Every person has been burned by household appliances at least once. Burns can be caused by hot dishes, boiling water, chemical compounds, steam, iron, prolonged exposure to the sun, or open fire. In all these cases, the burn can be mild or complex. With serious burns, pain is present only in the first moments of damage to the nerve endings. Oddly enough, with severe burns a person does not experience such severe pain, because the nerve endings quickly die. There can be no talk of home rehabilitation or self-relief of pain. In such a situation, urgent medical attention is needed.
Relief from pain at home can only be achieved with minor burns, when the skin turns red or small minor blisters form on it.
Nature of pain
Depending on the depth of tissue damage, there are 4 degrees of burns.
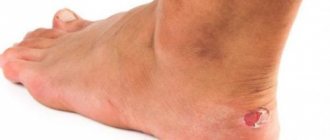
- Damage to the surface epithelium. It is accompanied by a strong burning sensation, but heals quickly even without treatment.
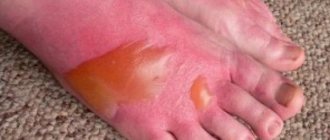
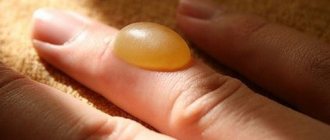
- Damage to the epithelium and upper layer of the dermis while maintaining the integrity of nerve fibers and blood vessels. Causes piercing, burning pain and the appearance of small blisters.
- The spread of pathological processes to the deep layers of the dermis, blood vessels, partial damage to the fiber. Accompanied by a decrease in pain sensitivity in the damaged area and the formation of large blisters.
- Damage to deep layers of tissue, covering subcutaneous tissue, blood vessels, nerve endings, muscle fibers, and sometimes bones.
With mild burns, pain after injury may be more intense and prolonged than with severe injuries, since the nerve endings remain intact and continue to perform their functions. With 3rd and 4th degree burns, nerve fibers are destroyed. Therefore, at the moment of contact with a damaging agent, the victim experiences unbearable pain, and after injury, pain sensitivity decreases or completely disappears.
When to see a doctor
Any burn of the mucous membrane of the eyes, respiratory tract and epidermis needs to be examined by a specialist. Superficial injuries not exceeding 5% of the skin do not require hospitalization. The doctor prescribes treatment, which the patient carries out at home.
You should seek medical help in the following cases:
- the bubble burst and the wound became infected;
- an accumulation of pus appeared at the burn site;
- I am worried about severe swelling and pain for several days;
- The temperature rose to 38 degrees.
Even minor injuries caused by steam should not be underestimated. Without proper treatment, they take a long time to heal and can cause serious complications.
First aid
Timely and competent provision of first aid for a burn reduces the severity of the injury by one. To reduce the pain from a burn and alleviate the condition of the victim, you must:
- stop exposure to the damaging agent;
- rinse the burn site under cold water (the duration of the procedure depends on the type of damaging agent);
- trying not to damage the wound, cut off the clothing;
- cover the wound surface with a sterile bandage;
- give a pain reliever;
- wrap up and provide warm drinks (to reduce the manifestations of intoxication that occurs from burns);
- In case of extensive and/or deep damage, call an ambulance.
Ice is often used to cool the wound. But this is strictly prohibited, otherwise, in addition to thermal damage, tissue frostbite occurs. Also, you should not wash the wound surface if there is a deep burn, accompanied by the formation of an open wound. In this case, a cooling compress is applied to the burn site.
Oil burn
An oil burn is a severe thermal injury. The boiling point of oils reaches 200° C, in addition, they have a thick consistency and have high heat transfer. When it comes into contact with the skin, the oil forms a dense film, which retains a high temperature for a long time, prevents the access of air, and, accordingly, complicates natural cooling.
The most important thing for an oil burn is to cool the damaged area. To do this, keep the wound under cool water for at least 20 minutes. The water should not be too cold (temperature at least 15°C).
Burns from boiling water and steam
Burns from boiling water are the most common household injury. If the skin is damaged by hot liquid, first aid also boils down to cooling the skin. For 1-2 degree burns, the wound is washed with cold water for 5-10 minutes; for deep injuries, a cooling compress is applied to the wound surface for 15-20 minutes.
Classification by severity
Burns from hot steam come in 3 degrees.
- The first (the easiest) is redness, swelling, itching, tingling, pain. Recovery occurs quickly.
- The second (medium) is the formation of blisters with serous fluid. The blisters may burst, causing scabs to appear. The wound heals in about 14 days if there are no complications.
- Third (severe) - peeling of the skin, loss of sensitivity. Rehabilitation is long-term and takes place in a hospital. Scars form.
The severity of the condition also depends on the size of the affected area. A burn of more than 15% of the skin can lead to shock, intoxication, and 50% - to death.
To assess the area of the wound, the “rule of the palm” is used - the palm is equal to 1% of the skin.
Painkillers for burns
For burns, both local painkillers (creams, ointments, aerosols, compresses with anesthetics) and systemic drugs (tablets, capsules, injection solutions) can be used.
Local preparations
Effective topical agents that help get rid of pain include the following:
- Panthenol. The drug based on dexpanthenol relieves pain, softens and moisturizes the skin, and accelerates healing. Available in the form of cream, ointment, aerosol. For burns, it is optimal to use Panthenol spray - it can be distributed over the surface of the burn without touching the damaged tissue with your hands, which avoids additional pain.
- Solcoseryl. The drug helps reduce pain and swelling and accelerates regeneration. Used for thermal and sunburns. Immediately after an injury, it is recommended to use Solcoseryl jelly, and at later stages of healing - ointment.
- Sulfargin. A product based on the sulfonamide component and silver ions quickly relieves pain, prevents wound infection, and accelerates healing. It is used for all types of burns, but for extensive injuries accompanied by painful shock, the use of the ointment is contraindicated.
- Bepanten Plus. A cream based on dexpanthenol and chlorhexidine has an analgesic, antiseptic and healing effect. For use only on superficial burns.
Activtex wipes
Another effective pain reliever for burns is sterile Activtex wipes impregnated with a special composition (lidocaine, chlorhexidine, sea buckthorn and eucalyptus oil, furagin, vitamins A and E). This is a modern dressing material, the use of which provides rapid pain relief, prevents the development of infectious complications, and promotes rapid healing.
Mode of application:
- moisten the material in physiological solution to form a gel-like polymer;
- apply a napkin to the damaged area;
- secure with a bandage.
Important! The dressing should always be moist, so it should be moistened with saline as needed. Otherwise, the polymer dries to the wound, which leads to tissue damage during dressings.
If there is no dressing material at hand, a compress with an anesthetic will help to numb the burn. Apply a sterile napkin sufficiently moistened with a solution of Lidocaine or Novocaine to the burn site.
Treatment of weeping wounds after burns
A weeping burn must be treated carefully. In order to reduce the risk of adverse events, it is necessary to thoroughly rinse the injured areas. Carefully remove dust, dirt and pus. A disinfectant medication is applied to damaged tissue. For this manipulation, antibacterial agents such as betadine are used. Hydrogen peroxide has a good effect. If this solution is not available, then soapy water can be used. The skin around the injury site is lubricated with alcohol solutions of brilliant green or iodine. This is done to dry the edges of the damage and prevent infection. The next step is to protect the wound from pathogenic flora. To do this, apply a bandage. If the burn penetrates deeply, you must take painkillers. In some cases, surgery cannot be avoided.
How to treat each stage?
Wet-type injuries have the following periods: the stage of inflammation, recovery and scarring.
So how to treat weeping wounds after a burn? During the inflammatory process, antiseptics are applied to the wound. You can use any available one. After this manipulation, it is necessary to apply a bandage made of sterile material, which will prevent the entry of moisture.
The fluid that flows from the affected area helps restore the wound and speeds up the healing process. During this period, it is necessary to change the dressing as often as possible. If excess moisture is released, then healing is carried out using the open method. For areas of the body where fluid production is highest, hygroscopic dressings are used.
During dressing it is necessary to treat with special means. Antibacterial drugs or alcohol-based products can only be used after being prescribed by a specialist.
If there is severe pain, then it is necessary to take analgesics. This can be in tablet form, injection solutions or special aerosols that are most convenient to apply.
During the purulent-necrotic period, agents with antibacterial activity are applied under the bandage. But you cannot use ordinary ointments with antibiotics for this; they do not cope with cleansing the wound. It is better to give preference to water-based ointments, such as Levosin or Levomekol.
At the second stage, when the inflammation process has already passed, and the lesion is clean and the tissues have been restored, special burn patches are applied to the site of injury. It is impregnated with medicinal preparations, which, upon contact with the skin under the influence of heat, transform into a gel structure and have a therapeutic effect.
In the third period, Solcoseryl is applied under the gauze. This helps speed up the recovery process and scar formation.
As part of complex therapy, vitamin and mineral complexes must be prescribed. Essential substances such as vitamin A, C and E help produce collagen and start the healing process.
Traditional methods
You can relieve the pain of a burn using various folk remedies.
- Raw potatoes. Grind the pulp, place the pulp in a sterile bandage, and apply to the damaged area. The pain will be reduced due to the starch contained in potatoes.
- Dairy products. Kefir, yogurt, sour cream soothe the skin well and reduce pain. Especially often used for sunburn.
- Egg white. Applied to damaged skin immediately after injury, it eliminates burning sensation well.
- Aloe juice. Soak a bandage in the fresh juice of the plant and apply it to the damaged area. The product disinfects well, reduces inflammation, and promotes regeneration.
- Toothpaste. Used only for minor burns, unless there is an open wound. Mint, which is part of toothpastes, has a cooling and distracting effect, helping to get rid of pain from a mild burn.
Folk remedies can help with very mild skin damage. But they must be used with caution. Self-medication can lead to further tissue damage, wound infection and other serious complications.
Rules for treating wound surfaces
If a weeping burn occurs, frequent dressings with appropriate treatment are required. Scheme for treating a weeping wound:
- Dressing and treatment are carried out in the appropriate room (dressing room);
- Instruments and dressings must be sterile;
- The old bandage is removed carefully without causing pain to the patient. After which the used dressing material is placed in a container filled with a disinfectant;
- The dressing is performed by a doctor and a nurse;
- If the wound is deep, then it is washed to thoroughly remove purulent exudate;
- If necessary, the doctor performs a revision of the wound;
- The burn is treated with antiseptic solutions that do not irritate tissue (Chlorhexidine, Furacilin, Hydrogen Peroxide, and so on);
- The edges of the wound are treated with alcohol antiseptics (Iodine, medical alcohol, etc.);
- If necessary, ultraviolet irradiation of wounds is carried out;
- Medicines are placed into the wound depending on the stage of the inflammatory process. If the wound is very wet, use drying agents in the form of powders that contain antibacterial agents;
- A bandage is applied.
It should be noted that dressing is done several times a day, depending on the degree of wetness and contamination of the dressing. At the very beginning of the inflammatory process, dressings are carried out up to 4 times a day.
What not to do with a weeping wound after a burn:
- Touch the surface of the burn with your hands;
- Use cotton wool to apply a bandage. When cotton wool is directly applied to the wound, its fibers will linger on the open surface. This will lead to even greater separation of exudate and the development of severe inflammation;
- Rinse the burn wound with water;
- based on fat and oils when dressing Such drugs create a greenhouse effect, which only aggravates the pathological process. A weeping wound must “breathe”, that is, oxygen must be provided to it, otherwise the inflammation intensifies;
- Injure the wound surface when performing dressings;
- Tear the bandages off the wound with force. If the dressing material has dried to the wound surface, then it is necessary to pour it generously with any non-alcohol antiseptic. As the material gets wet, it will come unstuck from the wound;
- Self-medicate and independently prescribe and discontinue medications.
The child has
Burns are especially dangerous for children. The physiological characteristics of a child’s body are such that even a moderately high temperature can cause tissue damage. In children, burns are much more severe than in adults and are often accompanied by the development of burn disease. Both the burns themselves and their consequences are dangerous - wet wounds that do not heal for a long time, infection of the burn surface, the formation of rough scars that become a serious cosmetic problem.
If a child is injured, it is necessary to urgently and correctly provide first aid to the child. Incorrect actions by parents can significantly complicate both diagnosis and further treatment.
After washing the damaged area, Panthenol aerosol (used from birth) or Olazol spray (pain relief, prevents infection, accelerates healing, used in the treatment of burns in children over 2 years old) will help to numb the child’s burn. If the pain is severe, you can give your baby a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (Panadol syrup, Nurofen, Ibufen).
It is forbidden to treat damaged skin with fatty substances (oil, baby cream, fat-based ointments) - they create a thick, oily film on the surface of the skin that prevents the natural cooling of the tissues.
After providing first aid, you need to wait for the ambulance to arrive or take the child to the hospital. Children under one year old, with an injury area of more than 2% of the body surface, with burn injuries to the face, eyes, and upper respiratory tract, are treated for burns only in a hospital setting.
A burn is always accompanied by severe pain, burning, and redness of the skin. To alleviate the condition of the victim, you need to rinse the damaged area with cold water or apply a cool compress and give a pain reliever. The further prognosis largely depends on the timeliness and quality of first aid.
Various folk remedies can also help relieve burn pain at home. But it is important to understand that they can only be used in cases of mild damage, accompanied by redness and the appearance of small blisters. Severe deep and/or extensive injuries often occur with the development of painful shock, disruption of the heart, kidneys, and liver, and therefore require competent drug treatment in a hospital setting.
Possible affected areas
In everyday life, it is possible to burn any part of the body with steam. Burns of the groin area, eyes, and respiratory tract are especially dangerous. Such injuries must be shown to a specialist.
Skin
The skin most often affected is the hands, face, chest and neck. Less often - legs, back. The area of each anatomical region is a percentage of the entire body that is a multiple of nine. Thus, a burn to the arms, chest or back will be equivalent to 18% of damage, legs - 36%, head and neck - 9%.
Eyes
Thermal burns of the organs of vision are often first or second degree. When foreign objects enter the eyes, they reflexively close, which protects against severe injury . The eyelids can be seriously damaged.
The main symptoms of an eye burn are:
- pain;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- corneal clouding;
- cutting sensations;
- decreased vision.
It is imperative to consult a doctor, only he can provide the correct help.
Larynx
When steam enters the respiratory tract, the muscles of the larynx begin to contract involuntarily. Thanks to this protective reaction, such burns are considered less dangerous. However, during the first 12 hours it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of the victim . Pulmonary edema and pneumonia may occur.
Further treatment
Superficial burns of the palm and hands can be treated at home with the help of medications and traditional medicine. The maximum duration of treatment is a month. For deep injuries, therapy can take years.
Medications
There are various medications that solve the question of what to apply to a burn on your hand. Some are designed to relieve inflammation, others to disinfect, and others to accelerate the regeneration of the damaged area. All of them are used externally. Particularly effective:
- Betadine is a widely used antiseptic.
- Karipazim - breaks down blood clots, secretions and dead tissue. Treats severe hand burns (prescribed for 3rd degree).
- Solcoseryl – stimulates regeneration.
- Amprovisol - used for local anesthesia. Soothes and relieves inflammation.
- Levomekol is an ointment with anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial effects.
- Inflarax - has an anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antimicrobial effect.
- Panthenol - restores damaged skin integrity of varying degrees of severity.
All medications have contraindications. Before use, you must read the instructions.
Folk remedies
You can treat mild hand burns at home. If the integrity of the skin is not compromised, the following traditional medicine recipes can be used:
- Sea buckthorn oil will relieve inflammation and speed up skin healing. Apply twice daily.
- Raw potatoes will relieve swelling and relieve pain. Grate the root vegetable and apply to the burn site as a compress. Once the potatoes are dry, replace them with new ones. Repeat the procedure 3-4 times.
- Aloe juice will relieve inflammation, reduce the risk of swelling and speed up healing. Cut the plant leaf lengthwise, apply it to the burned area and secure with a bandage. After an hour, remove the bandage.
- Black tea will reduce pain and relieve inflammation. Soak a sterile bandage in the tea leaves and apply to the injured surface of the hands. Change the compress as it dries. Use for a long time until the affected area heals.
- White cabbage will relieve pain. Grind the cabbage leaves in a meat grinder or blender. Apply the resulting mixture to the problem area of the hand. After anesthesia, wash off any residue with water and bactericidal soap.
When it comes to the question of how to quickly cure a burn, doctors advise using comprehensive measures, that is, using approved folk remedies only in combination with pharmaceutical drugs. This approach promotes rapid healing and recovery of a person after an injury.