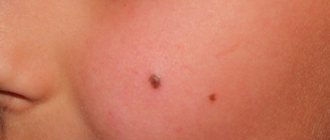
Some skin defects require urgent correction not only (and not so much) for the sake of aesthetics, but also to get rid of everyday physical discomfort and to protect your health from unnecessary risks. Such defects include warts and papillomas. This problem is more or less familiar to most of us (more than 80 percent of the entire population of the planet is at risk of developing these unpleasant formations, which can appear on any part of the skin of the body and even on mucous membranes).
Considering the diversity of such neoplasms and their different (often unpredictable) behavior, it is worth recalling the importance of a professional approach in solving the problem. The first step of treatment should be a consultation with a dermatologist, who will conduct a diagnosis, identify the problem and choose the most optimal treatment method.
In the article we will look at the types of tumors, the reasons for their appearance and modern methods of removing warts and papillomas, among which hardware technologies occupy a special place: electrocoagulation, laser and radio wave therapy.
Modern methods of getting rid of warts
What is the best method to remove papillomas? Modern medicine offers the following ways to eliminate skin growths:
- cauterization with chemicals;
- laser removal;
- electrocoagulation;
- freezing with liquid nitrogen;
- removal with a radio wave knife;
- surgical excision.
Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the localization of the rash. For example, for warts on the face, it is necessary to use more gentle methods than for rashes on the body. If papillomas are located in prominent places, then you should choose a removal method that leaves no visible marks on the skin.
It must also be remembered that warts are formed due to infection with papillomavirus. Such rashes are not just a cosmetic defect, but indicate the presence of an infectious disease - papillomatosis. Therefore, after removing warts, it is necessary to undergo a course of antiviral drug therapy.
Next, we will look in detail at various methods for removing skin tags.
Prognosis after removal
In most cases, a wart is a benign neoplasm that appears on the human body after infection with HPV strains belonging to the low oncogenic risk group. Therefore, removal of the growth coupled with drug treatment makes it possible to make favorable prognoses.
Difficult situations arise when a person is infected with strains that are at high oncogenic risk. The appearance of warts is the first alarming signal; activation of the virus can lead to malignancy processes. It is difficult to make predictions in this case, but it is known for certain that the sooner the process of malignancy is identified, the sooner adequate therapy is started, the greater the chances that everything will end well. That is why, if any warts appear on the body, it is important not to delay a visit to a dermatologist. The doctor will help you understand where papillomas come from and what to do next with them: observe them or is it better to remove them.
Chemical cauterization
There are pharmaceutical preparations for removing warts. These include:
- "Feresol".
- "Kondilin."
- "Solcoderm".
- "Super clean."
- "Verrukacid."
All these agents have a cauterizing effect. When applied to papilloma, they destroy neoplasm cells. The wart gradually dries out and dies.
This is the cheapest way to eliminate papillomas. However, it has many disadvantages. If cauterizing agents are used carelessly, there is a high risk of skin burns and scarring. Therefore, many pharmaceutical drugs are not intended for independent use. Chemical removal of papillomas is preferably carried out on an outpatient basis. Applying burning solutions to the area of the tumor may be accompanied by pain and discomfort.
What is the best way to remove papillomas? Can cauterization with chemicals become an alternative to professional cosmetology procedures? Eliminating a tumor using pharmaceutical products is a very long process. Warts usually die off within 3 to 4 weeks. In this way, only single small papillomas can be removed. For large and multiple rashes, this method is ineffective.
Drug treatment of papillomas
First of all, dermatologists recommend the use of medications to treat these tumors. Medicines help remove unpleasant-to-touch growths at home or in a doctor's office. There are a huge number of topical medications that relieve symptoms and significantly reduce the diameter of the affected area. Drug treatment allows you to quickly remove papillomas that have the following characteristics:
- The formations are located in an area with thin skin;
- They are pink, flesh-colored, white or light brown in color;
- Small sizes;
- Recent education.
Among the many modern drugs, the most popular and effective according to doctors and society should be highlighted.
Medicine Ferezol
The drug Feresol is a fairly effective drug for removing flat warts and genital warts. It consists of 60% of the active substance, phenol, and 40% of tricresol. Feresol is presented in the form of an oily liquid with a dark brown tint and a persistent phenol odor. The drug has a bactericidal and cauterizing effect on tumors caused by the papilloma virus. Removal of papillomas is carried out mainly due to the cauterizing effect, which is obtained as a result of a chemical burn of the skin and macromolecules of the growth.
The product is applied very carefully to the damaged area, without touching healthy skin. Application is carried out continuously for 15-45 minutes, the procedure time depends on the diameter of the wart. The formation on a thin stalk is removed by lubricating the stalk itself. The maximum number of repetitions of the procedure is 5 times.
Dermavit
Dermavit is a medicine that helps get rid of papillomatous formations, acting painlessly and preventing future relapses. Like the previous drug, Dermavit should be applied as carefully as possible, so as not to touch healthy areas of the skin. For this it is recommended to use a special patch. Dermavit is prohibited from being applied to papillomas located in the area of the mammary glands and armpits.
Super clean
One of the most popular and highly effective means for removing papillomas. As the name implies, the drug is presented in the form of a liquid based on the natural poison of celandine. The product is applied to the skin almost painlessly. After the procedure, peeling of the growth is observed within 5 days, and after a few more days the wart disappears. The use of Superclean is characterized by the complete destruction of HPV manifestations, due to which the skin becomes attractive again. The medicine is not recommended for use on warts on the face, since this area tends to have the most sensitive skin.
Isoprinosine
A modern generation antiviral drug designed to combat human papillomavirus infection. Isoprinosine is an immunomodulator and antiviral agent. Therefore, its range of effects is much wider and deeper than those of local applications. The medication stimulates the immune system, increasing the body's resistance to various viruses and infections. It restores the functions of lymphocytes in the process of weakening the immune system and thereby eliminates tumors caused by HPV. The drug is available in the form of tablets with the active ingredient 500 mg. Tablets should be taken after meals, two at a time. three times a day.
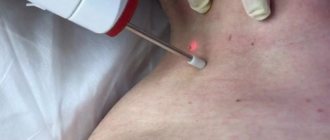
Laser therapy
Currently, the following types of lasers are used to get rid of warts:
- Carbon dioxide. These lasers burn out the tumor tissue.
- Erbium. Such devices evaporate the structure of the wart.
Before the procedure, a local anesthetic is injected into the treated area of skin. Then the tumor is exposed to a laser beam. After a few minutes, only a small crust remains at the site of the wart.
After such removal there are no visible marks left on the skin. The crust disappears on its own after 7 - 10 days. A light spot remains in its place for some time, but subsequently the skin color evens out.
Many patients consider laser therapy to be the best option. You can remove papillomas using this method absolutely painlessly and quickly. After all, the procedure lasts only a few minutes. In addition, laser treatment has the following advantages:
- no injury to the epidermis, bleeding or risk of infection;
- rapid skin recovery after the procedure;
- a small number of contraindications.
However, this method also has disadvantages. After all, when exposed to laser beams, the papilloma is completely destroyed. It is no longer possible to send neoplasm tissue for histological analysis. Multiple warts cannot always be removed the first time. If papillomas form a large conglomerate on an area of skin, then several sessions will be required to get rid of the rashes.
During the procedure, it is quite difficult to assess the depth of penetration of the laser beam. Therefore, the effectiveness of therapy largely depends on the qualifications and skills of the specialist.
Laser removal cannot be performed if the patient suffers from herpes, skin inflammation, and malignant tumors. This procedure is also contraindicated for pregnant women.
Equipping a room for laser tumor removal
General requirements for equipping an office for working with laser equipment, as well as other provisions governing work with laser equipment, are contained in the following regulatory documents:
- SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10. Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities.
- GOST R-50723-94. Laser safety. General safety requirements for the development and operation of laser products.
- Sanitary standards and rules for the design and operation of lasers No. 5804-91.
- OST 42-21-16-86. System of occupational safety standards. Departments, physiotherapy rooms. General safety requirements.
- Standard instructions on labor protection when working with laser devices (the instructions are developed by the head of the laser medicine department based on the Standard instructions on labor protection No. 06-14/20, taking into account the characteristics of a given medical institution).
- MU 287-113-00. Guidelines for disinfection, pre-sterilization cleaning and sterilization of medical devices.
Radio wave removal
This method of removing tumors involves cutting off the growth at its very base using an electrode attachment that emits high-frequency radio waves. This attachment is called a “radio knife”. During the procedure, the blood vessels are coagulated, which prevents the risk of infection of the wound. Depending on the location and size of the tumor, the doctor selects a nozzle of the required size and shape. To remove papilloma on a thin stalk, a loop attachment is used (the doctor pulls off the upper part of the papilloma with tweezers, and uses a loop attachment to cut it off at the base). The procedure is performed using local anesthesia.
The radio wave method can be used on all areas of the skin, but it is not used on mucous membranes. Its advantages are safety (no burns, complications), no bleeding and the possibility of conducting histological examination of excised tissue. The advantages also include a short rehabilitation period (lasts several days). As for the time of the procedure, it lasts about the same as electrocoagulation or laser removal (depending on the amount of work).
This procedure is most suitable for those papillomas and warts that have a narrow pedunculated base, as well as for thread-like papillomas. This method is ineffective for removing flat formations (laser removal or electrocoagulation will come to the rescue here).
Regardless of what equipment you decide to use to remove tumors, you will have to take care of good ventilation to remove combustion products, which should protect the doctor and patient from inhaling harmful substances during the work process. In addition, many serious clinics purchase a special smoke exhaust device for the office designed to perform such procedures.
What should you consider when choosing equipment?
- Availability of permits for the device.
- The price of the device and attachments, consumables.
- Technical characteristics (and at the same time the capabilities of the device).
- Reputation of the supplier company in the market.
- Experience of successful use of this device in other salons or clinics.
- Possibility of training doctors to use the device (when purchasing equipment and after). Will the training be paid or free (check in advance the cost and number of trainees if the training is paid).
- Conditions of warranty and post-warranty service of the device.
- If the company provides such an opportunity, test the device before purchasing.
It should be remembered that dermatovenereologists and surgeons who have received the necessary education and appropriate documentary evidence have the right to work on these types of equipment. To provide services for the removal of tumors using any type of equipment, an enterprise requires a medical license for dermatovenerology.
The editors would like to express gratitude for their assistance in preparing the material:
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher of the Department of Dermatovenereology of Northwestern State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikov, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea);
Anna Vladimirovna Lopatina, dermatovenerologist, dermatocosmetologist, specialist in the field of laser technologies and rehabilitation, consultant doctor at the Educational Center (Russia, Moscow).
Electrocoagulation
For this procedure, a special device is used - an electrocoagulator. Wart removal is carried out under local anesthesia.
To eliminate papillomas, a special metal loop is used. Using electric current, it is heated to a temperature of +80 degrees. The specialist quickly cuts off the wart with a hot loop. In this case, bleeding does not occur, since the capillaries are sealed under the influence of high temperatures. Removal this way takes about 1 minute.
A black crust remains at the site of the wart. The postoperative field should not be wet. The wound must be treated with antiseptics. After 2 weeks, the crust disappears, and a white spot or dimple may remain in its place. Before going outside, it is recommended to lubricate the depigmented area of skin with sunscreen. With proper skin care, no traces remain after the procedure.
The following advantages of electrocoagulation can be listed:
- possibility of histological analysis;
- no bleeding;
- rapid removal of the tumor.
However, this method can only be used to get rid of warts that rise above the skin. If the papilloma is located deep under the epidermis, then it is impossible to cut it off with an electric loop.
Removal using electrocoagulation is prohibited for the following diseases and conditions:
- herpes;
- oncological pathologies;
- low blood clotting;
- allergies to anesthetics;
- wearing a pacemaker;
- hypertension;
- heart diseases.
What is better to remove papillomas - laser or electrocoagulation? If there is a need for histological examination of neoplasm tissue, then it is better to resort to removal using an electric loop. After all, with this method, the wart is not destroyed, and it is possible to send it for microscopy. But electrocoagulation is more suitable for small papillomas. While with the help of a laser it is possible to remove tumors measuring 3 - 4 cm.
Laser therapy is a more gentle method. After electrocoagulation, the wound heals within 14 days. The site where papilloma is removed requires careful care. Laser treatment is less traumatic, so the skin recovers much faster after the procedure.
Warts and papillomas: distinctive features and types
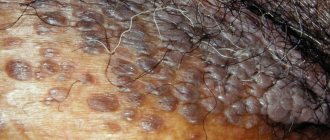
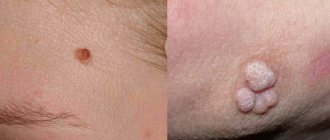
A wart is a rather dense growth formed by keratinized epidermal cells. The wart is nourished by an extensive network of capillaries. The durable surface protects the soft interior from damage. The upper part of the wart is usually uneven, but the growth itself has fairly clear boundaries. In this case, the wart may be irregular or round in shape. The size of the wart is 2–10 mm, its color can be flesh-colored, dirty gray or brown. A rod (a black dot surrounded by capillaries) may be located in the center of the wart. The most common locations for warts are the following: feet, palms, knees, elbows (that is, places of increased trauma). Most often, HPV type 2 causes warts.
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“A wart is morphologically a dirty yellow or dirty gray papule with an uneven, rough surface, often round in shape. The main histological process is papillomatosis, which is the proliferation of dermal papillae. As is known, they contain the vessels of the superficial network of the middle layer of the skin, therefore, with papillomatosis, the doctor and the patient pay attention to the presence of “black dots”, which in essence represent thrombosed vessels. In addition to papillomatosis, hyperkeratosis and acanthosis (pigmentary papillary skin dystrophy, a type of dermatosis) may be observed, which give the warts a dirty tint.”
The most common types of warts are:
- simple, or vulgar, - round, usually flesh-colored (may darken over time), capable of rising above the surface of the skin up to 5 mm. Such warts often grow. This type makes up 70 percent of the total number of skin neoplasms and occurs most often in young people. It is caused by HPV strains such as 1–4, 27, 29, 57;
- plantar - located on the feet and palms and look like spikes grown into the surface of the skin. They often cause discomfort or pain and interfere with walking. Appear due to the activity of HPV types 1, 3, 27, 29 and 57;
- flat (juvenile) - they have a flat surface, are flesh-colored or brown, and can rise above the skin by 1-2 mm. Appear on the back of the hands or on the face. These warts are usually caused by HPV types 3, 10, 28, 41.
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“Vulgar warts most often affect the area of the hands. With multiple warts, as a rule, there are “dropouts”. The most difficult in terms of destruction are periungual and subungual vulgar warts. Flat warts, as a rule, form in young people (usually on the skin of the face and back of the hands); proliferative processes such as acanthosis and hyperkeratosis are not so strongly expressed in them. It is necessary to differentiate flat warts from adenomas of the sebaceous glands, keratomas and other neoplasms.”
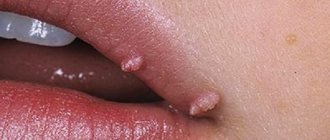
Papilloma has a round shape and has a soft structure. Often the papilloma has a wide papillary base and a thin stalk with which it is attached to the surface of the skin. The color of papilloma varies from flesh to brown. Usually papillomas do not cause pain, but sometimes they cause discomfort in the form of itching (if they grow during the period of virus activity). The size of the formation is usually in the range of 0.2–10 mm. HPV strains such as 6, 11, 16, 18, 30, 31, 33 and other types are related to the appearance of papillomas.
Here are the most common types of papillomas.
Simple (vulgar or ordinary) papillomas often appear on the back of the hand or in the groin area (but can occur on any part of the body), they rise slightly above the skin, reach 0.2–1 cm in diameter and usually do not differ in color from the surrounding ones skin areas. They occur due to HPV types 26–29, 41, 63, 77.
Flat papillomas most often appear on the arms, neck, external genitalia, around the anus, and on the cervix. They resemble flat, light yellow plaques in appearance, which rise slightly above the surface of the skin. They can lie deep in the skin. Flat papillomas of HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33 have a high risk of oncogenicity.
Thread-like papillomas, or acrochords, grow on a thin stalk; first appears as a tiny bulge, acquiring a long shape as it grows. These growths often hang from the skin and are soft and may feel watery to the touch. These tumors are caused by HPV types 2 and 7. Most often they appear in people after 40 years of age, located on the thin skin of the eyelids, neck, armpits, mammary glands, and also in the groin area.
Pointed papillomas, or condylomas (genital papillomas), are tiny papillary growths that, when growing in large quantities, form comb-like formations with a sharp edge. These types of papillomas are caused by sexually transmitted types of HPV (types 6 and 11). They are localized on the inner thighs, in the anogenital zone, on the surface of the vulva, inside the vagina and urethra, in the perianal region, on the cervix. They are characterized by rapid growth. Round papular pustules are one of the types of condyloma.
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“Acuminate condylomata are caused only by viruses types 6 and 11, which have a low risk of oncogenicity. Clinically, they appear as soft pink areas of mucous membranes, papules with a slightly uneven surface, and may be elevated, pointed, or have a lobular structure.”
Basal cell papillomas most often appear after the age of 50, develop from the basal layer of cells, the diameter ranges from 1 mm to 4 cm. They are formed on the open surface of the skin, near the hair follicle, grow very slowly in size and, as a rule, do not pose a risk of degeneration into a malignant formation (except in very rare cases).
Sometimes papillomas and warts are confused with moles (nevi), but moles have a completely different nature (they do not appear due to HPV).
General properties of papillomas and warts:
- appear due to HPV;
- affect the surface layer of the epidermis;
- have common risk factors (weakened immunity, stress, infectious diseases);
- have blood vessels (damage to the growth can be accompanied by severe bleeding, and also cause itching, irritation, and swelling of surrounding tissues);
- benign nature (which can change under the influence of various factors, and some formations can degenerate into malignant).
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“In my opinion, benign formations such as papillomas are not always formed in connection with HPV. The most common localizations of papillomas are the neck, axillary (axillary) hollows, folds under the mammary glands and inguinal-femoral folds, that is, those places where friction occurs on the surfaces of the skin and clothing, which are characterized by sweating. With such mechanical irritation, it is possible to form peculiar protrusions - papillomas, which, when traumatized, can become infected and degenerate into pyogenic granuloma.”
Differences between papillomas and warts:
- papillomas are usually localized in areas of profuse sweating (in the folds of the skin), while warts “grow” in open areas;
- usually papillomas are soft and have a thin stalk, and warts fit tightly to the surface of the skin (have a wide base);
- if the papilloma is able to change its size only in the direction of increasing, then the wart can decrease, and sometimes even disappear completely on its own;
- if the appearance of papilloma is caused by an oncogenic strain of the virus, then it can eventually degenerate from benign to malignant, and warts rarely create such a risk;
- papillomas, having appeared on the skin, do not “go away” on their own without therapy, but warts sometimes disappear on their own.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is the freezing of tumors with liquid nitrogen. This gas liquefies at extremely low temperatures. Exposure to cold leads to cell death and coagulation of proteins inside the papilloma.
Nitrogen is applied to a stick with cotton wool. In some cases, a special nozzle is used from which liquefied gas is supplied. Then the specialist touches the growth with the applicator and holds it for several seconds. Under the influence of cold, the neoplasm is destroyed.
After the procedure, the papilloma first turns pale, then swells and turns red. After 24 hours, a bubble appears in its place. Under no circumstances should it be pierced, otherwise a scar may remain. The bubble resolves on its own within 7 days. Then a crust appears in its place, and after it falls off, a pink spot remains. Over time, the skin color becomes even. It is recommended to treat the postoperative field with salicylic alcohol.
This method has the following advantages:
- no need for anesthesia;
- Possibility of use in children;
- painlessness;
- sterility.
Cryodestruction is contraindicated during pregnancy, as well as in case of infectious pathologies and exacerbation of any chronic diseases.
The disadvantages of the method include the impossibility of microscopy of papilloma tissue, since the wart is completely destroyed. If the tumor is located deep under the skin, several sessions of cryodestruction may be required.
What is better to remove papillomas - laser or nitrogen? With the help of laser beams you can get rid of larger papillomas. Only small warts can be treated with liquid nitrogen. In addition, the laser affects the tumor more accurately than an applicator with liquid nitrogen. Therefore, the risk of scar formation is lower than with cryodestruction.
Radio wave method
In this procedure, radio waves are used as a scalpel. This method is also called “radio knife”.
The affected area is treated with an antiseptic. Then an electrode is brought to the tumor. It is kept at some distance from the skin, without touching the wart. Through an electrode, radio radiation is supplied to the area of the papilloma, which dissects the tissue and cuts off the growth.
There are no burns after the procedure. Only a small crust appears, which falls off on its own after 7 days. The postoperative field should be protected from moisture and disinfected with antiseptics.
The following advantages of this method can be highlighted:
- low percentage of relapses of papillomatosis;
- no bleeding;
- fast healing;
- high efficiency;
- non-contact (radio waves act at a distance);
- possibility of histology of the removed tumor.
Removal by radio waves is contraindicated for pregnant women, as well as patients with herpes, skin inflammation and infectious diseases.
What is better to remove papillomas - laser or radio waves? The radio knife allows you to get rid of raised warts only. If the papilloma is located in the deep layers of the skin, then it is more advisable to use a laser.
In addition, the depth of penetration of laser beams is much easier to control than the effect of radio waves on the skin. When using a radioknife, there is a risk of accidental damage to healthy tissue. However, if there is a need for histological examination of wart cells, then it is better to use radio waves or electrocoagulation rather than a laser.
Preventive measures
The main point in preventing the manifestations of such neoplasms is considered to be regular strengthening of the immune system. There are also some precautions that everyone should know. After going to pools, baths and beaches, it is very important to take a shower and use disinfectants for the genitals. These include Miramistin and Chlorhexidine. It is also necessary to promptly treat damage to the skin and mucous membranes with iodine-based products. Preventive methods also include timely treatment of diseases that lead to decreased immunity. Neoplasms can reoccur when exposed to ultraviolet radiation, so it is recommended to protect the damaged area of skin from the sun in every possible way.
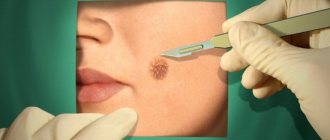
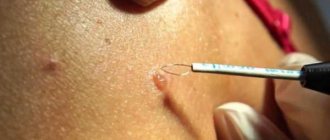
Surgical excision
Nowadays, removing warts with a scalpel is very rarely used. After all, there are more gentle and less traumatic methods of getting rid of skin growths. Surgical excision is used only in extreme cases. There are the following indications for this operation:
- very large wart size;
- location of papilloma in the deep layers of the epidermis;
- malignancy of the neoplasm;
- the presence of contraindications to removal by other methods.
The operation to remove papilloma is carried out according to the following algorithm:
- The papilloma and the surrounding area of the epidermis are anesthetized with a local anesthetic.
- The growth is removed using a scalpel. At the same time, part of the healthy skin near the wart is also cut off.
- The removed growth is sent to the laboratory for histology.
- The removal site is tightly bandaged to stop bleeding.
- Sutures are placed on the postoperative wound.
The main disadvantage of this method is its high invasiveness. The skin heals completely and is restored only after 1 month. After such an operation, scars remain on the epidermis. They have to be eliminated using a special patch that absorbs scar tissue.
In addition, with surgical removal there is a risk of spreading papillomatosis to healthy areas of the skin. After all, during the operation the scalpel comes into contact with the patient’s blood, which contains the virus.
What is better to remove papillomas - with a laser or a scalpel? Of course, exposure to rays is much less damaging to the skin than excision. However, if malignant changes have already begun in the papilloma cells, then the use of a laser is strictly contraindicated. In such advanced cases, it is no longer possible to use more modern and gentle methods and you have to resort to classic excision of the wart.
On the face and neck
The choice of wart removal method largely depends on the location of the rash. The face and neck are exposed areas of skin. Any postoperative changes are clearly visible on them. Therefore, it is better to choose methods of getting rid of growths that leave a minimum of traces.
What is the best way to remove papillomas on the face? Most experts recommend removing such warts with a laser. This is one of the least traumatic methods. There are no noticeable marks left after the procedure, and skin pigmentation at the site of the removed growth is quickly restored.
However, after laser treatment, the reappearance of warts cannot be ruled out. This is due to the fact that it is not always possible to control the depth of beam penetration. As a result, the tumor is not completely eliminated. What is the best way to remove papillomas on the face if the rashes constantly recur? In this case, doctors recommend combination treatment. Laser therapy is combined with exposure to liquid nitrogen. After removal of the rash, a course of antiviral therapy is required. This helps prevent relapses.
What is the best way to remove papillomas on the eyelids? Warts are quite often localized in the area around the eyes. Great care must be taken when eliminating rashes. Any awkward movement can lead to damage to eye tissue. Experts recommend eliminating tumors on the eyelids using a laser. This is the most minimally traumatic and painless method.
Under no circumstances should you remove growths on your eyelids yourself using pharmaceutical products. Otherwise, the cauterizing liquid may enter the eye and cause serious tissue damage.
What is the best way to remove papillomas on the neck? For single tumors, doctors recommend removing the wart using a radio knife. To avoid relapses, treatment is supplemented with cryodestruction. Then the patient needs a course of drug therapy.
New growths in the lower part of the neck are quite often rubbed by clothing and jewelry. This leads to the rapid formation of many secondary small warts around one large growth. What is the best way to remove papillomas on the neck if they have spread over a large area of skin? In such cases, laser therapy is indicated. Multiple treatments are usually required to completely get rid of multiple warts.
On the body
What is the best way to remove papillomas on the body? These areas of skin are usually covered by clothing. Therefore, warts can be eliminated using almost any method: cryodestruction, laser, electric loop or radio knife. In advanced cases, surgical excision is used. A single papilloma can be removed using pharmaceutical drugs.
Your doctor will advise you on the best method of removal. The choice of method largely depends on the nature of the papilloma and the depth of its location. After eliminating the growth, it is recommended to apply a bandage or plaster to the wart site. This will help avoid injury to the wound from clothing.
On the feet
Plantar warts (thorns) cause a lot of inconvenience to patients. Such tumors cause pain when walking and often bleed. Therefore, they are subject to mandatory removal.
What is the best way to remove papillomas on the feet? Getting rid of plantar warts is not easy. Such neoplasms have a root that grows deep under the skin. If it is not removed, plantar warts will constantly recur. Therefore, in this case, cryodestruction or laser therapy is most effective. Electrocoagulation and radioknife will not help get rid of the root of the wart.
In advanced cases, the spines are removed with a scalpel. In this case, it is necessary to scrape out the root of the papilloma using a special spoon.
Why do you need to remove papillomas and warts?
For the most part, benign neoplasms such as papillomas and warts do not cause direct harm to health. Some papillomas can remain on the skin for decades without changing their appearance or increasing in size. However, they create certain difficulties and risks. Thus, a wart on the foot often tends to grow and over time begins to poison life with everyday pain when walking. Warts on the fingers (these often appear in children) or hanging papillomas in the folds of the skin in women can lead to injury to soft tissues. For example, if papillomas are located in the chest or back area, then in the process of constant friction (for example, against a harness or bra clasp), the neoplasms can accidentally be torn off, bleed and become inflamed. Often others begin to appear near one papilloma.
There is an even more serious reason for timely removal of tumors. Among the numerous strains of papillomavirus, non-oncogenic, weakly oncogenic and types of HPV with a high level of oncogenicity are known. The latter are at risk of degeneration: neoplasms that appear due to their fault can, over time, turn from benign to malignant. By removing such tumors in a timely manner, skin cancer can be prevented.
The problem also lies in the fact that an ordinary person can mistake another, more dangerous neoplasm for a papilloma or wart, and either take up self-medication or simply not pay attention to it. Therefore, with all questions and doubts, it is important to go to a specialist (dermatologist), he will conduct a diagnosis, determine the origin of the tumors, the degree of danger and then suggest treatment methods that are optimal in this case.
It is highly not recommended to remove papillomas and warts on your own, without first examining a specialist: this may not only not bring the desired effect, but also aggravate the problem (especially you should not rip off or cut off the growths).
Alidzhan Ganemovich Khabbus, dermatovenerologist, cosmetologist, laser therapist, teacher at the Department of Dermatovenereology of North-Western State Medical University named after. I.I. Mechnikova, ICG certified specialist in fractional and laser devices Ilooda (Korea):
“Of course, viral warts require timely treatment, otherwise the process can spread significantly throughout the skin and also lead to infection of surrounding people. As for papillomas, the formations must be removed to prevent their growth, trauma, possible infection and for aesthetic reasons.”
In intimate places
Quite often, papillomas appear on the mucous membrane of the genitals. Doctors call such rashes genital warts. Warts appear during exacerbation of chronic papillomatosis. The HPV virus lives in the body of 90% of people and is activated with any decrease in immunity.
When rashes are localized on the mucous membranes, it is recommended to use gentle methods for removing papillomas. What is the best way to remove genital warts? The most commonly used is laser treatment or cryodestruction. For a small number of rashes, electrocoagulation can be used. However, before the procedure it is necessary to take a test and determine the type of virus. Some strains of HPV are oncogenic. In such cases, condylomas cannot be cut off with an electric loop.
Papillomas and warts: nature and causes of appearance
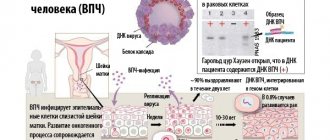
Papillomas and warts belong to the category of benign neoplasms, or tumors, that develop from epithelial tissue and can affect any part of the body, including mucous membranes and internal ducts. (Warts are often also called papillomas - due to the same source of occurrence, as well as due to external similarity. We will consider them separately, since the differences between these neoplasms will influence the choice of how to solve the problem.)
Papillomas and warts have a single source of appearance - the human papillomavirus (HPV). Damage occurs through direct contact (contact of skin or mucous membranes) or indirect (through contaminated objects, use of public baths, saunas, exercise equipment, etc.) subject to the presence of mechanical and other damage to the skin (wounds, scratches, chafing). Transmission of the virus is facilitated by excessive sweating. The immune characteristics of the body play a role: with a decrease in immunity, the formations may become larger and they are more resistant to elimination.
Human papillomavirus infection is widespread: according to some estimates, the problem affects 300 million people in the world (in Russia, about a third of the population suffers from it). Well, as mentioned earlier, more than 80 percent of the planet’s population are carriers of the virus. There are over 600 types of HPV strains.
Benign formations that arise due to HPV are divided according to the type of organisms affected (there is a human virus, but there are only animals), according to the appearance of the formation and its shape, according to the location (skin or mucous membranes), according to the rate of growth.
The virus manifests itself on the skin under the influence of the following factors: a decrease in immunity (including due to HIV infection, oncology, leukemia, taking immunosuppressive drugs such as glucocorticosteroids, cytostatics, radiation therapy), hormonal fluctuations, stress, hypovitaminosis, bad habits, skin damage (cuts, scratches, abrasions, etc.), ignoring the rules of personal hygiene, active sex life without the use of barrier contraception.
Patient reviews
You can find a large number of positive reviews about laser removal of growths. During the procedure, people did not feel any burning or pain. In most cases, the skin recovered very quickly. Patients emphasize that after the crust falls off, it is necessary to use sunscreen. Otherwise, a pigmented spot may remain on the skin.
Many patients believe that cryodestruction is one of the best methods. You can remove papillomas with liquid nitrogen without anesthesia, since the procedure is absolutely painless. This method is not contraindicated even for small children. Reviews note that the skin quickly recovers after cryodestruction. This method is also suitable for patients with allergies to anesthetics.
As for electrocoagulation and radioknife, conflicting reviews can be found about these procedures. Many patients did not experience any discomfort during the session. However, some reviews reported that cutting off the wart was quite painful. Here a lot depends on the individual pain threshold of a person.
Some reviews report recurrence of warts after removal. This was most often observed with multiple rashes. In such cases, it is necessary not only to eliminate the tumor, but also to undergo a course of therapy with antiviral drugs and immunomodulators. This will help suppress the activity of the virus and avoid the reappearance of papillomas.