A burn from sulfuric acid is one of the most dangerous chemical injuries. If previously it could be obtained mainly at work, now such injuries are very common in everyday life. Not everyone knows that first aid for a burn with sulfuric acid differs from those measures taken for thermal skin lesions and some other chemical burns. What to do if you are burned by a caustic chemical and how to help the victim? We will answer these questions in the article.
Why is a burn from sulfuric acid dangerous?
Burns from sulfuric acid are fraught with deep damage to soft and bone tissue. Contact of the reagent with the skin leads to:
- the formation of a white scab;
- ulceration of tissue under the crust;
- toxic poisoning of the body.
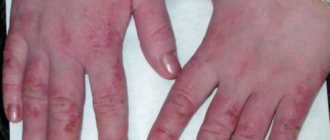
Upon contact with acid, skin necrosis occurs, and if large areas of the body are affected, burn shock occurs. Particularly dangerous are liquid vapors that penetrate the respiratory system. The burn causes severe pain and internal bleeding. Contact of the reagent with the eyes in 80% of cases results in partial or complete loss of vision.
Health effects [edit | edit code ]
If they come into contact with the skin, caustic substances cause a chemical burn and begin to corrode the tissue. Considering that the victim's face is often the target of the attacker, the auricle, eyelids, nose and lips are usually damaged. Long-term consequences include psychological trauma, dysfunction of the organs of hearing and vision.
The victim must be immediately sent to a specialized medical facility. As a first aid, remove the chemical without affecting healthy skin, rinse the affected areas with plenty of water and neutralize the acid.
Degree of skin damage
Burns occur due to careless handling of reagents at work and at home. The severity of a chemical injury is determined by the concentration of acid in the solution:
- diluted – the concentration of the oxidizing agent does not exceed 10%;
- electrolyte - a weakly concentrated solution with 22-30% reagent content;
- tower - a solution with nitrogen dioxide in which the acid concentration is 75%;
- concentrated – undiluted 96.5% acid.
When the substance acts on living tissues, intracellular protein is destroyed with the formation of organic and inorganic compounds - albumosis, proteinogenic amino acids, peptones, etc.
Using wet wipes or pieces of cloth soaked in water is strictly prohibited, as this can only worsen the situation.
There are 4 degrees of burns based on the depth of damage:
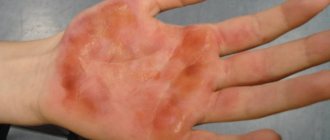
- First. The outer layers of the epidermis are destroyed, as indicated by moderate redness, pain, and swelling. The burn goes away within 3 days without any traces.
- Second. The epidermis is split down to the basal layer, which is directly adjacent to the dermis. Chemical injury is accompanied by pain, burning, and blistering rashes. By preserving the basal layer, the skin is restored within 2 weeks.
- Third. The reagent partially or completely affects the dermis. With 3A degree burns, the follicles and sebaceous glands are not damaged. A white scab appears on the burned area, with ulcerations underneath. 3B degree burns are characterized by the death of skin cells down to the hypodermis, that is, the subcutaneous fat layer.
- Fourth. Prolonged contact with a caustic liquid leads to charring of the skin, muscles and bone tissue.
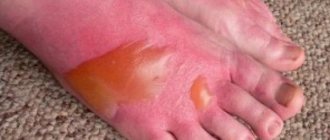
Burns with caustic acid lead to the formation of a white, loose crust with clear boundaries, which darkens over time. Outwardly, it seems that the injury is superficial and does not pose a danger. But ulcers form under the scab, and tissue death increases the risk of infectious inflammation.
Prevent infection
After treatment, a dry sterile bandage must be applied to the burn - this will help protect the damaged area from infection, and therefore speed up recovery. In addition, if blisters form on the surface of the skin, the bandage will protect them from accidental damage and rupture.
A minor burn, not a secondary infection, usually lasts 6-7 days.
Burns are among the most common household injuries. People are more likely to get burned while doing everyday housework than during fires, get sunburned on the beach or in a solarium, or accidentally spill vinegar essence or battery acid on their hands.
The first thing to do is to eliminate the impact of the damaging factor. During thermal treatment, you need to remove clothes that have been drenched in boiling water or that have been burnt (you cannot tear off pieces of fabric from the wound). Assess the degree of damage: if the skin is swollen, but the integrity of the skin is not compromised, we can talk about a first-degree burn.
READ MORE: How to gain weight with gastritis with high acidity - Healthy body
Third degree burns damage the deeper layers of the skin and require specialist intervention. A fourth-degree burn is accompanied by charring of the skin; subcutaneous tissue and even bone can be damaged - this is a very serious injury. Fortunately, most household burns are first or second degree, so you can administer first aid yourself.
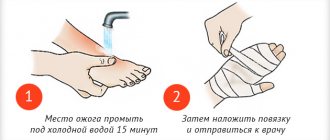
The affected area of the body needs to be cooled. If it is a limb, it should be placed under cold running water or placed in a container with cold water for 10-15 minutes. Only use water to cool first or second degree burns! If it is not possible to place the burned area of the body under running water, apply ice or a piece of frozen meat wrapped in a clean bag or towel.
Once the affected area is sufficiently cooled, a moist bandage can be applied. Special gel dressings are sold to facilitate healing and relieve pain. Anti-burn agents, for example, are best applied after the skin temperature in the area has been sufficiently reduced.
For chemical burns, wash off the caustic substance with water, then apply a bandage. This does not apply to burns caused by quicklime - exposure to water will cause a chemical reaction at the site of injury. The lime must be removed with a dry cloth, after which the affected area will need to be lubricated with oil.
If the burn is extensive (its area corresponds to approximately the area of 5 palms of the victim), it is better to consult a doctor, regardless of the degree of the burn.
Under no circumstances should you open the blisters that have formed, as this can lead to infection. Folk remedies should be avoided - egg whites, honey, cottage cheese and ink are best used for their intended purpose.
Do not lubricate the affected area with alcohol-containing liquids or iodine, as this will cause increased pain and further damage the injured skin.
Burns are also prohibited with oil or any greasy ointments - only special products recommended by a doctor are allowed, and they can be applied only after the skin has cooled.
A burn is a very serious injury. Depending on its degree, associated complications can occur, for example, infection or post-burn scars. Before answering the question “What to do if you get a burn?”, you need to determine what type of burn you received and what its degree is.
First aid for sulfuric acid burns
To provide medical assistance to the victim, it is necessary to have an understanding of the properties of caustic acids. Incorrect actions are fraught with deepening of the burn and life-threatening complications. In certain situations, you cannot even be near the victim without protective equipment - a respirator, rubber gloves, safety glasses. Inhalation of sulfuric acid fumes leads to destruction of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract.
First aid for burns with sulfuric acid involves:
- Reagent removal;
- cooling the affected areas;
- neutralization of acid with alkali;
- anesthesia;
- applying a sterile dressing.
In case of extensive burns, anti-shock and detoxification measures are carried out, which are aimed at reducing the toxic effect of the chemical on the body.
In case of skin damage
The algorithm for providing first aid if the reagent gets on the skin includes the following steps:
- Reagent removal. It is necessary to thoroughly rinse the affected area with water for 1 hour. Pre-burned tissues are dried to prevent deepening of the burn.
- Neutralization of acid. To do this, use a 10% soda solution - dissolve 1 tsp in 250 ml of water. baking soda. As an alternative, the affected areas of the skin are washed with slightly concentrated potassium permanganate or soap solution.
- Anesthesia. For severe pain, take NSAIDs - Ibuprofen, Ketanov, Naproxen. If the burning does not go away, use Novocaine solution.
Finally, a sterile bandage is applied and a doctor is called to the house or sent to the hospital.
If in eyes
Contact of sulfuric acid on the mucous membrane of the eye or cornea can lead to blindness. To prevent such complications, you should:
- rinse the affected area with plenty of running water;
- instill a 0.5% solution of Dicaine with adrenaline;
- anesthetize the eye with a 2% Novocaine solution.
After emergency assistance is provided, a specialist is called or sent to a burn center. Further therapy is determined by the ophthalmologist depending on the depth of penetration of the reagent into the eye.
In case of damage to the mucous membrane of the mouth and esophagus
The greatest danger to life is caused by burns of the gastrointestinal mucosa, stomach, and esophagus. Accidental ingestion of more than 5 mg of the substance is fatal.
Subsequently, after a chemical burn of internal organs, diseases such as pharyngitis, laryngitis, hemorrhagic pneumonia and others can develop.
In case of damage to internal organs, it is necessary:
- Rinse the stomach. The victim is given a solution of magnesium sulfate, which neutralizes the acids. If the drug is not at hand, use clean water.
- Treatment of the oral mucosa. Rinse with a 5% soda solution. If you inhale caustic fumes, you need to breathe in a soda solution through an inhaler.
- Drink plenty of fluids. Before the doctor arrives, provide plenty of fluids, clean water or milk.
To prevent even greater damage to the ENT organs, windows are opened in the room to allow fresh air to enter. Gastric lavage is effective only in the first 5-6 hours after injury.
It is strictly forbidden to provoke vomiting, as this can lead to rupture of the esophagus.
Attack statistics [edit | edit code ]
India ranks first in the absolute number of attacks, while Bangladesh leads in the number of acid attacks per 1,000 inhabitants. Both men and women are victims of assassination attempts, and both sexes are represented among attackers [9] .
A sulfuric acid burn is a dangerous chemical injury that is often fatal. The odorless and colorless oily liquid is a strong oxidizing agent. Upon contact with mucous membranes and skin, it instantly destroys epithelial cells. Inhalation of acid fumes leads to laryngitis, bronchitis, and hemorrhagic pneumonia. The degree of tissue damage depends on the percentage of the reagent in the solution. The principles of treating burns with caustic acids differ from the measures used for chemical injuries with other substances.
Further recovery
Corrosive acid rarely causes superficial injuries that do not require hospitalization. You should consult a doctor if:
- the burn is caused by highly concentrated acid;
- the affected area is large;
- acid entered the oral cavity, esophagus;
- the patient complains of acute pain.
Local therapy is limited to damage to only the superficial layers of the skin. Typically the treatment regimen includes:
- Baneocin is an antibacterial agent that reduces inflammation and pain. Prevents infectious inflammation of burn wounds.
- Panthenol is a fortified drug that accelerates metabolism. Heals uninfected wounds, increases local immunity.
- Actovegin is a wound-healing gel that cleanses the wound of charred tissue. Relieves pain, affects tissue metabolism, accelerating the healing of burns.
- Solcoseryl is an anti-inflammatory gel that dries weeping wounds. Accelerates the rejection of burned skin, stimulates its scarring.
For antiseptic treatment of affected areas, a solution of colloidal silver is used. For blistering rashes and tissue rejection, bandages with the following drugs are applied:
- Streptocide emulsion;
- Penicillin ointment;
- Vishnevsky ointment;
- Sudocrem, etc.
3rd degree acid burns are dangerous due to purulent complications. In case of wound infection with coccal infection, Miramistin and Chlorhexidine are used. For extensive lesions, systemic antimicrobial therapy is carried out with semisynthetic penicillins, aminoglycosides or cephalosporins - Gentamicin, Cefuroxime, Amoxicillin, Unazine, etc.
Destruction of the basal layer of skin is an indication for surgical intervention. The method of surgical treatment depends on the degree and extent of the damage - amputation, skin grafting. Even after successful treatment, acid leaves noticeable scars in the form of smudges.
In case of a gastrointestinal burn, bougienage is performed on the 7th day after the start of therapy. The essence of the procedure is the introduction of dilators - tubes of different diameters - into the esophagus. They prevent reduction of the lumen of the esophagus and scarring of the mucous membrane.
Symptoms
The damaging effects of sulfuric acid have much in common with burns from other chemicals. The main symptoms of a sulfuric acid burn include:
- the formation of a white crust on the skin with pronounced contours;
- burns are superficial, but the higher the concentration, the stronger the damaging effect;
- At first, after exposure to acid, the skin acquires a white tint, and then becomes gray or brown.
It is worth remembering that the symptoms that appear depend on the extent of the damage. The first stage is characterized by the formation of small swelling, accompanied by painful sensations. This happens if the acid had a low concentration.
The fourth degree burn is the most serious, since not only the top layer of skin is affected, but also tendons, as well as muscle and bone tissue. Necrosis can spread to nearby tissues. This stage is characterized by a rather long healing time and a large number of possible complications.
Burns with sulfuric acid provoke the development of a serious condition, the first symptoms of which are easily distinguished from other pathological conditions. Signs of damage directly depend on the location where the substance entered.
If a burn occurs due to acid vapor, the symptoms may be as follows:
- The mucous membrane of the respiratory organs is affected, swelling develops, and bleeding from the nose may occur;
- wheezing is observed during breathing, as well as spasms and pain in the chest area. In severe cases, suffocation may develop;
- damage to the digestive organs causes pronounced pain.
A burn injury from liquid acid provokes the following symptoms:
- When the substance gets ingested, severe pain is observed in all digestive organs. Severe vomiting with a large amount of blood appears;
- increased salivation and diarrhea develop;
- kidney damage provokes the release of bright red urine;
- the skin begins to turn blue;
- disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular system occur;
- Dark stains appear on the teeth.
When acid comes into contact with the skin, the following symptoms are observed:
- detachment of the upper skin;
- swelling;
- the formation of a soft white scab on the affected area;
- the affected area has clear contours;
- gradual darkening of the skin, the appearance of a brown tint;
- formation of coagulation type necrosis.
Dangerous complications
The destructive effect of acid is due to dehydration of tissues and the breakdown of protein components in them. The consequences are determined by the concentration of the caustic substance, its volume and duration of contact with the skin or mucous membranes. Highly active acid immediately provokes deep burns with charring of tissue.
Possible complications of chemical injury include:
- vomiting blood;
- toxic pulmonary edema;
- stenosis (narrowing) of the larynx;
- hemorrhagic pneumonia;
- subdural abscess;
- meningitis;
- purulent arthritis;
- phlegmon;
- burn shock;
- sepsis;
- gangrene.
If you do not provide assistance to the victim in time, this will lead to kidney or liver failure. In 93% of cases, such complications end in death. The risk zone includes patients with pyelonephritis, liver cirrhosis, glomerulonephritis, etc. Chemically active liquid provokes delayed complications. In 7% of cases, squamous cell carcinoma occurs at the site of scars.
Precautions when working with chemical agents
Burns from caustic acids occur in 67% of cases in people working in chemical industries. To minimize the risk of injury, you must follow safety precautions when working with concentrated oxidizing agents:
- chemicals must be stored in plastic or glass containers with an airtight lid;
- Before using the reagent, protect your eyes with goggles, your hands with rubber gloves, and your respiratory organs with a respirator;
- After work, the room is ventilated for 1-2 hours.
Chemicals should not be stored on the same shelf as food or medications. The acid should be out of reach of children.
Survival prognosis
The severity of the injury is determined by the concentration of the reagent and the location of the burn. The healing prognosis is determined by the rule of hundreds - the percentage of the burn area in relation to the remaining tissues is summed up with the age of the victim:
- less than 60 – favorable;
- up to 80 – relatively favorable;
- up to 100 – doubtful;
- more than 100 – unfavorable.
The prognosis for recovery depends on the location of the burn wounds and the depth of penetration of the reagent. The outcome of chemical injury worsens with burn shock and intoxication. Burns with concentrated acids are accompanied by prolonged inflammation. During healing, a lot of granulation tissue forms in the lesions. Therefore, burnt people develop noticeable scars that limit joint mobility.