First aid for electrical burns is provided for electrical damage and is carried out only after assessing the victim’s condition. All household appliances, industrial equipment - everything works using electricity.
Consult a doctor!
The site provides reference information . Adequate diagnosis and treatment of the disease is possible under the supervision of a conscientious doctor . Any medications have contraindications. Consultation with a specialist and detailed study of the instructions is necessary! Be sure to make an appointment with your doctor .
Causes of electrical burn
When a person touches a bare wire, it completes an electrical circuit. Tumors and injuries occur at the site of entry and exit of the discharge. Sometimes there are disturbances in brain function and soft tissue damage.
Experts name several main factors that can cause a burn:
- Contact with a poorly connected socket.
- Contact with the device with a wire on which the insulation is broken.
- Old wiring.
- Contact with high voltage line.
- Lightning strike.
Possible complications and prevention
Electrical burns have the following consequences:
- pulmonary paralysis;
- disruption of brain function;
- convulsions;
- destruction of bones and spinal column;
- diffuse changes in vital organs;
- scars on the body.
To prevent electrical injuries, you should follow safety precautions and rules for using electrical appliances. All wires in the house must be insulated and grounded. Then the risk of getting a burn is reduced to zero.
The article has been verified by the editors
Features of electrical burns
The current penetrates inside the human body and forms a “loop”. The most dangerous are:
- Closed loop - when the current passes through the arms or legs.
- Bottom loop - the charge passes through the feet.
- Full loop - the current enters the body through the legs and exits through the hands.
It is impossible to say exactly what will happen after an electric shock. It all depends on the strength of the discharge and the characteristics of the person. Contact with an object energized by 240 volts is often accompanied by convulsions. It is impossible to unclench your fingers; the cable remains in your hand.
The danger of such interaction lies in the duration. When struck by a high-power electric current, a person is thrown away from the source, but severe burns appear, which are accompanied by charring.
What are the types of electrical burns?
Electrical burns can occur at home, at work, or even in the natural environment. Various types of damage are possible:
- Thermal ones manifest themselves in the form of a burn on the skin.
- Biological - muscles contract convulsively, problems with the functioning of the respiratory system, open wounds on the skin, and sometimes fractures occur.
- Electrolytic - damage to lymph and blood flow is dangerous due to disruption of organ functioning.
Based on the type of interaction, there are two types.
Current (contact)
This type occurs when a person comes into contact with an object or wire through which current passes. Current penetrates in the case of direct interaction. The formation of a current burn is a consequence of the conversion of electricity into heat.
The skin suffers because it has a greater degree of resistance compared to other tissues. More often, grade 1 or 2 is diagnosed. Stronger ones are less common.
Arc
This type of electrical burn is explained by the impact on the body of an electric arc with high temperature (more than 3500 degrees) and high energy.
You can get it when working with high-voltage lines and other high-voltage devices. The injuries are grade 3 and 4. The general condition depends not so much on the force of the blow, but on the area of the affected area.
Types and features
There are 2 types of electrical damage.
- Contact (electric) burns are caused by direct interaction with a current conductor. Such injuries often occur when working with low-voltage electrical equipment, so electrical burns are characterized by a mild degree of injury.
- An arc burn results from the thermal effects (temperatures that can exceed 350°C) of an electric arc without current passing through the body. An electric arc burn often leads to very serious damage that extends into the deep structures of the skin.
In case of electric shock, in addition to burns, phenomena occur that are uncharacteristic of other types of damage (thermal, chemical).
- Many patients have characteristic marks in the area of contact with the current - oval, round, or in the form of stripes (in case of lightning) yellowish or brown areas. These marks have clear boundaries and are about 5-10 mm in size. Over time, they disappear, but the speed of restoration of skin sensitivity and its properties depends both on the degree of damage and on the individual characteristics of the patient.
- When an electric shock occurs, the current travels through the body in a path called a loop. As a result, burn damage occurs not only in the area of contact with the current source, but also at the point of its exit from the body (usually this is the area of the body in contact with the surface of the earth or metal). A full loop, characterized by the passage of current through both arms and legs, is the most dangerous. A more favorable prognosis for the victim is when the current passes only through the lower limbs (lower loop).
Electric shock causes various types of damage:
- thermal - often a current discharge is accompanied by a high-temperature effect, as a result of which the victim’s clothing catches fire, and a thermal burn is added to the electric shock;
- electrolytic – the composition of the blood changes, internal tissues are destroyed;
- mechanical - due to convulsive involuntary contraction of muscles caused by the influence of current, tissues are torn, deep (sometimes right up to the bone) wounds are formed on the skin, dislocations and even bone fractures often occur;
- biological - the functioning of the nervous system and the function of thermoregulation, cardiac activity are disrupted (myocardial infarction, ventricular fibrillation, cardiac arrest may occur), blood pressure increases, arrosive bleeding, pulmonary edema, glomerulonephritis, functional liver failure may develop;
- electroophthalmia - inflammation of the eyes caused by radiation burns of the cornea, retina (with a short circuit and the formation of an electric arc, in addition to a visible bright flash, intense ultraviolet radiation occurs, affecting the structures of the eyeball);
- metallization of the skin - tiny particles of molten metal are absorbed into the skin, the skin becomes hard and rough, and the victim has a feeling of the presence of a foreign body in the area of damage.
Types of burns
To properly provide first aid to a victim, you need to know the characteristics and types of electrical burns. Based on the method of production, they are divided into 3 groups.
Household
This kind of burn is often caused at home when safety precautions are ignored. This happens when working with a faulty electrical appliance, breaking the insulation of wires, repairing sockets, replacing light bulbs when the power is not turned off. These burns are the most harmless, but history has known cases of death.
Natural
This type can be obtained in the event of a natural disaster - a lightning strike. The survival rate is negligible, since the effect on the body is too strong.
Production
Electricians most often experience this type of burn while performing their job duties. They are constantly in contact with electrical appliances.
A person whose work involves electricity exposes himself to prolonged exposure to low voltage. However, short-term interaction is no less dangerous.
Features of injury, its main danger
Men are most often exposed to electrical burns due to their professional activities. But such injuries also occur in women or children. They are extremely dangerous and can cause disruption of all internal organs .
Due to the impact of electric current on the human body, a burn develops, which is significantly different from thermal. Its features are as follows:
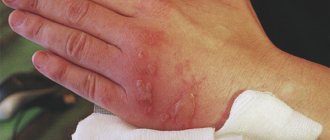
- Many victims develop specific markings on their skin. They appear as limited areas of yellow or gray color, which are often located as the current moves through the body. Over time, such signs disappear, and the properties of the skin are gradually restored.
- Mechanical injury to the epidermis occurs rarely - in no more than 3% of cases.
- In 10% of patients, metallization of the skin is observed. This means that the molten particles of the electric arc penetrate into the thickness of the dermis. Except in cases where the current affects the eyes, tissue restoration occurs quickly and is not accompanied by complications.
- Victims are often diagnosed with electroophthalmia, caused by sudden exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eyes (for example, a lightning strike). This condition requires qualified treatment - only this will allow you to restore vision as quickly as possible.
- Contact with current provokes intense contraction of all muscles. With sufficiently long-term exposure, this can lead to death due to impaired respiratory function and cardiac arrest.
Electrical injuries are especially dangerous for young children and pregnant women at any stage.
Degrees
In total, there are 4 degrees of electric shock strength. Each of them has its own differences, the nature of the damage to the body.
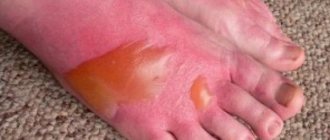
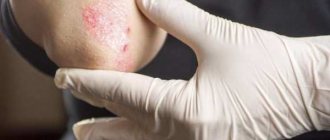
- The first degree is characterized by damage to the upper layers of the skin, slight swelling, and a burning sensation. The burn area is small. This kind of damage is the most harmless, so after a visit to the doctor you can continue treatment at home.
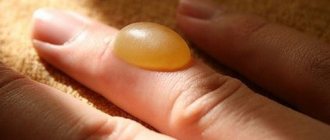
- In the second degree, deeper wounds appear, right down to the germ layer. The formation of blisters with exudate is typical at the entry and exit sites. The person feels severe pain and burning. If a small area is affected, you can treat it at home.
- The third degree is characterized by the death of the inner layer of skin. The skin turns red, and with more severe injuries, it may even turn black and blisters appear. Blood clots can be observed in the clear exudate in the blisters. The skin on the affected area dies and cannot regenerate.
- The fourth degree is considered the most dangerous. The injury is accompanied by damage to the skin, muscle tissue, and bones. Only a doctor can provide first aid. The skin does not regenerate, and restoration will require a transplant.
It is important to correctly determine the degree and area of the burn in order to provide first aid without causing harm. In case of incorrect identification, death is possible.
Classification, forms and types of damage
Main degrees of damage from electric current:
- 1st degree – impact on the upper layer of the dermis, hyperthermic attacks and mild swelling. The prognosis is favorable, since burns can be treated at home.
- 2nd degree - the skin is damaged down to the germ layer, blisters with liquid inside form. Stage 2 burns are characterized by severe pain after an electrical discharge. If the area of redness is small, self-treatment is possible.
- 3rd degree - the inner layers of the dermis die, blisters with blood appear and burst. An unprotected red surface appears, and in case of severe injury, a dark area of the epidermis appears. This indicates necrosis of the germ layer and the inability of cells to regenerate independently.
- Grade 4 – covers skin, muscle and bone tissue. First aid for the last stage of an electrical burn is provided to the victim only by a doctor: he performs an operation to transplant the epidermis.
Types of damage are divided into:
- current upon contact: occurs when current is directly applied to the skin by the conductive part - then the electric shock passes through the entire body;
- arc: appears on the dermis under the influence of an electric arc. These injuries cause sharp, severe pain and leave deep scars. In the photo they look like whitish strips of skin after healing.
When exposed to electric current, a person suffers various injuries:
- thermal: manifested by high temperatures, which causes the skin and outer clothing to ignite. Burns reach third and fourth degree;
- electrolytic: disrupt the composition of the blood, destroy organs;
- mechanical: characterized by ruptures of the skin, with the formation of deep wounds to the bones;
- biological: they destroy the internal processes of hematopoiesis and the conduction of nerve impulses.
An arc burn is often accompanied by inflammation of the eyes, and subsequently severe headache due to ultraviolet radiation.
How to understand that a person has suffered from an electric shock
You can find out about an electrical burn by looking at the marks from the electric arc. The skin of the affected area changes color. It turns red or purple-gray. With severe injuries, blackening or even charring may occur. There is no clear location of the pain; it spreads throughout the body. Electric shock is indicated by muscle spasms and convulsions.
The main signs of electrical injuries include:
- Weak breathing, shallow. Sometimes asphyxia may occur.
- Cardiopalmus.
- Muscle cramps.
- Impaired consciousness, memory loss.
- Disorientation in space.
- Loss of sensation in a limb.
- Unstable vision, inability to focus.
- A clear outline of the burn on the skin.
- Unintelligible speech.
- The victim may complain of nausea and dizziness.
The victim needs to be attentive to the victim. If the current is exposed for a long time, then characteristic marks will remain on the skin. Possible swelling and numbness.
Chemical burns
When body tissues come into contact with concentrated acids, alkalis and heavy metal salts, chemical burns occur. Acid burns occur A dry dark brown or black scab with clear boundaries forms on the skin and mucous membranes. In case of an acid burn, rinse the burn area with a stream of water for 15–20 minutes. The exception is sulfuric acid: it heats up when diluted with water, which can worsen a burn injury. Next, the burn area is washed with solutions with an alkaline reaction - soapy water, baking soda solution (1 teaspoon per glass of water). Alkali burns occur A wet, dirty green scab forms on the surface of the burn, with no clear boundaries. After 20 minutes of washing the burn area under running water, treat with solutions with an acidic reaction - a solution of 2% citric or acetic acid. After treatment, an aseptic bandage must be applied to the burn wound.
In case of phosphorus burns, it is necessary Next, treat the wound with a solution of copper sulfate. It is strictly forbidden to lubricate the burn after treatment with oil or fat, because this promotes the absorption of toxic phosphorus. Burns caused by quicklime should never Removal of the substance and processing is carried out with oil. After this, apply a gauze bandage. To the top»>
First aid
First of all, it is necessary to stop human contact with the current source. In this case, you need to be vigilant and take precautions. Rubber gloves are put on your hands, and shoes that do not have rubber or metal inserts are put on your feet.
Note! It is acceptable to use a wooden plank to push the person away from the source. In this case, you should stay at a safe distance from it. After the contact is suspended, it is important to turn off the switch and completely turn off the power supply.
If you notice that the victim’s skin color has changed at the site of contact with electricity, and he is suffering from severe pain, then you need to call an ambulance. To choose a treatment method, it is necessary to determine the duration of exposure to the electric discharge and the degree of damage.
Types of Electrical Injuries
Several types of electrical injuries are considered. Electrical injuries may include:
- Burns due to electric shock . This is the most common injury. Burns are considered to be a consequence of self-short circuits in electrical installations. Considering what causes electrical burns, depending on the conditions of occurrence, three types of burns are noted: current, arc, mixed. In the first case, injury occurs when current directly passes through the body due to human contact with a conductive part, that is, electrical burns occur when an electric shock occurs. In the second case, an electric arc is applied, but without current passing through the body. And in the latter case, both factors act simultaneously. In terms of severity, burns from electric shock can be of any degree.
- Metallization of leather . This injury refers to the penetration of small particles of melting metal into the skin under the influence of an electric arc. Damage can occur when switches and disconnectors are turned off under load or during short circuits. Usually, after a certain period of time, the damaged epidermis disappears, and the skin takes on a normal appearance. Only if the eyes are affected, treatment will be difficult and lengthy.
- Electrical signs . Such signs appear due to exposure to chemical or thermal, or the combined effects of electric current. The signs are characterized by a shape with clear contours and have a gray or pale yellow tint. Typically the signs are round or oval in shape. The damaged area becomes harder and cell death is observed. Typically, electrical signs do not cause pain and treatment is quick and successful. Over a certain period of time, the epidermis comes off and the skin becomes healthy.
- Electroophthalmia . This is exposure of the eyes to a source of strong radiation of ultraviolet rays, which appears when an electric arc occurs. A person experiences inflammation of the outer membranes of the eyes.
- Mechanical damage . These are dangerous injuries that occur as a result of a person being under voltage for a long time in installations up to 380 V. Mechanical injuries accompany electric shocks, as they are provoked by current passing through the body.
- Electric shock . Excitation of living tissues, provoked by an electric current passing through the body, and accompanied by spontaneous spasmodic muscle contractions.
Any injury associated with electrical contact is life-threatening.
Treatment
If the injury occurs at home, it is most likely minor. Small areas of skin can be treated independently. The wound heals within a couple of weeks.
The affected area should not be treated with iodine or brilliant green, as they will aggravate the burn. It is better to use creams and ointments for healing burns, which include an antibacterial and antiseptic component. Preparations with sodium fusidine help avoid tissue rotting.
In the first week, you need to take especially careful care of the wound:
- daily smear the injury with an antiseptic solution, anti-burn creams, as prescribed by your doctor;
- carry out dressings regularly;
- for pain, use painkillers;
- antihistamines are required.
For treatment in a hospital setting, 2 treatment methods are used: medication and surgery.
Drug treatment
If a person suffers from high voltage, then most likely he will lose consciousness. In this case, a disruption of the heart rhythm and disruption of the cardiovascular system are possible. In this case, doctors send the patient to the intensive care unit. He is prescribed infusion therapy with anti-inflammatory and painkillers. In some cases, a blood transfusion may be required.
After stabilizing the victim’s condition, therapy is supplemented with local treatment for a speedy recovery. All creams and ointments that can be used to treat burns with blisters prescribed by doctors have an antibacterial effect and stimulate regenerative processes.
If the nervous system is disrupted as a result of an electric shock, the patient is prescribed sedatives and sometimes antidepressants. To stabilize the functioning of the cardiovascular system - stimulants. If circulatory disorders or cerebral edema are detected, then taking dehydration medications is recommended.
Surgical intervention
Surgical intervention is necessary only for the 3rd or 4th degree of severity of the injury. Surgeons clean the affected area and transplant healthy skin.
In particularly severe situations, amputation may be required. It is recommended for those patients whose injury is not amenable to conservative treatment methods and skin grafting.
The decision is made individually, based on the patient’s condition. In some cases, surgery is required immediately when there is a real threat to life or health. Sometimes doctors decide to postpone intervention until the patient has partially recovered, that is, they give time to recover from the shock.
Treatment methods
- Apply ice to the burned area or immerse it in cold water for about fifteen minutes. This will ease the pain and the redness of the skin will subside a little.
- Treat electrical burns with a spray that contains dexpanthenol. The spray has the effect of rapid healing and cell regeneration, and an anti-inflammatory effect. You can use Panthenol spray. This medicine quickly eliminates the consequences of injury: redness, pain, swelling of the skin.
- If the injury is too serious, the victim is placed in a hospital, where tests are collected to determine the severity of the injury and its consequences on the body. Examine using x-rays for fractures. Urgent intervention by a surgeon may be required (incisions, ligation of blood vessels and, in extreme cases, amputation).
In case of severe damage, when all initial measures have been taken, you need to remain in bed for about 3 days.
Injections are given that tone the heart and breathing, diphenhydramine and vitamin C are used.
Rehabilitation after electric burns
At the stage of restoring the integrity of the skin, it is important to constantly disinfect the resulting wound. Very often, a blister with a clear liquid forms at the site of the electrical burn.
Attention! It is forbidden to burst the bubble yourself; it is best to entrust this to a specialist at the emergency room.
If you properly care for the affected area, then within a couple of weeks new skin will form under the fluid, and the blister will gradually dry out and fall off by this time. The new skin will be a little lighter and softer than the rest.
The process usually takes 1–2 weeks for grade 1, about 3–4 weeks for grade 2. For more serious injuries (grade 3–4), the recovery process is individual and depends on factors:
- general health;
- cell regeneration rate;
- presence of surgical intervention;
- individual attitude.
An unfavorable development of events is characterized by suppuration of the wound, which can only prolong the recovery period of the body. In this case, chills, weakness, and increased pain at the site of the injury may be felt.
Prevention of electrical injuries
In order not to suffer from the question of how to treat and how to numb the burn, you should follow safety precautions. The following can be identified as preventive measures:
- Compliance with the rules of operation of electrical appliances, carrying out timely repairs and maintenance.
- Prevent children from contacting electrical equipment, sockets, explanation of the prohibition.
- Warning about a high-risk area, the likelihood of injury to others.
- Educational conversations on behavior during thunderstorms and lightning.
The number of accidents involving electric current is growing. This suggests that the majority are not aware of the safety rules and first aid for electrical burns. Timely, competent assistance for electrical burns can save someone's life.
- about the author
- Recent publications
Mother of two children. I work as an economist. I love medicine, tourism and cars. I like to poke my nose in everywhere – that’s why I know a lot of things. I love sharing my knowledge!
All sorts of complications
Electrical burns can cause a number of different consequences:
- complete or partial paralysis;
- introduction of infection;
- development of cataracts;
- disorders of the cardiovascular system;
- damage to the nervous system;
- development of gangrene;
- bone fractures;
- occurrence of spasm.
In order to avoid such complications, at the first suspicion of such an injury, provide the victim with first aid for burns and immediately contact a medical facility.