A radical way to answer the question of how to get rid of papillomas on the face is the complete removal of the formations.
For this purpose, the following methods are used:
- cryodestruction (nitrogen freezing);
- laser exposure (the safest method of eliminating papillomas);
- radio wave therapy (warts are removed with a radio knife).
Other treatment methods that your doctor may recommend to remove papillomas on the face are antiviral drugs and therapy aimed at increasing a person’s immunity.
Drug therapy
Official medicine recommends treating papillomas with drugs that stimulate the immune system. This is Viferon, Genferon or Infagel.
You can also use oxolinic or tebron creams, which have antiviral activity. Products containing retinoic acid are no less effective.
How to treat papillomas on the face if it is not possible to remove them in the hospital?
At home, cauterizing alkalis or acids with a local necrotizing effect are used:
- Collomak;
- Dufilm;
- Super clean;
- Feresol;
- Solcoderm;
- Lapis pencil.
Treatment with folk remedies
How to remove papillomas on the face at home?
To eliminate formations caused by the Human Papillomavirus, iodine is used.
A thick cream is applied to the area around the papilloma. A cotton swab is soaked in iodine and the wart is burned with it. Therapeutic manipulation is done every 6 hours for 14 days.
Cauterization of growths is carried out using castor oil, which contains an acid that suppresses HPV. Just a few drops of extract helps remove papilloma in 1-2 weeks. The product is used to treat the formation up to 6 times a day. Lemon, eucalyptus or tea tree oil are used in a similar way.
Other folk remedies for papillomas on the face:
| Plant name | Mode of application | Number of procedures and duration of treatment |
| Kalanchoe | For large warts, a Kalanchoe leaf is cut lengthwise and the inside is applied to the growth. The top is covered with adhesive tape. | 2-3 times a day, 7 days |
| Garlic | The garlic clove is crushed. The gruel is applied to the affected area. | Up to 3 times a day, 14 days |
| Aloe and onion | Using a spoon, scrape the pulp from a leaf of the plant, which is combined with 10 g of onion juice. | Every 2 hours, 1-2 weeks |
| Potato | The raw vegetable is crushed and made into applications from the pulp. Procedure time – 20 minutes | Twice a day until the tumor disappears |
| Walnut | The juice of an unripe nut is used to lubricate the growth. | Up to 5 times a day, 14 days |
Condylomas affecting the face are treated with a mixture of garlic, flour, and vinegar. All ingredients are mixed and applied to the infected area of skin. From above everything is fixed with adhesive tape and left overnight. The wart should fall off in the morning when the compress is removed.
You can also apply a mixture of lemon juice, vinegar and hydrogen peroxide to papillomas. The product is applied to the new growths every three hours.
If the growths have appeared recently, they are removed with egg white. Apply whipped egg white to the affected skin every 2 hours. After the procedure, it is not advisable to expose your face to ultraviolet radiation.
Traditional medicine suggests treating Human Papillomavirus with laundry soap.
Before going to bed, the affected area is lubricated with soap foam, which should not be washed off until the morning. Treatment lasts from 4 to 7 days.
Pedicled papilloma: how to remove?
An effective way to treat pedunculated papilloma is to remove it. Studies have shown that the tumor can disappear on its own in only 10% of patients. The influence of immunomodulatory and antibacterial therapy does not give the desired result. The optimal treatment option can only be determined by a qualified specialist in a medical institution. Typically this is:
- chemical procedures using acidic compounds that burn out tumors;
- surgical procedures in which both the papilloma and the tissue adjacent to it are cut out;
- exposure to radio waves;
- cryodestruction, growths are simply frozen with nitrogen;
- Laser removal is considered one of the most effective ways to combat papillomas. This method does not cause any negative consequences.
Diagnostic measures
A person is always concerned about the oncogenicity of the papillomavirus detected in him, especially in the intimate area. At the appointment, the gynecologist will definitely examine the woman in the gynecological chair; papillomas in women are immediately detected.
A colposcopy and acetic acid test are performed. When applied, the papilloma turns gray-white in a few minutes.
If cancer is suspected, a cytological examination of a smear from the cervix is mandatory. PCR analysis is the most informative; it determines the presence of the virus and its type.