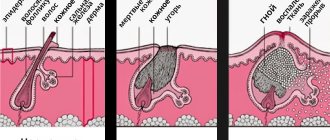
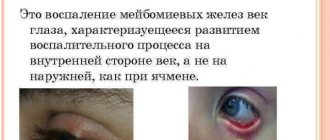
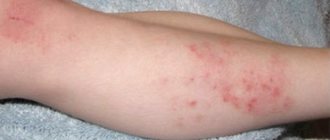
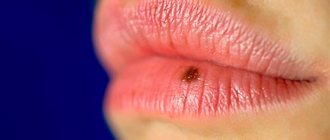
The skin is in many ways similar to soil: it has “holes” of pores, hair grows in “blades of grass” in one stem, there is a denser (keratinized) top layer and moisture-containing subsoil that nourishes its structures.
But just as there are places on the surface of the soil that are poorly suited for development and lush flowering, on the outer cover of the body you can also find areas of skin that are either not “fertile” at all, or such (dry sores) where only exceptionally hardy, undemanding to conditions can take root. life vegetation. This includes lichens (the full name is lichens - a symbiosis of fungus and algae) and bacteria (also known as microbes), which are primitive plants by nature.
Stains
Before we move on to the very concept of lichen and its varieties, we propose to consider the types of spots on the skin. Let's start with the fact that all spots on the skin can be divided into two large groups:
- vascular;
- pigmented.
The first group can be further divided into several types, which are shown in the table below with a brief explanation.
| Subspecies | Characteristic |
| Inflammatory | Rough spots on the skin that cause a lot of discomfort (itching, swelling, dryness, flaking). They do not have a clear boundary and occur when blood vessels dilate. Causes: allergies, dermatitis, infectious diseases, syphilis. |
| Non-inflammatory | Purple or blue circles that do not cause discomfort. Causes: nervous disorders or gastrointestinal problems. |
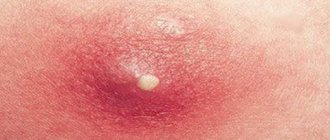
| Edema | Blisters. Reason for appearance: allergic reaction. |
| Hemorrhagic | Similar to a rash, sometimes forming the outline of bruises. Causes: mechanical impact, vascular pathologies. |
Also, the cause of spots can be lichen. What is it and how does lichen manifest itself in humans? Ringworm is a disease that appears as spots in different parts of the body. They bring a lot of discomfort to the patient (itching, necrosis, inflammation, and so on). Please note that there are many varieties of them. You can learn about them in detail below.
Gray spot on the white of a child's eye
In children, as in adults, various spots may appear on the white of the eye. By their nature they can be congenital or acquired. You can acquire a gray spot due to the heavy load of the optical apparatus.
The progression of the gray spot, namely the nevus, occurs in the form of the following manifestations. Even the slightest signs of the development of a gray spot should cause concern among parents. The main changes are the following:
- The child's vision deteriorates.
- The color intensity of the spot changes sharply.
- The nevus extends to the cornea of the eye.
- The gray spot increases significantly in size.
A favorable outcome and effective treatment are guaranteed only if you go to the hospital in a timely manner. Only the attending physician will be able to select the necessary treatment, determining the nature of the disease that provoked the appearance of the gray spot.
Varieties
Spots on the skin that look like lichen may indicate the presence of some type of this disease. Before looking elsewhere for the cause, study the different types of lichen. There are six of them in total: shingles, red, white, colored, trichophytosis, pink. Next, we will look at each type separately in detail. Now it is important to mention where the stains form. Ringworm can affect absolutely any area of the epidermis: from the face to the lower extremities (neck, groin, abdomen, back, and so on). Each species has chosen a special place for itself, you can find out about this by reading the article.
Reasons for appearance
If a dark spot appears on the skin, then to eliminate it it is necessary to determine the cause of formation. A change in the color of the skin indicates a disruption in the process of its pigmentation. This may indicate the accumulation of an excess amount of melanin in the epidermis (which causes the formation of melanosis) or a disruption of metabolic processes and an increase in the number of melanocytes.
Some diseases may also be associated with the appearance of a dark spot on the skin, especially if they are chronic. Such pathological conditions and processes include:
- liver diseases;
- various dysfunctions of the endocrine system organs;
- diabetes;
- hyperhidrosis;
- tuberculosis;
- kidney diseases.
This, of course, is not the entire list of provoking factors for the formation of dark spots on the skin, and if you do not have a history of such problems, perhaps the reason lies in something else.
Pityriasis rosea
Pityriasis-like spots on the skin that have a pinkish tint indicate the presence of pityriasis rosea. Initially, a small spot appears, the diameter of which does not exceed two centimeters. Very often this is the chest area. After some time, similar spots appear, only smaller in size, all over the body (stomach, back, arms, legs, groin, and so on). Please note that this variety can appear extremely rarely on the face.
The spot in the middle is scaly and can cause itching. The border of the spot does not have scales. After treatment, traces remain, which disappear after some time.
Symptoms:
- discomfort;
- malaise;
- prostration;
- elevated temperature;
- itching;
- pain in the affected areas;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
Treatment:
- "Suprastin";
- "Hydrocortisone";
- vitamins.
Treatment should be prescribed by a dermatologist. The sooner you address this problem, the faster you will get rid of it. If on the first day you take an increased dose of Acyclovir and undergo ultraviolet radiation, the disease will disappear quickly and will not bring consequences.
There are three common types of skin ulcers.
Arterial
(also known as ischemic) ulcers: These usually affect people with poor blood flow to the legs. Ulcers typically occur on the feet, especially the heels, toes, and near the nail beds.
Neurotrophic
(also known as diabetic) ulcers: If there is nerve damage that causes loss of sensation in the legs, neurotrophic ulcers may develop. This is often a problem for people who have nerve damage caused by diabetes. Ulcers most often appear on the feet, especially at pressure points on the soles of the feet or where shoes press against the skin.
Ulcers with venous stagnation:
Ulcers with venous stasis often occur in people with swollen legs, spider veins or varicose veins, or blood clots in the legs. They are always found on the lower leg, usually midway between the knee and ankle. Your doctor will determine what type of ulcer it is based on how it looks and where it is located.
What Causes Ulcers?
Ulcers form when the outer layer of skin, the epidermis, is damaged. The injury exposes the deeper layers of the skin, the dermis, leaving them open and vulnerable to infection. For most people, damaged outer layers of skin heal and do not cause problems. Ulcers usually occur when the skin does not heal due to some other health problem:
- diabetes;
- high blood pressure;
- skin infections;
- lymphedema, which is a buildup of fluid in the legs;
- nerve damage (neuropathy);
- poor blood circulation;
- vascular diseases (blood vessel abnormalities).
Smoking may also increase your risk of ulcers. This is because nicotine damages nerves and blood vessels. The risk of ulcer formation also increases if:
- the person wears tight clothes or inappropriate shoes;
- moves little;
- does not immediately treat wounds or infections.
The risk of ulcers may be genetic. If your parents or close relatives were prone to them, defects are more likely.
How to treat an ulcer?
An untreated ulcer can lead to serious problems, including the need for amputation (most commonly of the feet in diabetic feet). If defects occur on the skin, immediately take measures to disinfect them. For serious injuries involving a large area or depth of injury, be sure to consult a doctor. The sooner treatment begins, the less likely it is that another problem will arise. The doctor will examine the skin and may take an X-ray to determine whether the ulcer has affected nearby bone. In some cases, the specialist may use other tests to determine if there is blood vessel disease. The surgeon will treat the ulcer using a procedure called debridement. It removes unhealthy tissue from the wound to begin the healing process. Your doctor may also prescribe medications, such as antibiotics, to be taken by mouth or applied to the skin. We need to discuss how to treat an ulcer at home. You may need to: Clean the ulcer daily with soap and water. Do not use hydrogen peroxide or soak the wound in the bath. This can interfere with healing and increase the risk of infection. Wound care. It is important to keep the ulcer bandaged or covered with a wound dressing. Your doctor may recommend specific dressing steps. “Airing” a wound increases the likelihood of infection and slows down its healing. Apply medications such as saline, reparants, and substances that cause skin cell growth. Treat health problems such as diabetes or vascular disease. Do not put pressure on the ulcer, especially if it is on the leg. You may need crutches, special shoes, a brace, or other devices to relieve pressure and irritation to help the ulcer heal faster.
If the ulcer does not heal after about a month or becomes infected and spreads to the bones, surgery or hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be required. This is breathing pure oxygen in a special room to aid healing. Unhealed ulcers can lead to gangrene. This is a condition where tissue dies because there was not enough blood flow to the area. In this case, the doctor may have to remove the affected body part, such as a foot or leg.
Text: Alena Paretskaya.
Ringworm
This is a highly contagious infectious disease. Routes of infection:
- contact with the patient;
- sharing clothing, towels, shoes, etc.;
- use of hairdressing or manicure equipment that has not been processed.
Ringworm-like spots on the skin that gradually increase in diameter and are accompanied by slight itching are ringworm. The methods of infection are listed above, but some other factors are necessary for development, for example:
- skin trauma;
- weak immunity.
On what parts of the body is this variety found?
| Scalp | The lesions are round in shape, and thinning hair is found in these areas. Peeling is noticeable on the affected areas (similar to dandruff). |
| Smooth skin | Face, neck and body. Pronounced round spots that increase in diameter over time. The outline is small bubbles. The lesions look extremely unsightly and itching is observed. |
| Nails | Nails affected by fungus take on a gray tint and become very brittle and brittle. Thickening or thinning of the nail plate is possible. |
Treatment is carried out using a combination method (drugs and local therapy). The most popular tablets for the treatment of ringworm are Micoconazole and Mycoseptin.
Dark spots on the lower extremities
Black spots on the legs can appear for various reasons; they can indicate illness (for example, spots form on the skin due to intestinal diseases) or indicate an allergic reaction to depilatory products or shower gels.
With this phenomenon, the body can warn a person about problems with veins and blood vessels, especially if purple spots appear on the skin of the lower extremities.
Dark spots on the buttocks may be evidence of a person's sedentary work, an allergic reaction to the synthetics from which underwear or cosmetics are made.
Dark spots on the skin between the legs may appear due to wearing uncomfortable clothes or using inappropriate cosmetics. Age-related changes also play an important role. They appear very often, and all this happens because it is in these areas that the skin is very sensitive. We will now try to figure out how to get rid of dark spots between the legs and on other parts of the body.
Shingles
The causative agent of this type of lichen is the herpes virus. It is important to know that shingles has a negative effect not only on the skin, but also on the nervous system. In medicine, this lichen is considered a contagious infectious disease.
It can be found on the following areas of the body: genitals, buttocks, lower limbs, upper limbs, face, ribs, lower jaw, back of the head, neck and forehead. Shingles is hard to miss and its symptoms include:
- pain at the site of the lesion;
- burning;
- itching;
- weakness;
- headache;
- chills;
- enlarged lymph nodes.
The virus that causes the disease is already in our body if we have previously had chickenpox. The immune system keeps it under control by producing small amounts of antibodies. If there are disturbances in the functioning of the protective barrier, then the dormant virus is activated. It can be said that shingles is a form of chickenpox.
What are the causes of the disease? This issue is discussed in detail in the table.
| Cause | Characteristic |
| Elderly age | The explanation is very simple. When a person crosses the age of 50-60, a natural decline in immunity occurs. The risk of getting shingles increases many times over. Statistics indicate that more than five percent of pensioners consult doctors with this problem. The peak of diseases occurs in autumn and spring. |
| Immune system disorders | These include the following diseases: various blood diseases, immune deficiency, oncology, HIV, diabetes. In addition to these diseases, serious injuries can be the cause. |
Treatment comes down to taking the drugs Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, Famciclovir. If a person is not bothered by lichen, then the doctor does not prescribe treatment. The mild form goes away on its own within two weeks, but consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Causes of Dry Spots
Since this phenomenon can be either permanent or temporary, its nature can have different causes.
Thus, the constant presence of scaly spots on the skin (especially the face and hands) occupying a large area can be both a consequence of general dehydration of the senile body, and the result of living in an area with a constant sharp wind (sultry or icy).
In both cases, the reason for the appearance of dry skin over a large area is its desiccation, but if it is impossible to get rid of the first reason, then moving to a more “friendly” place is enough to eliminate the second.
The appearance of the same focal “desertification” of the skin due to its overdrying is also caused by the existence of a certain psychotype of personality – prone to creating and living in chronic stressful situations.
A few sleepless nights spent at the computer are quite enough to cause general dryness of the face and hands.
This condition occurs due to the existence of a long-term vasospasm (due to stress) in combination with a slight but prolonged effect of the device’s radiation on the areas of the skin accessible to it.
Local disorders of blood and lymph circulation, caused by reasons of either a reflex or dysmetabolic nature, can lead to the appearance of smaller foci or single spots.
Thus, the same work on the keyboard with prolonged exposure to certain skin zones of the fingers can cause a reflex slowdown in the circulation of biological fluids in the depths of a certain skin zone - the consequence will be a transient (but rather long-term) disorder of its trophism, evidenced by a change in the surface layer.
Dysmetabolic (caused by metabolic disorders with the accumulation of toxic waste products) causes of trophic disorders of the skin include almost any disease or condition with a long or chronic course - from regular constipation to diabetes, from pregnancy to menopause, from cholelithiasis to chronic ( complicated) hemorrhoids.
Lupus spots
Diseases of a systemic nature deserve special mention, the external “passport” of which is the characteristic damage to certain areas of the skin. For example, a lupus “butterfly” on the face is a red, dry spot that does not itch at any stage of its evolution.
The consequence of the presence of mental pathology (along with the phenomena of depression of the nervous system) are:
- neglect of hygiene standards;
- change in the vivacity of the body’s response to changes in the conditions of the social and natural environment;
- digestive disorders leading to vitamin deficiencies;
- parasite carriage (including giardiasis, ascariasis, demodicosis);
- tendency to allergic manifestations;
- infection with lichen infection.
Each of these factors individually, or their entire combination, can cause dry spots on the surface of the skin.
Video from Dr. Malysheva:
Lichen planus
This variety belongs to chronic dermatosis. A characteristic feature of the disease is papules (red dry spots). Locations can be very diverse:
- leather;
- mucous;
- nails.
Currently, medicine cannot accurately answer the question of the origin of the problem. It is a multicausal disease that manifests itself as a result of many factors, both internal and external. The immune system responds to this effect with an inadequate tissue response. It is very important to note hereditary predisposition. There have been cases when lichen planus was the body’s response to the effects of chemicals (the drugs “Bismuth” and “Tetracycline”) to stressful situations, to disturbances in the gastrointestinal tract, and others.
Symptoms:
- red papules (diameter up to five millimeters);
- peeling;
- itching;
- neurotic anxiety;
- sleep disorders.
Treatment is carried out with the help of drugs: “Chloropyramine”, “Clemastine”, “Cetirizine”, “Prednisolone”, “Betamethasone”, “Chlorin”, “Hydroxychloroquine”. In some cases, laser or radio wave therapy is used. If the mucous membranes are affected, then vegetable oils and phytoextracts are used for treatment.
Main reasons
Rashes on the body can appear for two groups of reasons. Some are associated with external factors, others with internal ones.
- Exogenous causes include: the use of low-quality cosmetics, frequent tanning under the sun or in a solarium, exposure of the skin to wind or frost. Often, defects occur on the skin of the hands, face, legs, neck and other open areas.
- The endogenous group is associated with age-related changes, hormonal imbalances, diseases of the endocrine gland or digestive organs, and skin pathologies.
White dry
White rashes occur due to a lack of melanocytes. These cells are located in the skin and are responsible for the shade of the dermis. Light spots are localized on the face, arms, neck, and torso.
Among the most common diseases are the following:
- Vitiligo is an autoimmune pathology, the causes of which are unknown. One or many colorless spots appear on the body, with a pronounced tendency to grow. Vitiligo can be located on any part of the body (except the palms and soles) and on the mucous membranes. Additional symptoms include early graying, and some patients report mild itching in the discolored areas. The defects do not itch, do not peel, and do not hurt.
- Guttate melanosis is a type of leukoderma. There are not enough melanocytes or they do not function well for various reasons. Most often women over 30 years of age are affected. Many light-colored areas appear on the body, similar to drops. The size of the defects is from 1 to 15 millimeters. White dry spots on the skin do not itch, do not flake, and do not hurt. They only cause psychological discomfort. Localization areas include arms, back, shoulders and chest.
- An apigmented nevus is a white, flat neoplasm with uneven and distinct edges. It is also called a birthmark. The nevus does not grow, does not affect health in any way, but does not disappear. It can often be seen in newborns. It is assumed that its appearance is associated with genetic disorders. The size varies, from a couple of millimeters to several centimeters. Localized on any part of the body, does not depend on gender.
- Pityriasis versicolor is a pathology caused by fungi, but it is not contagious. Asymmetrical spots of scarlet and dark color appear on the back, stomach, shoulders and head. When exposed to the sun or after tanning in a solarium, they turn white and yellow. A dry spot on the skin is flaky and moderately itchy.
Red dry
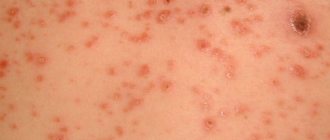
Vivid rashes occur for various reasons. The most common diseases are psoriasis, ringworm and lichen planus. Often a rash is an allergic reaction of the body.
- Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease, non-contagious, and chronic. Reddish plaques appear on the patient's body. They are easily removed, and in their place a silver film, similar to cellophane, is formed. If you remove it, pinpoint bleeding begins. Psoriasis is characterized by mild itching and flaking. If the disease is not treated, the rough spots on the skin grow and multiply, they can occupy up to 60% of the entire body.
- An allergy is the body's response to an irritant. Sometimes it appears on the skin in the form of red spots. The main feature is that rashes can appear within a few minutes after contact with the allergen. The formations are uneven and very itchy. Occurs on any part of the body. Gradually disappear after contact with the stimulus is interrupted. Additional symptoms are swelling, runny nose, lacrimation.
- Lichen planus is a chronic dermatological disease. The causes of its occurrence and pathogens are unknown. Red dry spots on the skin appear on the bends of the elbows and knees, in the groin, and on the thighs. Color red, purple tint possible. The size is small, up to 5 millimeters. Ringworm affects not only the skin, but also the mucous membranes. Externally, the rash is located so that it resembles a garland. Neoplasms tend to merge and grow.
- Ringworm is a contagious pathology caused by fungi. It usually affects children of primary school or preschool age. You can get ringworm after contact with a sick animal or infected person, or after using the patient’s personal belongings. A red defect, round, with clear edges, forms on the body or scalp. A dry spot on the skin itches. The hair above it falls out, then new, dull hair grows, breaking after 2-3 centimeters.
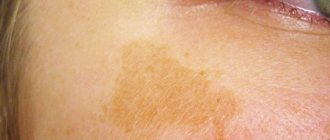
Dark defects
- Chloasma are uneven formations on the skin with clear edges. The color can be light or dark brown. Usually located on the face - forehead, temples, upper lip. Chloasma is safe and only causes aesthetic discomfort. They often appear due to hormonal imbalances: during pregnancy, breastfeeding or menopause. They can be small, up to 1 cm, or occupy half the face.
- Lentigo is a disorder of skin pigmentation. The rashes are benign in nature and can be oval or elongated. Brown spots on the skin are raised above the dermis. The boundaries are clear, the size rarely exceeds 5 millimeters.
- Freckles are dark dry rashes of brown or beige color, small in size up to 2 mm in diameter. Absolutely safe, never degenerate into oncology. Mostly appear in fair-skinned people, blonds or redheads. Freckles usually appear in summer and spring. Localized on the face, neck, shoulders, sternum, back.
- Moles or nevi appear in people regardless of gender and age. They can be flat or convex. Nevus can be large or small, the shape is regular - round or oval. The color varies from beige to dark brown, almost black. Moles can become malignant if they change color, shape, or begin to bleed. They are removed surgically.
Other diseases
- Lichen rosea - it is called Zhiber's lichen. It appears in people between 20 and 40 years old. The disease usually occurs in spring and autumn and goes away on its own in one to two months. Initially, a pink scaly maternal plaque up to 3-5 cm in diameter appears on the body. After a few days, many smaller rashes form. The defects look like round or oval plaques. They are not inclined to merge. The color changes, new spots are pink, and old ones are yellowish. Localization – stomach, chest, back, arms and legs.
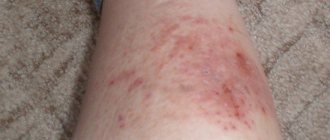
- Eczema is a non-contagious dermatological disease. It occurs in a chronic form, sometimes worsening. There are many types of eczema, each with its own symptoms. But there are also common signs: a red spot forms on the body. During an exacerbation, it becomes covered with pustules, papules or vesicles, they dry out and peel off. The affected area itches and burns. During periods of remission, it appears as a dry, pigmented area.
- Athlete's foot is a skin disease caused by fungi. It forms in places of large folds: under the armpits, in the groin, under the breasts in women. The defects are red and swollen, itchy and painful, causing severe discomfort. They are dry, but can become covered with crusts and bubbles with liquid.
Attention! In the photos on medical forums and websites you can see all types of spots and find out the names of the disease. But the information is presented for general information only; only a doctor is involved in diagnosis.
Tinea versicolor
This type of lichen is popularly called sun fungus. The disease was given this name because it appears after long exposure to the sun. It is also called pityriasis. Tinea versicolor is caused by a fungal infection that affects only the upper layers of the epidermis. A distinctive feature of the disease is its minimal infectiousness. The infection takes the form of a yeast fungus of one of the following forms:
- round;
- oval;
- mycelial.
Another peculiarity is that different forms of the fungus can transform into others. The reasons may be internal and external factors. More details are described in the table.
| Exogenous factors | Endogenous factors |
| Tight clothes | Weak immunity |
| Bad habits (smoking, drinking alcohol) | Gastrointestinal diseases |
| Long-term use of medications | Heavy sweating |
| Overdrying of the skin | Hormonal imbalances |
| Prolonged exposure to the sun | Overweight |
| Stress | Respiratory system diseases |
| Nervous tension | Heredity |
Symptoms:
- numerous spots that can merge into one large lesion;
- skin peels;
- sweating
The spots do not cause discomfort to the patient (no itching, burning, inflammation). Treatment can only be prescribed by a specialist. As a rule, complex therapy is used (external treatment and antifungal drugs). Drugs used for treatment:
- "Clotrimazole";
- "Bifonazole";
- "Mikospor";
- "Lamisil";
- "Ketoconazole";
- "Terbinafine";
- "Itraconazole" and others.
Treatment is aimed at accelerating the exfoliation of the affected areas with fungal spores from the upper layers of the epidermis.
Pityriasis alba
Pityriasis alba is caused by a fungus that is found on the skin of every tenth person. It looks like white spots, the causes of which are currently unknown. Children are most susceptible to the disease, but by the age of eighteen, in 99% of cases, all symptoms disappear. It is important to note that pityriasis alba is not contagious. It often appears on the face; if there are quite a lot of spots (more than 20), then they can merge into one large spot. The patient does not experience any discomfort.
The disease is treated with creams, ointments and solutions that can restore normal pigment.
Chickenpox
What are other reasons for the appearance of spots on the skin that look like lichen? Itchy skin rashes may indicate chickenpox. People call it chickenpox. It is important to note that children tolerate the disease much easier than adults (that is, without complications).
Chickenpox symptoms:
- headache;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- chills;
- heat;
- rash on the skin in the form of spots (papules and vesicles);
- itching
Please note that the formed bubbles should never be pierced or combed. Itching can be relieved with an antihistamine. If an infection gets into the wound, healing will be significantly more difficult.
Chickenpox is treated with medications that reduce itching and dry out the site of infection to form a crust:
- "Furacilin";
- boric acid;
- brilliant green (diamond green);
- "Acyclovir";
- "Fenistil" and so on.
Allergy
What else can cause red spots on the skin? Allergy! It occurs in every second inhabitant of the planet. The appearance of a rash is the body’s response to contact with any substance to which there is hypersensitivity. In this case, absolutely any substance can act as an allergen. Allergies to citrus fruits, pollen of certain plants, alcohol and dust are very common. If you have this reaction upon contact with a certain substance, then this is 100% likely an allergy.
Red spots on the skin can cause itching and burning. The following medications will help with these symptoms:
- "Tavegil";
- "Fenkarol";
- "Suprastin" and other antihistamines.
In addition, treatment includes sorbents that remove toxins from the body, physical therapy and immunomodulators.
Types of stains
When diagnosing, the nature of the red rashes is also taken into account. Depending on the diagnosis, the formations have different shapes, sizes, and shades.
Convex
Raised red lesions on the arms and legs are the result of excessive swelling. Tissues grow excessively near the affected area. Such neoplasms are characteristic of autoimmune pathological processes, for example, psoriasis. This is also how skin abnormalities and tissue injury manifest themselves.
Inflamed with swelling
Inflamed red spots on the body of an adult can be empty or filled with pus. Most often, the deviation has a non-infectious form, but it can also indicate autoimmune disorders.
Deviations of an inflammatory nature occur with an advanced form of an allergic reaction. The symptom can appear after an insect bite.
Red with blisters
Blisters appear after burns of various natures. Provoking factors include insect and animal bites, as well as calluses. The rashes are usually local. Blisters are located only in the affected area.
There is a red rim around the growths. There are a large number of blisters in the affected area.
Important! You can’t burst existing growths. This will cause scars to appear.
With clear boundaries
Rashes with clear boundaries usually have a certain geometric shape. Such neoplasms, for example, are pimples and acne. With active spread, the neoplasms merge together. The new formations are extensive and uneven in shape.
Rough and flaky
Red spots on the skin flake and itch frequently. Roughness indicates that the cover is getting rid of affected skin cells. The body is actively fighting the present disease. The surface of the body is renewed. The condition causes moral and physiological discomfort.
Itchy and non-itchy
If the affected areas peel and itch, this indicates skin regeneration. That is why any damage to the skin always provokes severe itching. The symptom develops due to damage by a pathogen or allergen. Otherwise, the neoplasms are not itchy.
When itching, the wound is usually weeping. Also, sometimes the skin begins to itch even before the pathology appears. This is the first symptom of a developing deviation.
Vascular spots
Vascular formations are also divided into other types:
- telangiectatic, which are the result of vasodilation;
- hemorrhagic, which are the result of hemorrhages;
- hyperemic, which indicates a rush of blood to certain areas of the skin.
Vascular formations are often the result of poor nutrition and poor lifestyle.
Spontaneously disappearing and appearing
If a red spot on the skin of the body peels off and then suddenly disappears, the person is sure that he has gotten rid of the disease. It turns out that the deviation has become latent.
Latent failures are usually the most dangerous. The patient does not suspect the development of a serious pathology for a long time. Symptoms of pathology occur when the disease is already at an advanced stage. Complications develop.
Syphilis
Round spots on the skin in the form of a rash may indicate the presence of a disease called syphilis. It is transmitted sexually, and the rash is a “gift” for promiscuity. Syphilis can be treated only in the initial stages; it is completely pointless if the disease has affected the brain.
Treatment of such an unpleasant symptom is carried out comprehensively. It is also important to note that a person must take the drugs (intramuscularly) every three hours for twenty-four days. Water-soluble penicillins are used to treat stains.
Drug therapy
Treatment should always begin with diagnosis.
Cases with bleeding, ulcerations, regional lymphadenitis, symptoms of intoxication and depression of the body require emergency care. After rapid diagnostics, the tumors are excised and subjected to a thorough histological examination.
In less alarming cases, a visual examination of the formation and its laboratory (and, if necessary, instrumental) examination are also carried out. Depending on the results obtained, either dynamic observation or treatment is prescribed based on the nature of the spot.
This may include drug therapy:
- antifungal (Griseofulvin);
- antiviral (Acyclovir);
- antiallergic (from the antihistamine group - Calcium gluconate to hormones - Prednisolone and the like).
In turn, depending on the capabilities of the drug and the desired effect, it can be used:
- locally (in the form of cream, ointment, spray);
- per os (in tablets, mixture);
- injection (intramuscular, intravenous).
In addition to treating the main problem, correction is made:
- metabolic and endocrine disorders;
- immunity;
- functioning of excretory systems (kidneys, liver, lungs).
You should not expect success of therapy without:
- treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases and reducing the level of autoaggression (allergies);
- elimination of parasite carriage;
- correction of nutrition and daily routine (treatment will not benefit someone who spends 24 hours at the computer).
Eczema
A rash on the body can also appear with eczema. It appears as small vesicles, erythema or papules that are filled with fluid. Over time, they burst and secrete a cloudy, sometimes purulent fluid.
There are a wide variety of varieties of the disease. For example, with seborrheic eczema, the skin peels and cracks appear. The following types are also distinguished: microbial, true, professional, dyshidrotic. Complex treatment:
- diet;
- treatment of concomitant diseases;
- limiting contact with the allergen;
- taking antiallergic drugs;
- local treatment.
Gray spots on human skin
The spots that trouble a person throughout his life can be completely different in color, shape, size and shade. It happens that over time all these characteristics may change. Changes in spots are an unfavorable factor that signals the progression of the disease. Any new spots that appear on different parts of the body are an alarming symptom that should never be ignored. Even if these spots do not pose a threat to health.
Grayish spots on human skin are likely to be a sign of the development of lichen or skin cancer. Such spots are often smooth to the touch, without raising above the surface of the skin. There is a classification of gray spots, their types and reasons for formation:
- Vascular spots . The color of spots of this nature can vary from a pinkish tint to gray - the characteristics depend on the color of the blood vessels.
- Pigmentation . Pigment spots appear for various reasons. Color coloring from the presence of melanin in the body.
To accurately and correctly establish a diagnosis, you will have to spend a lot of time and patience. Examinations and consultations with many specialists will be required: oncologist, dermatologist, therapist.
Dermatitis
This skin condition is often hereditary or occurs as a result of stress. Symptoms include:
- itching;
- redness;
- rashes;
- peeling.
The affected areas of the skin are treated with Chlorhexidine, and additionally treated with Levomycetin or Erythromycin. Bubbles that are large in volume must be burst and lotions with Burov's liquid applied. Antihistamines (for example, Suprastin) will help relieve itching.