general information
Any chemical burn is tissue damage that occurs under the influence of acids, salts of heavy metals, alkalis and other caustic liquids. Acid burns can occur for several reasons:
- traumatic situations in chemical production;
- accidents at home;
- violation of safety regulations when working with acids;
- as revenge;
- as a result of a suicide attempt.
The depth and severity of such a burn is influenced by the following factors:
- chemical concentration;
- amount of acid poured;
- the strength and mechanism of action of the chemical;
- degree of acid penetration;
- duration of exposure to the chemical.
Treatment is prescribed based on these factors.
Degrees of burns
Depending on the severity and depth of tissue damage, acid burns are divided into 4 degrees:
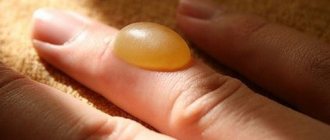
- I degree. The top layer of skin is damaged. Symptoms are characterized by slight redness, swelling and soreness on the injured part of the body.
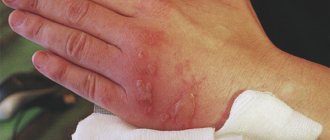
- II degree. At this level, sufficiently deep layers of skin are damaged. Signs of damage include blisters with clear contents on reddened and swollen skin.
- III degree. The lesion affects not just the deep layers of the skin, but also the subcutaneous adipose tissue. The blisters that appear after a burn are filled with a cloudy liquid containing blood. The victim is diagnosed with sensory impairment in the burn area.
- IV degree. The victim's condition is very serious. All layers of tissue are affected: skin, muscle fibers, tendons and even bones.
Extensive acid chemical burns can cause chills, fever, and fever. The victim may experience hallucinations and tremors of the limbs. The structure and color of the skin changes.
After an acid burn, a dry scab forms on the affected area of the body. Since acid is an aggressive substance, most often the victim receives third and fourth degree burns. With severe symptoms, a person needs first aid for an acid burn.
Features of different acids and their effects on the body
Most often, chemical injuries are caused by the following acids:
- Sulfuric. The affected area first becomes white, after which a dark brown scab forms on it.
- Household. Burns with acetic or citric acid cause severe redness and swelling, but no scab appears at the site of the injury.
- Nitrogen. Damaged skin becomes dark brown, the scab is delimited from healthy areas by a dark gray border.
- Solyanaya. A burn with hydrochloric acid is accompanied by the death of the epidermis; when the superficial vessels are damaged, the burned areas bleed.
- Salicylic. A pink crust forms on the body, which quickly peels off.
- Ant. The affected areas become whitish, they are separated from healthy skin by a bright red border.
According to statistics, more than 15% of burn wounds are caused by acids. The degree of damage is determined by the concentration of the substance and the duration of its contact with the skin.
Skin burn
If a person comes into contact with acid, they should remove all clothing that may have chemical residue on them. It is often not possible to undress the victim. In this case, it is recommended to cut the tissue, freeing the affected parts of the body.
First aid for a victim of acid burns includes washing the affected area. This will help wash away most of the chemical. Do not wash burns with hot water; it should be cool. It is necessary to wash the affected parts of the body under waste water; this cannot be done in a bathtub or basin. The water procedure should continue for a quarter of an hour. If help was not provided immediately, then the washing time should be increased to 30-40 minutes.
Increased pain after the water procedure indicates that the skin was not washed well enough. In this case, you should continue the process of washing the chemical off your body. After completing the procedure, you need to apply a dry bandage, for which you need to use a sterile bandage.
Do not remove acid using wet wipes or cotton pads. This will cause the chemical to rub into the skin, making the victim's condition worse.
The next step is to neutralize the chemical. Neutralization of acid is possible using:
- soap solution;
- 2% soda solution.
When providing first aid for acid burns, you must immediately minimize exposure to the chemical agent. If assistance is not provided in a timely manner, then even the first degree can progress to the second, and the patient’s condition will worsen.
Esophagus burn
You can burn your stomach and esophagus if you accidentally or intentionally drink acid. Most often, trouble occurs with vinegar when it is confused with water. Also, chemical substances are deliberately drunk as suicide. The clinical picture of the burn will be as follows:
- sharp pain;
- signs of respiratory distress due to a burn of the larynx;
- vomiting with mucus and blood.
Providing first aid for burns of the stomach and esophagus with acid consists of the following:
- Neutralizing the effects of a chemical . First aid for burns with acids and alkalis at this stage has a significant difference. When using acid, rinsing must be done with a soda solution. If a person accidentally drinks alkali, the stomach should be washed with a weak solution of vinegar.
- Amount of liquid . You need to drink a lot in order to reduce the acid concentration as much as possible and flush out the chemical from the stomach.
- Consultation with a doctor . Once emergency measures have been taken, you should go to the hospital.
If the victim is unable to get to a medical facility himself, it is necessary to call an ambulance.
Treatment of hydrochloric acid intoxication
Poisoning with liquid hydrochloric acid or its vapor must be treated in a hospital. The toxicologist prescribes symptomatic therapy. The first thing the doctor does is prescribe painkillers to eliminate pain shock.
Treatment includes medications to stop bleeding, maintain the functioning of the stomach and intestines, lungs, cardiovascular system, as well as the liver and kidneys. To prevent the development of the inflammatory process, the doctor may prescribe an antibiotic. The victim cannot eat for the first couple of days, and then he is prescribed a strict diet until the end of the course of treatment.
Burn of the mucous membrane of the eyes
Eye burns from acid always have serious consequences. It is important to provide first aid for burns of the mucous membrane of the eyes in the very first minutes, and then consult with an ophthalmologist. The complexity and severity of the injury is determined by:
- composition of the chemical;
- amount of acid;
- the strength of concentration of the chemical;
- temperature of the chemical.
Prompt emergency care reduces the risk of serious complications. Symptoms of such a burn will be as follows:
- severe cutting pain;
- fear of light;
- skin lesions near the burned eye;
- profuse tearing.
The algorithm for providing first aid for eye burns with acids should be clear:
- Eye wash . If this is not done immediately, the affected person may become completely blind. Rinsing should be done under running water. In this case, you should open the eyelid as wide as possible with your fingers.
- Duration of rinsing . It is necessary to rinse the affected eye for at least a quarter of an hour. The water pressure should not be very strong. The acid is washed out with cool water; for the alkali you will need milk.
- Bandage . After washing out the chemical, cover the eye with a bandage.
- Consultation with a doctor . You should immediately seek medical help.
In order to preserve your vision, you must strictly follow all the prescriptions and recommendations of the ophthalmologist.
Emergency medical care needed
For minor burns, it is enough to rinse the damaged area well and consult a doctor. But in more serious cases, professional help for acid burns is required. You should contact a medical facility under the following circumstances:
- Signs of shock. If the victim is in shock, he must be hospitalized immediately. This condition is characterized by pallor, shallow breathing and loss of consciousness.
- Unbearable pain. In case of severe pain that cannot be relieved with analgesics, the victim requires treatment in a hospital.
- Dimensions of the burn. An area of damage greater than 7 cm with a depth below the first layer of the epidermis requires treatment only under the supervision of a doctor in a hospital.
- It is especially important to immediately contact a specialist if the victim has an acid burn on the leg, arm, buttocks and face, and the eyes are also damaged.
It is necessary to show the doctor a sample of the chemical substance, this will make it easier for him to neutralize the chemical and help prescribe the correct therapy. In a medical facility, the victim is given:
- sedatives;
- antitetanus serum;
- analgesics.
The patient also removes dead pieces of skin and opens the burn blisters, after which a bandage with an antiseptic is applied. Once the healing process has begun, physical therapy treatment can be carried out.
How to remove Fukortsin stains from furniture, linoleum and clothing?
If handled carelessly, Fukortsin can get on household and interior items.
How to wash it in such cases?
- It is recommended to wash linoleum or other floor coverings with chlorine-containing compounds. This can be a bleach such as Domestos or whiteness. Such products will instantly wash off Fukortsin, but can damage the floor surface, so you need to work with them very quickly. The less effective, but safer “Vanish” will also wash off Fukortsin, but not the first time.
- The furniture can be cleaned with baking soda, which is applied to a sponge and rubbed into the stains. Use this method carefully as the crystals may scratch the surface.
- Chlorine-containing bleaches will remove traces of Fukortsin from white things. If the fabric allows it, you can load the laundry into an automatic machine and set the washing mode to a temperature of 90-95 degrees.
Colored linen will be saved by Vanish, designed for colored clothes. The soaking procedure will have to be repeated several times, but in the end the result will please you.
Treatment
At home, only minor burns with a small area of damage can be treated. Before using the medication, you need to do a test.
In any case, it is recommended to consult a doctor before treating a skin burn from acid. You can use the following medications:
- Panthenol . If you burn your hand with acid, you should immediately use this anti-burn drug. The product disinfects and accelerates the restoration of damaged tissues.
- Fusiderm . Thanks to its bactericidal and bacteriostatic effect, the ointment stimulates tissue regeneration in the burn area. For acid burns, the burned area of skin must be lubricated with the product several times a day.
- Sea buckthorn oil . The product softens the skin well, activates restoration and healing processes.
After providing medical care, you can use folk remedies, after consulting with your doctor.
Dangerous consequences
The damaging effect of acids depends on the location of the burn. When the reagent gets on the skin, the protein components of cells are destroyed, which leads to tissue necrosis. This is fraught with:
- infectious infection;
- suppuration;
- non-healing ulcers;
- gangrene.
If acid damages large areas of the body, scars form in the form of swellings. When joints are affected, contractures occur - limited mobility due to scarring of the skin.
Contact of concentrated acids with the eyes is dangerous:
- swelling and melting of the cornea;
- clouding of the lens;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- partial or complete blindness.
An acid burn of the esophagus is fraught with internal bleeding, respiratory failure, and the formation of esophageal-bronchial fistulas. Acids cause general poisoning, which leads to disruption of cardiac activity, consciousness and even death.
Folk remedies
Having received an acid burn, treatment can be carried out independently at home only in case of first and second degree damage. You can use traditional methods after consulting your doctor.
To speed up the healing process, it is recommended to use the following recipes:
- Aloe . It is necessary to cut the plant leaf in half and apply the fleshy part to the affected area of the body. You can grind the pulp to a paste and make a compress. The product is effective for hyperemia, swelling and pain after a burn. If there is no aloe, you can make a compress with a golden mustache.
- Potato . It is necessary to grate the tuber on a fine grater and place the pulp on the burned area, covering the top with a sterile bandage. The compress should be renewed every hour. This remedy is effective for minor fresh burns. You can also use juice or gruel of grated carrots.
- Echinacea tincture . It is necessary to fold the bandage in several layers and soak it in medicinal tincture, and then apply it to the burned area. The procedure can be done several times a day. In addition to burns, cuts and long-term non-healing wounds can be treated in this way. This method of therapy is suitable only for adults and is not recommended for burns in children.
Before deciding on a treatment method, it is recommended to consult a doctor before treating a burn with acid. You can only deal with minor burns on your own. If the skin is severely damaged, you should immediately consult a doctor, since often the first stage of treatment ends with the appearance of ulcers and oozing cracks.