Causes
The etiology of the disease is unknown. The main reasons for the development, according to doctors:
- Hereditary predisposition. It is not dermatitis itself that is inherited, but the conditions that contribute to its occurrence. It has been proven that with seborrheic dermatitis, the qualitative chemical composition of the secretion synthesized by the sebaceous glands changes.
- Formation of hormonal levels. In the early neonatal period, hormones received from the mother in utero are present in the blood of newborns. These substances have a stimulating effect on the sebaceous glands: they cause hyperplasia and hyperfunction.
- A decrease in local immunity leads to the activation of yeast-like fungi of the species Malassezia furfur, which are normally present on the skin in the form of spores. These fungi are called lipophilic because they feed on sebum. Rapid growth and proliferation of fungi cause inflammation, and overproduction of the sebaceous glands disrupts the process of physiological rejection of dead epithelial cells. They are glued together by sebum and remain on the skin in the form of scaly-cortical layers.
- Secondary immunodeficiency states as a result of intrauterine infection of the fetus.
- Diseases of the digestive tract associated with malabsorption (lack of microelements and vitamins involved in metabolic processes) or loss of fluid (dehydration).
- Poor nutrition of the mother (abuse of fatty, sweet foods) during lactation or incorrect selection of milk formulas if the child is bottle-fed.
- Frequent acute infectious diseases that weaken the immune system.
- Taking certain medications (glucocorticoids, antibiotics).
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Violations of the rules of hygienic child care, rare bathing.
- Wash your hair daily with allergenic products or soap. In this case, the protective fat film is washed off, which forces the sebaceous glands to increase sebum production.
- Overheating, which leads to increased sweating of the scalp when the child wears caps.
- Low indoor humidity.
Causes of seborrhea in infants
In most cases, seborrheic dermatitis in infants is a variant of the physiological form. This is explained by the fact that his skin is very soft and sensitive, and the sebaceous glands are not yet fully functioning.
Between the ages of birth and 1.5 years, seborrheic dermatitis occurs in every 4-5 children. Many doctors attribute the occurrence of such a deviation in a child to the influence of maternal hormones.
Reasons for the development of seborrheic dermatitis in infants:
- heredity,
- use of aggressive cosmetics,
- child's excessive sweating
- wrapping and high temperature in the room.
The child does not inherit the disease itself, but only a tendency to increased production of sebum. The use of inappropriate toilet soap and other cosmetics can provoke the development of such a deviation.
Symptoms
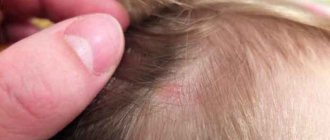
The main clinical manifestation of gneiss is the presence of fatty yellowish-white deposits on the crown of the baby around the large fontanel.
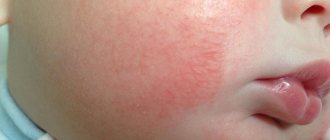
The skin underneath is unchanged, sometimes hyperemic. Less commonly, scaly formations are located on the face: on the forehead, near the eyebrows, on the cheeks, on the chin, behind the ears. Itching is absent or very mild.
The disease occurs in three forms: mild, moderate and severe.
- In mild forms, seborrhea in infants on the head looks like dandruff. The scales are easily separated from the skin, the epidermis underneath is not changed. There is no itching, the child’s general condition does not suffer.
- The average form is characterized by more extensive skin lesions, the scaly-cortical layers are dense and brown in color. When the crusts are rejected, inflamed, bright red skin is exposed. The pathological process extends not only to the face (forehead, eyebrows, bridge of the nose, temporal areas), but also to the back of the head, neck, torso and limbs. In the photo below you can see the manifestations of seborrheic dermatitis on the face.
- The severe form is characterized by the formation on the scalp of merging powerful scaly-cortical layers that cover the skull in the form of a “seborrheic cap.” The superficial layer of the epidermis is affected. The skin after peeling off the crusts is inflamed, red with areas of erosion and cracks. With this form of seborrhea, a secondary infection may occur. The hair growing in the affected area is also damaged: it becomes brittle and falls out easily. The child's general condition deteriorates significantly: itching, interrupted sleep, poor weight gain, restlessness and frequent crying appear.
Reasons for the development of the disease
The disease in infants has a special character. To date, scientists have not been able to establish under the influence of which factors it develops most often. Today there are several versions:
We recommend reading: Peeling skin in a newborn
- Completion of the formation of the hormonal system. Immediately after birth, the baby’s body will be stressed, especially if compared with the living conditions in the womb. His endocrine system is completing its formation and its further functioning is being established. Hormonal changes lead to increased activity of the sebaceous glands on the head. Each child has its own characteristics, so crusts can develop through negative internal processes.
- Seborrhea can develop under the influence of external negative factors. For example, if a baby is forced to constantly wear a hat, then his scalp sweats. The disease can also progress if you regularly bathe with harsh detergents. They disrupt the functioning of the sebaceous glands and dry out the skin. The process can be triggered by poor nutrition of the mother. The pathology is also inherent in children on artificial feeding. In this case, the mixture itself has a negative effect. There is no need to rush into introducing complementary foods. Some products cause unpleasant crusts to appear on your baby's skin.
- Seborrhea of the scalp also develops under the influence of yeast fungi. These microorganisms live on the skin and lead to the development of disease or dandruff. If the fungus develops actively, then scales form in the area of the sebaceous glands.
- The body’s protective functions are weak, so the yeast fungus can develop its active life activity. Infectious diseases, low weight or genetics can aggravate the situation. These factors negatively affect the functioning of the immune system and do not allow it to form.
If several causes are combined, then the patient may experience a worsening of seborrhea.
Complications
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp in babies is a benign disease that often goes away on its own without treatment.
With extensive scaly layers, the hair follicles are also damaged. In such cases, partial alopecia or baldness is possible. After treating seborrhea, hair growth is restored.
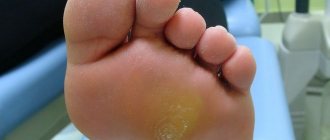
But in severe cases, in a weakened child, a secondary infection of the pathological focus occurs with pathogenic bacteria - streptococcus, staphylococcus. Symptoms appear in the form of ulcers on the scalp, which is especially dangerous because the veins located here have anastomoses, that is, they connect to the vessels of the brain. If not diagnosed and treated in a timely manner, this can lead to the occurrence of such serious diseases as meningitis or encephalitis.
What does seborrheic dermatitis look like?
The occurrence of the disease depends on the specific species. The following types of seborrheic dermatitis are distinguished:
- fatty;
- dry;
- mixed;
- physiological.
The oily form occurs as a result of the active work of the sebaceous glands. It manifests itself through the appearance of large pigs, which can combine into one extensive lesion.
The dry type of seborrheic dermatitis occurs due to insufficient functioning of the sebaceous glands. Most often, this type is observed in children under 1 year of age. These are white-gray and yellow-white scales that cover the baby's entire head. They can be combed out quite easily with a comb. In this case, the hair becomes very thin, and signs of partial alopecia may appear.
The dry type of seborrheic dermatitis can be accompanied by the formation of seborrheic lesions, that is, small red-pink spots. They occur in the face and other parts of the body.
The mixed type of lesion includes manifestations of the oily and dry forms of the disease. The physiological type often occurs in adolescence, as it occurs against the backdrop of hormonal changes in the body. It manifests itself through acne.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made on the basis of characteristic clinical symptoms: localization of pathology in the scalp in the form of scaly formations. Peeling on the face is finely lamellar, with whitish scales.
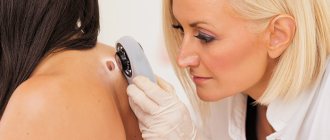
In unclear cases, diagnosis is carried out by a dermatologist. Using a dermatoscope under multiple magnification, pathological lesions on the skin are studied and microscopy of scales is performed.
If seborrheic dermatitis does not go away in the first year of life, but continues to progress, differential diagnosis with atopic, allergic dermatitis and psoriasis is necessary.
Clinical manifestations
Seborrhea often affects the scalp. To make a diagnosis, doctors examine the scalp and observe the baby’s behavior. Dermatitis is accompanied by itchy skin, so children become more capricious, often cry, rub their heads on the pillow, and refuse to put on a hat.
If parents notice such behavior in a child, then they need to check the skin and hair. Characteristic clinical manifestations can be identified:
- the crusts are hard and have a yellow-pink tint;
- small red pimples appear on the skin that look like prickly heat;
- hyperemia of the affected skin, skin irritation;
- dandruff.
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants is often confused with food allergies. For consultation you need to consult a doctor. He will monitor the child’s condition, give advice and recommendations on proper therapy. Pediatricians often prescribe effective medications, ointments and gels.
Therapy
There is no drug treatment for seborrheic lesions in infants. The famous pediatrician Dr. Komarovsky advises parents to provide their child with comfortable living conditions for any type of dermatitis: a certain temperature and humidity of the room.
Light forms of gneiss are physiological and do not require treatment. It is only necessary to establish proper hygienic care for the child.
To cleanse the epidermis of crusts, the following procedures are used:
- An hour before bathing, lubricate the scalp with olive, burdock or any other vegetable oil and put on a cotton cap. After bathing, carefully remove softened crusts with a brush. Manipulation should be carried out daily until the crusts completely disappear.
- Wash your hair with antifungal shampoos: Nizoral, Sebulex, Ionil. You can use them 2 times a week.
- The scalp is lubricated with a drying cream: Friderm, Bioderma, Zinc ointment.
- Bioderma Sensebio DS+ healing cream is applied in a thin layer to dry skin and not washed off. It has anti-inflammatory and fungicidal effects, regulates sebum synthesis. Particularly effective when used on the face.
- The scales can be removed by applying baby cream at night. In the morning, the head is washed with shampoo, the hair is carefully combed with a soft massage brush.
For bacterial infection, antibiotic therapy or systemic medications (tablets, injections) are prescribed.
If, despite the measures taken, scaly rashes do not decrease or other skin elements (papules, vesicles) appear that are not characteristic of seborrhea, you should consult a doctor.
Treatment for infants
Initially, the child develops several small milky crusts on the head; they go away on their own and do not cause discomfort. If seborrhea develops at an accelerated pace, you should consult a doctor so that he can select treatment.
Scraping off seborrheic crusts with a sharp object is strictly prohibited. The skin of a newborn is quite delicate, so it can be easily injured, and this will lead to the development of an infectious process.
Drug treatment involves taking the following medications:
- sedatives,
- antifungal,
- restorative,
- vitamin complexes,
- biogenic stimulants.
In parallel with taking medications internally, the use of external agents is prescribed. It is recommended to use shampoo containing tar, zinc and ketoconazole. The following external remedies are effective in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis:
- Sulfuric ointment,
- paste and sulsena soap,
- olive or baby oil,
- tar-based products.
As an additional effect for seborrhea on the head, cryomassage is recommended. Procedures such as laser puncture and darsonvalization are quite effective.
During treatment, it is necessary to pay special attention to the child’s diet. If the baby is breastfed, then the mother needs to give up canned, salty and fatty foods. The diet should contain a large amount of fruits, vegetables and foods that are rich in fiber, vitamins and beneficial minerals.
It is important to follow all hygiene rules. It is necessary to cleanse the baby's skin of dirt, peeling and crusts. Overheating should not be allowed; the baby should always be dressed for the weather.
Folk remedies
Seborrheic dermatitis can be treated with decoctions of medicinal plants after consulting a doctor.
Recipes:
- Take 15 g of dry roots of burdock, elecampane, and St. John's wort flowers. Place a tablespoon of the mixture in a thermos and add a glass of boiling water. After 8 hours, strain. After each shampoo, rub the infusion into the affected areas.
- Place 20 g of dry sage herb in a container, add 200 ml of hot water, boil for 15 minutes. After cooling and straining, moisten the skin daily in areas where crusts have accumulated.
- Pour 25 g of crushed oak bark into a saucepan, add 200 ml of boiling water, keep in a water bath for 5 minutes. Leave for 3 hours. Strain and rub the broth into sore spots.
- Make a mixture of equal parts of plantain leaves, calendula and chamomile flowers. Pour a tablespoon of the mixture into a thermos with 300 ml of boiling water. Leave for 3 hours. Use a gauze swab dipped in liquid to wipe the affected areas.
Traditional methods are effective when used regularly. Before using herbal infusions in a child, you should make sure that there is no allergy to a particular remedy . To do this, attach a cotton pad soaked in a herbal infusion to the inner surface of the baby’s arm near the wrist with an adhesive plaster. If the skin does not turn red after 24 hours, you can use the test product for treatment.
Pharmacy products
The pharmacy has many products for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children. Doctors may prescribe the following medications:
- Nizoral. The composition contains an antifungal component - ketoconazole. It helps eliminate itching and flaking. The product is used for the treatment of seborrhea no more than twice a week for 30 days. As a preventative measure, it is recommended to use shampoo once a month. This product has no age restrictions. Analogues are Sebozol, Dermazol, Ionel.
- Skin Cap. The main potent component is zinc pyrithioneate. It has an antibacterial and antifungal effect. With regular use, the intensity of itching and flaking decreases. Additionally, repeated relapse and complications of infectious etiology are prevented. The drug is prescribed to children who are already 1 year old. The duration of therapy is 2 weeks. An analogue is Friederm Zinc.
- Cynovitis. The composition includes a complex of main components - zinc pyrithione, urea, dexpanthenol, climbazole. The action of the medicine is anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, antifungal. Additionally, the skin is moisturized and dead cells are exfoliated. With regular and correct use, regenerative processes in soft tissues are activated.
The drug Cynovit in the form of shampoo should be used for a month, twice a week. The drug is suitable for dry and oily seborrhea. The medicine is prescribed to children over 1 year of age.
Prevention
To prevent seborrheic dermatitis, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During pregnancy, the expectant mother should lead a healthy lifestyle with good nutrition, avoid stress and contact with infections.
- Strictly follow all hygienic measures to care for the baby.
- When bathing your baby, use only hypoallergenic, fragrance-free baby soap.
- Avoid overheating the scalp by wearing numerous hats and scarves. At home, the baby's head should be open.
Seborrheic dermatitis is not a dangerous disease, but it is still not worth treating a child on your own without consulting a doctor.
Under the mask of harmless dandruff, other childhood dermatoses (atopic dermatitis and psoriasis) can be hidden, which without timely treatment become chronic forms that significantly worsen the child’s quality of life.
Treatment of the disease
In most cases, the disease in children under one year of age is not treated with medications: dermatitis can go away on its own after the child is 4 to 6 months old . And only occasionally, crusts on the head and face may not go away until 2 or 3 years.
But in order for the symptoms of the disease in young children to go away faster, parents must follow a number of rules:
- Do not put caps or caps on your child in a warm room . When going outside, you need to dress him according to the weather; if he sweats a lot, fungi will multiply more actively. The room temperature should be within 20 degrees, then sweating will be minimal.
- When bathing your baby, use only specialized products for children ; do not use foams or shampoos for older children. It is recommended to use the simplest soap and not even every day.
However, if the crusts on the head are already very extensive and cause discomfort, then, as prescribed by the doctor, use special antifungal agents and perform special manipulations to remove them.
You need to remove crusts on your head after softening. Previously, heated vegetable oil was used for this; now, in addition to it, you can use baby cream, Vaseline oil or special baby oil for the skin.
After lubricating, wait about 20 minutes and use a comb or head brush to carefully comb out the crusts. By then they will be very soft and will come off without pain. Then wash your baby's hair with shampoo.
Doctors in some cases prescribe not creams for seborrhea, but ointments to comb out the crusts. Their advantages are:
- they have a fattier consistency;
- the crusts will soften better;
- absorb slowly and cleanse the skin more gently.
Ointments also differ in composition. So, in some of them the active substance and auxiliary components are more concentrated.
The procedure for washing hair and combing out crusts in children is not recommended to be carried out more than once a week. After finishing bathing, lubricate the areas that have been freed from crusts with Bepanten for children. It will dry out inflamed areas or moisturize them if necessary.
Ointments are also prescribed when the rash spreads throughout the body, causing the baby discomfort when touched. Typically these are clotrimazole or hydrocortisone based products. Antibiotic ointments may be prescribed if crusts form or attempts to remove them fail to cause a secondary bacterial infection.
Stronger medications are prescribed by the doctor for severe forms of the disease. Only he can determine the degree of its severity, so self-medication is strictly forbidden.
To prevent complications with seborrheic dermatitis in infants, parents should treat the crusts strictly according to the algorithm:
- moisturizing and softening;
- combing;
- washing head;
- cream treatment.
It is strictly forbidden to touch or try to tear off dry crusts; this can injure the skin and cause infections. Baths for bathing and softening crusts based on folk remedies: string, oak bark or chamomile are allowed.
Recommended products
When seborrheic crusts appear on the baby’s head, parents think about how to remove them using modern baby care products. Among the large number of varieties of such cosmetics, the most effective can be named:
- BabyBorn baby soap. The product contains special oils that easily cope with seborrheic crusts.
- Cream STELAKER. It is produced by Mustela. It was developed specifically to combat baby's milk crusts.
- Biolane shampoo. The product removes plaque and moisturizes the skin. As a result, sebaceous formations soften.
In addition to these cosmetics, you can choose others. For them to be useful, it is necessary to carefully study the composition of the drug. After all, some remedies can cause harm, aggravating the situation. In this case, you will have to remove the crusts from the child with medications.
Features of care
Choosing the right shampoo is a priority, but not the main task. Parents should not constantly wrap their child in a blanket. You should not put a hat on your baby's head if he is indoors.
Many pediatricians talk about maintaining the correct temperature regime. They are sure that overheating leads to various irritations on the skin.
Proper care of children's hair is promoted by:
- Individual comb and comb. They should be soft and made from natural fabrics.
- Carefully wash your hair and comb it carefully.
- The use of loose elastic bands and rounded hairpins.
Proper care of your child's hair will help prevent the occurrence of seborrheic crusts on the baby's head. All the problems that arise in a baby can be overcome, and the first modest fluff will soon turn into thick and shiny curls.
Manifestations of seborrhea
Seborrhea on the head of a newborn appears approximately in the third week of his life. The work of the sebaceous glands intensifies around the third or fourth month of a baby’s life, so at this time you can see the largest number of crusts. Uncomplicated infant seborrhea resolves by about 8-10 months without special treatment.
It is not difficult to determine that the appearance of crusts on the face, eyebrows, and head is caused by the excessive work of the sebaceous glands. Seborrhea of the skin appears in the form of small, slightly raised spots with a greasy texture; their color is usually yellowish, but in some newborns it can almost merge with the shade of the skin. The crusts that appear in infants do not cause any changes in well-being, that is, there is no irritation, itching, or tightness of the skin. The only problem is the baby’s unkempt appearance, which naturally worries the mother more.
Individual crusts can merge with each other, and then seborrhea will affect almost the entire skin on the head. This change is often called "cradle cap". When combing a baby's hair, the scales easily come off and remain on the head, resembling dandruff.
ethnoscience
To eliminate seborrhea, it is recommended to regularly use oils. Additionally, parents are allowed to remove the scabs mechanically. Each time after water procedures, cosmetic oil is applied to the child’s skin. It is recommended to wear the cap for at least half an hour. Only after this can you comb your hair with a soft comb. Long hair should be cut. In this case, it will be much more convenient to remove the crusts and you will be able to pay maximum attention to this area.
Milk crusts should not be torn apart by hand when they are dry. The removal method must be correct. Otherwise, the risk of re-formation of scales increases.
The baby's skin is delicate, so any damage is dangerous due to the possibility of infection entering the surface. Mommy must understand that an allergic reaction can occur even to a special shampoo. In this case, it is not advisable to continue using this treatment option.
Opinion of a famous pediatrician
Dr. Komarovsky claims that seborrheic crusts on the head of infants are an age-related feature of many babies. He associates this with hyperfunction of the sebaceous glands. The child is usually not bothered by the scabs themselves, but by the process of combing them out, which is not mandatory. If your baby has long hair, it is impossible to get rid of the crusts without a haircut.
Parents should know that the plaque on the baby’s head goes away on its own sooner or later. However, in order to comb them out, you need to give your child a haircut.
Before removing crusts on the head, they can be softened with any vegetable oil. Then use a blunt-toothed comb.